Huifeng Guo
Don't Start Over: A Cost-Effective Framework for Migrating Personalized Prompts Between LLMs
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:Personalization in Large Language Models (LLMs) often relies on user-specific soft prompts. However, these prompts become obsolete when the foundation model is upgraded, necessitating costly, full-scale retraining. To overcome this limitation, we propose the Prompt-level User Migration Adapter (PUMA), a lightweight framework to efficiently migrate personalized prompts across incompatible models. PUMA utilizes a parameter-efficient adapter to bridge the semantic gap, combined with a group-based user selection strategy to significantly reduce training costs. Experiments on three large-scale datasets show our method matches or even surpasses the performance of retraining from scratch, reducing computational cost by up to 98%. The framework demonstrates strong generalization across diverse model architectures and robustness in advanced scenarios like chained and aggregated migrations, offering a practical path for the sustainable evolution of personalized AI by decoupling user assets from the underlying models.
Exploring Recommender System Evaluation: A Multi-Modal User Agent Framework for A/B Testing
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:In recommender systems, online A/B testing is a crucial method for evaluating the performance of different models. However, conducting online A/B testing often presents significant challenges, including substantial economic costs, user experience degradation, and considerable time requirements. With the Large Language Models' powerful capacity, LLM-based agent shows great potential to replace traditional online A/B testing. Nonetheless, current agents fail to simulate the perception process and interaction patterns, due to the lack of real environments and visual perception capability. To address these challenges, we introduce a multi-modal user agent for A/B testing (A/B Agent). Specifically, we construct a recommendation sandbox environment for A/B testing, enabling multimodal and multi-page interactions that align with real user behavior on online platforms. The designed agent leverages multimodal information perception, fine-grained user preferences, and integrates profiles, action memory retrieval, and a fatigue system to simulate complex human decision-making. We validated the potential of the agent as an alternative to traditional A/B testing from three perspectives: model, data, and features. Furthermore, we found that the data generated by A/B Agent can effectively enhance the capabilities of recommendation models. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/Applied-Machine-Learning-Lab/ABAgent.
No One Left Behind: How to Exploit the Incomplete and Skewed Multi-Label Data for Conversion Rate Prediction
Dec 15, 2025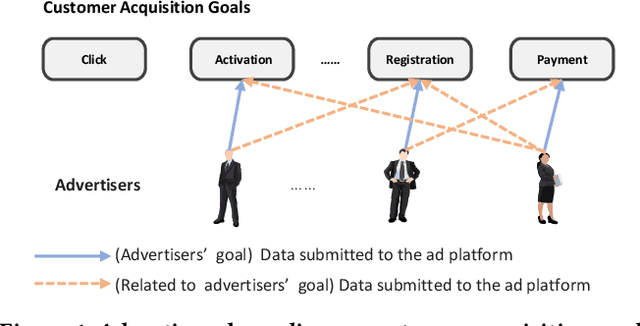
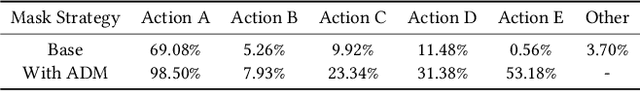
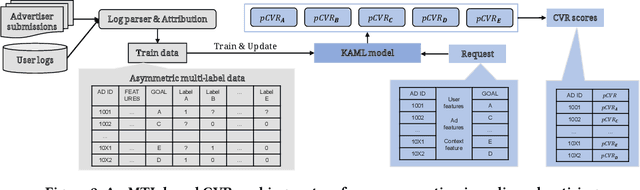
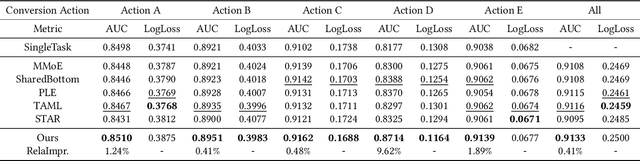
Abstract:In most real-world online advertising systems, advertisers typically have diverse customer acquisition goals. A common solution is to use multi-task learning (MTL) to train a unified model on post-click data to estimate the conversion rate (CVR) for these diverse targets. In practice, CVR prediction often encounters missing conversion data as many advertisers submit only a subset of user conversion actions due to privacy or other constraints, making the labels of multi-task data incomplete. If the model is trained on all available samples where advertisers submit user conversion actions, it may struggle when deployed to serve a subset of advertisers targeting specific conversion actions, as the training and deployment data distributions are mismatched. While considerable MTL efforts have been made, a long-standing challenge is how to effectively train a unified model with the incomplete and skewed multi-label data. In this paper, we propose a fine-grained Knowledge transfer framework for Asymmetric Multi-Label data (KAML). We introduce an attribution-driven masking strategy (ADM) to better utilize data with asymmetric multi-label data in training. However, the more relaxed masking in ADM is a double-edged sword: it provides additional training signals but also introduces noise due to skewed data. To address this, we propose a hierarchical knowledge extraction mechanism (HKE) to model the sample discrepancy within the target task tower. Finally, to maximize the utility of unlabeled samples, we incorporate ranking loss strategy to further enhance our model. The effectiveness of KAML has been demonstrated through comprehensive evaluations on offline industry datasets and online A/B tests, which show significant performance improvements over existing MTL baselines.
FuXi-$γ$: Efficient Sequential Recommendation with Exponential-Power Temporal Encoder and Diagonal-Sparse Positional Mechanism
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:Sequential recommendation aims to model users' evolving preferences based on their historical interactions. Recent advances leverage Transformer-based architectures to capture global dependencies, but existing methods often suffer from high computational overhead, primarily due to discontinuous memory access in temporal encoding and dense attention over long sequences. To address these limitations, we propose FuXi-$γ$, a novel sequential recommendation framework that improves both effectiveness and efficiency through principled architectural design. FuXi-$γ$ adopts a decoder-only Transformer structure and introduces two key innovations: (1) An exponential-power temporal encoder that encodes relative temporal intervals using a tunable exponential decay function inspired by the Ebbinghaus forgetting curve. This encoder enables flexible modeling of both short-term and long-term preferences while maintaining high efficiency through continuous memory access and pure matrix operations. (2) A diagonal-sparse positional mechanism that prunes low-contribution attention blocks using a diagonal-sliding strategy guided by the persymmetry of Toeplitz matrix. Extensive experiments on four real-world datasets demonstrate that FuXi-$γ$ achieves state-of-the-art performance in recommendation quality, while accelerating training by up to 4.74$\times$ and inference by up to 6.18$\times$, making it a practical and scalable solution for long-sequence recommendation. Our code is available at https://github.com/Yeedzhi/FuXi-gamma.
Towards Multi-Granularity Memory Association and Selection for Long-Term Conversational Agents
May 26, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have recently been widely adopted in conversational agents. However, the increasingly long interactions between users and agents accumulate extensive dialogue records, making it difficult for LLMs with limited context windows to maintain a coherent long-term dialogue memory and deliver personalized responses. While retrieval-augmented memory systems have emerged to address this issue, existing methods often depend on single-granularity memory segmentation and retrieval. This approach falls short in capturing deep memory connections, leading to partial retrieval of useful information or substantial noise, resulting in suboptimal performance. To tackle these limits, we propose MemGAS, a framework that enhances memory consolidation by constructing multi-granularity association, adaptive selection, and retrieval. MemGAS is based on multi-granularity memory units and employs Gaussian Mixture Models to cluster and associate new memories with historical ones. An entropy-based router adaptively selects optimal granularity by evaluating query relevance distributions and balancing information completeness and noise. Retrieved memories are further refined via LLM-based filtering. Experiments on four long-term memory benchmarks demonstrate that MemGAS outperforms state-of-the-art methods on both question answer and retrieval tasks, achieving superior performance across different query types and top-K settings.
Align-GRAG: Reasoning-Guided Dual Alignment for Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation
May 22, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities, but still struggle with issues like hallucinations and outdated information. Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) addresses these issues by grounding LLM outputs in external knowledge with an Information Retrieval (IR) system. Building on this foundation, graph-based RAG systems go a step further by retrieving subgraphs, which preserve the relationships between knowledge entities and provide more comprehensive context. However, graph RAG faces two challenges: (1) Retrieving relevant information introduces irrelevant nodes (especially in dense graph databases, where retrieval usually extends to adjacent nodes), and leads to overly lengthy inputs that hinder efficiency; (2) The representation gap between graph and language during generation with LLMs limits the ability to fully leverage graph structures for enhanced understanding. To address these limitations, we propose Align-GRAG, a novel reasoning-guided dual alignment framework in post-retrieval phrase. It first formulates a subgraph by retrieving nodes and edges. Then an Aligner is proposed to jointly optimizes a graph encoder with LLM-summarized reasoning. It achieves dual alignment of graph node and representation by leveraging KL divergence loss and contrastive loss, facilitating efficient pruning of irrelevant knowledge and establishing a unified semantic space. The Generator integrates the aligned graph data with LLM to produce coherent and accurate answers. Experiments on GraphQA benchmark across three tasks (including common sense reasoning, scene graph understanding, and knowledge graph reasoning) validate the effectiveness of our method. The code will be available upon accepted.
Process vs. Outcome Reward: Which is Better for Agentic RAG Reinforcement Learning
May 20, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) enhances the text generation capabilities of large language models (LLMs) by integrating external knowledge and up-to-date information. However, traditional RAG systems are limited by static workflows and lack the adaptability required for multistep reasoning and complex task management. To address these limitations, agentic RAG systems (e.g., DeepResearch) have been proposed, enabling dynamic retrieval strategies, iterative context refinement, and adaptive workflows for handling complex search queries beyond the capabilities of conventional RAG. Recent advances, such as Search-R1, have demonstrated promising gains using outcome-based reinforcement learning, where the correctness of the final answer serves as the reward signal. Nevertheless, such outcome-supervised agentic RAG methods face challenges including low exploration efficiency, gradient conflict, and sparse reward signals. To overcome these challenges, we propose to utilize fine-grained, process-level rewards to improve training stability, reduce computational costs, and enhance efficiency. Specifically, we introduce a novel method ReasonRAG that automatically constructs RAG-ProGuide, a high-quality dataset providing process-level rewards for (i) query generation, (ii) evidence extraction, and (iii) answer generation, thereby enhancing model inherent capabilities via process-supervised reinforcement learning. With the process-level policy optimization, the proposed framework empowers LLMs to autonomously invoke search, generate queries, extract relevant evidence, and produce final answers. Compared to existing approaches such as Search-R1 and traditional RAG systems, ReasonRAG, leveraging RAG-ProGuide, achieves superior performance on five benchmark datasets using only 5k training instances, significantly fewer than the 90k training instances required by Search-R1.
LSRP: A Leader-Subordinate Retrieval Framework for Privacy-Preserving Cloud-Device Collaboration
May 08, 2025Abstract:Cloud-device collaboration leverages on-cloud Large Language Models (LLMs) for handling public user queries and on-device Small Language Models (SLMs) for processing private user data, collectively forming a powerful and privacy-preserving solution. However, existing approaches often fail to fully leverage the scalable problem-solving capabilities of on-cloud LLMs while underutilizing the advantage of on-device SLMs in accessing and processing personalized data. This leads to two interconnected issues: 1) Limited utilization of the problem-solving capabilities of on-cloud LLMs, which fail to align with personalized user-task needs, and 2) Inadequate integration of user data into on-device SLM responses, resulting in mismatches in contextual user information. In this paper, we propose a Leader-Subordinate Retrieval framework for Privacy-preserving cloud-device collaboration (LSRP), a novel solution that bridges these gaps by: 1) enhancing on-cloud LLM guidance to on-device SLM through a dynamic selection of task-specific leader strategies named as user-to-user retrieval-augmented generation (U-U-RAG), and 2) integrating the data advantages of on-device SLMs through small model feedback Direct Preference Optimization (SMFB-DPO) for aligning the on-cloud LLM with the on-device SLM. Experiments on two datasets demonstrate that LSRP consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, significantly improving question-answer relevance and personalization, while preserving user privacy through efficient on-device retrieval. Our code is available at: https://github.com/Zhang-Yingyi/LSRP.
Killing Two Birds with One Stone: Unifying Retrieval and Ranking with a Single Generative Recommendation Model
Apr 23, 2025Abstract:In recommendation systems, the traditional multi-stage paradigm, which includes retrieval and ranking, often suffers from information loss between stages and diminishes performance. Recent advances in generative models, inspired by natural language processing, suggest the potential for unifying these stages to mitigate such loss. This paper presents the Unified Generative Recommendation Framework (UniGRF), a novel approach that integrates retrieval and ranking into a single generative model. By treating both stages as sequence generation tasks, UniGRF enables sufficient information sharing without additional computational costs, while remaining model-agnostic. To enhance inter-stage collaboration, UniGRF introduces a ranking-driven enhancer module that leverages the precision of the ranking stage to refine retrieval processes, creating an enhancement loop. Besides, a gradient-guided adaptive weighter is incorporated to dynamically balance the optimization of retrieval and ranking, ensuring synchronized performance improvements. Extensive experiments demonstrate that UniGRF significantly outperforms existing models on benchmark datasets, confirming its effectiveness in facilitating information transfer. Ablation studies and further experiments reveal that UniGRF not only promotes efficient collaboration between stages but also achieves synchronized optimization. UniGRF provides an effective, scalable, and compatible framework for generative recommendation systems.
From Human Memory to AI Memory: A Survey on Memory Mechanisms in the Era of LLMs
Apr 22, 2025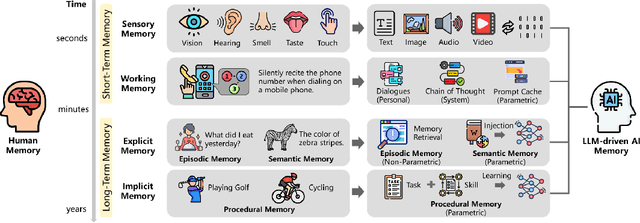
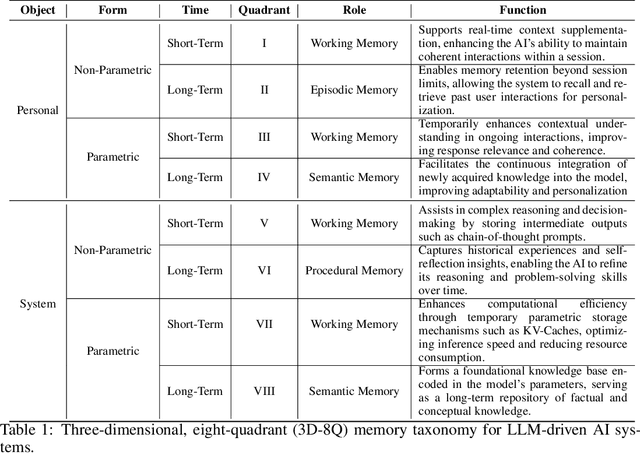
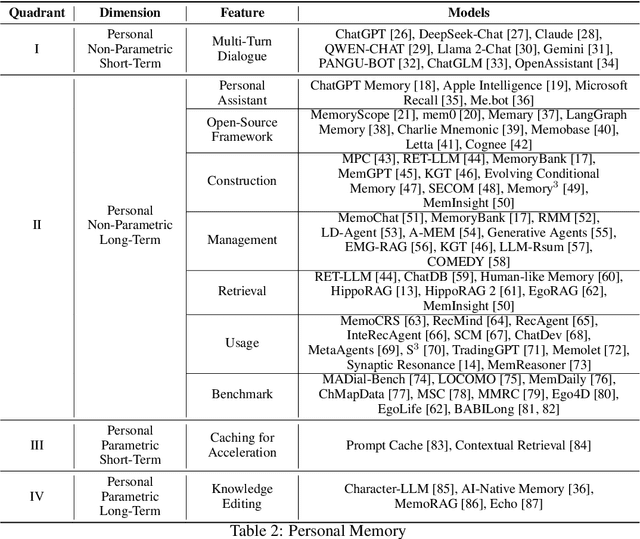
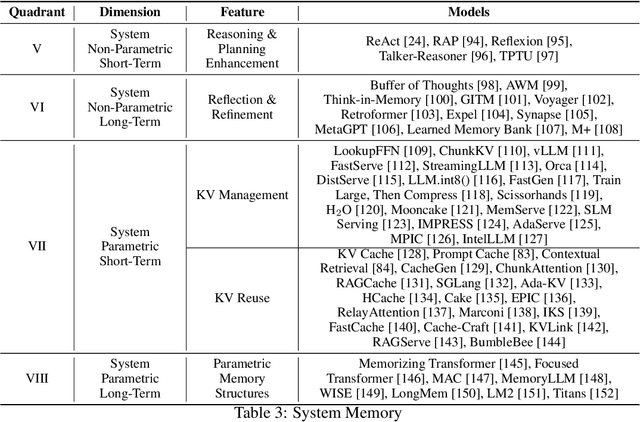
Abstract:Memory is the process of encoding, storing, and retrieving information, allowing humans to retain experiences, knowledge, skills, and facts over time, and serving as the foundation for growth and effective interaction with the world. It plays a crucial role in shaping our identity, making decisions, learning from past experiences, building relationships, and adapting to changes. In the era of large language models (LLMs), memory refers to the ability of an AI system to retain, recall, and use information from past interactions to improve future responses and interactions. Although previous research and reviews have provided detailed descriptions of memory mechanisms, there is still a lack of a systematic review that summarizes and analyzes the relationship between the memory of LLM-driven AI systems and human memory, as well as how we can be inspired by human memory to construct more powerful memory systems. To achieve this, in this paper, we propose a comprehensive survey on the memory of LLM-driven AI systems. In particular, we first conduct a detailed analysis of the categories of human memory and relate them to the memory of AI systems. Second, we systematically organize existing memory-related work and propose a categorization method based on three dimensions (object, form, and time) and eight quadrants. Finally, we illustrate some open problems regarding the memory of current AI systems and outline possible future directions for memory in the era of large language models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge