Fan Li
PlanViz: Evaluating Planning-Oriented Image Generation and Editing for Computer-Use Tasks
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Unified multimodal models (UMMs) have shown impressive capabilities in generating natural images and supporting multimodal reasoning. However, their potential in supporting computer-use planning tasks, which are closely related to our lives, remain underexplored. Image generation and editing in computer-use tasks require capabilities like spatial reasoning and procedural understanding, and it is still unknown whether UMMs have these capabilities to finish these tasks or not. Therefore, we propose PlanViz, a new benchmark designed to evaluate image generation and editing for computer-use tasks. To achieve the goal of our evaluation, we focus on sub-tasks which frequently involve in daily life and require planning steps. Specifically, three new sub-tasks are designed: route planning, work diagramming, and web&UI displaying. We address challenges in data quality ensuring by curating human-annotated questions and reference images, and a quality control process. For challenges of comprehensive and exact evaluation, a task-adaptive score, PlanScore, is proposed. The score helps understanding the correctness, visual quality and efficiency of generated images. Through experiments, we highlight key limitations and opportunities for future research on this topic.
ERNIE 5.0 Technical Report
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In this report, we introduce ERNIE 5.0, a natively autoregressive foundation model desinged for unified multimodal understanding and generation across text, image, video, and audio. All modalities are trained from scratch under a unified next-group-of-tokens prediction objective, based on an ultra-sparse mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture with modality-agnostic expert routing. To address practical challenges in large-scale deployment under diverse resource constraints, ERNIE 5.0 adopts a novel elastic training paradigm. Within a single pre-training run, the model learns a family of sub-models with varying depths, expert capacities, and routing sparsity, enabling flexible trade-offs among performance, model size, and inference latency in memory- or time-constrained scenarios. Moreover, we systematically address the challenges of scaling reinforcement learning to unified foundation models, thereby guaranteeing efficient and stable post-training under ultra-sparse MoE architectures and diverse multimodal settings. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ERNIE 5.0 achieves strong and balanced performance across multiple modalities. To the best of our knowledge, among publicly disclosed models, ERNIE 5.0 represents the first production-scale realization of a trillion-parameter unified autoregressive model that supports both multimodal understanding and generation. To facilitate further research, we present detailed visualizations of modality-agnostic expert routing in the unified model, alongside comprehensive empirical analysis of elastic training, aiming to offer profound insights to the community.
Enhancing Foundation VLM Robustness to Missing Modality: Scalable Diffusion for Bi-directional Feature Restoration
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Vision Language Models (VLMs) typically assume complete modality input during inference. However, their effectiveness drops sharply when certain modalities are unavailable or incomplete. Current research primarily faces two dilemmas: Prompt-based methods struggle to restore missing yet indispensable features and impair generalization of VLMs. Imputation-based approaches, lacking effective guidance, are prone to generating semantically irrelevant noise. Restoring precise semantics while sustaining VLM generalization remains challenging. Therefore, we propose a general missing modality restoration strategy in this paper. We introduce an enhanced diffusion model as a pluggable mid-stage training module to effectively restore missing features. Our strategy introduces two key innovations: (I) Dynamic Modality Gating, which adaptively leverages conditional features to steer the generation of semantically consistent features; (II) Cross-Modal Mutual Learning mechanism, which bridges the semantic spaces of dual encoders to achieve bidirectional alignment. Zero-shot evaluations across benchmark datasets demonstrate that our approach outperforms existing baseline methods. Extensive experiments and ablation studies confirm our model as a robust and scalable extension for VLMs in missing modality scenarios, ensuring reliability across diverse missing rates and environments. Our code and models will be publicly available.
Comparison of Single Carrier FTN-QAM and PCS-QAM for Amplifier-less Coherent Communication Systems
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:A performance comparison of FTN-QAM and PCS-QAM for amplifier-less short-reach coherent communication systems is provided. With the applications of phase tracking partial response DFE and turbo equalization strategy, FTN-16QAM exhibits about 0.9dB power margin advantage over PCS-64QAM.
HeadHunt-VAD: Hunting Robust Anomaly-Sensitive Heads in MLLM for Tuning-Free Video Anomaly Detection
Dec 23, 2025
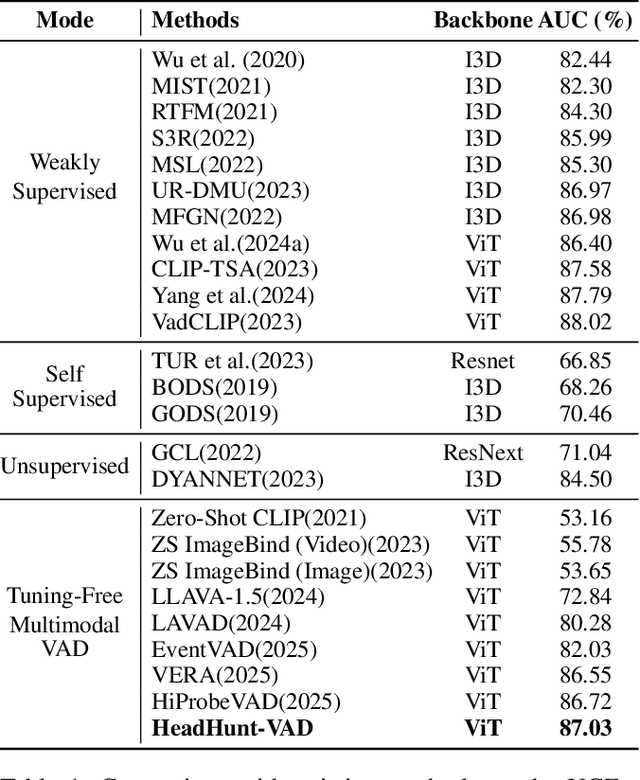
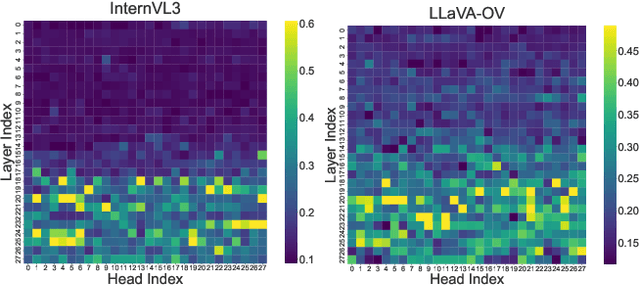
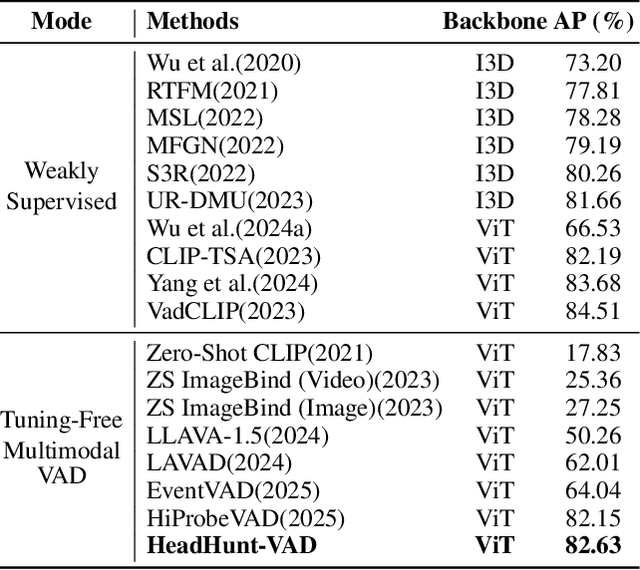
Abstract:Video Anomaly Detection (VAD) aims to locate events that deviate from normal patterns in videos. Traditional approaches often rely on extensive labeled data and incur high computational costs. Recent tuning-free methods based on Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) offer a promising alternative by leveraging their rich world knowledge. However, these methods typically rely on textual outputs, which introduces information loss, exhibits normalcy bias, and suffers from prompt sensitivity, making them insufficient for capturing subtle anomalous cues. To address these constraints, we propose HeadHunt-VAD, a novel tuning-free VAD paradigm that bypasses textual generation by directly hunting robust anomaly-sensitive internal attention heads within the frozen MLLM. Central to our method is a Robust Head Identification module that systematically evaluates all attention heads using a multi-criteria analysis of saliency and stability, identifying a sparse subset of heads that are consistently discriminative across diverse prompts. Features from these expert heads are then fed into a lightweight anomaly scorer and a temporal locator, enabling efficient and accurate anomaly detection with interpretable outputs. Extensive experiments show that HeadHunt-VAD achieves state-of-the-art performance among tuning-free methods on two major VAD benchmarks while maintaining high efficiency, validating head-level probing in MLLMs as a powerful and practical solution for real-world anomaly detection.
Generative Human-Object Interaction Detection via Differentiable Cognitive Steering of Multi-modal LLMs
Dec 19, 2025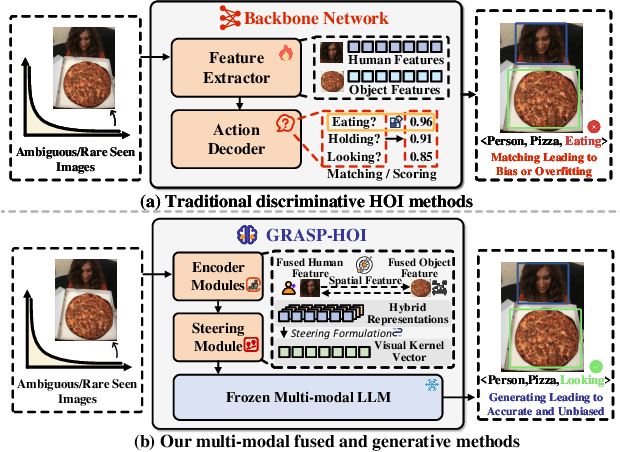
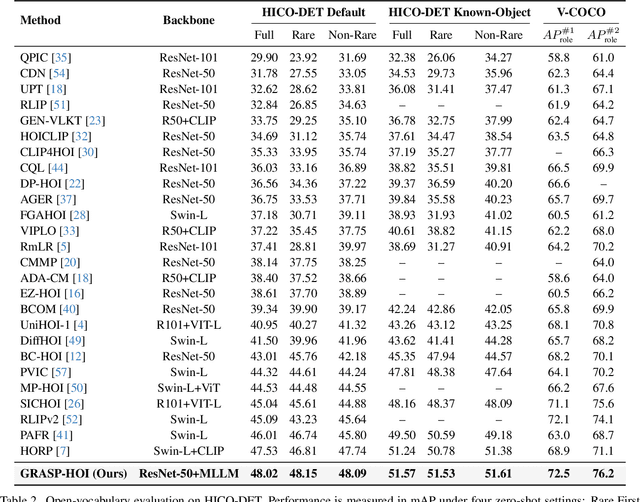
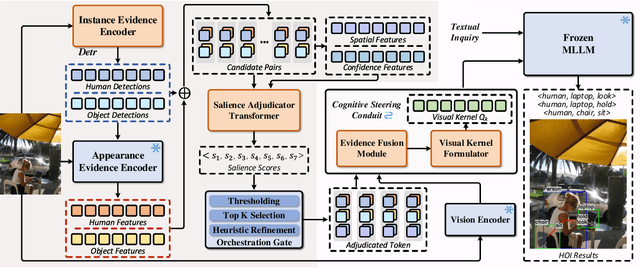
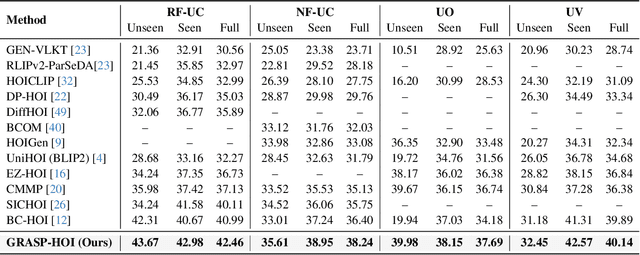
Abstract:Human-object interaction (HOI) detection aims to localize human-object pairs and the interactions between them. Existing methods operate under a closed-world assumption, treating the task as a classification problem over a small, predefined verb set, which struggles to generalize to the long-tail of unseen or ambiguous interactions in the wild. While recent multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) possess the rich world knowledge required for open-vocabulary understanding, they remain decoupled from existing HOI detectors since fine-tuning them is computationally prohibitive. To address these constraints, we propose \GRASP-HO}, a novel Generative Reasoning And Steerable Perception framework that reformulates HOI detection from the closed-set classification task to the open-vocabulary generation problem. To bridge the vision and cognitive, we first extract hybrid interaction representations, then design a lightweight learnable cognitive steering conduit (CSC) module to inject the fine-grained visual evidence into a frozen MLLM for effective reasoning. To address the supervision mismatch between classification-based HOI datasets and open-vocabulary generative models, we introduce a hybrid guidance strategy that coupling the language modeling loss and auxiliary classification loss, enabling discriminative grounding without sacrificing generative flexibility. Experiments demonstrate state-of-the-art closed-set performance and strong zero-shot generalization, achieving a unified paradigm that seamlessly bridges discriminative perception and generative reasoning for open-world HOI detection.
What Your Features Reveal: Data-Efficient Black-Box Feature Inversion Attack for Split DNNs
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Split DNNs enable edge devices by offloading intensive computation to a cloud server, but this paradigm exposes privacy vulnerabilities, as the intermediate features can be exploited to reconstruct the private inputs via Feature Inversion Attack (FIA). Existing FIA methods often produce limited reconstruction quality, making it difficult to assess the true extent of privacy leakage. To reveal the privacy risk of the leaked features, we introduce FIA-Flow, a black-box FIA framework that achieves high-fidelity image reconstruction from intermediate features. To exploit the semantic information within intermediate features, we design a Latent Feature Space Alignment Module (LFSAM) to bridge the semantic gap between the intermediate feature space and the latent space. Furthermore, to rectify distributional mismatch, we develop Deterministic Inversion Flow Matching (DIFM), which projects off-manifold features onto the target manifold with one-step inference. This decoupled design simplifies learning and enables effective training with few image-feature pairs. To quantify privacy leakage from a human perspective, we also propose two metrics based on a large vision-language model. Experiments show that FIA-Flow achieves more faithful and semantically aligned feature inversion across various models (AlexNet, ResNet, Swin Transformer, DINO, and YOLO11) and layers, revealing a more severe privacy threat in Split DNNs than previously recognized.
MTMed3D: A Multi-Task Transformer-Based Model for 3D Medical Imaging
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:In the field of medical imaging, AI-assisted techniques such as object detection, segmentation, and classification are widely employed to alleviate the workload of physicians and doctors. However, single-task models are predominantly used, overlooking the shared information across tasks. This oversight leads to inefficiencies in real-life applications. In this work, we propose MTMed3D, a novel end-to-end Multi-task Transformer-based model to address the limitations of single-task models by jointly performing 3D detection, segmentation, and classification in medical imaging. Our model uses a Transformer as the shared encoder to generate multi-scale features, followed by CNN-based task-specific decoders. The proposed framework was evaluated on the BraTS 2018 and 2019 datasets, achieving promising results across all three tasks, especially in detection, where our method achieves better results than prior works. Additionally, we compare our multi-task model with equivalent single-task variants trained separately. Our multi-task model significantly reduces computational costs and achieves faster inference speed while maintaining comparable performance to the single-task models, highlighting its efficiency advantage. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to leverage Transformers for multi-task learning that simultaneously covers detection, segmentation, and classification tasks in 3D medical imaging, presenting its potential to enhance diagnostic processes. The code is available at https://github.com/fanlimua/MTMed3D.git.
Invisible Triggers, Visible Threats! Road-Style Adversarial Creation Attack for Visual 3D Detection in Autonomous Driving
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Modern autonomous driving (AD) systems leverage 3D object detection to perceive foreground objects in 3D environments for subsequent prediction and planning. Visual 3D detection based on RGB cameras provides a cost-effective solution compared to the LiDAR paradigm. While achieving promising detection accuracy, current deep neural network-based models remain highly susceptible to adversarial examples. The underlying safety concerns motivate us to investigate realistic adversarial attacks in AD scenarios. Previous work has demonstrated the feasibility of placing adversarial posters on the road surface to induce hallucinations in the detector. However, the unnatural appearance of the posters makes them easily noticeable by humans, and their fixed content can be readily targeted and defended. To address these limitations, we propose the AdvRoad to generate diverse road-style adversarial posters. The adversaries have naturalistic appearances resembling the road surface while compromising the detector to perceive non-existent objects at the attack locations. We employ a two-stage approach, termed Road-Style Adversary Generation and Scenario-Associated Adaptation, to maximize the attack effectiveness on the input scene while ensuring the natural appearance of the poster, allowing the attack to be carried out stealthily without drawing human attention. Extensive experiments show that AdvRoad generalizes well to different detectors, scenes, and spoofing locations. Moreover, physical attacks further demonstrate the practical threats in real-world environments.
Efficient Model-Agnostic Continual Learning for Next POI Recommendation
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Next point-of-interest (POI) recommendation improves personalized location-based services by predicting users' next destinations based on their historical check-ins. However, most existing methods rely on static datasets and fixed models, limiting their ability to adapt to changes in user behavior over time. To address this limitation, we explore a novel task termed continual next POI recommendation, where models dynamically adapt to evolving user interests through continual updates. This task is particularly challenging, as it requires capturing shifting user behaviors while retaining previously learned knowledge. Moreover, it is essential to ensure efficiency in update time and memory usage for real-world deployment. To this end, we propose GIRAM (Generative Key-based Interest Retrieval and Adaptive Modeling), an efficient, model-agnostic framework that integrates context-aware sustained interests with recent interests. GIRAM comprises four components: (1) an interest memory to preserve historical preferences; (2) a context-aware key encoding module for unified interest key representation; (3) a generative key-based retrieval module to identify diverse and relevant sustained interests; and (4) an adaptive interest update and fusion module to update the interest memory and balance sustained and recent interests. In particular, GIRAM can be seamlessly integrated with existing next POI recommendation models. Experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate that GIRAM consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods while maintaining high efficiency in both update time and memory consumption.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge