Yaguang Song
Explicit Uncertainty Modeling for Active CLIP Adaptation with Dual Prompt Tuning
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Pre-trained vision-language models such as CLIP exhibit strong transferability, yet adapting them to downstream image classification tasks under limited annotation budgets remains challenging. In active learning settings, the model must select the most informative samples for annotation from a large pool of unlabeled data. Existing approaches typically estimate uncertainty via entropy-based criteria or representation clustering, without explicitly modeling uncertainty from the model perspective. In this work, we propose a robust uncertainty modeling framework for active CLIP adaptation based on dual-prompt tuning. We introduce two learnable prompts in the textual branch of CLIP. The positive prompt enhances the discriminability of task-specific textual embeddings corresponding to light-weight tuned visual embeddings, improving classification reliability. Meanwhile, the negative prompt is trained in an reversed manner to explicitly model the probability that the predicted label is correct, providing a principled uncertainty signal for guiding active sample selection. Extensive experiments across different fine-tuning paradigms demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms existing active learning methods under the same annotation budget.
Fine-tuning Pre-trained Vision-Language Models in a Human-Annotation-Free Manner
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Large-scale vision-language models (VLMs) such as CLIP exhibit strong zero-shot generalization, but adapting them to downstream tasks typically requires costly labeled data. Existing unsupervised self-training methods rely on pseudo-labeling, yet often suffer from unreliable confidence filtering, confirmation bias, and underutilization of low-confidence samples. We propose Collaborative Fine-Tuning (CoFT), an unsupervised adaptation framework that leverages unlabeled data through a dual-model, cross-modal collaboration mechanism. CoFT introduces a dual-prompt learning strategy with positive and negative textual prompts to explicitly model pseudo-label cleanliness in a sample-dependent manner, removing the need for hand-crafted thresholds or noise assumptions. The negative prompt also regularizes lightweight visual adaptation modules, improving robustness under noisy supervision. CoFT employs a two-phase training scheme, transitioning from parameter-efficient fine-tuning on high-confidence samples to full fine-tuning guided by collaboratively filtered pseudo-labels. Building on CoFT, CoFT+ further enhances adaptation via iterative fine-tuning, momentum contrastive learning, and LLM-generated prompts. Extensive experiments demonstrate consistent gains over existing unsupervised methods and even few-shot supervised baselines.
Harmony: A Unified Framework for Modality Incremental Learning
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:Incremental learning aims to enable models to continuously acquire knowledge from evolving data streams while preserving previously learned capabilities. While current research predominantly focuses on unimodal incremental learning and multimodal incremental learning where the modalities are consistent, real-world scenarios often present data from entirely new modalities, posing additional challenges. This paper investigates the feasibility of developing a unified model capable of incremental learning across continuously evolving modal sequences. To this end, we introduce a novel paradigm called Modality Incremental Learning (MIL), where each learning stage involves data from distinct modalities. To address this task, we propose a novel framework named Harmony, designed to achieve modal alignment and knowledge retention, enabling the model to reduce the modal discrepancy and learn from a sequence of distinct modalities, ultimately completing tasks across multiple modalities within a unified framework. Our approach introduces the adaptive compatible feature modulation and cumulative modal bridging. Through constructing historical modal features and performing modal knowledge accumulation and alignment, the proposed components collaboratively bridge modal differences and maintain knowledge retention, even with solely unimodal data available at each learning phase.These components work in concert to establish effective modality connections and maintain knowledge retention, even when only unimodal data is available at each learning stage. Extensive experiments on the MIL task demonstrate that our proposed method significantly outperforms existing incremental learning methods, validating its effectiveness in MIL scenarios.
Libra: Building Decoupled Vision System on Large Language Models
May 16, 2024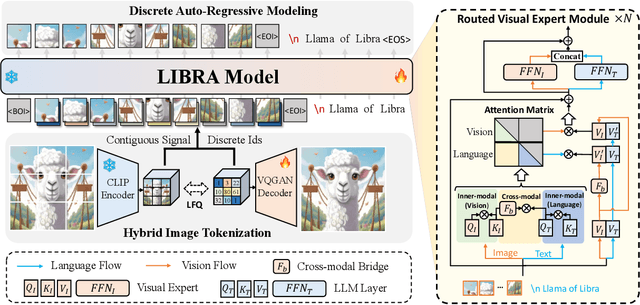



Abstract:In this work, we introduce Libra, a prototype model with a decoupled vision system on a large language model (LLM). The decoupled vision system decouples inner-modal modeling and cross-modal interaction, yielding unique visual information modeling and effective cross-modal comprehension. Libra is trained through discrete auto-regressive modeling on both vision and language inputs. Specifically, we incorporate a routed visual expert with a cross-modal bridge module into a pretrained LLM to route the vision and language flows during attention computing to enable different attention patterns in inner-modal modeling and cross-modal interaction scenarios. Experimental results demonstrate that the dedicated design of Libra achieves a strong MLLM baseline that rivals existing works in the image-to-text scenario with merely 50 million training data, providing a new perspective for future multimodal foundation models. Code is available at https://github.com/YifanXu74/Libra.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge