Qing Shi
Thor: Towards Human-Level Whole-Body Reactions for Intense Contact-Rich Environments
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Humanoids hold great potential for service, industrial, and rescue applications, in which robots must sustain whole-body stability while performing intense, contact-rich interactions with the environment. However, enabling humanoids to generate human-like, adaptive responses under such conditions remains a major challenge. To address this, we propose Thor, a humanoid framework for human-level whole-body reactions in contact-rich environments. Based on the robot's force analysis, we design a force-adaptive torso-tilt (FAT2) reward function to encourage humanoids to exhibit human-like responses during force-interaction tasks. To mitigate the high-dimensional challenges of humanoid control, Thor introduces a reinforcement learning architecture that decouples the upper body, waist, and lower body. Each component shares global observations of the whole body and jointly updates its parameters. Finally, we deploy Thor on the Unitree G1, and it substantially outperforms baselines in force-interaction tasks. Specifically, the robot achieves a peak pulling force of 167.7 N (approximately 48% of the G1's body weight) when moving backward and 145.5 N when moving forward, representing improvements of 68.9% and 74.7%, respectively, compared with the best-performing baseline. Moreover, Thor is capable of pulling a loaded rack (130 N) and opening a fire door with one hand (60 N). These results highlight Thor's effectiveness in enhancing humanoid force-interaction capabilities.
Modeling and simulation of a mechanism for suppressing the flipping problem of a jumping robot
May 20, 2024



Abstract:In order to solve the problem of stable jumping of micro robot, we design a special mechanism: elastic passive joint (EPJ). EPJ can assist in achieving smooth jumping through the opening-closing process when the robot jumps. First, we introduce the composition and operation principle of EPJ, and perform a dynamic modeling of the robot's jumping process. Then, in order to verify the effectiveness of EPJ in controlling the robot's smooth jump, we design a simulation experiment based on MATLAB. Through comparative experiments, it was proved that EPJ can greatly adjust the angular velocity of the robot and increase the jump distance of the robot. Finally, we analyze each parameter in EPJ and performs parameter optimization. After optimization, EPJ achieves a completely flip-free jump of the robot, laying an important foundation for improving the mobility of micro-robot.
TimeTuner: Diagnosing Time Representations for Time-Series Forecasting with Counterfactual Explanations
Jul 27, 2023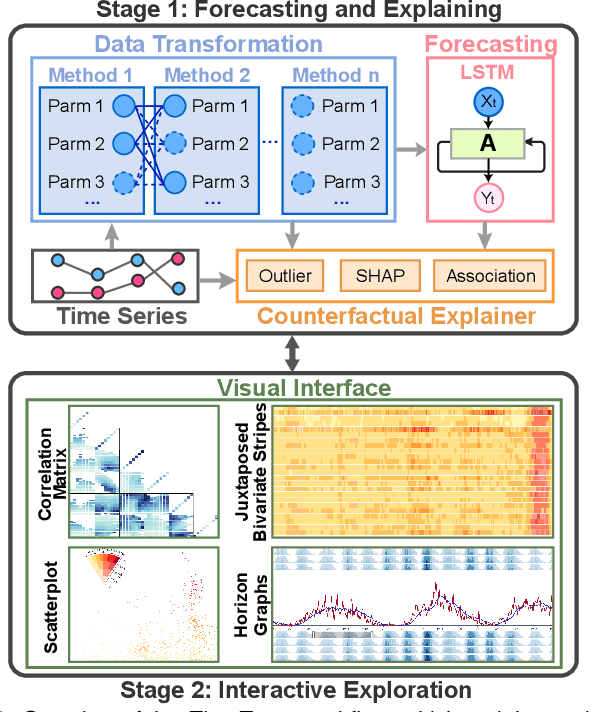
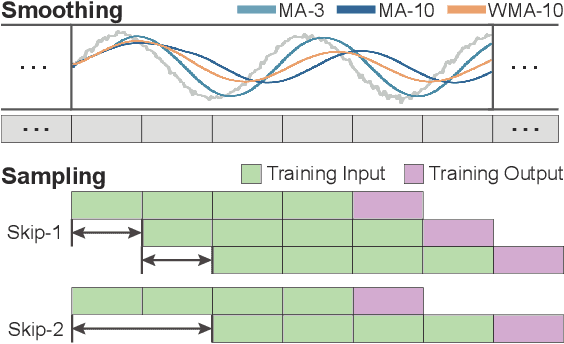
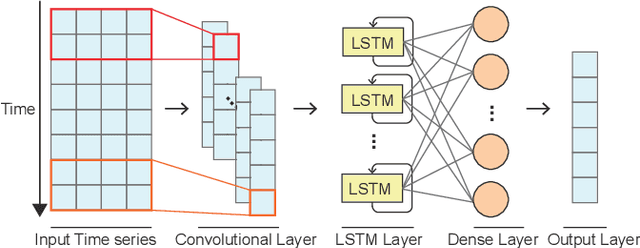
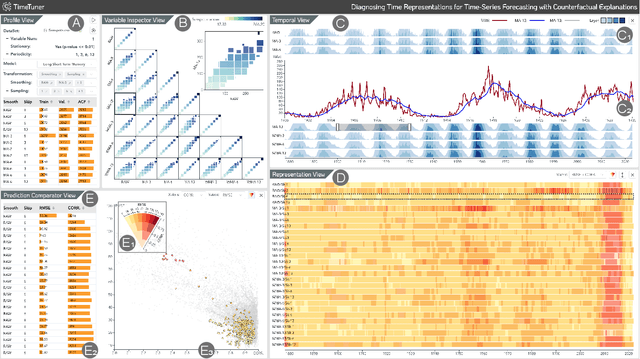
Abstract:Deep learning (DL) approaches are being increasingly used for time-series forecasting, with many efforts devoted to designing complex DL models. Recent studies have shown that the DL success is often attributed to effective data representations, fostering the fields of feature engineering and representation learning. However, automated approaches for feature learning are typically limited with respect to incorporating prior knowledge, identifying interactions among variables, and choosing evaluation metrics to ensure that the models are reliable. To improve on these limitations, this paper contributes a novel visual analytics framework, namely TimeTuner, designed to help analysts understand how model behaviors are associated with localized correlations, stationarity, and granularity of time-series representations. The system mainly consists of the following two-stage technique: We first leverage counterfactual explanations to connect the relationships among time-series representations, multivariate features and model predictions. Next, we design multiple coordinated views including a partition-based correlation matrix and juxtaposed bivariate stripes, and provide a set of interactions that allow users to step into the transformation selection process, navigate through the feature space, and reason the model performance. We instantiate TimeTuner with two transformation methods of smoothing and sampling, and demonstrate its applicability on real-world time-series forecasting of univariate sunspots and multivariate air pollutants. Feedback from domain experts indicates that our system can help characterize time-series representations and guide the feature engineering processes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge