Fei Chao
Out of the Memory Barrier: A Highly Memory Efficient Training System for LLMs with Million-Token Contexts
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Training Large Language Models (LLMs) on long contexts is severely constrained by prohibitive GPU memory overhead, not training time. The primary culprits are the activations, whose memory footprints scale linearly with sequence length. We introduce OOMB, a highly memory-efficient training system that directly confronts this barrier. Our approach employs a chunk-recurrent training framework with on-the-fly activation recomputation, which maintains a constant activation memory footprint (O(1)) and shifts the primary bottleneck to the growing KV cache. To manage the KV cache, OOMB integrates a suite of synergistic optimizations: a paged memory manager for both the KV cache and its gradients to eliminate fragmentation, asynchronous CPU offloading to hide data transfer latency, and page-level sparse attention to reduce both computational complexity and communication overhead. The synergy of these techniques yields exceptional efficiency. Our empirical results show that for every additional 10K tokens of context, the end-to-end training memory overhead increases by a mere 10MB for Qwen2.5-7B. This allows training Qwen2.5-7B with a 4M-token context on a single H200 GPU, a feat that would otherwise require a large cluster using context parallelism. This work represents a substantial advance in resource efficiency for long-context LLM training. The source code is available at https://github.com/wenhaoli-xmu/OOMB.
Polybasic Speculative Decoding Through a Theoretical Perspective
Oct 30, 2025



Abstract:Inference latency stands as a critical bottleneck in the large-scale deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs). Speculative decoding methods have recently shown promise in accelerating inference without compromising the output distribution. However, existing work typically relies on a dualistic draft-verify framework and lacks rigorous theoretical grounding. In this paper, we introduce a novel \emph{polybasic} speculative decoding framework, underpinned by a comprehensive theoretical analysis. Specifically, we prove a fundamental theorem that characterizes the optimal inference time for multi-model speculative decoding systems, shedding light on how to extend beyond the dualistic approach to a more general polybasic paradigm. Through our theoretical investigation of multi-model token generation, we expose and optimize the interplay between model capabilities, acceptance lengths, and overall computational cost. Our framework supports both standalone implementation and integration with existing speculative techniques, leading to accelerated performance in practice. Experimental results across multiple model families demonstrate that our approach yields speedup ratios ranging from $3.31\times$ to $4.01\times$ for LLaMA2-Chat 7B, up to $3.87 \times$ for LLaMA3-8B, up to $4.43 \times$ for Vicuna-7B and up to $3.85 \times$ for Qwen2-7B -- all while preserving the original output distribution. We release our theoretical proofs and implementation code to facilitate further investigation into polybasic speculative decoding.
CCF: A Context Compression Framework for Efficient Long-Sequence Language Modeling
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:Scaling language models to longer contexts is essential for capturing rich dependencies across extended discourse. However, na\"ive context extension imposes significant computational and memory burdens, often resulting in inefficiencies during both training and inference. In this work, we propose CCF, a novel context compression framework designed to enable efficient long-context modeling by learning hierarchical latent representations that preserve global semantics while aggressively reducing input redundancy. CCF integrates segment-wise semantic aggregation with key-value memory encoding, forming compact representations that support accurate reconstruction and long-range understanding. To further enhance scalability, we introduce a training-efficient optimization strategy that couples incremental segment decoding with sparse reservoir sampling, substantially reducing memory overhead without degrading performance. Empirical results on multiple long-context language modeling benchmarks demonstrate that CCF achieves competitive perplexity under high compression ratios, and significantly improves throughput and memory efficiency compared to existing approaches. These findings highlight the potential of structured compression for scalable and effective long-context language modeling.
Spotlight Attention: Towards Efficient LLM Generation via Non-linear Hashing-based KV Cache Retrieval
Aug 27, 2025

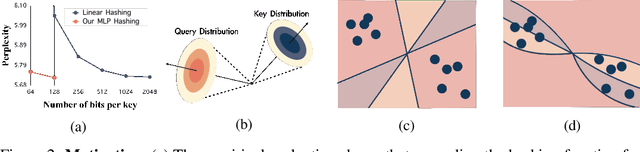

Abstract:Reducing the key-value (KV) cache burden in Large Language Models (LLMs) significantly accelerates inference. Dynamically selecting critical KV caches during decoding helps maintain performance. Existing methods use random linear hashing to identify important tokens, but this approach is inefficient due to the orthogonal distribution of queries and keys within two narrow cones in LLMs. We introduce Spotlight Attention, a novel method that employs non-linear hashing functions to optimize the embedding distribution of queries and keys, enhancing coding efficiency and robustness. We also developed a lightweight, stable training framework using a Bradley-Terry ranking-based loss, enabling optimization of the non-linear hashing module on GPUs with 16GB memory in 8 hours. Experimental results show that Spotlight Attention drastically improves retrieval precision while shortening the length of the hash code at least 5$\times$ compared to traditional linear hashing. Finally, we exploit the computational advantages of bitwise operations by implementing specialized CUDA kernels, achieving hashing retrieval for 512K tokens in under 100$\mu$s on a single A100 GPU, with end-to-end throughput up to 3$\times$ higher than vanilla decoding.
VISA: Group-wise Visual Token Selection and Aggregation via Graph Summarization for Efficient MLLMs Inference
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:In this study, we introduce a novel method called group-wise \textbf{VI}sual token \textbf{S}election and \textbf{A}ggregation (VISA) to address the issue of inefficient inference stemming from excessive visual tokens in multimoal large language models (MLLMs). Compared with previous token pruning approaches, our method can preserve more visual information while compressing visual tokens. We first propose a graph-based visual token aggregation (VTA) module. VTA treats each visual token as a node, forming a graph based on semantic similarity among visual tokens. It then aggregates information from removed tokens into kept tokens based on this graph, producing a more compact visual token representation. Additionally, we introduce a group-wise token selection strategy (GTS) to divide visual tokens into kept and removed ones, guided by text tokens from the final layers of each group. This strategy progressively aggregates visual information, enhancing the stability of the visual information extraction process. We conduct comprehensive experiments on LLaVA-1.5, LLaVA-NeXT, and Video-LLaVA across various benchmarks to validate the efficacy of VISA. Our method consistently outperforms previous methods, achieving a superior trade-off between model performance and inference speed. The code is available at https://github.com/mobiushy/VISA.
GS-Bias: Global-Spatial Bias Learner for Single-Image Test-Time Adaptation of Vision-Language Models
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in test-time adaptation (TTA) for Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have garnered increasing attention, particularly through the use of multiple augmented views of a single image to boost zero-shot generalization. Unfortunately, existing methods fail to strike a satisfactory balance between performance and efficiency, either due to excessive overhead of tuning text prompts or unstable benefits from handcrafted, training-free visual feature enhancement. In this paper, we present Global-Spatial Bias Learner (GS-Bias), an efficient and effective TTA paradigm that incorporates two learnable biases during TTA, unfolded as the global bias and spatial bias. Particularly, the global bias captures the global semantic features of a test image by learning consistency across augmented views, while spatial bias learns the semantic coherence between regions in the image's spatial visual representation. It is worth highlighting that these two sets of biases are directly added to the logits outputed by the pretrained VLMs, which circumvent the full backpropagation through VLM that hinders the efficiency of existing TTA methods. This endows GS-Bias with extremely high efficiency while achieving state-of-the-art performance on 15 benchmark datasets. For example, it achieves a 2.23% improvement over TPT in cross-dataset generalization and a 2.72% improvement in domain generalization, while requiring only 6.5% of TPT's memory usage on ImageNet.
Towards Efficient Automatic Self-Pruning of Large Language Models
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Despite exceptional capabilities, Large Language Models (LLMs) still face deployment challenges due to their enormous size. Post-training structured pruning is a promising solution that prunes LLMs without the need for retraining, reducing computational overhead, and it is hardware-deployment friendly. However, the training-free nature of post-training structured pruning leads to significant performance degradation. We argue that the key to mitigating this issue lies in accurately determining the pruning rate for each layer. Meanwhile, we find that LLMs may have prior knowledge about their own redundancy. Based on this insight, we introduce $\textbf{Self-Pruner}$ an end-to-end automatic self-pruning framework for LLMs, which efficiently search layer-wise pruning rates. Specifically, $\textbf{Self-Pruner}$ leverages LLMs to autonomously execute the entire evolutionary search process to search for pruning rate configurations. In this process, LLMs are used to generate populations, select parent solutions from the current population, and perform crossover and mutation operations to produce offspring solutions. In this way, LLMs automatically generate and evaluate a large number of candidate solutions, effectively converging to find the pruning rate configurations with minimal human intervention. Extensive experiments demonstrate $\textbf{Self-Pruner}$'s better performance compared to existing state-of-the-art methods. Notably, $\textbf{Self-Pruner}$ prunes LLaMA-2-70B to 49B level with only 0.80$\%$ drop in accuracy across seven commonsense reasoning tasks, achieving a 1.39$\times$ speedup on NVIDIA A100 80GB GPU. Further pruning to 35B level resulted in only a 3.80$\%$ decrease in accuracy while obtaining a 1.70$\times$ speedup.
Determining Layer-wise Sparsity for Large Language Models Through a Theoretical Perspective
Feb 20, 2025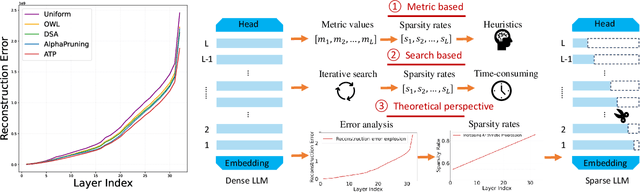
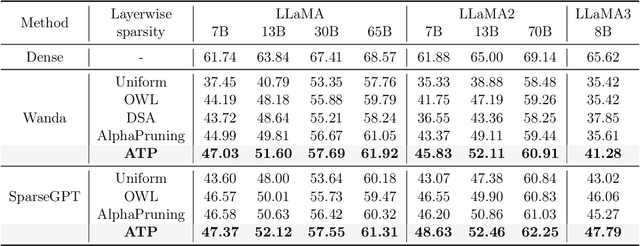
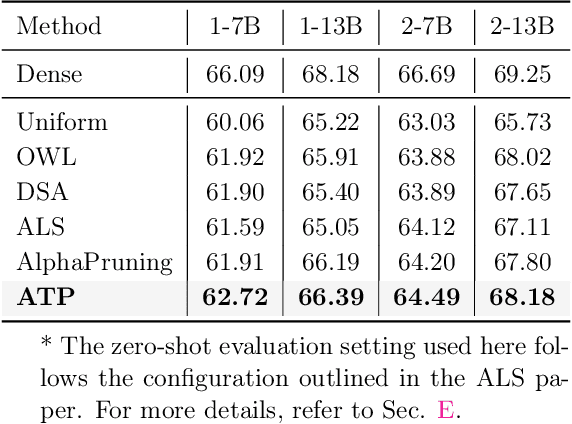
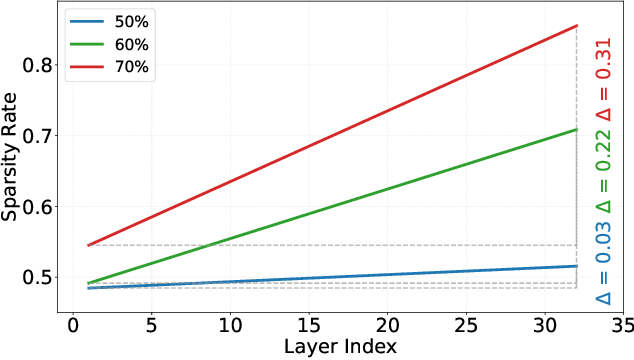
Abstract:In this paper, we address the challenge of determining the layer-wise sparsity rates of large language models (LLMs) through a theoretical perspective. Specifically, we identify a critical issue of ''$\textbf{reconstruction error explosion}$'' in existing LLMs sparsification methods. This refers to the cumulative effect of reconstruction errors throughout the sparsification process, where errors from earlier layers propagate and amplify in subsequent layers. As a result, the overall reconstruction error increases significantly, leading to a substantial degradation in model performance. Through theoretical analysis, we derive a simple yet effective approach to layer-wise sparsity allocation that mitigates this issue. Our method uses a monotonically increasing arithmetic progression, reducing the process of determining sparsity rates for multiple layers to the determination of a single common difference hyperparameter. Remarkably, this allows for the optimal layer-wise sparsity rates to be identified with just a few trials. Both our theoretical analysis and experimental results demonstrate that this sparsity allocation scheme is near optimal. Extensive experiments show that our method significantly improves the performance of sparse LLMs across various architectures, outperforming existing layer-wise sparsity methods. Furthermore, it enhances the performance of various compression techniques and is applicable to vision and multimodal models. Notably, our method achieves a reduction of 52.10 in perplexity for the 70$\%$ sparse LLaMA2-7B model obtained via Wanda, improves average zero-shot accuracy by 10.50$\%$, and delivers speedups of 2.63$\times$ and 2.23$\times$ on CPU and GPU, respectively.
A Survey on Image Quality Assessment: Insights, Analysis, and Future Outlook
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Image quality assessment (IQA) represents a pivotal challenge in image-focused technologies, significantly influencing the advancement trajectory of image processing and computer vision. Recently, IQA has witnessed a notable surge in innovative research efforts, driven by the emergence of novel architectural paradigms and sophisticated computational techniques. This survey delivers an extensive analysis of contemporary IQA methodologies, organized according to their application scenarios, serving as a beneficial reference for both beginners and experienced researchers. We analyze the advantages and limitations of current approaches and suggest potential future research pathways. The survey encompasses both general and specific IQA methodologies, including conventional statistical measures, machine learning techniques, and cutting-edge deep learning models such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and Transformer models. The analysis within this survey highlights the necessity for distortion-specific IQA methods tailored to various application scenarios, emphasizing the significance of practicality, interpretability, and ease of implementation in future developments.
Semantics Prompting Data-Free Quantization for Low-Bit Vision Transformers
Dec 21, 2024Abstract:Data-free quantization (DFQ), which facilitates model quantization without real data to address increasing concerns about data security, has garnered significant attention within the model compression community. Recently, the unique architecture of vision transformers (ViTs) has driven the development of specialized DFQ techniques. However, we observe that the synthetic images from existing methods suffer from the deficient semantics issue compared to real images, thereby compromising performance. Motivated by this, we propose SPDFQ, a Semantics Prompting Data-Free Quantization method for ViTs. First, SPDFQ incorporates Attention Priors Alignment (APA), which uses randomly generated attention priors to enhance the semantics of synthetic images. Second, SPDFQ introduces Multi-Semantic Reinforcement (MSR), which utilizes localized patch optimization to prompt efficient parameterization and diverse semantics in synthetic images. Finally, SPDFQ employs Softlabel Learning (SL), where soft learning targets are adapted to encourage more complex semantics and accommodate images augmented by MSR. Experimental results demonstrate that SPDFQ significantly outperforms existing methods. For instance, SPDFQ achieves a 15.52% increase in top-1 accuracy on ImageNet for W4A4 ViT-B
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge