Xudong Zhang
LiDARDraft: Generating LiDAR Point Cloud from Versatile Inputs
Dec 23, 2025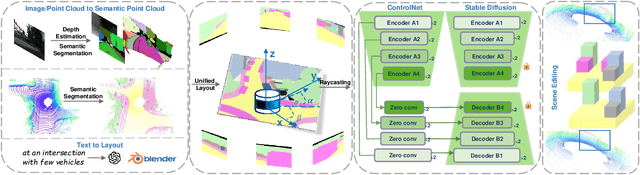
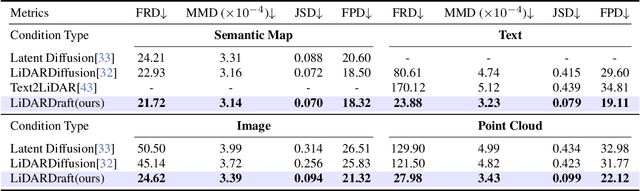
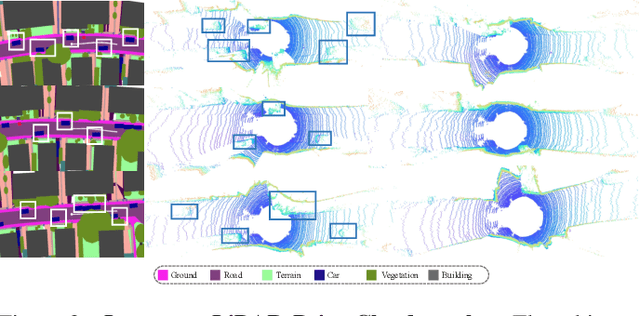
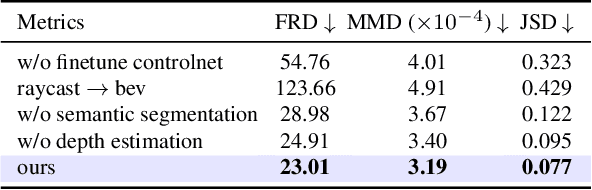
Abstract:Generating realistic and diverse LiDAR point clouds is crucial for autonomous driving simulation. Although previous methods achieve LiDAR point cloud generation from user inputs, they struggle to attain high-quality results while enabling versatile controllability, due to the imbalance between the complex distribution of LiDAR point clouds and the simple control signals. To address the limitation, we propose LiDARDraft, which utilizes the 3D layout to build a bridge between versatile conditional signals and LiDAR point clouds. The 3D layout can be trivially generated from various user inputs such as textual descriptions and images. Specifically, we represent text, images, and point clouds as unified 3D layouts, which are further transformed into semantic and depth control signals. Then, we employ a rangemap-based ControlNet to guide LiDAR point cloud generation. This pixel-level alignment approach demonstrates excellent performance in controllable LiDAR point clouds generation, enabling "simulation from scratch", allowing self-driving environments to be created from arbitrary textual descriptions, images and sketches.
Efficient Reinforcement Learning for Zero-Shot Coordination in Evolving Games
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Zero-shot coordination(ZSC), a key challenge in multi-agent game theory, has become a hot topic in reinforcement learning (RL) research recently, especially in complex evolving games. It focuses on the generalization ability of agents, requiring them to coordinate well with collaborators from a diverse, potentially evolving, pool of partners that are not seen before without any fine-tuning. Population-based training, which approximates such an evolving partner pool, has been proven to provide good zero-shot coordination performance; nevertheless, existing methods are limited by computational resources, mainly focusing on optimizing diversity in small populations while neglecting the potential performance gains from scaling population size. To address this issue, this paper proposes the Scalable Population Training (ScaPT), an efficient RL training framework comprising two key components: a meta-agent that efficiently realizes a population by selectively sharing parameters across agents, and a mutual information regularizer that guarantees population diversity. To empirically validate the effectiveness of ScaPT, this paper evaluates it along with representational frameworks in Hanabi cooperative game and confirms its superiority.
Efficient Agent: Optimizing Planning Capability for Multimodal Retrieval Augmented Generation
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Retrieval-Augmented Generation (mRAG) has emerged as a promising solution to address the temporal limitations of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in real-world scenarios like news analysis and trending topics. However, existing approaches often suffer from rigid retrieval strategies and under-utilization of visual information. To bridge this gap, we propose E-Agent, an agent framework featuring two key innovations: a mRAG planner trained to dynamically orchestrate multimodal tools based on contextual reasoning, and a task executor employing tool-aware execution sequencing to implement optimized mRAG workflows. E-Agent adopts a one-time mRAG planning strategy that enables efficient information retrieval while minimizing redundant tool invocations. To rigorously assess the planning capabilities of mRAG systems, we introduce the Real-World mRAG Planning (RemPlan) benchmark. This novel benchmark contains both retrieval-dependent and retrieval-independent question types, systematically annotated with essential retrieval tools required for each instance. The benchmark's explicit mRAG planning annotations and diverse question design enhance its practical relevance by simulating real-world scenarios requiring dynamic mRAG decisions. Experiments across RemPlan and three established benchmarks demonstrate E-Agent's superiority: 13% accuracy gain over state-of-the-art mRAG methods while reducing redundant searches by 37%.
Scalable unsupervised feature selection via weight stability
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Unsupervised feature selection is critical for improving clustering performance in high-dimensional data, where irrelevant features can obscure meaningful structure. In this work, we introduce the Minkowski weighted $k$-means++, a novel initialisation strategy for the Minkowski Weighted $k$-means. Our initialisation selects centroids probabilistically using feature relevance estimates derived from the data itself. Building on this, we propose two new feature selection algorithms, FS-MWK++, which aggregates feature weights across a range of Minkowski exponents to identify stable and informative features, and SFS-MWK++, a scalable variant based on subsampling. We support our approach with a theoretical guarantee under mild assumptions and extensive experiments showing that our methods consistently outperform existing alternatives.
Non-stationary BERT: Exploring Augmented IMU Data For Robust Human Activity Recognition
Sep 25, 2024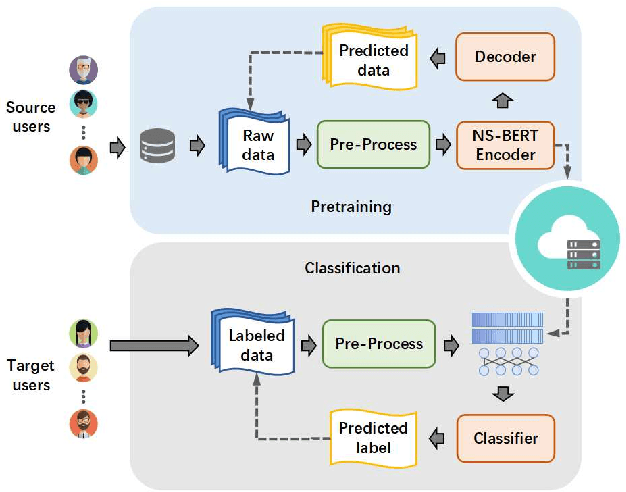
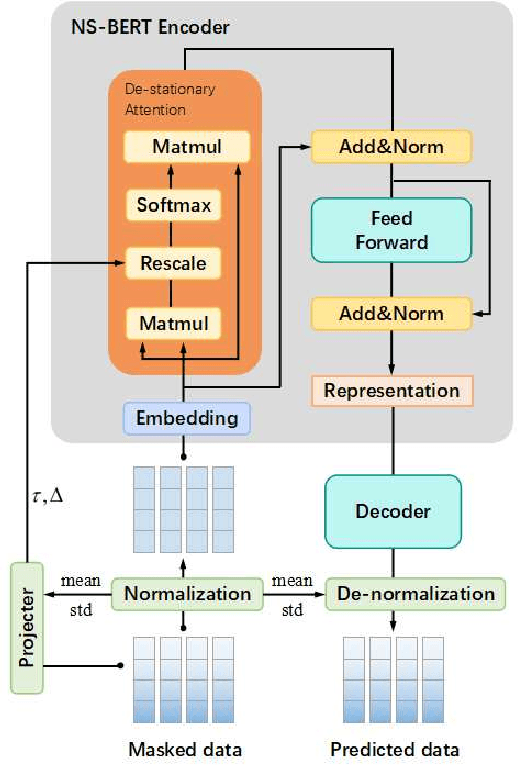
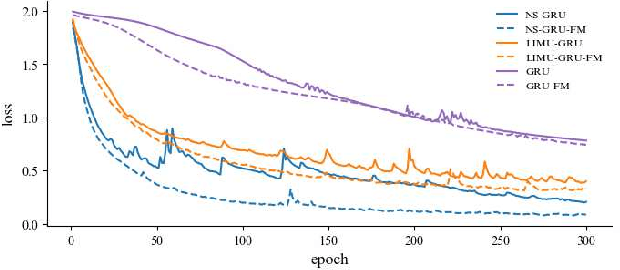
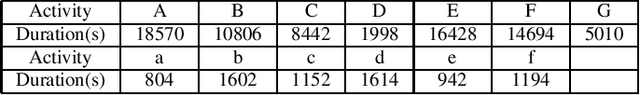
Abstract:Human Activity Recognition (HAR) has gained great attention from researchers due to the popularity of mobile devices and the need to observe users' daily activity data for better human-computer interaction. In this work, we collect a human activity recognition dataset called OPPOHAR consisting of phone IMU data. To facilitate the employment of HAR system in mobile phone and to achieve user-specific activity recognition, we propose a novel light-weight network called Non-stationary BERT with a two-stage training method. We also propose a simple yet effective data augmentation method to explore the deeper relationship between the accelerator and gyroscope data from the IMU. The network achieves the state-of-the-art performance testing on various activity recognition datasets and the data augmentation method demonstrates its wide applicability.
Scale-Translation Equivariant Network for Oceanic Internal Solitary Wave Localization
Jun 18, 2024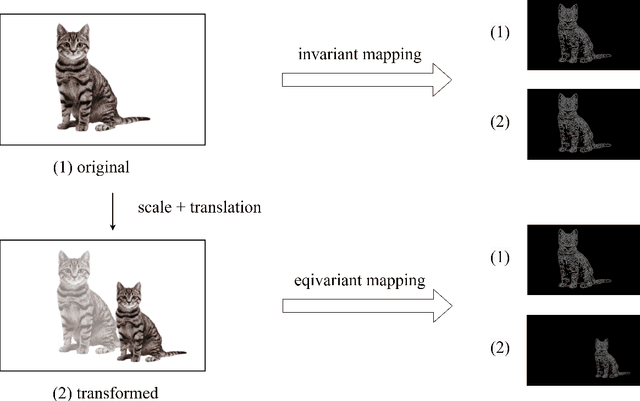
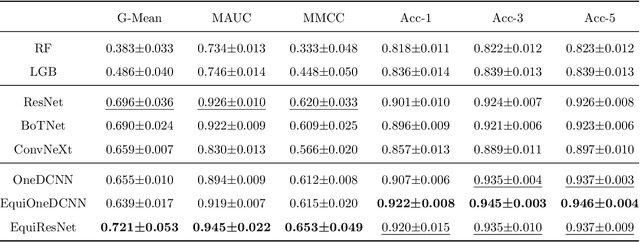
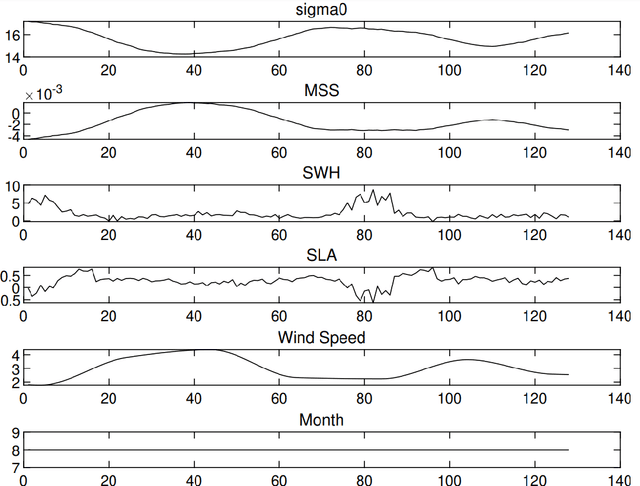
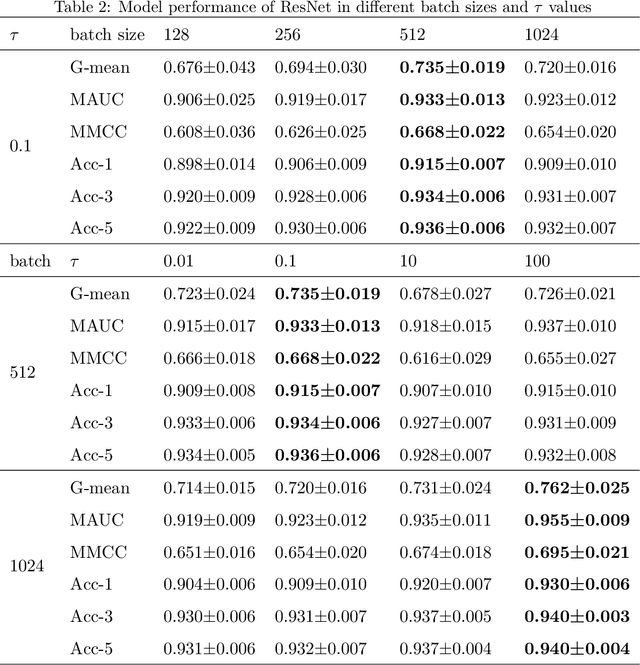
Abstract:Internal solitary waves (ISWs) are gravity waves that are often observed in the interior ocean rather than the surface. They hold significant importance due to their capacity to carry substantial energy, thus influence pollutant transport, oil platform operations, submarine navigation, etc. Researchers have studied ISWs through optical images, synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images, and altimeter data from remote sensing instruments. However, cloud cover in optical remote sensing images variably obscures ground information, leading to blurred or missing surface observations. As such, this paper aims at altimeter-based machine learning solutions to automatically locate ISWs. The challenges, however, lie in the following two aspects: 1) the altimeter data has low resolution, which requires a strong machine learner; 2) labeling data is extremely labor-intensive, leading to very limited data for training. In recent years, the grand progress of deep learning demonstrates strong learning capacity given abundant data. Besides, more recent studies on efficient learning and self-supervised learning laid solid foundations to tackle the aforementioned challenges. In this paper, we propose to inject prior knowledge to achieve a strong and efficient learner. Specifically, intrinsic patterns in altimetry data are efficiently captured using a scale-translation equivariant convolutional neural network (ST-ECNN). By considering inherent symmetries in neural network design, ST-ECNN achieves higher efficiency and better performance than baseline models. Furthermore, we also introduce prior knowledge from massive unsupervised data to enhance our solution using the SimCLR framework for pre-training. Our final solution achieves an overall better performance than baselines on our handcrafted altimetry dataset. Data and codes are available at https://github.com/ZhangWan-byte/Internal_Solitary_Wave_Localization .
Monocular Localization with Semantics Map for Autonomous Vehicles
Jun 06, 2024
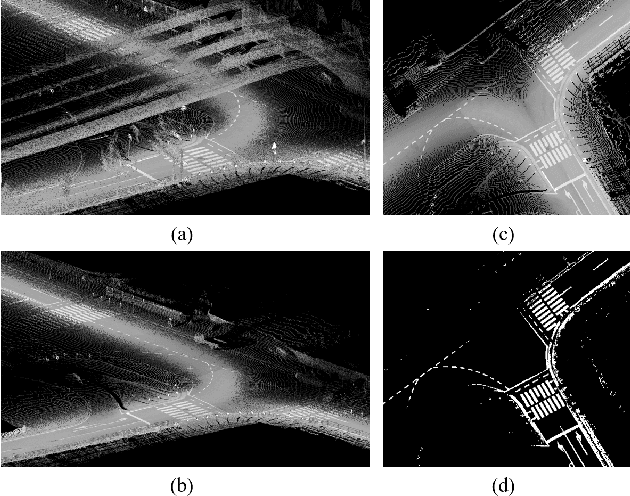
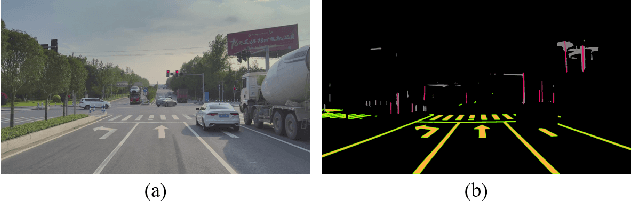
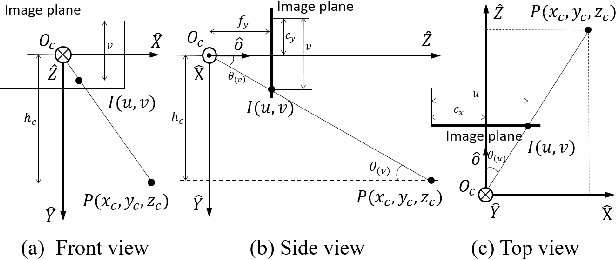
Abstract:Accurate and robust localization remains a significant challenge for autonomous vehicles. The cost of sensors and limitations in local computational efficiency make it difficult to scale to large commercial applications. Traditional vision-based approaches focus on texture features that are susceptible to changes in lighting, season, perspective, and appearance. Additionally, the large storage size of maps with descriptors and complex optimization processes hinder system performance. To balance efficiency and accuracy, we propose a novel lightweight visual semantic localization algorithm that employs stable semantic features instead of low-level texture features. First, semantic maps are constructed offline by detecting semantic objects, such as ground markers, lane lines, and poles, using cameras or LiDAR sensors. Then, online visual localization is performed through data association of semantic features and map objects. We evaluated our proposed localization framework in the publicly available KAIST Urban dataset and in scenarios recorded by ourselves. The experimental results demonstrate that our method is a reliable and practical localization solution in various autonomous driving localization tasks.
Samsung Research China-Beijing at SemEval-2024 Task 3: A multi-stage framework for Emotion-Cause Pair Extraction in Conversations
Apr 25, 2024



Abstract:In human-computer interaction, it is crucial for agents to respond to human by understanding their emotions. Unraveling the causes of emotions is more challenging. A new task named Multimodal Emotion-Cause Pair Extraction in Conversations is responsible for recognizing emotion and identifying causal expressions. In this study, we propose a multi-stage framework to generate emotion and extract the emotion causal pairs given the target emotion. In the first stage, Llama-2-based InstructERC is utilized to extract the emotion category of each utterance in a conversation. After emotion recognition, a two-stream attention model is employed to extract the emotion causal pairs given the target emotion for subtask 2 while MuTEC is employed to extract causal span for subtask 1. Our approach achieved first place for both of the two subtasks in the competition.
Robust Communicative Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning with Active Defense
Dec 16, 2023



Abstract:Communication in multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) has been proven to effectively promote cooperation among agents recently. Since communication in real-world scenarios is vulnerable to noises and adversarial attacks, it is crucial to develop robust communicative MARL technique. However, existing research in this domain has predominantly focused on passive defense strategies, where agents receive all messages equally, making it hard to balance performance and robustness. We propose an active defense strategy, where agents automatically reduce the impact of potentially harmful messages on the final decision. There are two challenges to implement this strategy, that are defining unreliable messages and adjusting the unreliable messages' impact on the final decision properly. To address them, we design an Active Defense Multi-Agent Communication framework (ADMAC), which estimates the reliability of received messages and adjusts their impact on the final decision accordingly with the help of a decomposable decision structure. The superiority of ADMAC over existing methods is validated by experiments in three communication-critical tasks under four types of attacks.
Data Augmentation of Bridging the Delay Gap for DL-based Massive MIMO CSI Feedback
Aug 01, 2023Abstract:In massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems under the frequency division duplexing (FDD) mode, the user equipment (UE) needs to feed channel state information (CSI) back to the base station (BS). Though deep learning approaches have made a hit in the CSI feedback problem, whether they can remain excellent in actual environments needs to be further investigated. In this letter, we point out that the real-time dataset in application often has the domain gap from the training dataset caused by the time delay. To bridge the gap, we propose bubble-shift (B-S) data augmentation, which attempts to offset performance degradation by changing the delay and remaining the channel information as much as possible. Moreover, random-generation (R-G) data augmentation is especially proposed for outdoor scenarios due to the complex distribution of its channels. It generalizes the characteristics of the channel matrix and alleviates the over-fitting problem. Simulation results show that the proposed data augmentation boosts the robustness of networks in both indoor and outdoor environments. The open source codes are available at https://github.com/zhanghy23/CRNet-Aug.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge