Yuan Shen
EGAM: Extended Graph Attention Model for Solving Routing Problems
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Neural combinatorial optimization (NCO) solvers, implemented with graph neural networks (GNNs), have introduced new approaches for solving routing problems. Trained with reinforcement learning (RL), the state-of-the-art graph attention model (GAM) achieves near-optimal solutions without requiring expert knowledge or labeled data. In this work, we generalize the existing graph attention mechanism and propose the extended graph attention model (EGAM). Our model utilizes multi-head dot-product attention to update both node and edge embeddings, addressing the limitations of the conventional GAM, which considers only node features. We employ an autoregressive encoder-decoder architecture and train it with policy gradient algorithms that incorporate a specially designed baseline. Experiments show that EGAM matches or outperforms existing methods across various routing problems. Notably, the proposed model demonstrates exceptional performance on highly constrained problems, highlighting its efficiency in handling complex graph structures.
LoGoPlanner: Localization Grounded Navigation Policy with Metric-aware Visual Geometry
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Trajectory planning in unstructured environments is a fundamental and challenging capability for mobile robots. Traditional modular pipelines suffer from latency and cascading errors across perception, localization, mapping, and planning modules. Recent end-to-end learning methods map raw visual observations directly to control signals or trajectories, promising greater performance and efficiency in open-world settings. However, most prior end-to-end approaches still rely on separate localization modules that depend on accurate sensor extrinsic calibration for self-state estimation, thereby limiting generalization across embodiments and environments. We introduce LoGoPlanner, a localization-grounded, end-to-end navigation framework that addresses these limitations by: (1) finetuning a long-horizon visual-geometry backbone to ground predictions with absolute metric scale, thereby providing implicit state estimation for accurate localization; (2) reconstructing surrounding scene geometry from historical observations to supply dense, fine-grained environmental awareness for reliable obstacle avoidance; and (3) conditioning the policy on implicit geometry bootstrapped by the aforementioned auxiliary tasks, thereby reducing error propagation. We evaluate LoGoPlanner in both simulation and real-world settings, where its fully end-to-end design reduces cumulative error while metric-aware geometry memory enhances planning consistency and obstacle avoidance, leading to more than a 27.3\% improvement over oracle-localization baselines and strong generalization across embodiments and environments. The code and models have been made publicly available on the https://steinate.github.io/logoplanner.github.io.
AI-MASLD Metabolic Dysfunction and Information Steatosis of Large Language Models in Unstructured Clinical Narratives
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:This study aims to simulate real-world clinical scenarios to systematically evaluate the ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to extract core medical information from patient chief complaints laden with noise and redundancy, and to verify whether they exhibit a functional decline analogous to Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). We employed a cross-sectional analysis design based on standardized medical probes, selecting four mainstream LLMs as research subjects: GPT-4o, Gemini 2.5, DeepSeek 3.1, and Qwen3-Max. An evaluation system comprising twenty medical probes across five core dimensions was used to simulate a genuine clinical communication environment. All probes had gold-standard answers defined by clinical experts and were assessed via a double-blind, inverse rating scale by two independent clinicians. The results show that all tested models exhibited functional defects to varying degrees, with Qwen3-Max demonstrating the best overall performance and Gemini 2.5 the worst. Under conditions of extreme noise, most models experienced a functional collapse. Notably, GPT-4o made a severe misjudgment in the risk assessment for pulmonary embolism (PE) secondary to deep vein thrombosis (DVT). This research is the first to empirically confirm that LLMs exhibit features resembling metabolic dysfunction when processing clinical information, proposing the innovative concept of "AI-Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (AI-MASLD)". These findings offer a crucial safety warning for the application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in healthcare, emphasizing that current LLMs must be used as auxiliary tools under human expert supervision, as there remains a significant gap between their theoretical knowledge and practical clinical application.
Validating the Effectiveness of a Large Language Model-based Approach for Identifying Children's Development across Various Free Play Settings in Kindergarten
May 06, 2025Abstract:Free play is a fundamental aspect of early childhood education, supporting children's cognitive, social, emotional, and motor development. However, assessing children's development during free play poses significant challenges due to the unstructured and spontaneous nature of the activity. Traditional assessment methods often rely on direct observations by teachers, parents, or researchers, which may fail to capture comprehensive insights from free play and provide timely feedback to educators. This study proposes an innovative approach combining Large Language Models (LLMs) with learning analytics to analyze children's self-narratives of their play experiences. The LLM identifies developmental abilities, while performance scores across different play settings are calculated using learning analytics techniques. We collected 2,224 play narratives from 29 children in a kindergarten, covering four distinct play areas over one semester. According to the evaluation results from eight professionals, the LLM-based approach achieved high accuracy in identifying cognitive, motor, and social abilities, with accuracy exceeding 90% in most domains. Moreover, significant differences in developmental outcomes were observed across play settings, highlighting each area's unique contributions to specific abilities. These findings confirm that the proposed approach is effective in identifying children's development across various free play settings. This study demonstrates the potential of integrating LLMs and learning analytics to provide child-centered insights into developmental trajectories, offering educators valuable data to support personalized learning and enhance early childhood education practices.
Towards Latency-Aware 3D Streaming Perception for Autonomous Driving
Apr 27, 2025Abstract:Although existing 3D perception algorithms have demonstrated significant improvements in performance, their deployment on edge devices continues to encounter critical challenges due to substantial runtime latency. We propose a new benchmark tailored for online evaluation by considering runtime latency. Based on the benchmark, we build a Latency-Aware 3D Streaming Perception (LASP) framework that addresses the latency issue through two primary components: 1) latency-aware history integration, which extends query propagation into a continuous process, ensuring the integration of historical feature regardless of varying latency; 2) latency-aware predictive detection, a module that compensates the detection results with the predicted trajectory and the posterior accessed latency. By incorporating the latency-aware mechanism, our method shows generalization across various latency levels, achieving an online performance that closely aligns with 80\% of its offline evaluation on the Jetson AGX Orin without any acceleration techniques.
Bias-Eliminated PnP for Stereo Visual Odometry: Provably Consistent and Large-Scale Localization
Apr 24, 2025



Abstract:In this paper, we first present a bias-eliminated weighted (Bias-Eli-W) perspective-n-point (PnP) estimator for stereo visual odometry (VO) with provable consistency. Specifically, leveraging statistical theory, we develop an asymptotically unbiased and $\sqrt {n}$-consistent PnP estimator that accounts for varying 3D triangulation uncertainties, ensuring that the relative pose estimate converges to the ground truth as the number of features increases. Next, on the stereo VO pipeline side, we propose a framework that continuously triangulates contemporary features for tracking new frames, effectively decoupling temporal dependencies between pose and 3D point errors. We integrate the Bias-Eli-W PnP estimator into the proposed stereo VO pipeline, creating a synergistic effect that enhances the suppression of pose estimation errors. We validate the performance of our method on the KITTI and Oxford RobotCar datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that our method: 1) achieves significant improvements in both relative pose error and absolute trajectory error in large-scale environments; 2) provides reliable localization under erratic and unpredictable robot motions. The successful implementation of the Bias-Eli-W PnP in stereo VO indicates the importance of information screening in robotic estimation tasks with high-uncertainty measurements, shedding light on diverse applications where PnP is a key ingredient.
Localization and Tracking for Cooperative Users in Multi-RIS-assisted Systems: Theoretical Analysis and Principles of Interpretations
Apr 07, 2025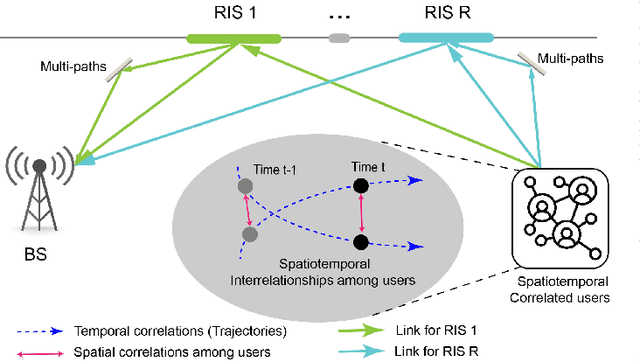
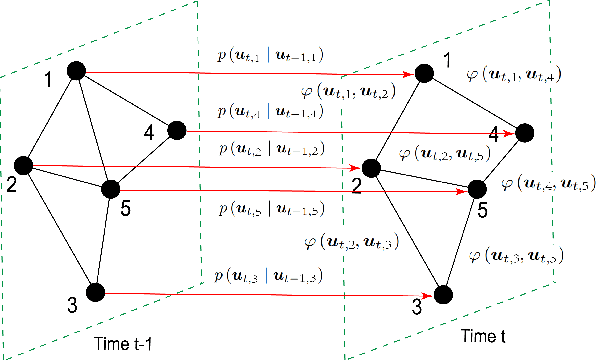
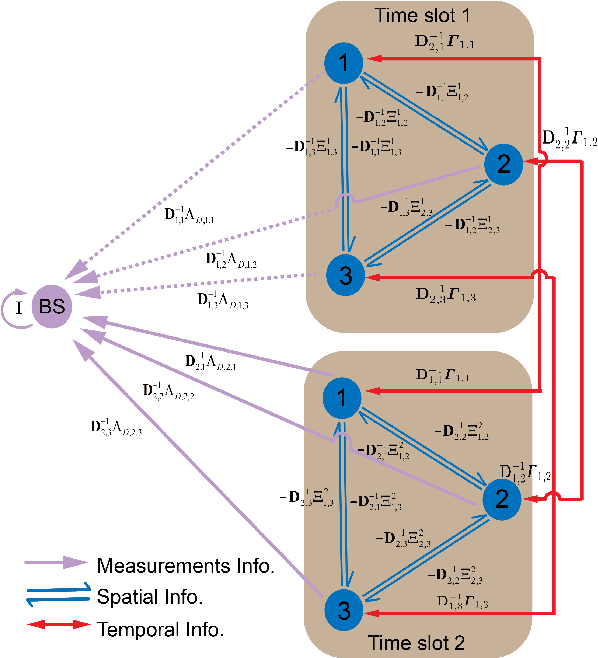
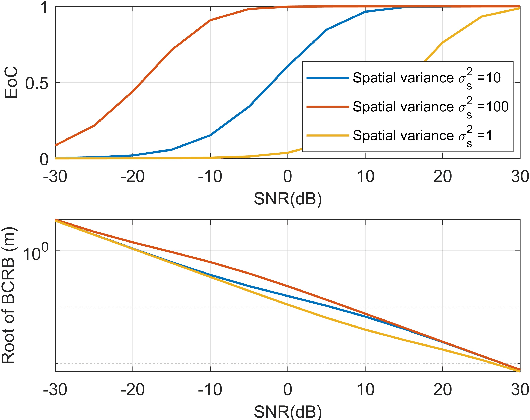
Abstract:Localization and tracking (LocTrack) are fundamental enablers for a wide range of emerging applications. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) have emerged as key components for enhancing the LocTrack performance. This paper investigates a multi-RIS-assisted multi-user (MRMU) LocTrack system, where multiple RISs collaboratively reflect the position-bearing signals for information fusion at the base station, leveraging spatial-temporal correlations in user positions. While studies have shown these correlations improve localization accuracy, their trade-offs with system complexity remain unclear. To address this gap, we characterize the effectiveness of spatial-temporal correlation priors (STPs) utilization in MRMU LocTrack systems using a metric, termed efficiency of correlation (EoC). To further elucidate correlation propagation and RIS interactions, we provide a "correlation information routing" interpretation of EoC through random walk theory. EoC provides a principled performance evaluation metric, that enables system designers to balance localization accuracy enhancement against the increased complexity. Additionally, we investigate the error propagation phenomenon, analyzing its convergence and asymptotic behavior in MRMU LocTrack systems. Finally, we validate the theoretical results through extensive numerical simulations.
Beware of Metacognitive Laziness: Effects of Generative Artificial Intelligence on Learning Motivation, Processes, and Performance
Dec 12, 2024
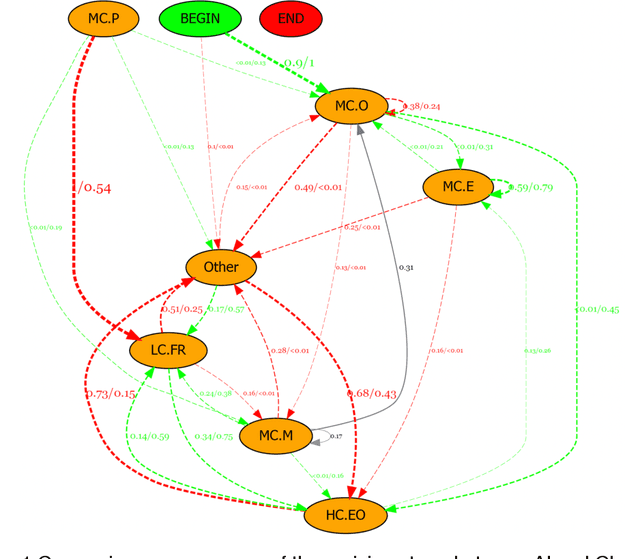
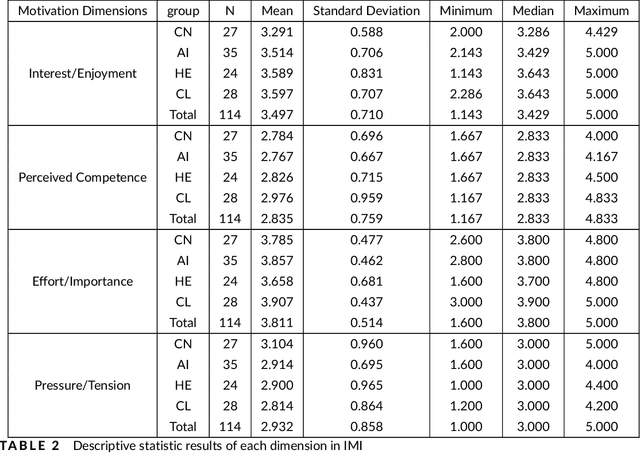
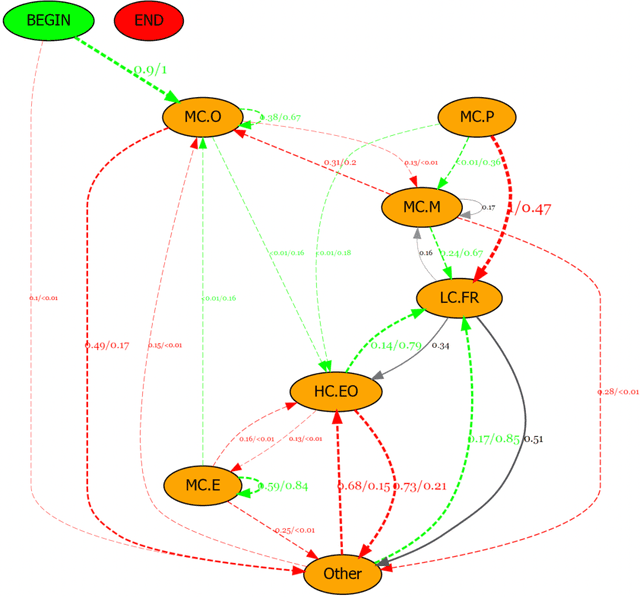
Abstract:With the continuous development of technological and educational innovation, learners nowadays can obtain a variety of support from agents such as teachers, peers, education technologies, and recently, generative artificial intelligence such as ChatGPT. The concept of hybrid intelligence is still at a nascent stage, and how learners can benefit from a symbiotic relationship with various agents such as AI, human experts and intelligent learning systems is still unknown. The emerging concept of hybrid intelligence also lacks deep insights and understanding of the mechanisms and consequences of hybrid human-AI learning based on strong empirical research. In order to address this gap, we conducted a randomised experimental study and compared learners' motivations, self-regulated learning processes and learning performances on a writing task among different groups who had support from different agents (ChatGPT, human expert, writing analytics tools, and no extra tool). A total of 117 university students were recruited, and their multi-channel learning, performance and motivation data were collected and analysed. The results revealed that: learners who received different learning support showed no difference in post-task intrinsic motivation; there were significant differences in the frequency and sequences of the self-regulated learning processes among groups; ChatGPT group outperformed in the essay score improvement but their knowledge gain and transfer were not significantly different. Our research found that in the absence of differences in motivation, learners with different supports still exhibited different self-regulated learning processes, ultimately leading to differentiated performance. What is particularly noteworthy is that AI technologies such as ChatGPT may promote learners' dependence on technology and potentially trigger metacognitive laziness.
Fundamental Limits of Pulse Based UWB ISAC Systems: A Parameter Estimation Perspective
Oct 17, 2024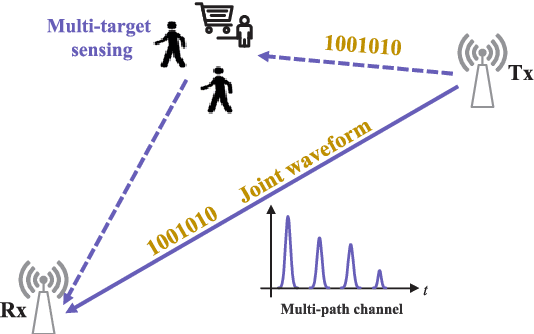
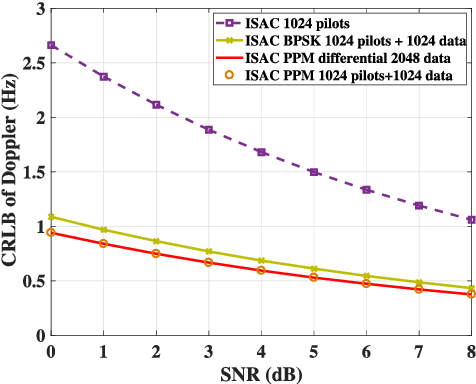
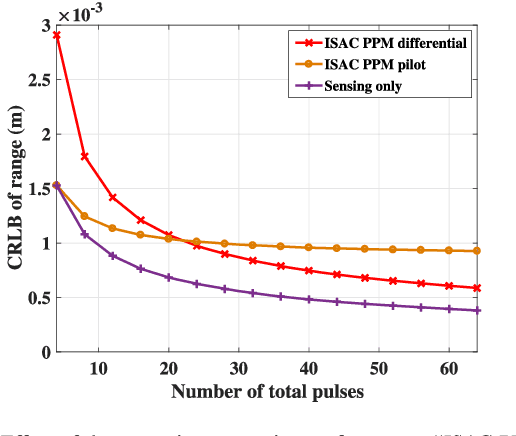
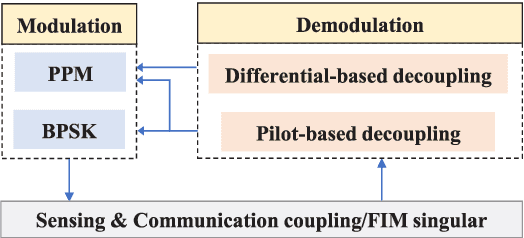
Abstract:Impulse radio ultra-wideband (IR-UWB) signals stand out for their high temporal resolution, low cost, and large bandwidth, making them a highly promising option for integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) systems. In this paper, we design an ISAC system for a bi-static passive sensing scenario that accommodates multiple targets. Specifically, we introduce two typical modulation schemes, PPM and BPSK, for data transmission. The essential coupling between sensing and communication is examined through the Fisher information matrix (FIM). Accordingly, we introduce a pilot-based decoupling approach that relies on known time-delays, as well as a differential decoupling strategy that uses a known starting symbol position. Finally, we assess the sensing and communication performance under various modulation and demodulation schemes under the constraints of current UWB standards. This assessment utilizes the Cramer-Rao Lower Bound (CRLB) for sensing and the Shannon capacity limit for communication, offering theoretical insights into choosing suitable data signal processing methods in real-world applications.
EarthGen: Generating the World from Top-Down Views
Sep 02, 2024
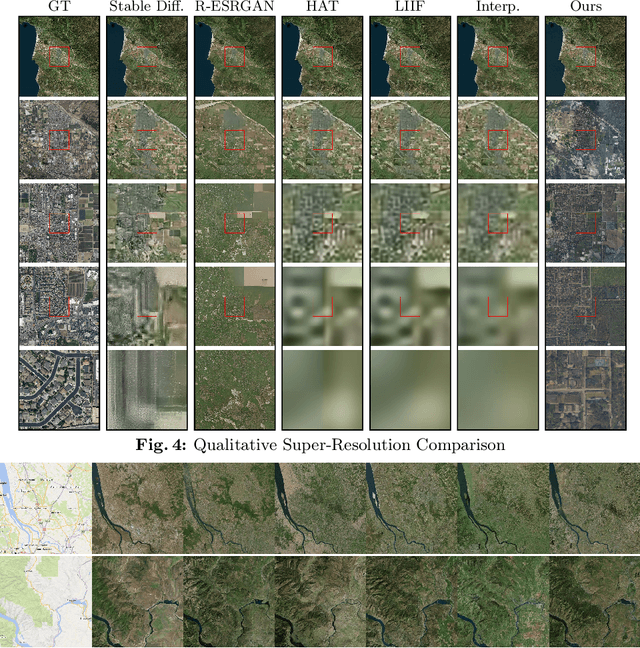

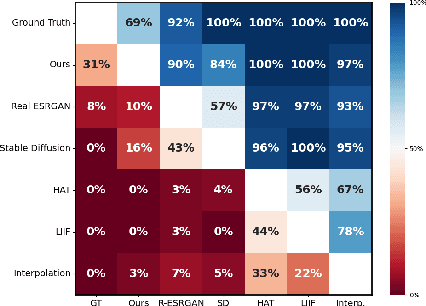

Abstract:In this work, we present a novel method for extensive multi-scale generative terrain modeling. At the core of our model is a cascade of superresolution diffusion models that can be combined to produce consistent images across multiple resolutions. Pairing this concept with a tiled generation method yields a scalable system that can generate thousands of square kilometers of realistic Earth surfaces at high resolution. We evaluate our method on a dataset collected from Bing Maps and show that it outperforms super-resolution baselines on the extreme super-resolution task of 1024x zoom. We also demonstrate its ability to create diverse and coherent scenes via an interactive gigapixel-scale generated map. Finally, we demonstrate how our system can be extended to enable novel content creation applications including controllable world generation and 3D scene generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge