Panagiotis D. Diamantoulakis
Improving Reliability of Hybrid Bit-Semantic Communications for Cellular Networks
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Semantic communications (SemComs) have been considered as a promising solution to reduce the amount of transmitted information, thus paving the way for more energy-and spectrum-efficient wireless networks. Nevertheless, SemComs rely heavily on the utilization of deep neural networks (DNNs) at the transceivers, which limit the accuracy between the original and reconstructed data and are challenging to implement in practice due to increased architecture complexity. Thus, hybrid cellular networks that utilize both conventional bit communications (BitComs) and SemComs have been introduced to bridge the gap between required and existing infrastructure. To facilitate such networks, in this work, we investigate reliability by deriving closed-form expressions for the outage probability of the network. Additionally, we propose a generalized outage probability through which the cell radius that achieves a desired outage threshold for a specific range of users is calculated in closed form. Additionally, to consider the practical limitations caused by the specialized dedicated hardware and the increased memory and computational resources that are required to support SemCom, a semantic utilization metric is proposed. Based on this metric, we express the probability that a specific number of users select SemCom transmission and calculate the optimal cell radius for that number in closed form. Simulation results validate the derived analytical expressions and the characterized design properties of the cell radius found through the proposed metrics, providing useful insights.
Pinching Antenna-aided NOMA Systems with Internal Eavesdropping
Dec 25, 2025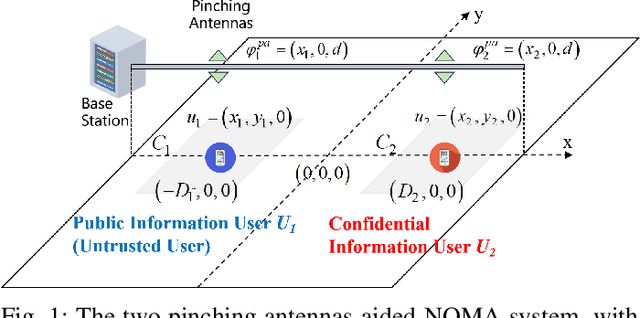
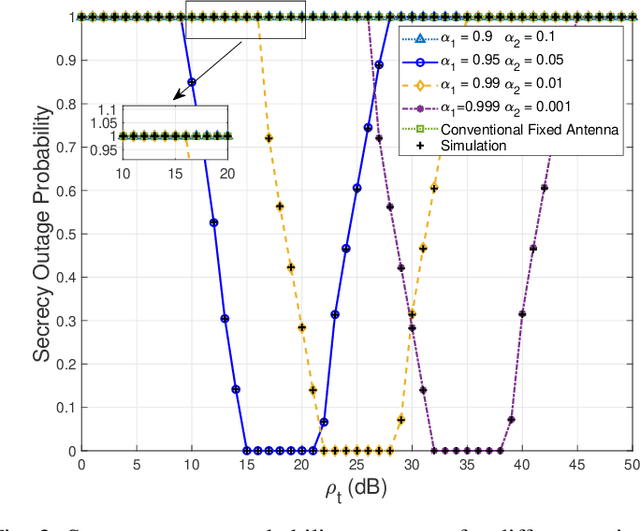
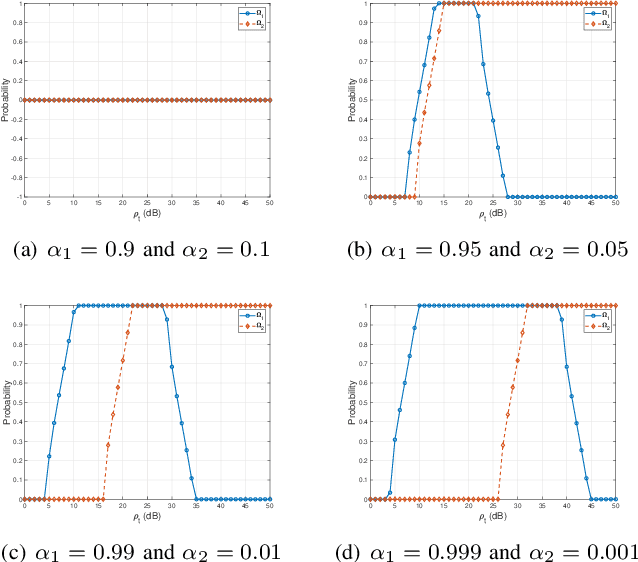
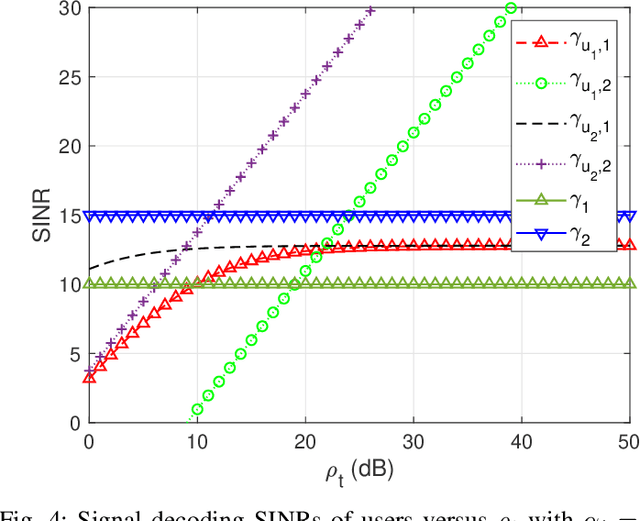
Abstract:As a novel member of flexible antennas, the pinching antenna (PA) is realized by integrating small dielectric particles on a waveguide, offering unique regulatory capabilities on constructing line-of-sight (LoS) links and enhancing transceiver channels, reducing path loss and signal blockage. Meanwhile, non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) has become a potential technology of next-generation communications due to its remarkable advantages in spectrum efficiency and user access capability. The integration of PA and NOMA enables synergistic leveraging of PA's channel regulation capability and NOMA's multi-user multiplexing advantage, forming a complementary technical framework to deliver high-performance communication solutions. However, the use of successive interference cancellation (SIC) introduces significant security risks to power-domain NOMA systems when internal eavesdropping is present. To this end, this paper investigates the physical layer security of a PA-aided NOMA system where a nearby user is considered as an internal eavesdropper. We enhance the security of the NOMA system through optimizing the radiated power of PAs and analyze the secrecy performance by deriving the closed-form expressions for the secrecy outage probability (SOP). Furthermore, we extend the characterization of PA flexibility beyond deployment and scale adjustment to include flexible regulation of PA coupling length. Based on two conventional PA power models, i.e., the equal power model and the proportional power model, we propose a flexible power strategy to achieve secure transmission. The results highlight the potential of the PA-aided NOMA system in mitigating internal eavesdropping risks, and provide an effective strategy for optimizing power allocation and cell range of user activity.
Viterbi State Selection for Discrete Pinching Antenna Systems
Dec 23, 2025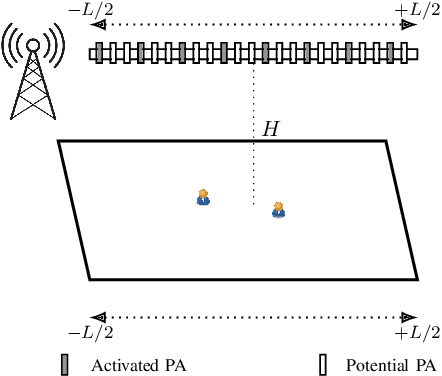
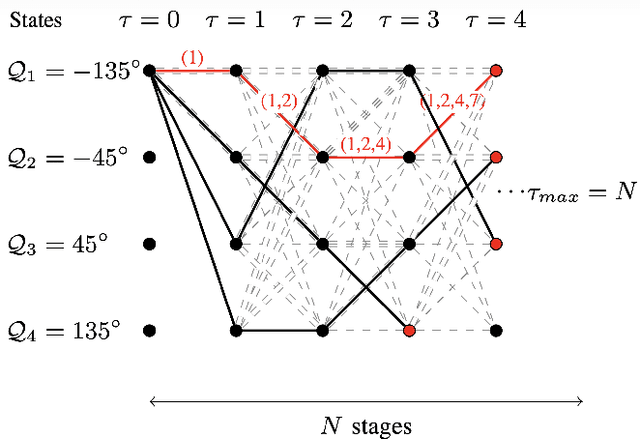
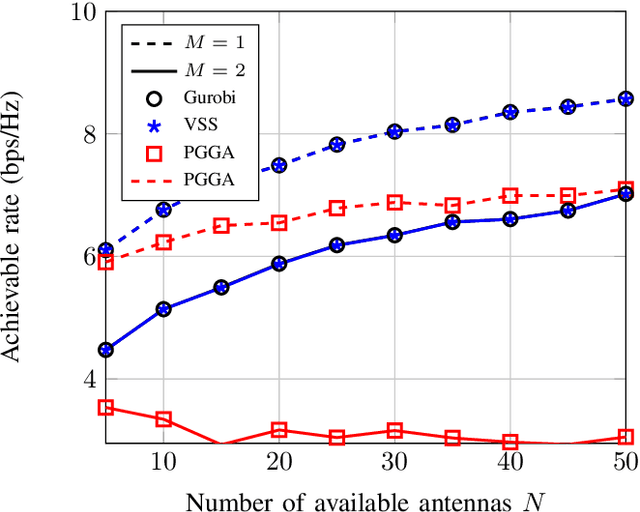
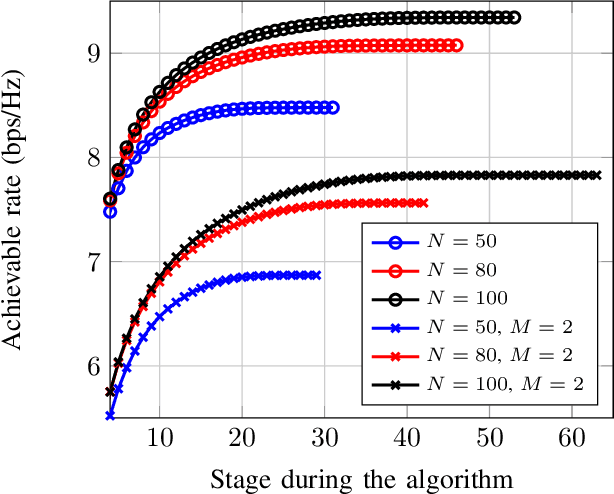
Abstract:Pinching antennas enable dynamic control of electromagnetic wave propagation through reconfigurable radiating structures, but selecting an optimal subset of antennas remains a combinatorial problem with exponential complexity. This letter considers antenna subset selection for a waveguide-fed pinching antenna array serving ground users under a time-division access scheme. The achievable rate depends on the coherent superposition of the effective complex channel gains and is therefore highly sensitive to the relative phase alignment of the activated antennas. To address the prohibitive complexity of exhaustive search, we propose a Viterbi state selection (VSS) algorithm that exploits the phase structure of the combined received signal. The trellis state is defined by a quantized representation of the phase of the accumulated complex gain, and a Viterbi-based survivor rule is used to prune dominated antenna subsets across stages. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves the same antenna selection and rate as exhaustive search, while reducing the computational complexity from exponential to polynomial in the number of available antennas.
How Many Pinching Antennas Are Enough?
Dec 21, 2025
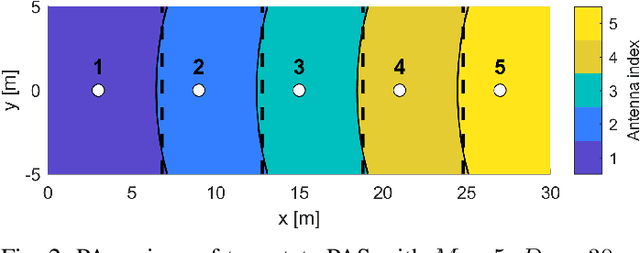
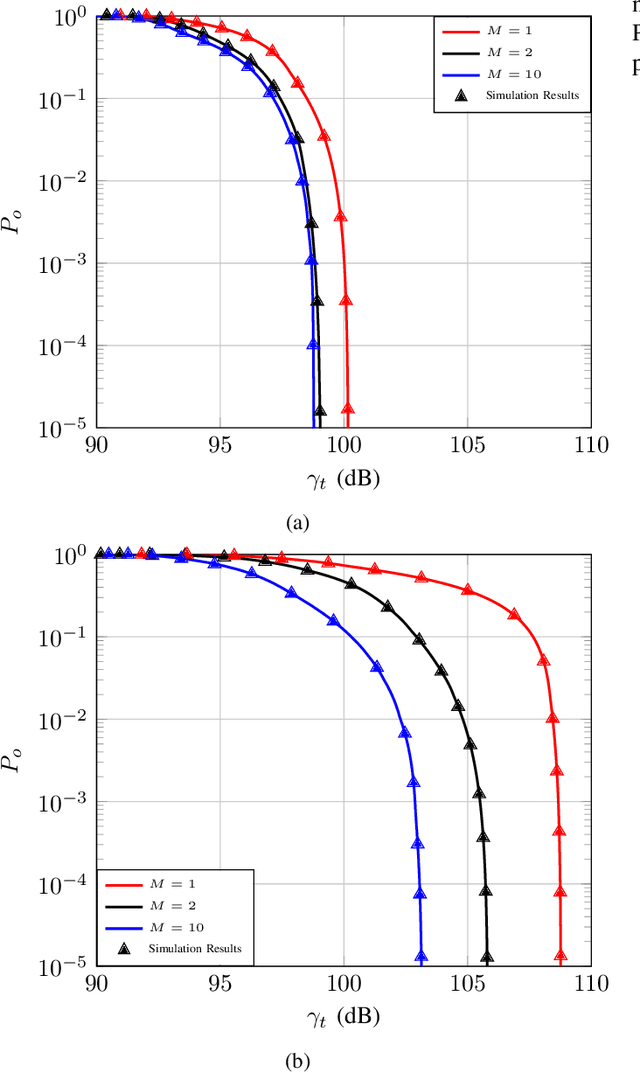
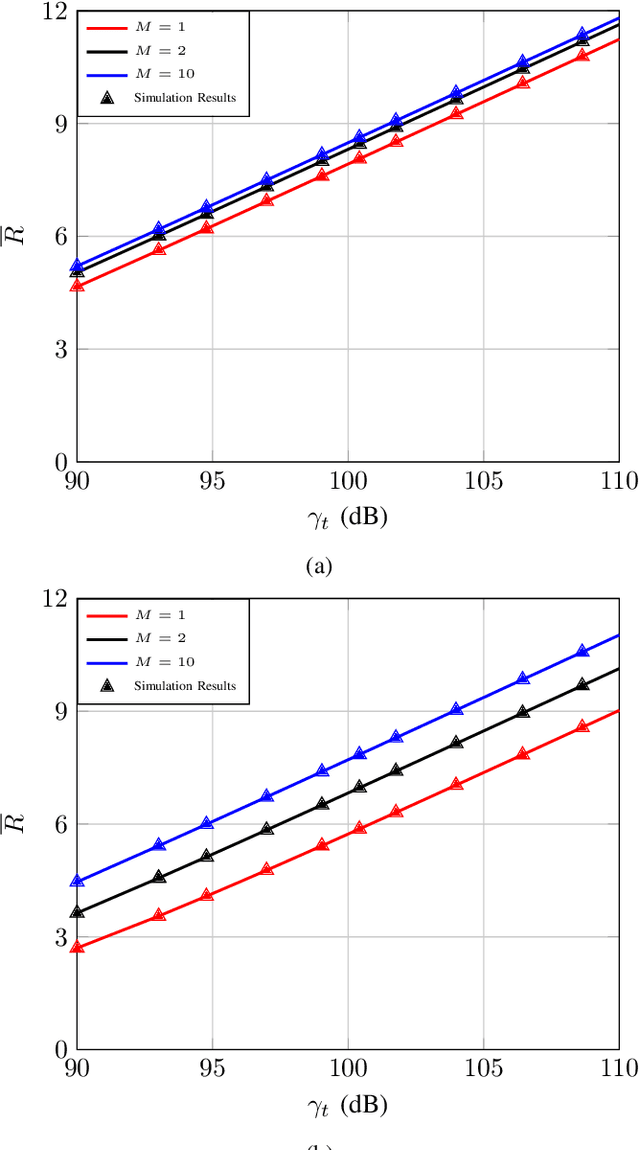
Abstract:Programmable wireless environments (PWEs) have emerged as a key paradigm for next-generation communication networks, aiming to transform wireless propagation from an uncontrollable phenomenon into a reconfigurable process that can adapt to diverse service requirements. In this framework, pinching-antenna systems (PASs) have recently been proposed as a promising enabling technology, as they allow the radiation location and effective propagation distance to be adjusted by selectively exciting radiating points along a dielectric waveguide. However, most existing studies on PASs rely on the idealized assumption that pinching-antenna (PA) positions can be continuously adjusted along the waveguide, while realistically only a finite set of pinching locations is available. Motivated by this, this paper analyzes the performance of two-state PASs, where the PA positions are fixed and only their activation state can be controlled. By explicitly accounting for the spatial discreteness of the available pinching points, closed-form analytical expressions for the outage probability and the ergodic achievable data rate are derived. In addition, we introduce the pinching discretization efficiency to quantify the performance gap between discrete and continuous pinching configurations, enabling a direct assessment of the number of PAs required to approximate the ideal continuous case. Finally, numerical results validate the analytical framework and show that near-continuous performance can be achieved with a limited number of PAs, offering useful insights for the design and deployment of PASs in PWEs.
Constellation Design and Detection under Generalized Hardware Impairments
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a maximum-likelihood detection framework that jointly mitigates hardware (HW) impairments in both amplitude and phase. By modeling transceiver distortions as residual amplitude and phase noise, we introduce the approximate phase-and-amplitude distortion detector (PAD-D), which operates in the polar domain and effectively mitigates both distortion components through distortion-aware weighting. The proposed detector performs reliable detection under generalized HW impairment conditions, achieving substantial performance gains over the conventional Euclidean detector (EUC-D) and the Gaussian-assumption phase noise detector (GAP-D), which is primarily designed to address phase distortions. In addition, we derive a closed-form high-SNR symbol error probability (SEP) approximation, which offers a generic analytical expression applicable to arbitrary constellations. Simulation results demonstrate that the PAD-D achieves up to an order-of-magnitude reduction in the error floor relative to EUC-D and GAP-D for both high-order quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) and super amplitude phase-shift keying (SAPSK) constellations, establishing a unified and practical framework for detection under realistic transceiver impairments. Building on this framework, we further develop optimized constellations tailored to PAD-D, where the symbol positions are optimized in the complex plane to minimize SEP. The optimality of these constellations is confirmed through extensive simulations, which also verify the accuracy of the proposed analytical SEP approximation, even for the optimized designs.
Performance Analysis of Wireless-Powered Pinching Antenna Systems
Nov 05, 2025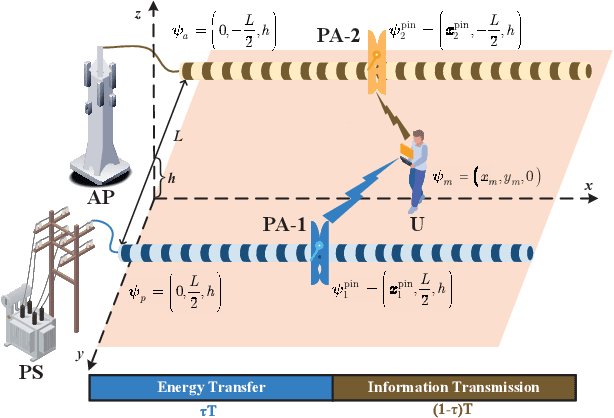
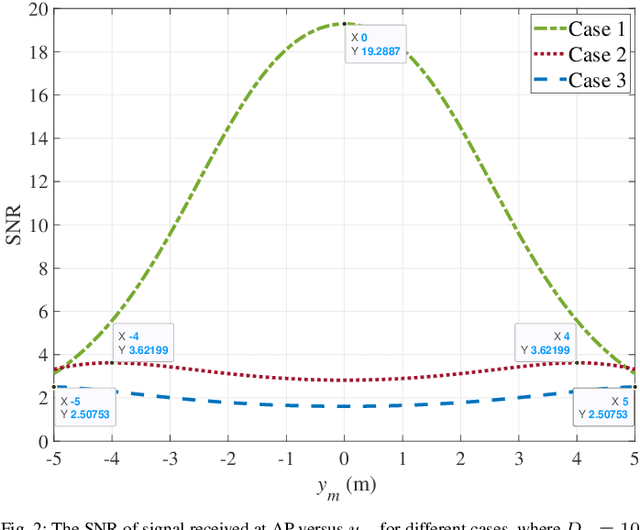
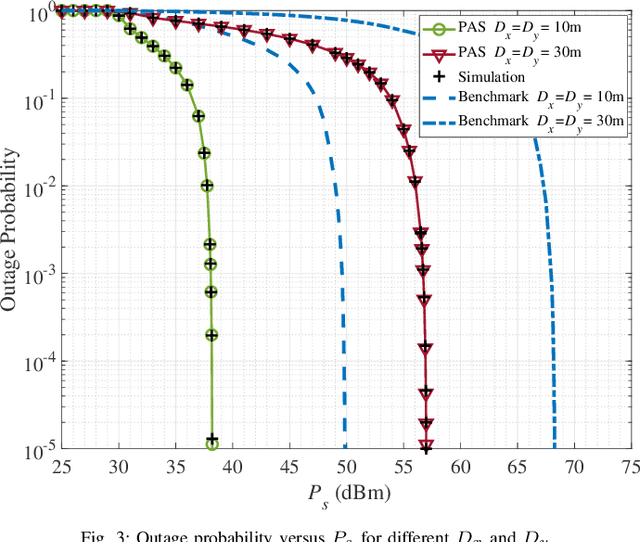
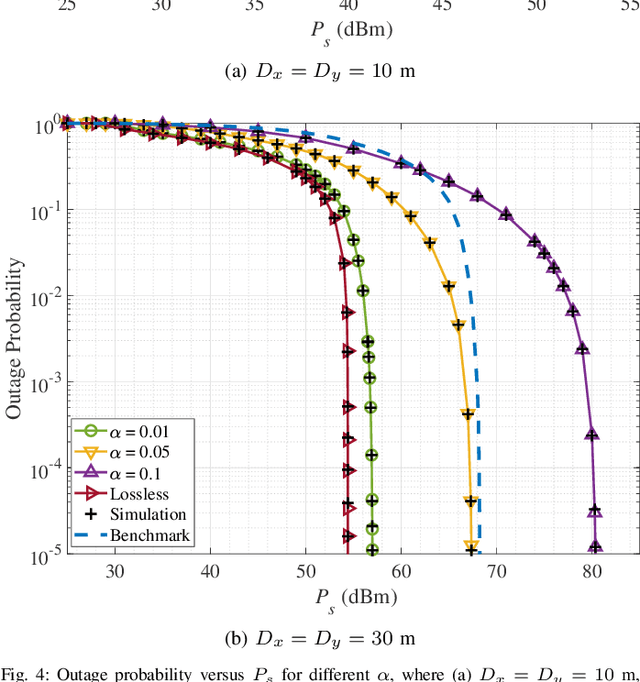
Abstract:Pinching antenna system (PAS) serves as a groundbreaking paradigm that enhances wireless communications by flexibly adjusting the position of pinching antenna (PA) and establishing a strong line-of-sight (LoS) link, thereby reducing the free-space path loss. This paper introduces the concept of wireless-powered PAS, and investigates the reliability of wireless-powered PAS to explore the advantages of PA in improving the performance of wireless-powered communication (WPC) system. In addition, we derive the closed-form expressions of outage probability and ergodic rate for the practical lossy waveguide case and ideal lossless waveguide case, respectively, and analyze the optimal deployment of waveguides and user to provide valuable insights for guiding their deployments. The results show that an increase in the absorption coefficient and in the dimensions of the user area leads to higher in-waveguide and free-space propagation losses, respectively, which in turn increase the outage probability and reduce the ergodic rate of the wireless-powered PAS. However, the performance of wireless-powered PAS is severely affected by the absorption coefficient and the waveguide length, e.g., under conditions of high absorption coefficient and long waveguide, the outage probability of wireless-powered PAS is even worse than that of traditional WPC system. While the ergodic rate of wireless-powered PAS is better than that of traditional WPC system under conditions of high absorption coefficient and long waveguide. Interestingly, the wireless-powered PAS has the optimal time allocation factor and optimal distance between power station (PS) and access point (AP) to minimize the outage probability or maximize the ergodic rate. Moreover, the system performance of PS and AP separated at the optimal distance between PS and AP is superior to that of PS and AP integrated into a hybrid access point.
Deep Learning Optimization of Two-State Pinching Antennas Systems
Jul 08, 2025Abstract:The evolution of wireless communication systems requires flexible, energy-efficient, and cost-effective antenna technologies. Pinching antennas (PAs), which can dynamically control electromagnetic wave propagation through binary activation states, have recently emerged as a promising candidate. In this work, we investigate the problem of optimally selecting a subset of fixed-position PAs to activate in a waveguide, when the aim is to maximize the communication rate at a user terminal. Due to the complex interplay between antenna activation, waveguide-induced phase shifts, and power division, this problem is formulated as a combinatorial fractional 0-1 quadratic program. To efficiently solve this challenging problem, we use neural network architectures of varying complexity to learn activation policies directly from data, leveraging spatial features and signal structure. Furthermore, we incorporate user location uncertainty into our training and evaluation pipeline to simulate realistic deployment conditions. Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed models.
Fluid Aerial Networks: UAV Rotation for Inter-Cell Interference Mitigation
Jul 02, 2025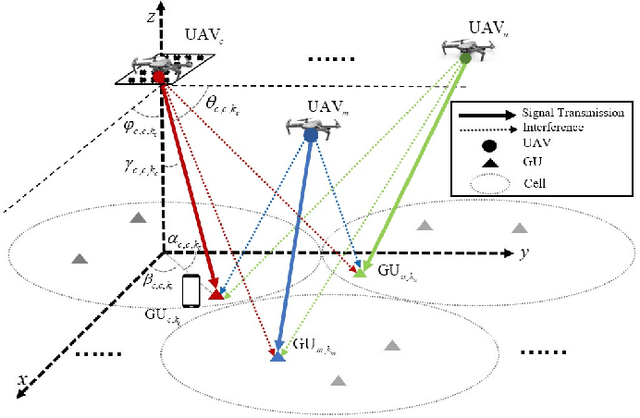
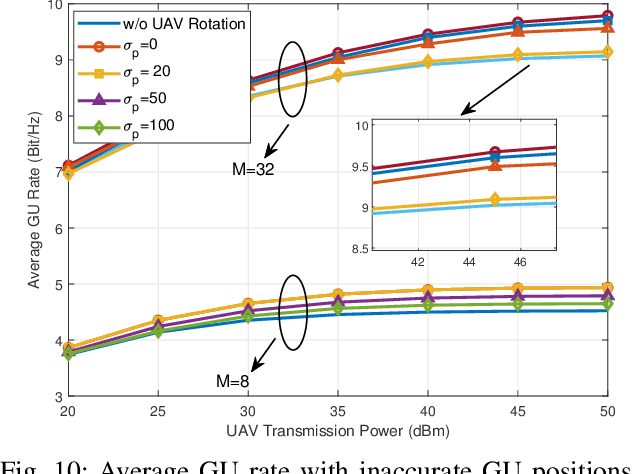
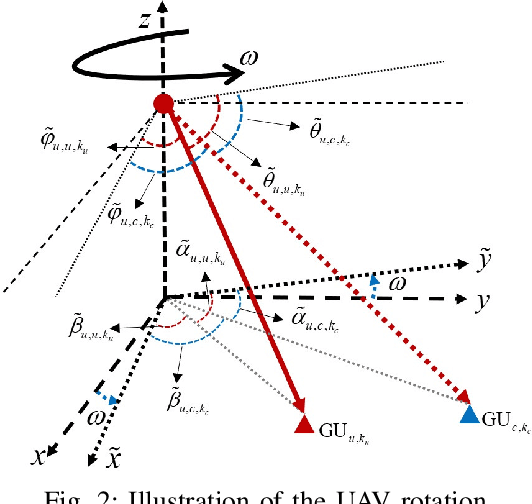
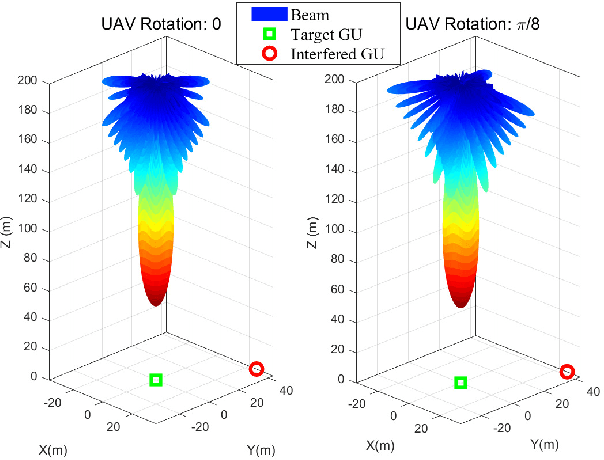
Abstract:With the rapid development of aerial infrastructure, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) that function as aerial base stations (ABSs) extend terrestrial network services into the sky, enabling on-demand connectivity and enhancing emergency communication capabilities in cellular networks by leveraging the flexibility and mobility of UAVs. In such a UAV-assisted network, this paper investigates position-based beamforming between ABSs and ground users (GUs). To mitigate inter-cell interference, we propose a novel fluid aerial network that leverages ABS rotation to increase multi-cell capacity and overall network efficiency. Specifically, considering the line-of-sight channel model, the spatial beamforming weights are determined by the orientation angles of the GUs. In this direction, we examine the beamforming gain of a two-dimensional multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) array at various ground positions, revealing that ABS rotation significantly affects multi-user channel correlation and inter-cell interference. Based on these findings, we propose an alternative low-complexity algorithm to design the optimal rotation angle for ABSs, aiming to reduce inter-cell interference and thus maximize the sum rate of multi-cell systems. In simulations, exhaustive search serves as a benchmark to validate the optimization performance of the proposed sequential ABS rotation scheme. Moreover, simulation results demonstrate that, in interference-limited regions, the proposed ABS rotation paradigm can significantly reduce inter-cell interference in terrestrial networks and improve the multi-cell sum rate by approximately 10\% compared to fixed-direction ABSs without rotation.
Cognitive-Radio Functionality: A Novel Configuration for STAR-RIS assisted RSMA Networks
May 30, 2025Abstract:Cognitive radio rate-splitting multiple access (CR-RSMA) has emerged as a promising multiple access framework that can efficiently manage interference and adapt dynamically to heterogeneous quality-of-service (QoS) requirements. To effectively support such demanding access schemes, programmable wireless environments have attracted considerable attention, especially through simultaneously transmitting and reflecting reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (STAR-RISs), which can enable full-space control of signal propagation in asymmetric user deployments. In this paper, we propose the cognitive radio (CR) functionality for STAR-RIS-assisted CR-RSMA systems, leveraging the unique capability of the STAR-RIS to combine element and power splitting for adaptive control of transmission and reflection in CR scenarios. Specifically, the proposed CR functionality partitions the STAR-RIS into two regions independently controlling the transmission and reflection of signals, simultaneously ensuring the required QoS for the primary user and enhancing the performance of the secondary user. To accurately characterize the system performance, we derive analytical expressions for the ergodic rate of the secondary user and the outage rate of the primary user under Nakagami-m fading. Finally, simulation results show that the proposed approach effectively manages interference, guarantees the QoS of the primary user, and significantly improves the throughput of the secondary user, highlighting STAR-RIS as an efficient solution for CR-RSMA-based services.
OFDMA for Pinching Antenna Systems
May 26, 2025Abstract:Pinching-antenna (PA) systems route millimeter wave (mmWave) signals through a leaky waveguide and radiate them at "pinch" apertures, offering low-cost line-of-sight (LoS) coverage. However, when multiple PAs serve multiple users simultaneously, the downlink channel becomes strongly frequency-selective, creating inter-symbol interference (ISI) that existing single-carrier designs overlook. This paper models the overall channel as a finite impulse response (FIR) filter, characterizes its frequency selectivity, and explicitly accounts for the resulting ISI. To overcome ISI, we introduce an orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA)-based framework and formulate a max-min resource-allocation problem to achieve user fairness. A lightweight two-stage heuristic-greedy subcarrier assignment, followed by per-user water-filling, achieves near-optimal fairness with polynomial complexity. Simulation results for an indoor layout demonstrate that the proposed scheme notably increases the minimum user rate compared to time-division single-carrier baselines and remains robust under moderate LoS blockage.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge