Chaoyang Zhu
Pseudo-Label Quality Decoupling and Correction for Semi-Supervised Instance Segmentation
May 16, 2025Abstract:Semi-Supervised Instance Segmentation (SSIS) involves classifying and grouping image pixels into distinct object instances using limited labeled data. This learning paradigm usually faces a significant challenge of unstable performance caused by noisy pseudo-labels of instance categories and pixel masks. We find that the prevalent practice of filtering instance pseudo-labels assessing both class and mask quality with a single score threshold, frequently leads to compromises in the trade-off between the qualities of class and mask labels. In this paper, we introduce a novel Pseudo-Label Quality Decoupling and Correction (PL-DC) framework for SSIS to tackle the above challenges. Firstly, at the instance level, a decoupled dual-threshold filtering mechanism is designed to decouple class and mask quality estimations for instance-level pseudo-labels, thereby independently controlling pixel classifying and grouping qualities. Secondly, at the category level, we introduce a dynamic instance category correction module to dynamically correct the pseudo-labels of instance categories, effectively alleviating category confusion. Lastly, we introduce a pixel-level mask uncertainty-aware mechanism at the pixel level to re-weight the mask loss for different pixels, thereby reducing the impact of noise introduced by pixel-level mask pseudo-labels. Extensive experiments on the COCO and Cityscapes datasets demonstrate that the proposed PL-DC achieves significant performance improvements, setting new state-of-the-art results for SSIS. Notably, our PL-DC shows substantial gains even with minimal labeled data, achieving an improvement of +11.6 mAP with just 1% COCO labeled data and +15.5 mAP with 5% Cityscapes labeled data. The code will be public.
Cyclic Contrastive Knowledge Transfer for Open-Vocabulary Object Detection
Mar 14, 2025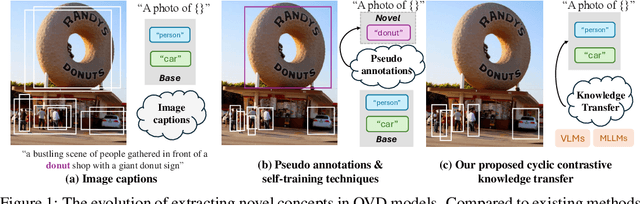

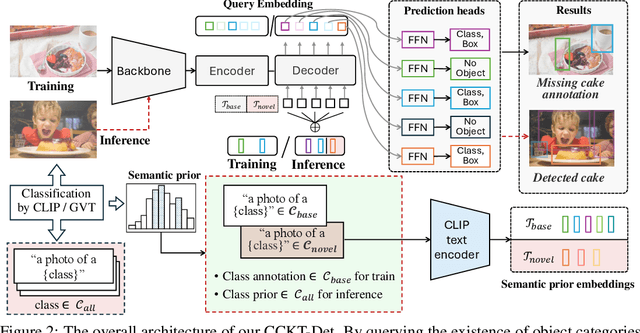

Abstract:In pursuit of detecting unstinted objects that extend beyond predefined categories, prior arts of open-vocabulary object detection (OVD) typically resort to pretrained vision-language models (VLMs) for base-to-novel category generalization. However, to mitigate the misalignment between upstream image-text pretraining and downstream region-level perception, additional supervisions are indispensable, eg, image-text pairs or pseudo annotations generated via self-training strategies. In this work, we propose CCKT-Det trained without any extra supervision. The proposed framework constructs a cyclic and dynamic knowledge transfer from language queries and visual region features extracted from VLMs, which forces the detector to closely align with the visual-semantic space of VLMs. Specifically, 1) we prefilter and inject semantic priors to guide the learning of queries, and 2) introduce a regional contrastive loss to improve the awareness of queries on novel objects. CCKT-Det can consistently improve performance as the scale of VLMs increases, all while requiring the detector at a moderate level of computation overhead. Comprehensive experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves performance gain of +2.9% and +10.2% AP50 over previous state-of-the-arts on the challenging COCO benchmark, both without and with a stronger teacher model. The code is provided at https://github.com/ZCHUHan/CCKT-Det.
* 10 pages, 5 figures, Published as a conference paper at ICLR 2025
Deep Instruction Tuning for Segment Anything Model
Mar 31, 2024Abstract:Segment Anything Model (SAM) exhibits powerful yet versatile capabilities on (un) conditional image segmentation tasks recently. Although SAM can support various segmentation prompts, we note that, compared to point- and box-guided segmentation, it performs much worse on text-instructed tasks. We argue that deep text instruction tuning is key to mitigate such shortcoming caused by the shallow fusion scheme in its default light-weight mask decoder. In this paper, two \emph{deep instruction tuning} (DIT) methods are proposed, one is end-to-end and the other is layer-wise. With these tuning methods, we can regard the image encoder of SAM as a stand-alone vision-language learner in contrast to building another deep fusion branch. Extensive experiments on three highly competitive benchmark datasets of referring image segmentation show that a simple end-to-end DIT improves SAM by a large margin, with layer-wise DIT further boosts the performance to state-of-the-art. Our code is anonymously released at: https://github.com/wysnzzzz/DIT.
A Survey on Open-Vocabulary Detection and Segmentation: Past, Present, and Future
Jul 18, 2023Abstract:As the most fundamental tasks of computer vision, object detection and segmentation have made tremendous progress in the deep learning era. Due to the expensive manual labeling, the annotated categories in existing datasets are often small-scale and pre-defined, i.e., state-of-the-art detectors and segmentors fail to generalize beyond the closed-vocabulary. To resolve this limitation, the last few years have witnessed increasing attention toward Open-Vocabulary Detection (OVD) and Segmentation (OVS). In this survey, we provide a comprehensive review on the past and recent development of OVD and OVS. To this end, we develop a taxonomy according to the type of task and methodology. We find that the permission and usage of weak supervision signals can well discriminate different methodologies, including: visual-semantic space mapping, novel visual feature synthesis, region-aware training, pseudo-labeling, knowledge distillation-based, and transfer learning-based. The proposed taxonomy is universal across different tasks, covering object detection, semantic/instance/panoptic segmentation, 3D scene and video understanding. In each category, its main principles, key challenges, development routes, strengths, and weaknesses are thoroughly discussed. In addition, we benchmark each task along with the vital components of each method. Finally, several promising directions are provided to stimulate future research.
SeqTR: A Simple yet Universal Network for Visual Grounding
Mar 30, 2022



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a simple yet universal network termed SeqTR for visual grounding tasks, e.g., phrase localization, referring expression comprehension (REC) and segmentation (RES). The canonical paradigms for visual grounding often require substantial expertise in designing network architectures and loss functions, making them hard to generalize across tasks. To simplify and unify the modeling, we cast visual grounding as a point prediction problem conditioned on image and text inputs, where either the bounding box or binary mask is represented as a sequence of discrete coordinate tokens. Under this paradigm, visual grounding tasks are unified in our SeqTR network without task-specific branches or heads, e.g., the convolutional mask decoder for RES, which greatly reduces the complexity of multi-task modeling. In addition, SeqTR also shares the same optimization objective for all tasks with a simple cross-entropy loss, further reducing the complexity of deploying hand-crafted loss functions. Experiments on five benchmark datasets demonstrate that the proposed SeqTR outperforms (or is on par with) the existing state-of-the-arts, proving that a simple yet universal approach for visual grounding is indeed feasible.
Place recognition: An Overview of Vision Perspective
Jun 17, 2017



Abstract:Place recognition is one of the most fundamental topics in computer vision and robotics communities, where the task is to accurately and efficiently recognize the location of a given query image. Despite years of wisdom accumulated in this field, place recognition still remains an open problem due to the various ways in which the appearance of real-world places may differ. This paper presents an overview of the place recognition literature. Since condition invariant and viewpoint invariant features are essential factors to long-term robust visual place recognition system, We start with traditional image description methodology developed in the past, which exploit techniques from image retrieval field. Recently, the rapid advances of related fields such as object detection and image classification have inspired a new technique to improve visual place recognition system, i.e., convolutional neural networks (CNNs). Thus we then introduce recent progress of visual place recognition system based on CNNs to automatically learn better image representations for places. Eventually, we close with discussions and future work of place recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge