Ruotong Liao
VideoINSTA: Zero-shot Long Video Understanding via Informative Spatial-Temporal Reasoning with LLMs
Sep 30, 2024



Abstract:In the video-language domain, recent works in leveraging zero-shot Large Language Model-based reasoning for video understanding have become competitive challengers to previous end-to-end models. However, long video understanding presents unique challenges due to the complexity of reasoning over extended timespans, even for zero-shot LLM-based approaches. The challenge of information redundancy in long videos prompts the question of what specific information is essential for large language models (LLMs) and how to leverage them for complex spatial-temporal reasoning in long-form video analysis. We propose a framework VideoINSTA, i.e. INformative Spatial-TemporAl Reasoning for zero-shot long-form video understanding. VideoINSTA contributes (1) a zero-shot framework for long video understanding using LLMs; (2) an event-based temporal reasoning and content-based spatial reasoning approach for LLMs to reason over spatial-temporal information in videos; (3) a self-reflective information reasoning scheme balancing temporal factors based on information sufficiency and prediction confidence. Our model significantly improves the state-of-the-art on three long video question-answering benchmarks: EgoSchema, NextQA, and IntentQA, and the open question answering dataset ActivityNetQA. The code is released here: https://github.com/mayhugotong/VideoINSTA.
EchoScene: Indoor Scene Generation via Information Echo over Scene Graph Diffusion
May 02, 2024Abstract:We present EchoScene, an interactive and controllable generative model that generates 3D indoor scenes on scene graphs. EchoScene leverages a dual-branch diffusion model that dynamically adapts to scene graphs. Existing methods struggle to handle scene graphs due to varying numbers of nodes, multiple edge combinations, and manipulator-induced node-edge operations. EchoScene overcomes this by associating each node with a denoising process and enables collaborative information exchange, enhancing controllable and consistent generation aware of global constraints. This is achieved through an information echo scheme in both shape and layout branches. At every denoising step, all processes share their denoising data with an information exchange unit that combines these updates using graph convolution. The scheme ensures that the denoising processes are influenced by a holistic understanding of the scene graph, facilitating the generation of globally coherent scenes. The resulting scenes can be manipulated during inference by editing the input scene graph and sampling the noise in the diffusion model. Extensive experiments validate our approach, which maintains scene controllability and surpasses previous methods in generation fidelity. Moreover, the generated scenes are of high quality and thus directly compatible with off-the-shelf texture generation. Code and trained models are open-sourced.
Zero-Shot Relational Learning on Temporal Knowledge Graphs with Large Language Models
Nov 15, 2023
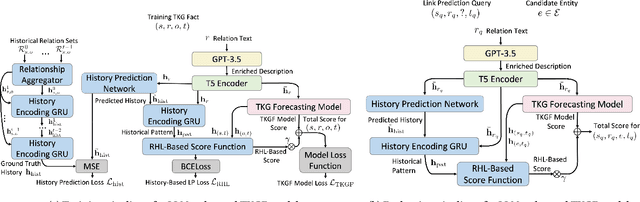
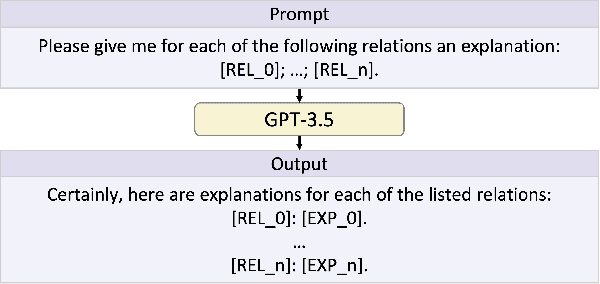
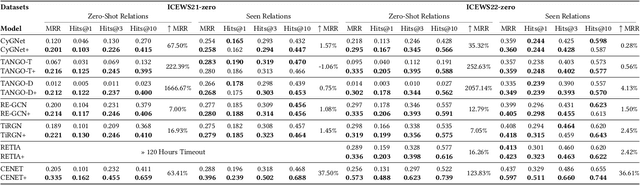
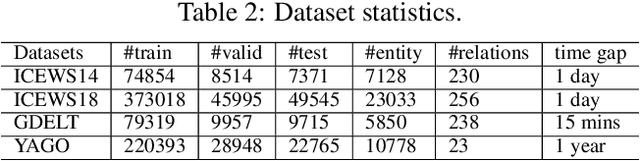
Abstract:In recent years, modeling evolving knowledge over temporal knowledge graphs (TKGs) has become a heated topic. Various methods have been proposed to forecast links on TKGs. Most of them are embedding-based, where hidden representations are learned to represent knowledge graph (KG) entities and relations based on the observed graph contexts. Although these methods show strong performance on traditional TKG forecasting (TKGF) benchmarks, they naturally face a strong challenge when they are asked to model the unseen zero-shot relations that has no prior graph context. In this paper, we try to mitigate this problem as follows. We first input the text descriptions of KG relations into large language models (LLMs) for generating relation representations, and then introduce them into embedding-based TKGF methods. LLM-empowered representations can capture the semantic information in the relation descriptions. This makes the relations, whether seen or unseen, with similar semantic meanings stay close in the embedding space, enabling TKGF models to recognize zero-shot relations even without any observed graph context. Experimental results show that our approach helps TKGF models to achieve much better performance in forecasting the facts with previously unseen relations, while still maintaining their ability in link forecasting regarding seen relations.
GraphextQA: A Benchmark for Evaluating Graph-Enhanced Large Language Models
Oct 12, 2023Abstract:While multi-modal models have successfully integrated information from image, video, and audio modalities, integrating graph modality into large language models (LLMs) remains unexplored. This discrepancy largely stems from the inherent divergence between structured graph data and unstructured text data. Incorporating graph knowledge provides a reliable source of information, enabling potential solutions to address issues in text generation, e.g., hallucination, and lack of domain knowledge. To evaluate the integration of graph knowledge into language models, a dedicated dataset is needed. However, there is currently no benchmark dataset specifically designed for multimodal graph-language models. To address this gap, we propose GraphextQA, a question answering dataset with paired subgraphs, retrieved from Wikidata, to facilitate the evaluation and future development of graph-language models. Additionally, we introduce a baseline model called CrossGNN, which conditions answer generation on the paired graphs by cross-attending question-aware graph features at decoding. The proposed dataset is designed to evaluate graph-language models' ability to understand graphs and make use of it for answer generation. We perform experiments with language-only models and the proposed graph-language model to validate the usefulness of the paired graphs and to demonstrate the difficulty of the task.
GenTKG: Generative Forecasting on Temporal Knowledge Graph
Oct 11, 2023


Abstract:The rapid advancements in large language models (LLMs) have ignited interest in the temporal knowledge graph (tKG) domain, where conventional carefully designed embedding-based and rule-based models dominate. The question remains open of whether pre-trained LLMs can understand structured temporal relational data and replace them as the foundation model for temporal relational forecasting. Therefore, we bring temporal knowledge forecasting into the generative setting. However, challenges occur in the huge chasms between complex temporal graph data structure and sequential natural expressions LLMs can handle, and between the enormous data sizes of tKGs and heavy computation costs of finetuning LLMs. To address these challenges, we propose a novel retrieval augmented generation framework that performs generative forecasting on tKGs named GenTKG, which combines a temporal logical rule-based retrieval strategy and lightweight parameter-efficient instruction tuning. Extensive experiments have shown that GenTKG outperforms conventional methods of temporal relational forecasting under low computation resources. GenTKG also highlights remarkable transferability with exceeding performance on unseen datasets without re-training. Our work reveals the huge potential of LLMs in the tKG domain and opens a new frontier for generative forecasting on tKGs.
A Systematic Survey of Prompt Engineering on Vision-Language Foundation Models
Jul 24, 2023Abstract:Prompt engineering is a technique that involves augmenting a large pre-trained model with task-specific hints, known as prompts, to adapt the model to new tasks. Prompts can be created manually as natural language instructions or generated automatically as either natural language instructions or vector representations. Prompt engineering enables the ability to perform predictions based solely on prompts without updating model parameters, and the easier application of large pre-trained models in real-world tasks. In past years, Prompt engineering has been well-studied in natural language processing. Recently, it has also been intensively studied in vision-language modeling. However, there is currently a lack of a systematic overview of prompt engineering on pre-trained vision-language models. This paper aims to provide a comprehensive survey of cutting-edge research in prompt engineering on three types of vision-language models: multimodal-to-text generation models (e.g. Flamingo), image-text matching models (e.g. CLIP), and text-to-image generation models (e.g. Stable Diffusion). For each type of model, a brief model summary, prompting methods, prompting-based applications, and the corresponding responsibility and integrity issues are summarized and discussed. Furthermore, the commonalities and differences between prompting on vision-language models, language models, and vision models are also discussed. The challenges, future directions, and research opportunities are summarized to foster future research on this topic.
Enhanced Temporal Knowledge Embeddings with Contextualized Language Representations
Mar 21, 2022



Abstract:With the emerging research effort to integrate structured and unstructured knowledge, many approaches incorporate factual knowledge into pre-trained language models (PLMs) and apply the knowledge-enhanced PLMs on downstream NLP tasks. However, (1) they only consider static factual knowledge, but knowledge graphs (KGs) also contain temporal facts or events indicating evolutionary relationships among entities at different timestamps. (2) PLMs cannot be directly applied to many KG tasks, such as temporal KG completion. In this paper, we focus on \textbf{e}nhancing temporal knowledge embeddings with \textbf{co}ntextualized \textbf{la}nguage representations (ECOLA). We align structured knowledge contained in temporal knowledge graphs with their textual descriptions extracted from news articles and propose a novel knowledge-text prediction task to inject the abundant information from descriptions into temporal knowledge embeddings. ECOLA jointly optimizes the knowledge-text prediction objective and the temporal knowledge embeddings, which can simultaneously take full advantage of textual and knowledge information. For training ECOLA, we introduce three temporal KG datasets with aligned textual descriptions. Experimental results on the temporal knowledge graph completion task show that ECOLA outperforms state-of-the-art temporal KG models by a large margin. The proposed datasets can serve as new temporal KG benchmarks and facilitate future research on structured and unstructured knowledge integration.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge