Liang Yang
Propagating Similarity, Mitigating Uncertainty: Similarity Propagation-enhanced Uncertainty for Multimodal Recommendation
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Recommendation (MMR) systems are crucial for modern platforms but are often hampered by inherent noise and uncertainty in modal features, such as blurry images, diverse visual appearances, or ambiguous text. Existing methods often overlook this modality-specific uncertainty, leading to ineffective feature fusion. Furthermore, they fail to leverage rich similarity patterns among users and items to refine representations and their corresponding uncertainty estimates. To address these challenges, we propose a novel framework, Similarity Propagation-enhanced Uncertainty for Multimodal Recommendation (SPUMR). SPUMR explicitly models and mitigates uncertainty by first constructing the Modality Similarity Graph and the Collaborative Similarity Graph to refine representations from both content and behavioral perspectives. The Uncertainty-aware Preference Aggregation module then adaptively fuses the refined multimodal features, assigning greater weight to more reliable modalities. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that SPUMR achieves significant improvements over existing leading methods.
The Straight and Narrow: Do LLMs Possess an Internal Moral Path?
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Enhancing the moral alignment of Large Language Models (LLMs) is a critical challenge in AI safety. Current alignment techniques often act as superficial guardrails, leaving the intrinsic moral representations of LLMs largely untouched. In this paper, we bridge this gap by leveraging Moral Foundations Theory (MFT) to map and manipulate the fine-grained moral landscape of LLMs. Through cross-lingual linear probing, we validate the shared nature of moral representations in middle layers and uncover a shared yet different moral subspace between English and Chinese. Building upon this, we extract steerable Moral Vectors and successfully validate their efficacy at both internal and behavioral levels. Leveraging the high generalizability of morality, we propose Adaptive Moral Fusion (AMF), a dynamic inference-time intervention that synergizes probe detection with vector injection to tackle the safety-helpfulness trade-off. Empirical results confirm that our approach acts as a targeted intrinsic defense, effectively reducing incorrect refusals on benign queries while minimizing jailbreak success rates compared to standard baselines.
Sensing-enabled Secure Rotatable Array System Enhanced by Multi-Layer Transmitting RIS
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Programmable metasurfaces and adjustable antennas are promising technologies. The security of a rotatable array system is investigated in this paper. A dual-base-station (BS) architecture is adopted, in which the BSs collaboratively perform integrated sensing of the eavesdropper (the target) and communication tasks. To address the security challenge when the sensing target is located on the main communication link, the problem of maximizing the secrecy rate (SR) under sensing signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio requirements and discrete constraints is formulated. This problem involves the joint optimization of the array pose, the antenna distribution on the array surface, the multi-layer transmitting RIS phase matrices, and the beamforming matrices, which is non-convex. To solve this challenge, an two-stage online algorithm based on the generalized Rayleigh quotient and an offline algorithm based on the Multi-Agent Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient are proposed. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithms. Compared to conventional schemes without array pose adjustment, the proposed approach achieves approximately 22\% improvement in SR. Furthermore, array rotation provides higher performance gains than position changes.
FOUND: Fourier-based von Mises Distribution for Robust Single Domain Generalization in Object Detection
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Single Domain Generalization (SDG) for object detection aims to train a model on a single source domain that can generalize effectively to unseen target domains. While recent methods like CLIP-based semantic augmentation have shown promise, they often overlook the underlying structure of feature distributions and frequency-domain characteristics that are critical for robustness. In this paper, we propose a novel framework that enhances SDG object detection by integrating the von Mises-Fisher (vMF) distribution and Fourier transformation into a CLIP-guided pipeline. Specifically, we model the directional features of object representations using vMF to better capture domain-invariant semantic structures in the embedding space. Additionally, we introduce a Fourier-based augmentation strategy that perturbs amplitude and phase components to simulate domain shifts in the frequency domain, further improving feature robustness. Our method not only preserves the semantic alignment benefits of CLIP but also enriches feature diversity and structural consistency across domains. Extensive experiments on the diverse weather-driving benchmark demonstrate that our approach outperforms the existing state-of-the-art method.
Probing the Critical Point (CritPt) of AI Reasoning: a Frontier Physics Research Benchmark
Oct 01, 2025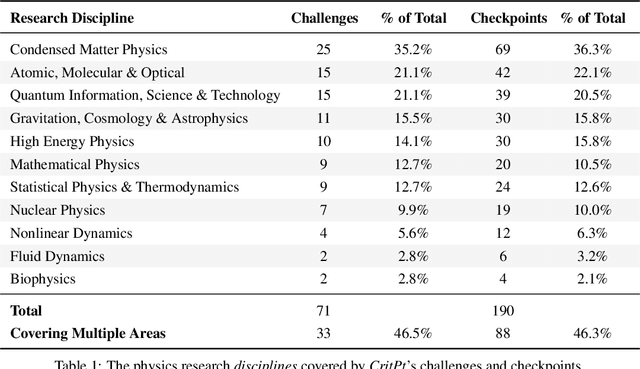
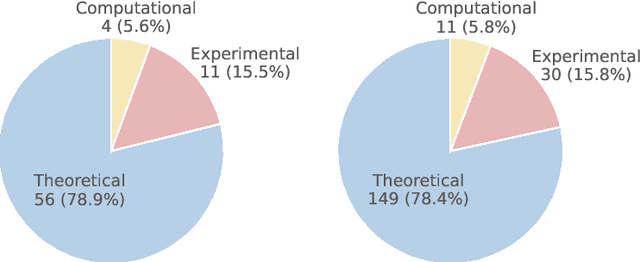
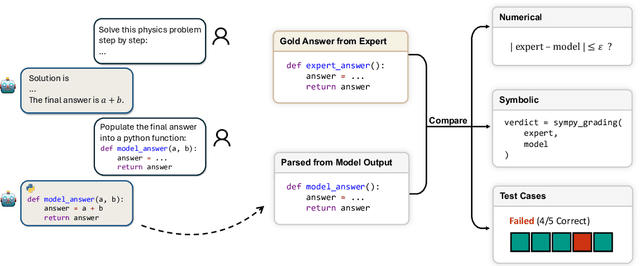
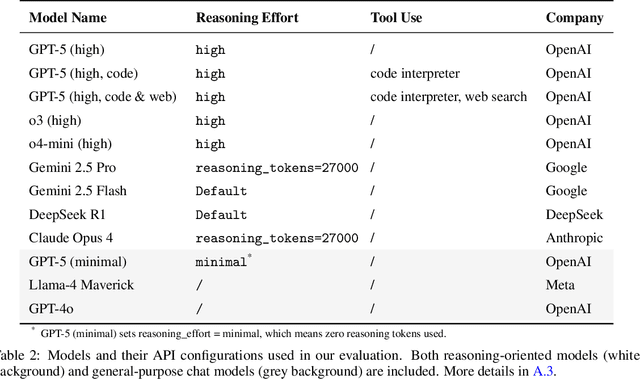
Abstract:While large language models (LLMs) with reasoning capabilities are progressing rapidly on high-school math competitions and coding, can they reason effectively through complex, open-ended challenges found in frontier physics research? And crucially, what kinds of reasoning tasks do physicists want LLMs to assist with? To address these questions, we present the CritPt (Complex Research using Integrated Thinking - Physics Test, pronounced "critical point"), the first benchmark designed to test LLMs on unpublished, research-level reasoning tasks that broadly covers modern physics research areas, including condensed matter, quantum physics, atomic, molecular & optical physics, astrophysics, high energy physics, mathematical physics, statistical physics, nuclear physics, nonlinear dynamics, fluid dynamics and biophysics. CritPt consists of 71 composite research challenges designed to simulate full-scale research projects at the entry level, which are also decomposed to 190 simpler checkpoint tasks for more fine-grained insights. All problems are newly created by 50+ active physics researchers based on their own research. Every problem is hand-curated to admit a guess-resistant and machine-verifiable answer and is evaluated by an automated grading pipeline heavily customized for advanced physics-specific output formats. We find that while current state-of-the-art LLMs show early promise on isolated checkpoints, they remain far from being able to reliably solve full research-scale challenges: the best average accuracy among base models is only 4.0% , achieved by GPT-5 (high), moderately rising to around 10% when equipped with coding tools. Through the realistic yet standardized evaluation offered by CritPt, we highlight a large disconnect between current model capabilities and realistic physics research demands, offering a foundation to guide the development of scientifically grounded AI tools.
Rethinking Contrastive Learning in Session-based Recommendation
Jun 05, 2025



Abstract:Session-based recommendation aims to predict intents of anonymous users based on limited behaviors. With the ability in alleviating data sparsity, contrastive learning is prevailing in the task. However, we spot that existing contrastive learning based methods still suffer from three obstacles: (1) they overlook item-level sparsity and primarily focus on session-level sparsity; (2) they typically augment sessions using item IDs like crop, mask and reorder, failing to ensure the semantic consistency of augmented views; (3) they treat all positive-negative signals equally, without considering their varying utility. To this end, we propose a novel multi-modal adaptive contrastive learning framework called MACL for session-based recommendation. In MACL, a multi-modal augmentation is devised to generate semantically consistent views at both item and session levels by leveraging item multi-modal features. Besides, we present an adaptive contrastive loss that distinguishes varying contributions of positive-negative signals to improve self-supervised learning. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate the superiority of MACL over state-of-the-art methods.
AI-empowered Channel Estimation for Block-based Active IRS-enhanced Hybrid-field IoT Network
May 20, 2025Abstract:In this paper, channel estimation (CE) for uplink hybrid-field communications involving multiple Internet of Things (IoT) devices assisted by an active intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) is investigated. Firstly, to reduce the complexity of near-field (NF) channel modeling and estimation between IoT devices and active IRS, a sub-blocking strategy for active IRS is proposed. Specifically, the entire active IRS is divided into multiple smaller sub-blocks, so that IoT devices are located in the far-field (FF) region of each sub block, while also being located in the NF region of the entire active IRS. This strategy significantly simplifies the channel model and reduces the parameter estimation dimension by decoupling the high-dimensional NF channel parameter space into low dimensional FF sub channels. Subsequently, the relationship between channel approximation error and CE error with respect to the number of sub blocks is derived, and the optimal number of sub blocks is solved based on the criterion of minimizing the total error. In addition, considering that the amplification capability of active IRS requires power consumption, a closed-form expression for the optimal power allocation factor is derived. To further reduce the pilot overhead, a lightweight CE algorithm based on convolutional autoencoder (CAE) and multi-head attention mechanism, called CAEformer, is designed. The Cramer-Rao lower bound is derived to evaluate the proposed algorithm's performance. Finally, simulation results demonstrate the proposed CAEformer network significantly outperforms the conventional least square and minimum mean square error scheme in terms of estimation accuracy.
TransMedSeg: A Transferable Semantic Framework for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
May 20, 2025Abstract:Semi-supervised learning (SSL) has achieved significant progress in medical image segmentation (SSMIS) through effective utilization of limited labeled data. While current SSL methods for medical images predominantly rely on consistency regularization and pseudo-labeling, they often overlook transferable semantic relationships across different clinical domains and imaging modalities. To address this, we propose TransMedSeg, a novel transferable semantic framework for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. Our approach introduces a Transferable Semantic Augmentation (TSA) module, which implicitly enhances feature representations by aligning domain-invariant semantics through cross-domain distribution matching and intra-domain structural preservation. Specifically, TransMedSeg constructs a unified feature space where teacher network features are adaptively augmented towards student network semantics via a lightweight memory module, enabling implicit semantic transformation without explicit data generation. Interestingly, this augmentation is implicitly realized through an expected transferable cross-entropy loss computed over the augmented teacher distribution. An upper bound of the expected loss is theoretically derived and minimized during training, incurring negligible computational overhead. Extensive experiments on medical image datasets demonstrate that TransMedSeg outperforms existing semi-supervised methods, establishing a new direction for transferable representation learning in medical image analysis.
2DXformer: Dual Transformers for Wind Power Forecasting with Dual Exogenous Variables
May 02, 2025Abstract:Accurate wind power forecasting can help formulate scientific dispatch plans, which is of great significance for maintaining the safety, stability, and efficient operation of the power system. In recent years, wind power forecasting methods based on deep learning have focused on extracting the spatiotemporal correlations among data, achieving significant improvements in forecasting accuracy. However, they exhibit two limitations. First, there is a lack of modeling for the inter-variable relationships, which limits the accuracy of the forecasts. Second, by treating endogenous and exogenous variables equally, it leads to unnecessary interactions between the endogenous and exogenous variables, increasing the complexity of the model. In this paper, we propose the 2DXformer, which, building upon the previous work's focus on spatiotemporal correlations, addresses the aforementioned two limitations. Specifically, we classify the inputs of the model into three types: exogenous static variables, exogenous dynamic variables, and endogenous variables. First, we embed these variables as variable tokens in a channel-independent manner. Then, we use the attention mechanism to capture the correlations among exogenous variables. Finally, we employ a multi-layer perceptron with residual connections to model the impact of exogenous variables on endogenous variables. Experimental results on two real-world large-scale datasets indicate that our proposed 2DXformer can further improve the performance of wind power forecasting. The code is available in this repository: \href{https://github.com/jseaj/2DXformer}{https://github.com/jseaj/2DXformer}.
Adaptive Decision Boundary for Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning
Apr 15, 2025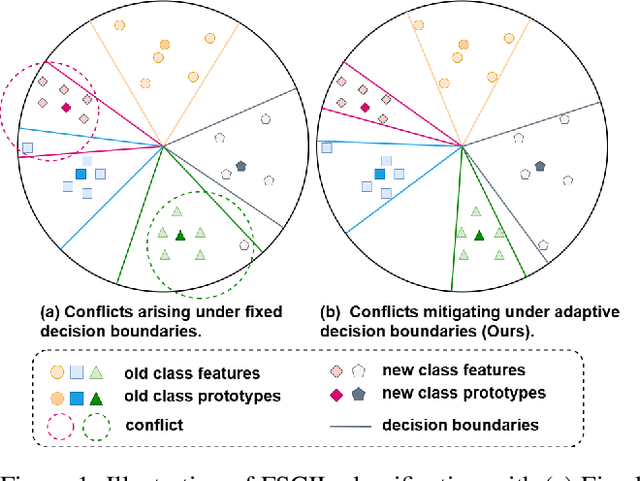
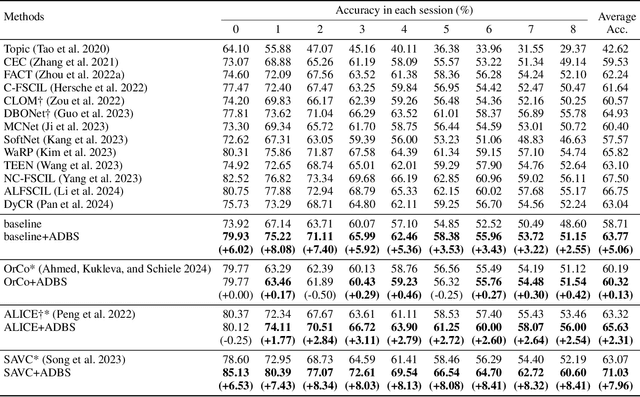
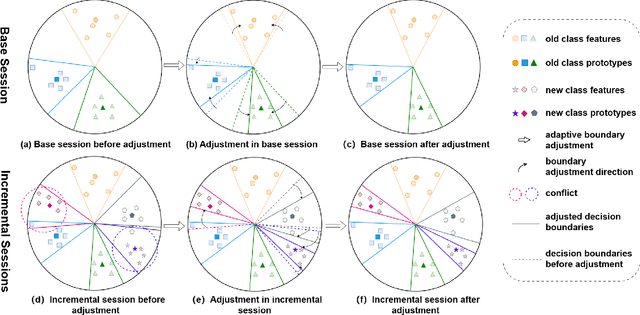
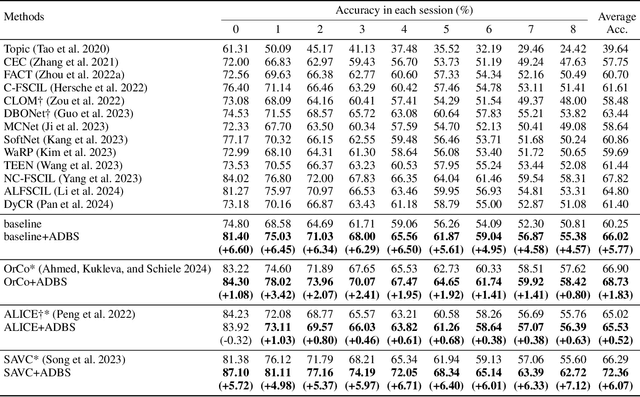
Abstract:Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning (FSCIL) aims to continuously learn new classes from a limited set of training samples without forgetting knowledge of previously learned classes. Conventional FSCIL methods typically build a robust feature extractor during the base training session with abundant training samples and subsequently freeze this extractor, only fine-tuning the classifier in subsequent incremental phases. However, current strategies primarily focus on preventing catastrophic forgetting, considering only the relationship between novel and base classes, without paying attention to the specific decision spaces of each class. To address this challenge, we propose a plug-and-play Adaptive Decision Boundary Strategy (ADBS), which is compatible with most FSCIL methods. Specifically, we assign a specific decision boundary to each class and adaptively adjust these boundaries during training to optimally refine the decision spaces for the classes in each session. Furthermore, to amplify the distinctiveness between classes, we employ a novel inter-class constraint loss that optimizes the decision boundaries and prototypes for each class. Extensive experiments on three benchmarks, namely CIFAR100, miniImageNet, and CUB200, demonstrate that incorporating our ADBS method with existing FSCIL techniques significantly improves performance, achieving overall state-of-the-art results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge