Zhaohan Zhang
GrACE: A Generative Approach to Better Confidence Elicitation in Large Language Models
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:Assessing the reliability of Large Language Models (LLMs) by confidence elicitation is a prominent approach to AI safety in high-stakes applications, such as healthcare and finance. Existing methods either require expensive computational overhead or suffer from poor calibration, making them impractical and unreliable for real-world deployment. In this work, we propose GrACE, a Generative Approach to Confidence Elicitation that enables scalable and reliable confidence elicitation for LLMs. GrACE adopts a novel mechanism in which the model expresses confidence by the similarity between the last hidden state and the embedding of a special token appended to the vocabulary, in real-time. We fine-tune the model for calibrating the confidence with calibration targets associated with accuracy. Experiments with three LLMs and two benchmark datasets show that the confidence produced by GrACE achieves the best discriminative capacity and calibration on open-ended generation tasks, outperforming six competing methods without resorting to additional sampling or an auxiliary model. Moreover, we propose two strategies for improving test-time scaling based on confidence induced by GrACE. Experimental results show that using GrACE not only improves the accuracy of the final decision but also significantly reduces the number of required samples in the test-time scaling scheme, indicating the potential of GrACE as a practical solution for deploying LLMs with scalable, reliable, and real-time confidence estimation.
Iron Sharpens Iron: Defending Against Attacks in Machine-Generated Text Detection with Adversarial Training
Feb 18, 2025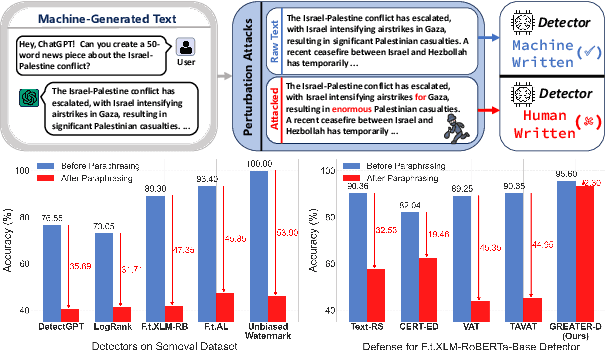
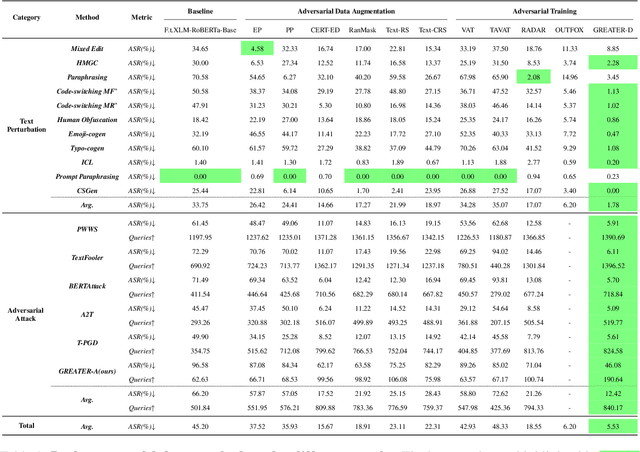
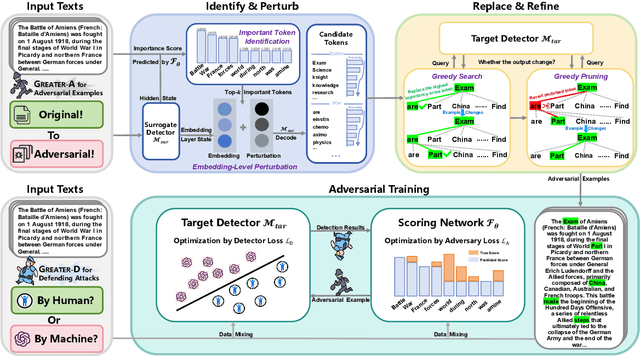
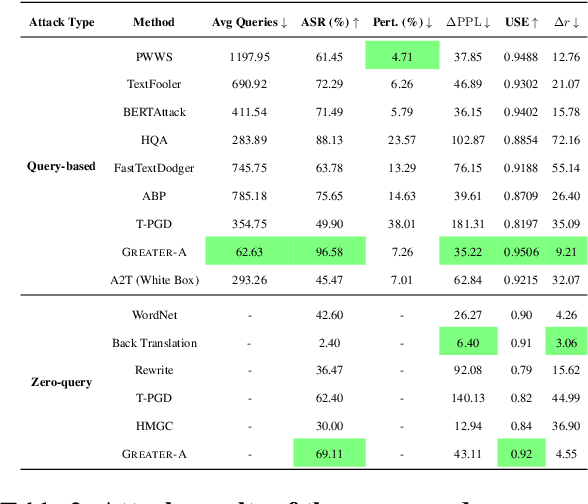
Abstract:Machine-generated Text (MGT) detection is crucial for regulating and attributing online texts. While the existing MGT detectors achieve strong performance, they remain vulnerable to simple perturbations and adversarial attacks. To build an effective defense against malicious perturbations, we view MGT detection from a threat modeling perspective, that is, analyzing the model's vulnerability from an adversary's point of view and exploring effective mitigations. To this end, we introduce an adversarial framework for training a robust MGT detector, named GREedy Adversary PromoTed DefendER (GREATER). The GREATER consists of two key components: an adversary GREATER-A and a detector GREATER-D. The GREATER-D learns to defend against the adversarial attack from GREATER-A and generalizes the defense to other attacks. GREATER-A identifies and perturbs the critical tokens in embedding space, along with greedy search and pruning to generate stealthy and disruptive adversarial examples. Besides, we update the GREATER-A and GREATER-D synchronously, encouraging the GREATER-D to generalize its defense to different attacks and varying attack intensities. Our experimental results across 9 text perturbation strategies and 5 adversarial attacks show that our GREATER-D reduces the Attack Success Rate (ASR) by 10.61% compared with SOTA defense methods while our GREATER-A is demonstrated to be more effective and efficient than SOTA attack approaches.
Get Confused Cautiously: Textual Sequence Memorization Erasure with Selective Entropy Maximization
Aug 09, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have been found to memorize and recite some of the textual sequences from their training set verbatim, raising broad concerns about privacy and copyright issues when using LLMs. This Textual Sequence Memorization (TSM) phenomenon leads to a high demand to regulate LLM output to prevent it from generating certain memorized text to meet user requirements. However, our empirical study reveals that existing methods for TSM erasure fail to forget massive memorized samples without substantially jeopardizing the model utility. To achieve a better trade-off between the effectiveness of TSM erasure and model utility in LLMs, our paper proposes a new framework based on Entropy Maximization with Selective Optimization (EMSO), where the updated weights are chosen with a novel contrastive gradient metric without any participation of additional model or data. Our analysis shows that training with the entropy maximization loss has a more stable optimization process and better keeps model utility than existing methods. The contrastive gradient metric localizes the most influential weight for TSM erasure by taking both the gradient magnitude and direction into consideration. Extensive experiments across three model scales demonstrate that our method excels in handling large-scale forgetting requests while preserving model ability in language generation and reasoning.
Concentrate Attention: Towards Domain-Generalizable Prompt Optimization for Language Models
Jun 15, 2024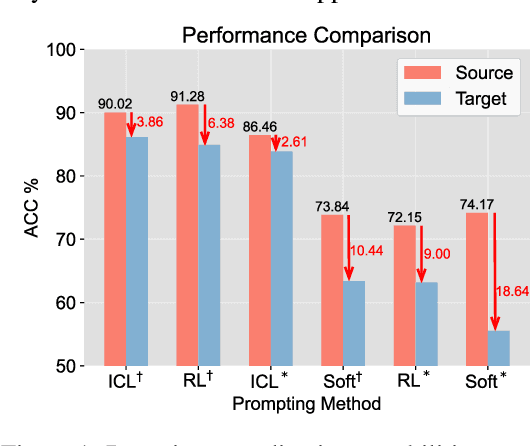
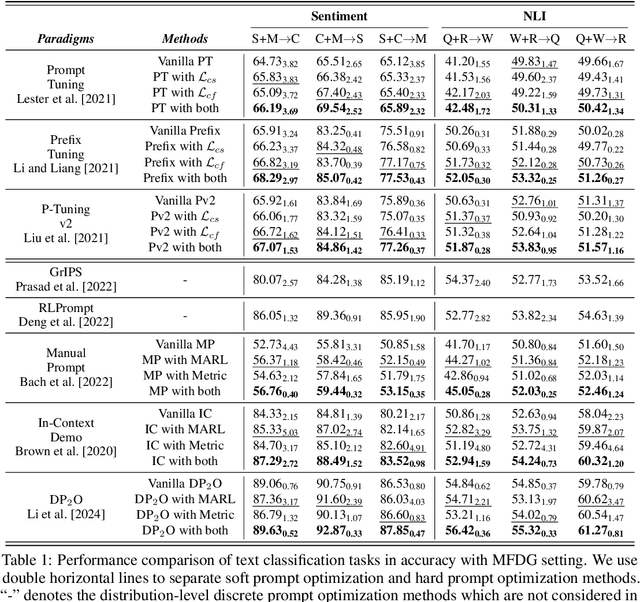
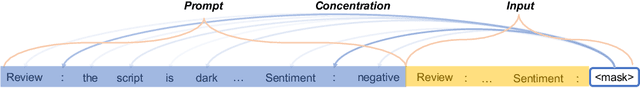
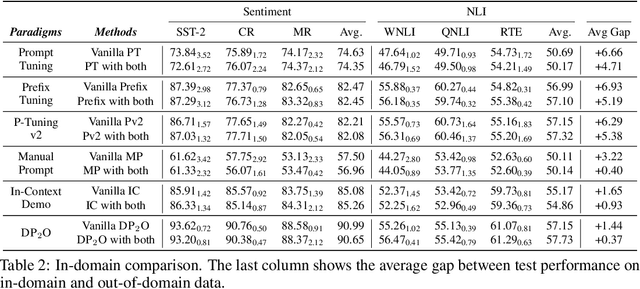
Abstract:Recent advances in prompt optimization have notably enhanced the performance of pre-trained language models (PLMs) on downstream tasks. However, the potential of optimized prompts on domain generalization has been under-explored. To explore the nature of prompt generalization on unknown domains, we conduct pilot experiments and find that (i) Prompts gaining more attention weight from PLMs' deep layers are more generalizable and (ii) Prompts with more stable attention distributions in PLMs' deep layers are more generalizable. Thus, we offer a fresh objective towards domain-generalizable prompts optimization named "Concentration", which represents the "lookback" attention from the current decoding token to the prompt tokens, to increase the attention strength on prompts and reduce the fluctuation of attention distribution. We adapt this new objective to popular soft prompt and hard prompt optimization methods, respectively. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our idea improves comparison prompt optimization methods by 1.42% for soft prompt generalization and 2.16% for hard prompt generalization in accuracy on the multi-source domain generalization setting, while maintaining satisfying in-domain performance. The promising results validate the effectiveness of our proposed prompt optimization objective and provide key insights into domain-generalizable prompts.
StablePT: Towards Stable Prompting for Few-shot Learning via Input Separation
Apr 30, 2024Abstract:Large language models have shown their ability to become effective few-shot learners with prompting, revoluting the paradigm of learning with data scarcity. However, this approach largely depends on the quality of prompt initialization, and always exhibits large variability among different runs. Such property makes prompt tuning highly unreliable and vulnerable to poorly constructed prompts, which limits its extension to more real-world applications. To tackle this issue, we propose to treat the hard prompt and soft prompt as separate inputs to mitigate noise brought by the prompt initialization. Furthermore, we optimize soft prompts with contrastive learning for utilizing class-aware information in the training process to maintain model performance. Experimental results demonstrate that \sysname outperforms state-of-the-art methods by 7.20% in accuracy and reduces the standard deviation by 2.02 on average. Furthermore, extensive experiments underscore its robustness and stability across 7 datasets covering various tasks.
Does DetectGPT Fully Utilize Perturbation? Selective Perturbation on Model-Based Contrastive Learning Detector would be Better
Feb 04, 2024



Abstract:The burgeoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) have raised growing concerns about abuse. DetectGPT, a zero-shot metric-based unsupervised machine-generated text detector, first introduces perturbation and shows great performance improvement. However, DetectGPT's random perturbation strategy might introduce noise, limiting the distinguishability and further performance improvements. Moreover, its logit regression module relies on setting the threshold, which harms the generalizability and applicability of individual or small-batch inputs. Hence, we propose a novel detector, Pecola, which uses selective strategy perturbation to relieve the information loss caused by random masking, and multi-pair contrastive learning to capture the implicit pattern information during perturbation, facilitating few-shot performance. The experiments show that Pecola outperforms the SOTA method by 1.20% in accuracy on average on four public datasets. We further analyze the effectiveness, robustness, and generalization of our perturbation method.
CoCo: Coherence-Enhanced Machine-Generated Text Detection Under Data Limitation With Contrastive Learning
Dec 20, 2022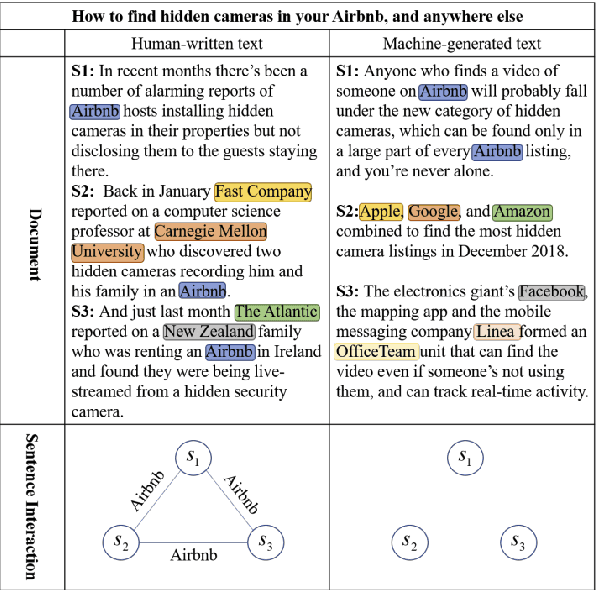
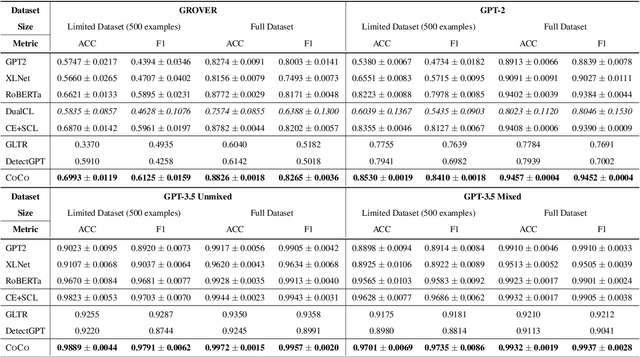
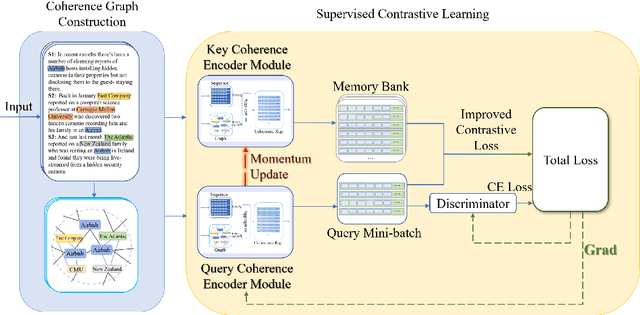
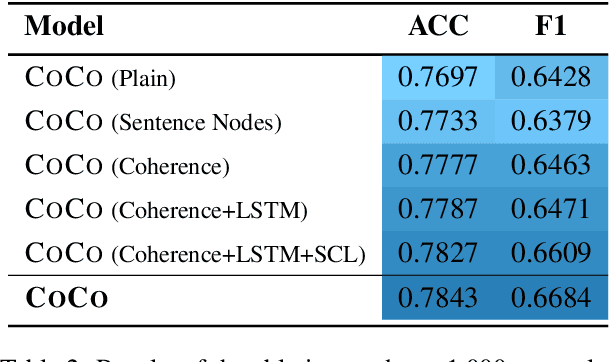
Abstract:Machine-Generated Text (MGT) detection, a task that discriminates MGT from Human-Written Text (HWT), plays a crucial role in preventing misuse of text generative models, which excel in mimicking human writing style recently. Latest proposed detectors usually take coarse text sequence as input and output some good results by fine-tune pretrained models with standard cross-entropy loss. However, these methods fail to consider the linguistic aspect of text (e.g., coherence) and sentence-level structures. Moreover, they lack the ability to handle the low-resource problem which could often happen in practice considering the enormous amount of textual data online. In this paper, we present a coherence-based contrastive learning model named CoCo to detect the possible MGT under low-resource scenario. Inspired by the distinctiveness and permanence properties of linguistic feature, we represent text as a coherence graph to capture its entity consistency, which is further encoded by the pretrained model and graph neural network. To tackle the challenges of data limitations, we employ a contrastive learning framework and propose an improved contrastive loss for making full use of hard negative samples in training stage. The experiment results on two public datasets prove our approach outperforms the state-of-art methods significantly.
A Duet Recommendation Algorithm Based on Jointly Local and Global Representation Learning
Dec 03, 2020



Abstract:Knowledge graph (KG), as the side information, is widely utilized to learn the semantic representations of item/user for recommendation system. The traditional recommendation algorithms usually just depend on user-item interactions, but ignore the inherent web information describing the item/user, which could be formulated by the knowledge graph embedding (KGE) methods to significantly improve applications' performance. In this paper, we propose a knowledge-aware-based recommendation algorithm to capture the local and global representation learning from heterogeneous information. Specifically, the local model and global model can naturally depict the inner patterns in the content-based heterogeneous information and interactive behaviors among the users and items. Based on the method that local and global representations are learned jointly by graph convolutional networks with attention mechanism, the final recommendation probability is calculated by a fully-connected neural network. Extensive experiments are conducted on two real-world datasets to verify the proposed algorithm's validation. The evaluation results indicate that the proposed algorithm surpasses state-of-arts by $10.0\%$, $5.1\%$, $2.5\%$ and $1.8\%$ in metrics of MAE, RMSE, AUC and F1-score at least, respectively. The significant improvements reveal the capacity of our proposal to recommend user/item effectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge