Dong Zhang
Training Beyond Convergence: Grokking nnU-Net for Glioma Segmentation in Sub-Saharan MRI
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Gliomas are placing an increasingly clinical burden on Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA). In the region, the median survival for patients remains under two years, and access to diagnostic imaging is extremely limited. These constraints highlight an urgent need for automated tools that can extract the maximum possible information from each available scan, tools that are specifically trained on local data, rather than adapted from high-income settings where conditions are vastly different. We utilize the Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) Africa 2025 Challenge dataset, an expert annotated collection of glioma MRIs. Our objectives are: (i) establish a strong baseline with nnUNet on this dataset, and (ii) explore whether the celebrated "grokking" phenomenon an abrupt, late training jump from memorization to superior generalization can be triggered to push performance without extra labels. We evaluate two training regimes. The first is a fast, budget-conscious approach that limits optimization to just a few epochs, reflecting the constrained GPU resources typically available in African institutions. Despite this limitation, nnUNet achieves strong Dice scores: 92.3% for whole tumor (WH), 86.6% for tumor core (TC), and 86.3% for enhancing tumor (ET). The second regime extends training well beyond the point of convergence, aiming to trigger a grokking-driven performance leap. With this approach, we were able to achieve grokking and enhanced our results to higher Dice scores: 92.2% for whole tumor (WH), 90.1% for tumor core (TC), and 90.2% for enhancing tumor (ET).
Agentic AI for Self-Driving Laboratories in Soft Matter: Taxonomy, Benchmarks,and Open Challenges
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Self-driving laboratories (SDLs) close the loop between experiment design, automated execution, and data-driven decision making, and they provide a demanding testbed for agentic AI under expensive actions, noisy and delayed feedback, strict feasibility and safety constraints, and non-stationarity. This survey uses soft matter as a representative setting but focuses on the AI questions that arise in real laboratories. We frame SDL autonomy as an agent environment interaction problem with explicit observations, actions, costs, and constraints, and we use this formulation to connect common SDL pipelines to established AI principles. We review the main method families that enable closed loop experimentation, including Bayesian optimization and active learning for sample efficient experiment selection, planning and reinforcement learning for long horizon protocol optimization, and tool using agents that orchestrate heterogeneous instruments and software. We emphasize verifiable and provenance aware policies that support debugging, reproducibility, and safe operation. We then propose a capability driven taxonomy that organizes systems by decision horizon, uncertainty modeling, action parameterization, constraint handling, failure recovery, and human involvement. To enable meaningful comparison, we synthesize benchmark task templates and evaluation metrics that prioritize cost aware performance, robustness to drift, constraint violation behavior, and reproducibility. Finally, we distill lessons from deployed SDLs and outline open challenges in multi-modal representation, calibrated uncertainty, safe exploration, and shared benchmark infrastructure.
Bridging Semantic Understanding and Popularity Bias with LLMs
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Semantic understanding of popularity bias is a crucial yet underexplored challenge in recommender systems, where popular items are often favored at the expense of niche content. Most existing debiasing methods treat the semantic understanding of popularity bias as a matter of diversity enhancement or long-tail coverage, neglecting the deeper semantic layer that embodies the causal origins of the bias itself. Consequently, such shallow interpretations limit both their debiasing effectiveness and recommendation accuracy. In this paper, we propose FairLRM, a novel framework that bridges the gap in the semantic understanding of popularity bias with Recommendation via Large Language Model (RecLLM). FairLRM decomposes popularity bias into item-side and user-side components, using structured instruction-based prompts to enhance the model's comprehension of both global item distributions and individual user preferences. Unlike traditional methods that rely on surface-level features such as "diversity" or "debiasing", FairLRM improves the model's ability to semantically interpret and address the underlying bias. Through empirical evaluation, we show that FairLRM significantly enhances both fairness and recommendation accuracy, providing a more semantically aware and trustworthy approach to enhance the semantic understanding of popularity bias. The implementation is available at https://github.com/LuoRenqiang/FairLRM.
MiMo-V2-Flash Technical Report
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:We present MiMo-V2-Flash, a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model with 309B total parameters and 15B active parameters, designed for fast, strong reasoning and agentic capabilities. MiMo-V2-Flash adopts a hybrid attention architecture that interleaves Sliding Window Attention (SWA) with global attention, with a 128-token sliding window under a 5:1 hybrid ratio. The model is pre-trained on 27 trillion tokens with Multi-Token Prediction (MTP), employing a native 32k context length and subsequently extended to 256k. To efficiently scale post-training compute, MiMo-V2-Flash introduces a novel Multi-Teacher On-Policy Distillation (MOPD) paradigm. In this framework, domain-specialized teachers (e.g., trained via large-scale reinforcement learning) provide dense and token-level reward, enabling the student model to perfectly master teacher expertise. MiMo-V2-Flash rivals top-tier open-weight models such as DeepSeek-V3.2 and Kimi-K2, despite using only 1/2 and 1/3 of their total parameters, respectively. During inference, by repurposing MTP as a draft model for speculative decoding, MiMo-V2-Flash achieves up to 3.6 acceptance length and 2.6x decoding speedup with three MTP layers. We open-source both the model weights and the three-layer MTP weights to foster open research and community collaboration.
WESR: Scaling and Evaluating Word-level Event-Speech Recognition
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Speech conveys not only linguistic information but also rich non-verbal vocal events such as laughing and crying. While semantic transcription is well-studied, the precise localization of non-verbal events remains a critical yet under-explored challenge. Current methods suffer from insufficient task definitions with limited category coverage and ambiguous temporal granularity. They also lack standardized evaluation frameworks, hindering the development of downstream applications. To bridge this gap, we first develop a refined taxonomy of 21 vocal events, with a new categorization into discrete (standalone) versus continuous (mixed with speech) types. Based on the refined taxonomy, we introduce WESR-Bench, an expert-annotated evaluation set (900+ utterances) with a novel position-aware protocol that disentangles ASR errors from event detection, enabling precise localization measurement for both discrete and continuous events. We also build a strong baseline by constructing a 1,700+ hour corpus, and train specialized models, surpassing both open-source audio-language models and commercial APIs while preserving ASR quality. We anticipate that WESR will serve as a foundational resource for future research in modeling rich, real-world auditory scenes.
Robust Mesh Saliency GT Acquisition in VR via View Cone Sampling and Geometric Smoothing
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Reliable 3D mesh saliency ground truth (GT) is essential for human-centric visual modeling in virtual reality (VR). However, current 3D mesh saliency GT acquisition methods are generally consistent with 2D image methods, ignoring the differences between 3D geometry topology and 2D image array. Current VR eye-tracking pipelines rely on single ray sampling and Euclidean smoothing, triggering texture attention and signal leakage across gaps. This paper proposes a robust framework to address these limitations. We first introduce a view cone sampling (VCS) strategy, which simulates the human foveal receptive field via Gaussian-distributed ray bundles to improve sampling robustness for complex topologies. Furthermore, a hybrid Manifold-Euclidean constrained diffusion (HCD) algorithm is developed, fusing manifold geodesic constraints with Euclidean scales to ensure topologically-consistent saliency propagation. By mitigating "topological short-circuits" and aliasing, our framework provides a high-fidelity 3D attention acquisition paradigm that aligns with natural human perception, offering a more accurate and robust baseline for 3D mesh saliency research.
MiMo-Audio: Audio Language Models are Few-Shot Learners
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Existing audio language models typically rely on task-specific fine-tuning to accomplish particular audio tasks. In contrast, humans are able to generalize to new audio tasks with only a few examples or simple instructions. GPT-3 has shown that scaling next-token prediction pretraining enables strong generalization capabilities in text, and we believe this paradigm is equally applicable to the audio domain. By scaling MiMo-Audio's pretraining data to over one hundred million of hours, we observe the emergence of few-shot learning capabilities across a diverse set of audio tasks. We develop a systematic evaluation of these capabilities and find that MiMo-Audio-7B-Base achieves SOTA performance on both speech intelligence and audio understanding benchmarks among open-source models. Beyond standard metrics, MiMo-Audio-7B-Base generalizes to tasks absent from its training data, such as voice conversion, style transfer, and speech editing. MiMo-Audio-7B-Base also demonstrates powerful speech continuation capabilities, capable of generating highly realistic talk shows, recitations, livestreaming and debates. At the post-training stage, we curate a diverse instruction-tuning corpus and introduce thinking mechanisms into both audio understanding and generation. MiMo-Audio-7B-Instruct achieves open-source SOTA on audio understanding benchmarks (MMSU, MMAU, MMAR, MMAU-Pro), spoken dialogue benchmarks (Big Bench Audio, MultiChallenge Audio) and instruct-TTS evaluations, approaching or surpassing closed-source models. Model checkpoints and full evaluation suite are available at https://github.com/XiaomiMiMo/MiMo-Audio.
AI Code in the Wild: Measuring Security Risks and Ecosystem Shifts of AI-Generated Code in Modern Software
Dec 21, 2025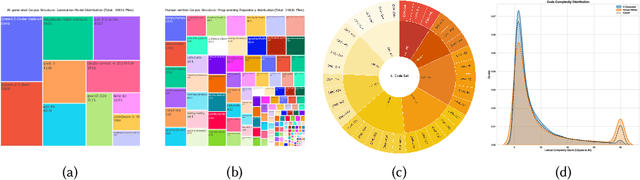
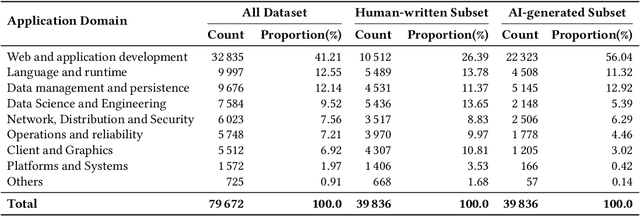
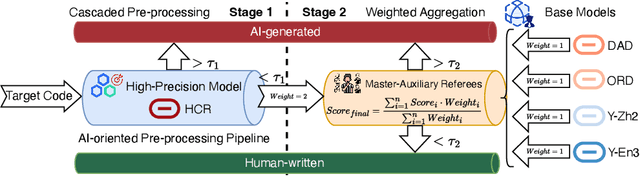
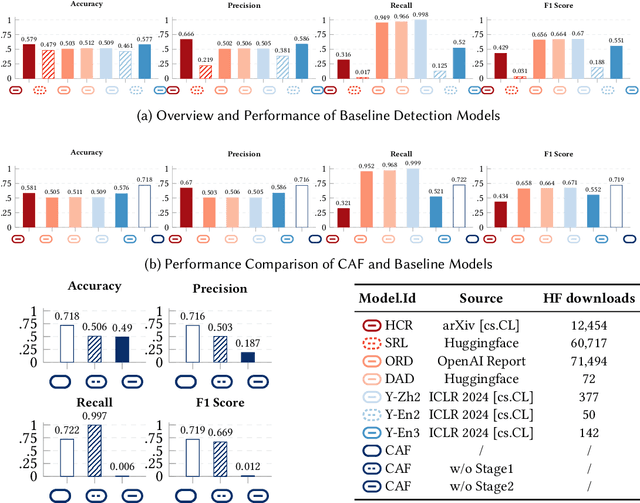
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) for code generation are becoming integral to modern software development, but their real-world prevalence and security impact remain poorly understood. We present the first large-scale empirical study of AI-generated code (AIGCode) in the wild. We build a high-precision detection pipeline and a representative benchmark to distinguish AIGCode from human-written code, and apply them to (i) development commits from the top 1,000 GitHub repositories (2022-2025) and (ii) 7,000+ recent CVE-linked code changes. This lets us label commits, files, and functions along a human/AI axis and trace how AIGCode moves through projects and vulnerability life cycles. Our measurements show three ecological patterns. First, AIGCode is already a substantial fraction of new code, but adoption is structured: AI concentrates in glue code, tests, refactoring, documentation, and other boilerplate, while core logic and security-critical configurations remain mostly human-written. Second, adoption has security consequences: some CWE families are overrepresented in AI-tagged code, and near-identical insecure templates recur across unrelated projects, suggesting "AI-induced vulnerabilities" propagated by shared models rather than shared maintainers. Third, in human-AI edit chains, AI introduces high-throughput changes while humans act as security gatekeepers; when review is shallow, AI-introduced defects persist longer, remain exposed on network-accessible surfaces, and spread to more files and repositories. We will open-source the complete dataset and release analysis artifacts and fine-grained documentation of our methodology and findings.
A 28nm 0.22 μJ/token memory-compute-intensity-aware CNN-Transformer accelerator with hybrid-attention-based layer-fusion and cascaded pruning for semanticsegmentation
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:This work presents a 28nm 13.93mm2 CNN-Transformer accelerator for semantic segmentation, achieving 3.86-to-10.91x energy reduction over previous designs. It features a hybrid attention unit, layer-fusion scheduler, and cascaded feature-map pruner, with peak energy efficiency of 52.90TOPS/W (INT8).
* 3 pages,7 pages, 2025 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC)
MMRAG-RFT: Two-stage Reinforcement Fine-tuning for Explainable Multi-modal Retrieval-augmented Generation
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Multi-modal Retrieval-Augmented Generation (MMRAG) enables highly credible generation by integrating external multi-modal knowledge, thus demonstrating impressive performance in complex multi-modal scenarios. However, existing MMRAG methods fail to clarify the reasoning logic behind retrieval and response generation, which limits the explainability of the results. To address this gap, we propose to introduce reinforcement learning into multi-modal retrieval-augmented generation, enhancing the reasoning capabilities of multi-modal large language models through a two-stage reinforcement fine-tuning framework to achieve explainable multi-modal retrieval-augmented generation. Specifically, in the first stage, rule-based reinforcement fine-tuning is employed to perform coarse-grained point-wise ranking of multi-modal documents, effectively filtering out those that are significantly irrelevant. In the second stage, reasoning-based reinforcement fine-tuning is utilized to jointly optimize fine-grained list-wise ranking and answer generation, guiding multi-modal large language models to output explainable reasoning logic in the MMRAG process. Our method achieves state-of-the-art results on WebQA and MultimodalQA, two benchmark datasets for multi-modal retrieval-augmented generation, and its effectiveness is validated through comprehensive ablation experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge