Yunhang Shen
Youtu-VL: Unleashing Visual Potential via Unified Vision-Language Supervision
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Despite the significant advancements represented by Vision-Language Models (VLMs), current architectures often exhibit limitations in retaining fine-grained visual information, leading to coarse-grained multimodal comprehension. We attribute this deficiency to a suboptimal training paradigm inherent in prevailing VLMs, which exhibits a text-dominant optimization bias by conceptualizing visual signals merely as passive conditional inputs rather than supervisory targets. To mitigate this, we introduce Youtu-VL, a framework leveraging the Vision-Language Unified Autoregressive Supervision (VLUAS) paradigm, which fundamentally shifts the optimization objective from ``vision-as-input'' to ``vision-as-target.'' By integrating visual tokens directly into the prediction stream, Youtu-VL applies unified autoregressive supervision to both visual details and linguistic content. Furthermore, we extend this paradigm to encompass vision-centric tasks, enabling a standard VLM to perform vision-centric tasks without task-specific additions. Extensive empirical evaluations demonstrate that Youtu-VL achieves competitive performance on both general multimodal tasks and vision-centric tasks, establishing a robust foundation for the development of comprehensive generalist visual agents.
SMART: Shot-Aware Multimodal Video Moment Retrieval with Audio-Enhanced MLLM
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Video Moment Retrieval is a task in video understanding that aims to localize a specific temporal segment in an untrimmed video based on a natural language query. Despite recent progress in moment retrieval from videos using both traditional techniques and Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLM), most existing methods still rely on coarse temporal understanding and a single visual modality, limiting performance on complex videos. To address this, we introduce \textit{S}hot-aware \textit{M}ultimodal \textit{A}udio-enhanced \textit{R}etrieval of \textit{T}emporal \textit{S}egments (SMART), an MLLM-based framework that integrates audio cues and leverages shot-level temporal structure. SMART enriches multimodal representations by combining audio and visual features while applying \textbf{Shot-aware Token Compression}, which selectively retains high-information tokens within each shot to reduce redundancy and preserve fine-grained temporal details. We also refine prompt design to better utilize audio-visual cues. Evaluations on Charades-STA and QVHighlights show that SMART achieves significant improvements over state-of-the-art methods, including a 1.61\% increase in R1@0.5 and 2.59\% gain in R1@0.7 on Charades-STA.
VITA-VLA: Efficiently Teaching Vision-Language Models to Act via Action Expert Distillation
Oct 10, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language Action (VLA) models significantly advance robotic manipulation by leveraging the strong perception capabilities of pretrained vision-language models (VLMs). By integrating action modules into these pretrained models, VLA methods exhibit improved generalization. However, training them from scratch is costly. In this work, we propose a simple yet effective distillation-based framework that equips VLMs with action-execution capability by transferring knowledge from pretrained small action models. Our architecture retains the original VLM structure, adding only an action token and a state encoder to incorporate physical inputs. To distill action knowledge, we adopt a two-stage training strategy. First, we perform lightweight alignment by mapping VLM hidden states into the action space of the small action model, enabling effective reuse of its pretrained action decoder and avoiding expensive pretraining. Second, we selectively fine-tune the language model, state encoder, and action modules, enabling the system to integrate multimodal inputs with precise action generation. Specifically, the action token provides the VLM with a direct handle for predicting future actions, while the state encoder allows the model to incorporate robot dynamics not captured by vision alone. This design yields substantial efficiency gains over training large VLA models from scratch. Compared with previous state-of-the-art methods, our method achieves 97.3% average success rate on LIBERO (11.8% improvement) and 93.5% on LIBERO-LONG (24.5% improvement). In real-world experiments across five manipulation tasks, our method consistently outperforms the teacher model, achieving 82.0% success rate (17% improvement), which demonstrate that action distillation effectively enables VLMs to generate precise actions while substantially reducing training costs.
Zooming from Context to Cue: Hierarchical Preference Optimization for Multi-Image MLLMs
May 28, 2025Abstract:Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) excel at single-image tasks but struggle with multi-image understanding due to cross-modal misalignment, leading to hallucinations (context omission, conflation, and misinterpretation). Existing methods using Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) constrain optimization to a solitary image reference within the input sequence, neglecting holistic context modeling. We propose Context-to-Cue Direct Preference Optimization (CcDPO), a multi-level preference optimization framework that enhances per-image perception in multi-image settings by zooming into visual clues -- from sequential context to local details. It features: (i) Context-Level Optimization : Re-evaluates cognitive biases underlying MLLMs' multi-image context comprehension and integrates a spectrum of low-cost global sequence preferences for bias mitigation. (ii) Needle-Level Optimization : Directs attention to fine-grained visual details through region-targeted visual prompts and multimodal preference supervision. To support scalable optimization, we also construct MultiScope-42k, an automatically generated dataset with high-quality multi-level preference pairs. Experiments show that CcDPO significantly reduces hallucinations and yields consistent performance gains across general single- and multi-image tasks.
What You Perceive Is What You Conceive: A Cognition-Inspired Framework for Open Vocabulary Image Segmentation
May 26, 2025



Abstract:Open vocabulary image segmentation tackles the challenge of recognizing dynamically adjustable, predefined novel categories at inference time by leveraging vision-language alignment. However, existing paradigms typically perform class-agnostic region segmentation followed by category matching, which deviates from the human visual system's process of recognizing objects based on semantic concepts, leading to poor alignment between region segmentation and target concepts. To bridge this gap, we propose a novel Cognition-Inspired Framework for open vocabulary image segmentation that emulates the human visual recognition process: first forming a conceptual understanding of an object, then perceiving its spatial extent. The framework consists of three core components: (1) A Generative Vision-Language Model (G-VLM) that mimics human cognition by generating object concepts to provide semantic guidance for region segmentation. (2) A Concept-Aware Visual Enhancer Module that fuses textual concept features with global visual representations, enabling adaptive visual perception based on target concepts. (3) A Cognition-Inspired Decoder that integrates local instance features with G-VLM-provided semantic cues, allowing selective classification over a subset of relevant categories. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our framework achieves significant improvements, reaching $27.2$ PQ, $17.0$ mAP, and $35.3$ mIoU on A-150. It further attains $56.2$, $28.2$, $15.4$, $59.2$, $18.7$, and $95.8$ mIoU on Cityscapes, Mapillary Vistas, A-847, PC-59, PC-459, and PAS-20, respectively. In addition, our framework supports vocabulary-free segmentation, offering enhanced flexibility in recognizing unseen categories. Code will be public.
Pseudo-Label Quality Decoupling and Correction for Semi-Supervised Instance Segmentation
May 16, 2025Abstract:Semi-Supervised Instance Segmentation (SSIS) involves classifying and grouping image pixels into distinct object instances using limited labeled data. This learning paradigm usually faces a significant challenge of unstable performance caused by noisy pseudo-labels of instance categories and pixel masks. We find that the prevalent practice of filtering instance pseudo-labels assessing both class and mask quality with a single score threshold, frequently leads to compromises in the trade-off between the qualities of class and mask labels. In this paper, we introduce a novel Pseudo-Label Quality Decoupling and Correction (PL-DC) framework for SSIS to tackle the above challenges. Firstly, at the instance level, a decoupled dual-threshold filtering mechanism is designed to decouple class and mask quality estimations for instance-level pseudo-labels, thereby independently controlling pixel classifying and grouping qualities. Secondly, at the category level, we introduce a dynamic instance category correction module to dynamically correct the pseudo-labels of instance categories, effectively alleviating category confusion. Lastly, we introduce a pixel-level mask uncertainty-aware mechanism at the pixel level to re-weight the mask loss for different pixels, thereby reducing the impact of noise introduced by pixel-level mask pseudo-labels. Extensive experiments on the COCO and Cityscapes datasets demonstrate that the proposed PL-DC achieves significant performance improvements, setting new state-of-the-art results for SSIS. Notably, our PL-DC shows substantial gains even with minimal labeled data, achieving an improvement of +11.6 mAP with just 1% COCO labeled data and +15.5 mAP with 5% Cityscapes labeled data. The code will be public.
VITA-Audio: Fast Interleaved Cross-Modal Token Generation for Efficient Large Speech-Language Model
May 06, 2025Abstract:With the growing requirement for natural human-computer interaction, speech-based systems receive increasing attention as speech is one of the most common forms of daily communication. However, the existing speech models still experience high latency when generating the first audio token during streaming, which poses a significant bottleneck for deployment. To address this issue, we propose VITA-Audio, an end-to-end large speech model with fast audio-text token generation. Specifically, we introduce a lightweight Multiple Cross-modal Token Prediction (MCTP) module that efficiently generates multiple audio tokens within a single model forward pass, which not only accelerates the inference but also significantly reduces the latency for generating the first audio in streaming scenarios. In addition, a four-stage progressive training strategy is explored to achieve model acceleration with minimal loss of speech quality. To our knowledge, VITA-Audio is the first multi-modal large language model capable of generating audio output during the first forward pass, enabling real-time conversational capabilities with minimal latency. VITA-Audio is fully reproducible and is trained on open-source data only. Experimental results demonstrate that our model achieves an inference speedup of 3~5x at the 7B parameter scale, but also significantly outperforms open-source models of similar model size on multiple benchmarks for automatic speech recognition (ASR), text-to-speech (TTS), and spoken question answering (SQA) tasks.
BUFF: Bayesian Uncertainty Guided Diffusion Probabilistic Model for Single Image Super-Resolution
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:Super-resolution (SR) techniques are critical for enhancing image quality, particularly in scenarios where high-resolution imagery is essential yet limited by hardware constraints. Existing diffusion models for SR have relied predominantly on Gaussian models for noise generation, which often fall short when dealing with the complex and variable texture inherent in natural scenes. To address these deficiencies, we introduce the Bayesian Uncertainty Guided Diffusion Probabilistic Model (BUFF). BUFF distinguishes itself by incorporating a Bayesian network to generate high-resolution uncertainty masks. These masks guide the diffusion process, allowing for the adjustment of noise intensity in a manner that is both context-aware and adaptive. This novel approach not only enhances the fidelity of super-resolved images to their original high-resolution counterparts but also significantly mitigates artifacts and blurring in areas characterized by complex textures and fine details. The model demonstrates exceptional robustness against complex noise patterns and showcases superior adaptability in handling textures and edges within images. Empirical evidence, supported by visual results, illustrates the model's robustness, especially in challenging scenarios, and its effectiveness in addressing common SR issues such as blurring. Experimental evaluations conducted on the DIV2K dataset reveal that BUFF achieves a notable improvement, with a +0.61 increase compared to baseline in SSIM on BSD100, surpassing traditional diffusion approaches by an average additional +0.20dB PSNR gain. These findings underscore the potential of Bayesian methods in enhancing diffusion processes for SR, paving the way for future advancements in the field.
Aligning Multimodal LLM with Human Preference: A Survey
Mar 18, 2025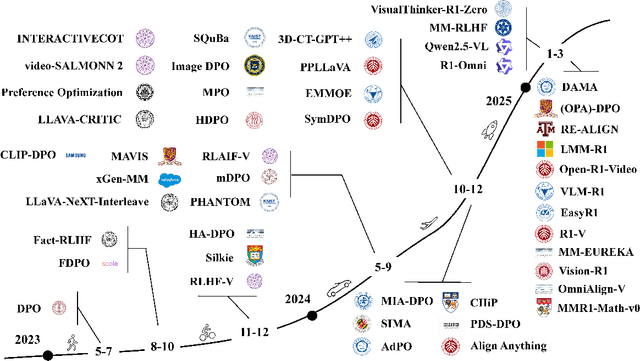
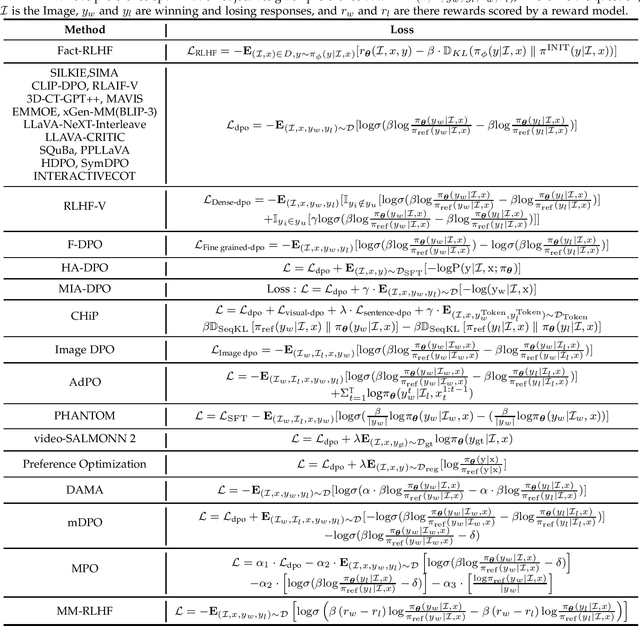
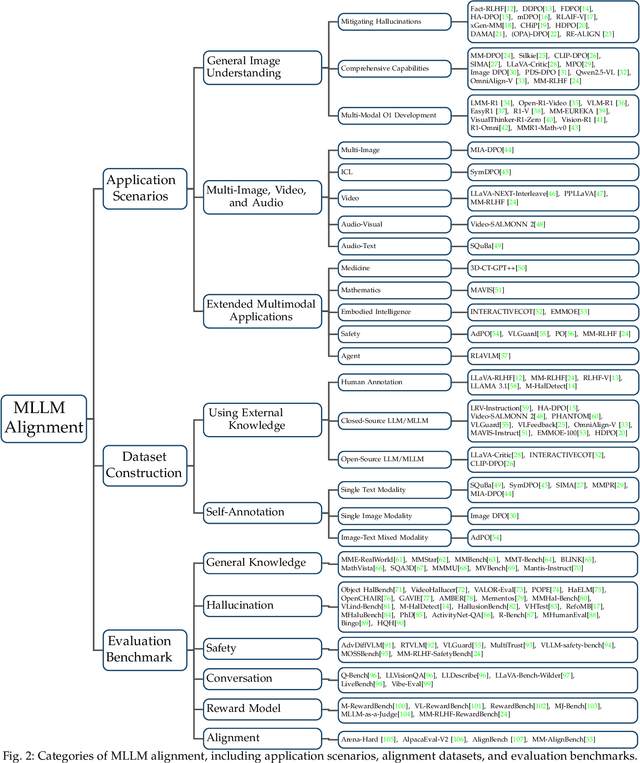
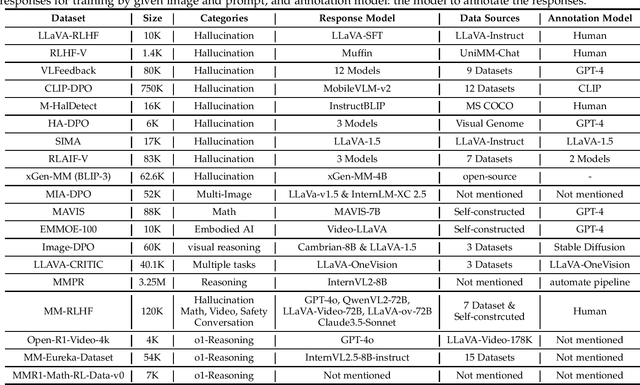
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) can handle a wide variety of general tasks with simple prompts, without the need for task-specific training. Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), built upon LLMs, have demonstrated impressive potential in tackling complex tasks involving visual, auditory, and textual data. However, critical issues related to truthfulness, safety, o1-like reasoning, and alignment with human preference remain insufficiently addressed. This gap has spurred the emergence of various alignment algorithms, each targeting different application scenarios and optimization goals. Recent studies have shown that alignment algorithms are a powerful approach to resolving the aforementioned challenges. In this paper, we aim to provide a comprehensive and systematic review of alignment algorithms for MLLMs. Specifically, we explore four key aspects: (1) the application scenarios covered by alignment algorithms, including general image understanding, multi-image, video, and audio, and extended multimodal applications; (2) the core factors in constructing alignment datasets, including data sources, model responses, and preference annotations; (3) the benchmarks used to evaluate alignment algorithms; and (4) a discussion of potential future directions for the development of alignment algorithms. This work seeks to help researchers organize current advancements in the field and inspire better alignment methods. The project page of this paper is available at https://github.com/BradyFU/Awesome-Multimodal-Large-Language-Models/tree/Alignment.
LLaVA-RadZ: Can Multimodal Large Language Models Effectively Tackle Zero-shot Radiology Recognition?
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:Recently, multimodal large models (MLLMs) have demonstrated exceptional capabilities in visual understanding and reasoning across various vision-language tasks. However, MLLMs usually perform poorly in zero-shot medical disease recognition, as they do not fully exploit the captured features and available medical knowledge. To address this challenge, we propose LLaVA-RadZ, a simple yet effective framework for zero-shot medical disease recognition. Specifically, we design an end-to-end training strategy, termed Decoding-Side Feature Alignment Training (DFAT) to take advantage of the characteristics of the MLLM decoder architecture and incorporate modality-specific tokens tailored for different modalities, which effectively utilizes image and text representations and facilitates robust cross-modal alignment. Additionally, we introduce a Domain Knowledge Anchoring Module (DKAM) to exploit the intrinsic medical knowledge of large models, which mitigates the category semantic gap in image-text alignment. DKAM improves category-level alignment, allowing for accurate disease recognition. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmarks demonstrate that our LLaVA-RadZ significantly outperforms traditional MLLMs in zero-shot disease recognition and exhibits the state-of-the-art performance compared to the well-established and highly-optimized CLIP-based approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge