Xiawu Zheng
Reasoning via Video: The First Evaluation of Video Models' Reasoning Abilities through Maze-Solving Tasks
Nov 19, 2025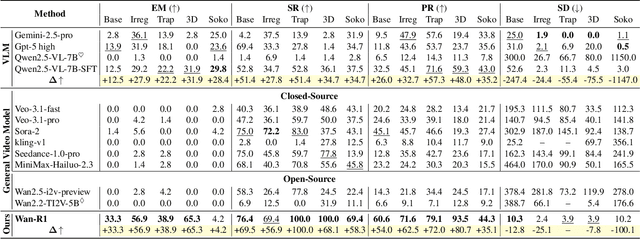

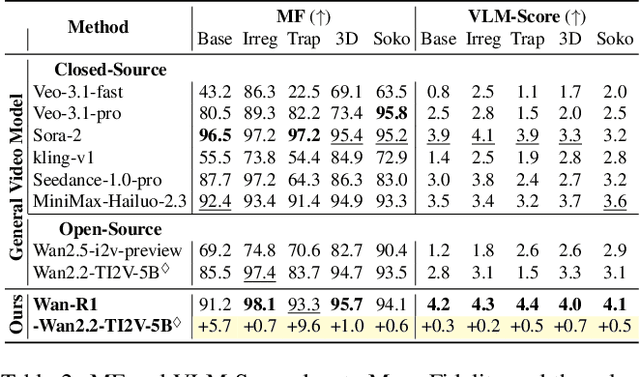
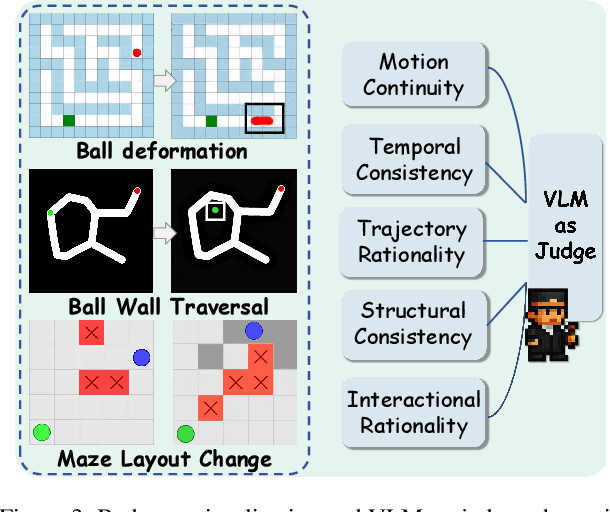
Abstract:Video Models have achieved remarkable success in high-fidelity video generation with coherent motion dynamics. Analogous to the development from text generation to text-based reasoning in language modeling, the development of video models motivates us to ask: Can video models reason via video generation? Compared with the discrete text corpus, video grounds reasoning in explicit spatial layouts and temporal continuity, which serves as an ideal substrate for spatial reasoning. In this work, we explore the reasoning via video paradigm and introduce VR-Bench -- a comprehensive benchmark designed to systematically evaluate video models' reasoning capabilities. Grounded in maze-solving tasks that inherently require spatial planning and multi-step reasoning, VR-Bench contains 7,920 procedurally generated videos across five maze types and diverse visual styles. Our empirical analysis demonstrates that SFT can efficiently elicit the reasoning ability of video model. Video models exhibit stronger spatial perception during reasoning, outperforming leading VLMs and generalizing well across diverse scenarios, tasks, and levels of complexity. We further discover a test-time scaling effect, where diverse sampling during inference improves reasoning reliability by 10--20%. These findings highlight the unique potential and scalability of reasoning via video for spatial reasoning tasks.
Polybasic Speculative Decoding Through a Theoretical Perspective
Oct 30, 2025



Abstract:Inference latency stands as a critical bottleneck in the large-scale deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs). Speculative decoding methods have recently shown promise in accelerating inference without compromising the output distribution. However, existing work typically relies on a dualistic draft-verify framework and lacks rigorous theoretical grounding. In this paper, we introduce a novel \emph{polybasic} speculative decoding framework, underpinned by a comprehensive theoretical analysis. Specifically, we prove a fundamental theorem that characterizes the optimal inference time for multi-model speculative decoding systems, shedding light on how to extend beyond the dualistic approach to a more general polybasic paradigm. Through our theoretical investigation of multi-model token generation, we expose and optimize the interplay between model capabilities, acceptance lengths, and overall computational cost. Our framework supports both standalone implementation and integration with existing speculative techniques, leading to accelerated performance in practice. Experimental results across multiple model families demonstrate that our approach yields speedup ratios ranging from $3.31\times$ to $4.01\times$ for LLaMA2-Chat 7B, up to $3.87 \times$ for LLaMA3-8B, up to $4.43 \times$ for Vicuna-7B and up to $3.85 \times$ for Qwen2-7B -- all while preserving the original output distribution. We release our theoretical proofs and implementation code to facilitate further investigation into polybasic speculative decoding.
UI-AGILE: Advancing GUI Agents with Effective Reinforcement Learning and Precise Inference-Time Grounding
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:The emergence of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) has driven significant advances in Graphical User Interface (GUI) agent capabilities. Nevertheless, existing GUI agent training and inference techniques still suffer from a dilemma for reasoning designs, ineffective reward, and visual noise. To address these issues, we introduce UI-AGILE, a comprehensive framework enhancing GUI agents at both the training and inference stages. For training, we propose a suite of improvements to the Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) process: 1) a Continuous Reward function to incentivize high-precision grounding; 2) a "Simple Thinking" reward to balance planning with speed and grounding accuracy; and 3) a Cropping-based Resampling strategy to mitigate the sparse reward problem and improve learning on complex tasks. For inference, we present Decomposed Grounding with Selection, a novel method that dramatically improves grounding accuracy on high-resolution displays by breaking the image into smaller, manageable parts. Experiments show that UI-AGILE achieves the state-of-the-art performance on two benchmarks ScreenSpot-Pro and ScreenSpot-v2. For instance, using both our proposed training and inference enhancement methods brings 23% grounding accuracy improvement over the best baseline on ScreenSpot-Pro.
Zooming from Context to Cue: Hierarchical Preference Optimization for Multi-Image MLLMs
May 28, 2025Abstract:Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) excel at single-image tasks but struggle with multi-image understanding due to cross-modal misalignment, leading to hallucinations (context omission, conflation, and misinterpretation). Existing methods using Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) constrain optimization to a solitary image reference within the input sequence, neglecting holistic context modeling. We propose Context-to-Cue Direct Preference Optimization (CcDPO), a multi-level preference optimization framework that enhances per-image perception in multi-image settings by zooming into visual clues -- from sequential context to local details. It features: (i) Context-Level Optimization : Re-evaluates cognitive biases underlying MLLMs' multi-image context comprehension and integrates a spectrum of low-cost global sequence preferences for bias mitigation. (ii) Needle-Level Optimization : Directs attention to fine-grained visual details through region-targeted visual prompts and multimodal preference supervision. To support scalable optimization, we also construct MultiScope-42k, an automatically generated dataset with high-quality multi-level preference pairs. Experiments show that CcDPO significantly reduces hallucinations and yields consistent performance gains across general single- and multi-image tasks.
Benchmarking Abstract and Reasoning Abilities Through A Theoretical Perspective
May 28, 2025



Abstract:In this paper, we aim to establish a simple, effective, and theoretically grounded benchmark for rigorously probing abstract reasoning in Large Language Models (LLMs). To achieve this, we first develop a mathematic framework that defines abstract reasoning as the ability to: (i) extract essential patterns independent of surface representations, and (ii) apply consistent rules to these abstract patterns. Based on this framework, we introduce two novel complementary metrics: \(\scoreGamma\) measures basic reasoning accuracy, while \(\scoreDelta\) quantifies a model's reliance on specific symbols rather than underlying patterns - a key indicator of true abstraction versus mere memorization. To implement this measurement, we design a benchmark: systematic symbol remapping in rule-based tasks, which forces models to demonstrate genuine pattern recognition beyond superficial token matching. Extensive LLM evaluations using this benchmark (commercial API models, 7B-70B, multi-agent) reveal:1) critical limitations in non-decimal arithmetic and symbolic reasoning; 2) persistent abstraction gaps despite chain-of-thought prompting; and 3) \(\scoreDelta\)'s effectiveness in robustly measuring memory dependence by quantifying performance degradation under symbol remapping, particularly highlighting operand-specific memorization. These findings underscore that current LLMs, despite domain-specific strengths, still lack robust abstract reasoning, highlighting key areas for future improvement.
QuoTA: Query-oriented Token Assignment via CoT Query Decouple for Long Video Comprehension
Mar 11, 2025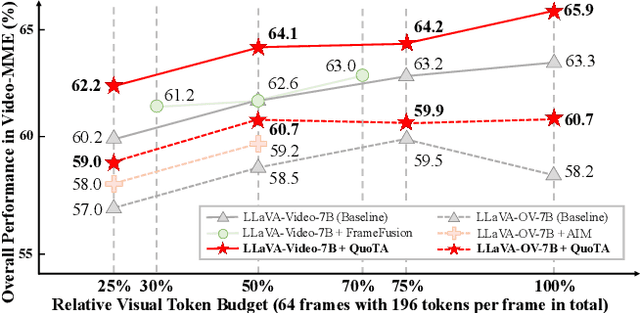
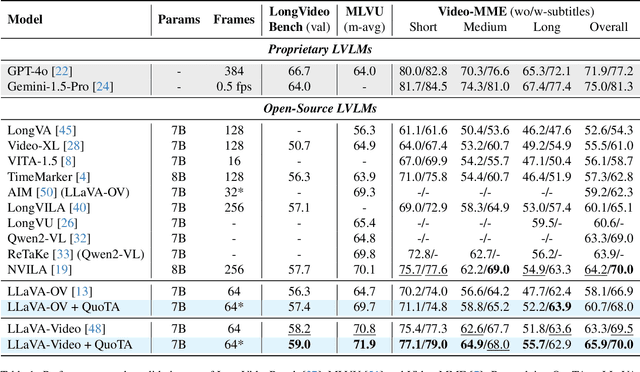
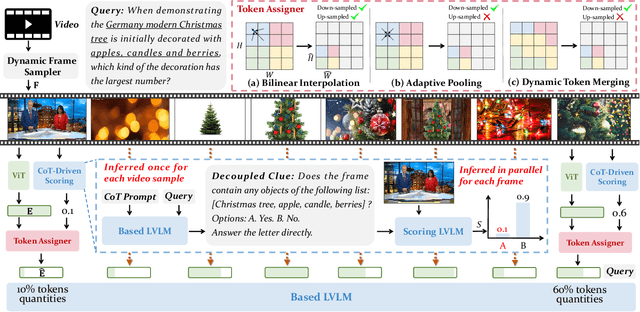
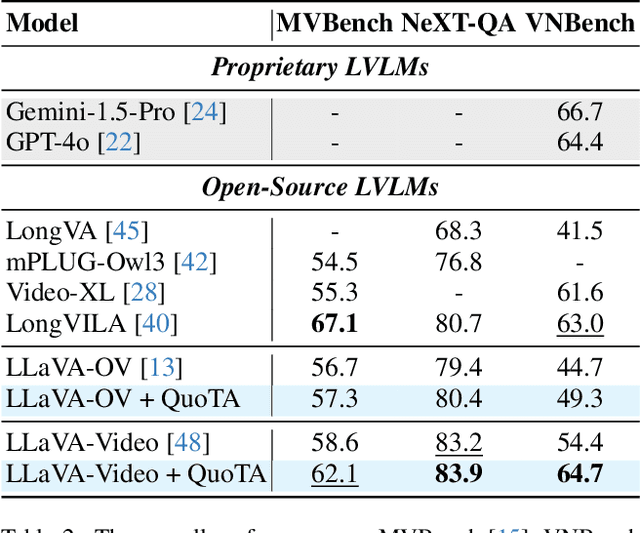
Abstract:Recent advances in long video understanding typically mitigate visual redundancy through visual token pruning based on attention distribution. However, while existing methods employ post-hoc low-response token pruning in decoder layers, they overlook the input-level semantic correlation between visual tokens and instructions (query). In this paper, we propose QuoTA, an ante-hoc training-free modular that extends existing large video-language models (LVLMs) for visual token assignment based on query-oriented frame-level importance assessment. The query-oriented token selection is crucial as it aligns visual processing with task-specific requirements, optimizing token budget utilization while preserving semantically relevant content. Specifically, (i) QuoTA strategically allocates frame-level importance scores based on query relevance, enabling one-time visual token assignment before cross-modal interactions in decoder layers, (ii) we decouple the query through Chain-of-Thoughts reasoning to facilitate more precise LVLM-based frame importance scoring, and (iii) QuoTA offers a plug-and-play functionality that extends to existing LVLMs. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that implementing QuoTA with LLaVA-Video-7B yields an average performance improvement of 3.2% across six benchmarks (including Video-MME and MLVU) while operating within an identical visual token budget as the baseline. Codes are open-sourced at https://github.com/MAC-AutoML/QuoTA.
Dynamic Low-Rank Sparse Adaptation for Large Language Models
Feb 20, 2025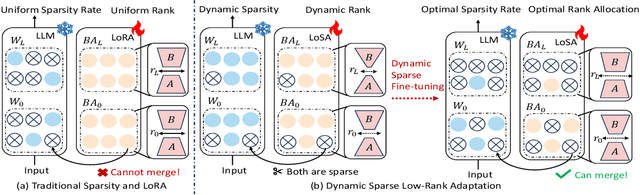
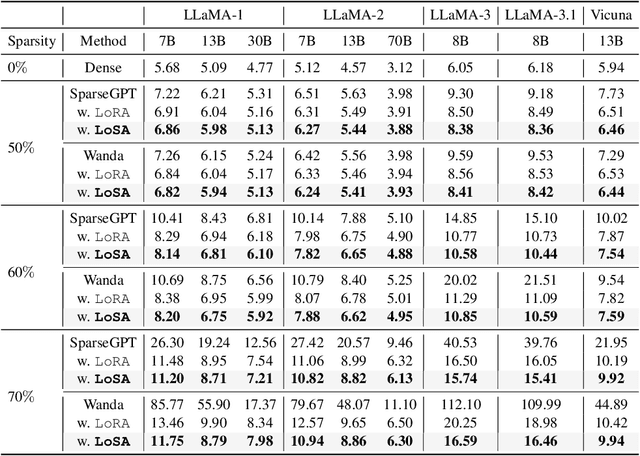
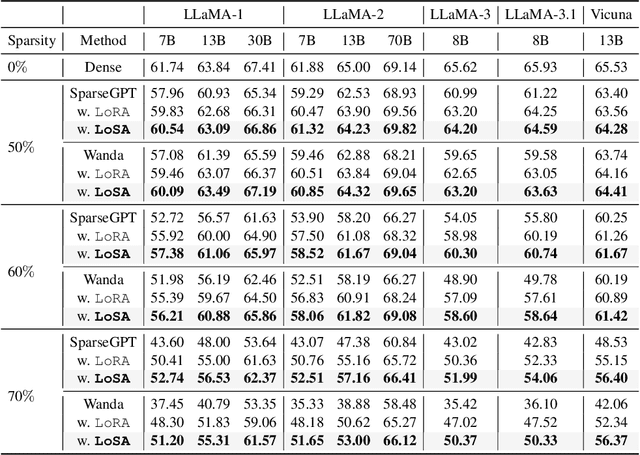
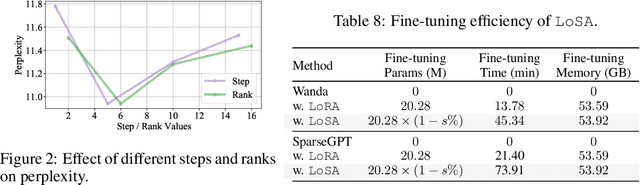
Abstract:Despite the efficacy of network sparsity in alleviating the deployment strain of Large Language Models (LLMs), it endures significant performance degradation. Applying Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) to fine-tune the sparse LLMs offers an intuitive approach to counter this predicament, while it holds shortcomings include: 1) The inability to integrate LoRA weights into sparse LLMs post-training, and 2) Insufficient performance recovery at high sparsity ratios. In this paper, we introduce dynamic Low-rank Sparse Adaptation (LoSA), a novel method that seamlessly integrates low-rank adaptation into LLM sparsity within a unified framework, thereby enhancing the performance of sparse LLMs without increasing the inference latency. In particular, LoSA dynamically sparsifies the LoRA outcomes based on the corresponding sparse weights during fine-tuning, thus guaranteeing that the LoRA module can be integrated into the sparse LLMs post-training. Besides, LoSA leverages Representation Mutual Information (RMI) as an indicator to determine the importance of layers, thereby efficiently determining the layer-wise sparsity rates during fine-tuning. Predicated on this, LoSA adjusts the rank of the LoRA module based on the variability in layer-wise reconstruction errors, allocating an appropriate fine-tuning for each layer to reduce the output discrepancies between dense and sparse LLMs. Extensive experiments tell that LoSA can efficiently boost the efficacy of sparse LLMs within a few hours, without introducing any additional inferential burden. For example, LoSA reduced the perplexity of sparse LLaMA-2-7B by 68.73 and increased zero-shot accuracy by 16.32$\%$, achieving a 2.60$\times$ speedup on CPU and 2.23$\times$ speedup on GPU, requiring only 45 minutes of fine-tuning on a single NVIDIA A100 80GB GPU. Code is available at https://github.com/wzhuang-xmu/LoSA.
Towards Efficient Automatic Self-Pruning of Large Language Models
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Despite exceptional capabilities, Large Language Models (LLMs) still face deployment challenges due to their enormous size. Post-training structured pruning is a promising solution that prunes LLMs without the need for retraining, reducing computational overhead, and it is hardware-deployment friendly. However, the training-free nature of post-training structured pruning leads to significant performance degradation. We argue that the key to mitigating this issue lies in accurately determining the pruning rate for each layer. Meanwhile, we find that LLMs may have prior knowledge about their own redundancy. Based on this insight, we introduce $\textbf{Self-Pruner}$ an end-to-end automatic self-pruning framework for LLMs, which efficiently search layer-wise pruning rates. Specifically, $\textbf{Self-Pruner}$ leverages LLMs to autonomously execute the entire evolutionary search process to search for pruning rate configurations. In this process, LLMs are used to generate populations, select parent solutions from the current population, and perform crossover and mutation operations to produce offspring solutions. In this way, LLMs automatically generate and evaluate a large number of candidate solutions, effectively converging to find the pruning rate configurations with minimal human intervention. Extensive experiments demonstrate $\textbf{Self-Pruner}$'s better performance compared to existing state-of-the-art methods. Notably, $\textbf{Self-Pruner}$ prunes LLaMA-2-70B to 49B level with only 0.80$\%$ drop in accuracy across seven commonsense reasoning tasks, achieving a 1.39$\times$ speedup on NVIDIA A100 80GB GPU. Further pruning to 35B level resulted in only a 3.80$\%$ decrease in accuracy while obtaining a 1.70$\times$ speedup.
Determining Layer-wise Sparsity for Large Language Models Through a Theoretical Perspective
Feb 20, 2025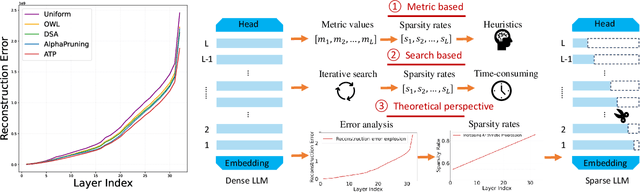
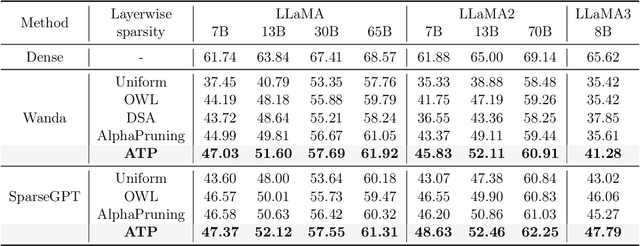
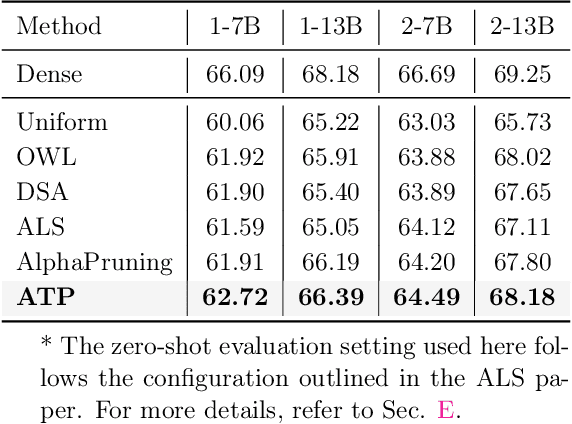
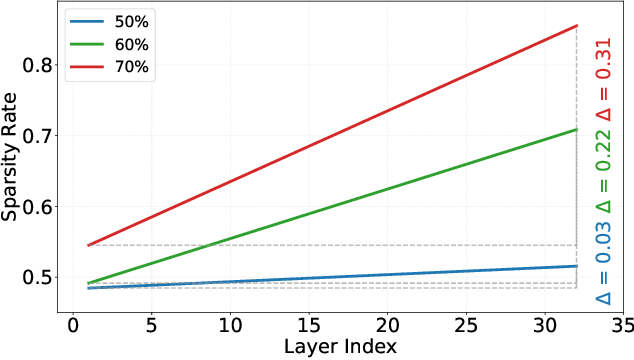
Abstract:In this paper, we address the challenge of determining the layer-wise sparsity rates of large language models (LLMs) through a theoretical perspective. Specifically, we identify a critical issue of ''$\textbf{reconstruction error explosion}$'' in existing LLMs sparsification methods. This refers to the cumulative effect of reconstruction errors throughout the sparsification process, where errors from earlier layers propagate and amplify in subsequent layers. As a result, the overall reconstruction error increases significantly, leading to a substantial degradation in model performance. Through theoretical analysis, we derive a simple yet effective approach to layer-wise sparsity allocation that mitigates this issue. Our method uses a monotonically increasing arithmetic progression, reducing the process of determining sparsity rates for multiple layers to the determination of a single common difference hyperparameter. Remarkably, this allows for the optimal layer-wise sparsity rates to be identified with just a few trials. Both our theoretical analysis and experimental results demonstrate that this sparsity allocation scheme is near optimal. Extensive experiments show that our method significantly improves the performance of sparse LLMs across various architectures, outperforming existing layer-wise sparsity methods. Furthermore, it enhances the performance of various compression techniques and is applicable to vision and multimodal models. Notably, our method achieves a reduction of 52.10 in perplexity for the 70$\%$ sparse LLaMA2-7B model obtained via Wanda, improves average zero-shot accuracy by 10.50$\%$, and delivers speedups of 2.63$\times$ and 2.23$\times$ on CPU and GPU, respectively.
Training-free Anomaly Event Detection via LLM-guided Symbolic Pattern Discovery
Feb 09, 2025



Abstract:Anomaly event detection plays a crucial role in various real-world applications. However, current approaches predominantly rely on supervised learning, which faces significant challenges: the requirement for extensive labeled training data and lack of interpretability in decision-making processes. To address these limitations, we present a training-free framework that integrates open-set object detection with symbolic regression, powered by Large Language Models (LLMs) for efficient symbolic pattern discovery. The LLMs guide the symbolic reasoning process, establishing logical relationships between detected entities. Through extensive experiments across multiple domains, our framework demonstrates several key advantages: (1) achieving superior detection accuracy through direct reasoning without any training process; (2) providing highly interpretable logical expressions that are readily comprehensible to humans; and (3) requiring minimal annotation effort - approximately 1% of the data needed by traditional training-based methods.To facilitate comprehensive evaluation and future research, we introduce two datasets: a large-scale private dataset containing over 110,000 annotated images covering various anomaly scenarios including construction site safety violations, illegal fishing activities, and industrial hazards, along with a public benchmark dataset of 5,000 samples with detailed anomaly event annotations. Code is available at here.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge