Heting Gao
VITA-Audio: Fast Interleaved Cross-Modal Token Generation for Efficient Large Speech-Language Model
May 06, 2025Abstract:With the growing requirement for natural human-computer interaction, speech-based systems receive increasing attention as speech is one of the most common forms of daily communication. However, the existing speech models still experience high latency when generating the first audio token during streaming, which poses a significant bottleneck for deployment. To address this issue, we propose VITA-Audio, an end-to-end large speech model with fast audio-text token generation. Specifically, we introduce a lightweight Multiple Cross-modal Token Prediction (MCTP) module that efficiently generates multiple audio tokens within a single model forward pass, which not only accelerates the inference but also significantly reduces the latency for generating the first audio in streaming scenarios. In addition, a four-stage progressive training strategy is explored to achieve model acceleration with minimal loss of speech quality. To our knowledge, VITA-Audio is the first multi-modal large language model capable of generating audio output during the first forward pass, enabling real-time conversational capabilities with minimal latency. VITA-Audio is fully reproducible and is trained on open-source data only. Experimental results demonstrate that our model achieves an inference speedup of 3~5x at the 7B parameter scale, but also significantly outperforms open-source models of similar model size on multiple benchmarks for automatic speech recognition (ASR), text-to-speech (TTS), and spoken question answering (SQA) tasks.
SyncDiff: Diffusion-based Talking Head Synthesis with Bottlenecked Temporal Visual Prior for Improved Synchronization
Mar 17, 2025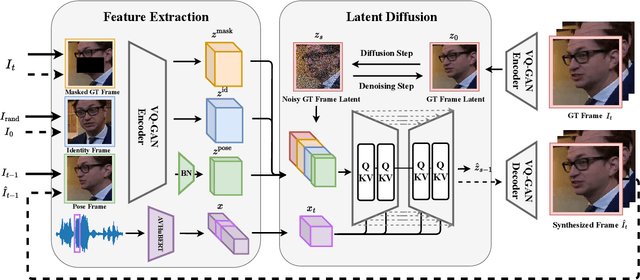
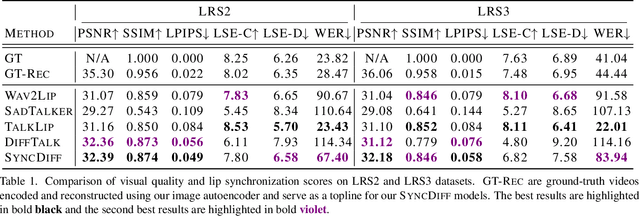
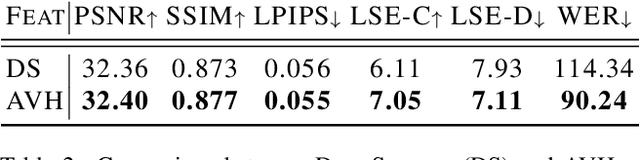
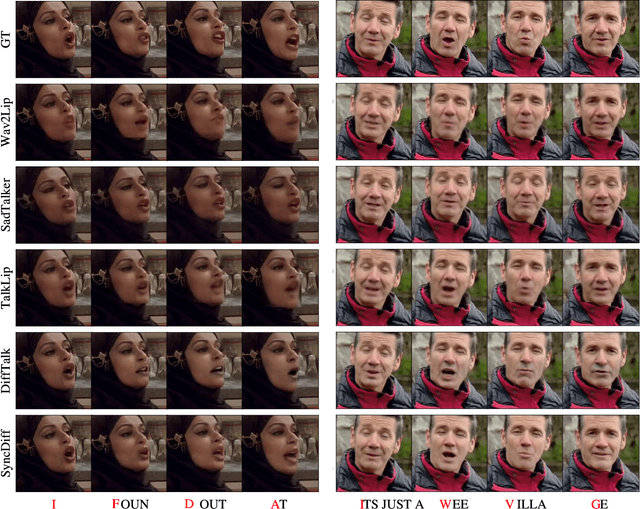
Abstract:Talking head synthesis, also known as speech-to-lip synthesis, reconstructs the facial motions that align with the given audio tracks. The synthesized videos are evaluated on mainly two aspects, lip-speech synchronization and image fidelity. Recent studies demonstrate that GAN-based and diffusion-based models achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on this task, with diffusion-based models achieving superior image fidelity but experiencing lower synchronization compared to their GAN-based counterparts. To this end, we propose SyncDiff, a simple yet effective approach to improve diffusion-based models using a temporal pose frame with information bottleneck and facial-informative audio features extracted from AVHuBERT, as conditioning input into the diffusion process. We evaluate SyncDiff on two canonical talking head datasets, LRS2 and LRS3 for direct comparison with other SOTA models. Experiments on LRS2/LRS3 datasets show that SyncDiff achieves a synchronization score 27.7%/62.3% relatively higher than previous diffusion-based methods, while preserving their high-fidelity characteristics.
LUCY: Linguistic Understanding and Control Yielding Early Stage of Her
Jan 27, 2025



Abstract:The film Her features Samantha, a sophisticated AI audio agent who is capable of understanding both linguistic and paralinguistic information in human speech and delivering real-time responses that are natural, informative and sensitive to emotional subtleties. Moving one step toward more sophisticated audio agent from recent advancement in end-to-end (E2E) speech systems, we propose LUCY, a E2E speech model that (1) senses and responds to user's emotion, (2) deliver responses in a succinct and natural style, and (3) use external tool to answer real-time inquiries. Experiment results show that LUCY is better at emotion control than peer models, generating emotional responses based on linguistic emotional instructions and responding to paralinguistic emotional cues. Lucy is also able to generate responses in a more natural style, as judged by external language models, without sacrificing much performance on general question answering. Finally, LUCY can leverage function calls to answer questions that are out of its knowledge scope.
VITA-1.5: Towards GPT-4o Level Real-Time Vision and Speech Interaction
Jan 03, 2025



Abstract:Recent Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have typically focused on integrating visual and textual modalities, with less emphasis placed on the role of speech in enhancing interaction. However, speech plays a crucial role in multimodal dialogue systems, and implementing high-performance in both vision and speech tasks remains a significant challenge due to the fundamental modality differences. In this paper, we propose a carefully designed multi-stage training methodology that progressively trains LLM to understand both visual and speech information, ultimately enabling fluent vision and speech interaction. Our approach not only preserves strong vision-language capacity, but also enables efficient speech-to-speech dialogue capabilities without separate ASR and TTS modules, significantly accelerating multimodal end-to-end response speed. By comparing our method against state-of-the-art counterparts across benchmarks for image, video, and speech tasks, we demonstrate that our model is equipped with both strong visual and speech capabilities, making near real-time vision and speech interaction.
SX-Stitch: An Efficient VMS-UNet Based Framework for Intraoperative Scoliosis X-Ray Image Stitching
Sep 09, 2024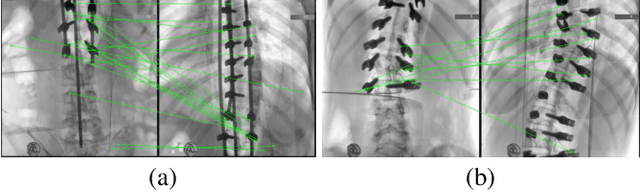
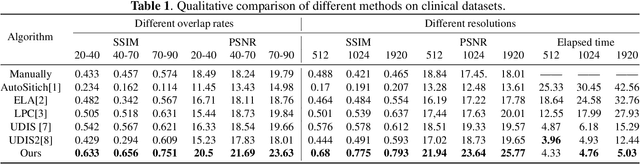
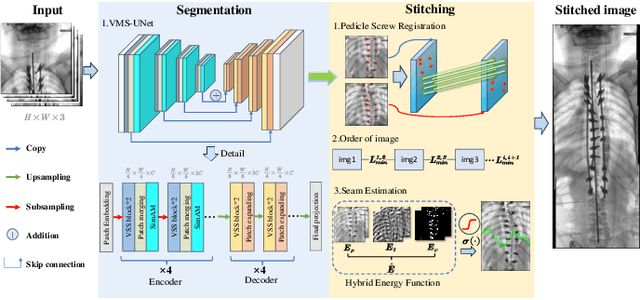
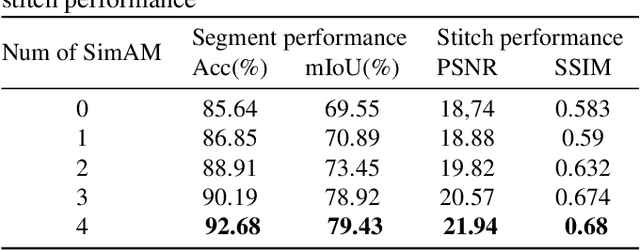
Abstract:In scoliosis surgery, the limited field of view of the C-arm X-ray machine restricts the surgeons' holistic analysis of spinal structures .This paper presents an end-to-end efficient and robust intraoperative X-ray image stitching method for scoliosis surgery,named SX-Stitch. The method is divided into two stages:segmentation and stitching. In the segmentation stage, We propose a medical image segmentation model named Vision Mamba of Spine-UNet (VMS-UNet), which utilizes the state space Mamba to capture long-distance contextual information while maintaining linear computational complexity, and incorporates the SimAM attention mechanism, significantly improving the segmentation performance.In the stitching stage, we simplify the alignment process between images to the minimization of a registration energy function. The total energy function is then optimized to order unordered images, and a hybrid energy function is introduced to optimize the best seam, effectively eliminating parallax artifacts. On the clinical dataset, Sx-Stitch demonstrates superiority over SOTA schemes both qualitatively and quantitatively.
Towards Unsupervised Speech Recognition Without Pronunciation Models
Jun 12, 2024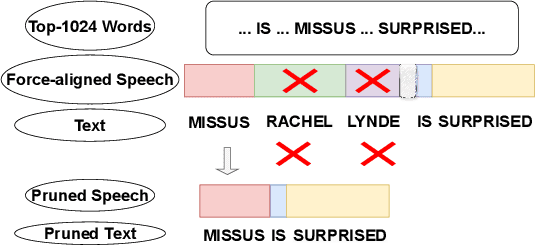
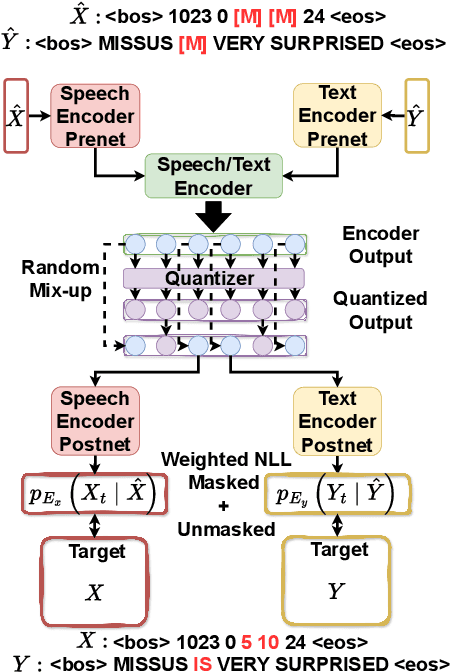
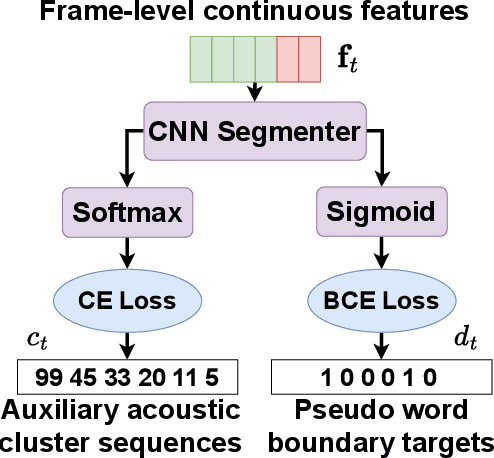
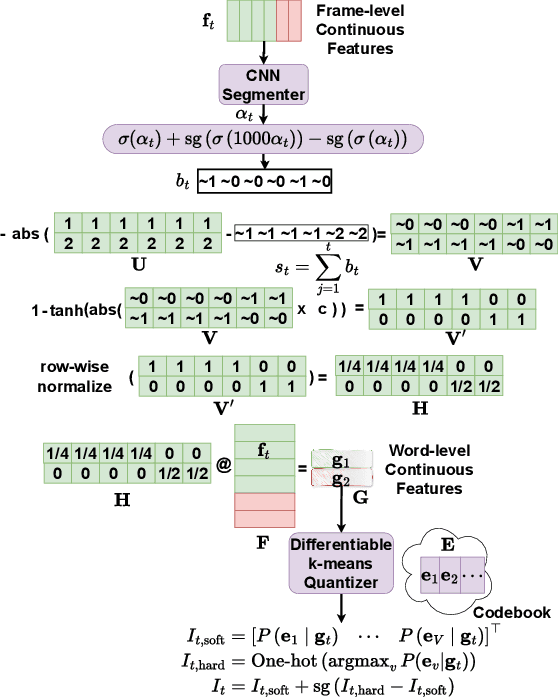
Abstract:Recent advancements in supervised automatic speech recognition (ASR) have achieved remarkable performance, largely due to the growing availability of large transcribed speech corpora. However, most languages lack sufficient paired speech and text data to effectively train these systems. In this article, we tackle the challenge of developing ASR systems without paired speech and text corpora by proposing the removal of reliance on a phoneme lexicon. We explore a new research direction: word-level unsupervised ASR. Using a curated speech corpus containing only high-frequency English words, our system achieves a word error rate of nearly 20% without parallel transcripts or oracle word boundaries. Furthermore, we experimentally demonstrate that an unsupervised speech recognizer can emerge from joint speech-to-speech and text-to-text masked token-infilling. This innovative model surpasses the performance of previous unsupervised ASR models trained with direct distribution matching.
Mitigating the Exposure Bias in Sentence-Level Grapheme-to-Phoneme (G2P) Transduction
Aug 16, 2023



Abstract:Text-to-Text Transfer Transformer (T5) has recently been considered for the Grapheme-to-Phoneme (G2P) transduction. As a follow-up, a tokenizer-free byte-level model based on T5 referred to as ByT5, recently gave promising results on word-level G2P conversion by representing each input character with its corresponding UTF-8 encoding. Although it is generally understood that sentence-level or paragraph-level G2P can improve usability in real-world applications as it is better suited to perform on heteronyms and linking sounds between words, we find that using ByT5 for these scenarios is nontrivial. Since ByT5 operates on the character level, it requires longer decoding steps, which deteriorates the performance due to the exposure bias commonly observed in auto-regressive generation models. This paper shows that the performance of sentence-level and paragraph-level G2P can be improved by mitigating such exposure bias using our proposed loss-based sampling method.
Improving Self-Supervised Speech Representations by Disentangling Speakers
Apr 20, 2022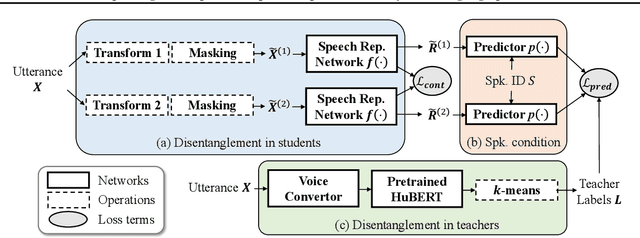
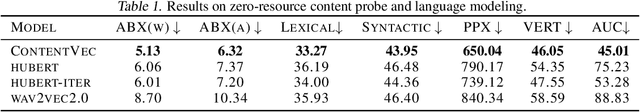
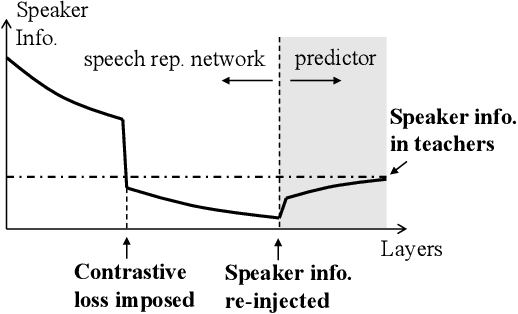
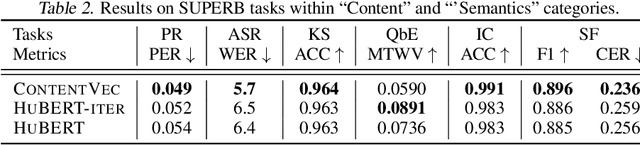
Abstract:Self-supervised learning in speech involves training a speech representation network on a large-scale unannotated speech corpus, and then applying the learned representations to downstream tasks. Since the majority of the downstream tasks of SSL learning in speech largely focus on the content information in speech, the most desirable speech representations should be able to disentangle unwanted variations, such as speaker variations, from the content. However, disentangling speakers is very challenging, because removing the speaker information could easily result in a loss of content as well, and the damage of the latter usually far outweighs the benefit of the former. In this paper, we propose a new SSL method that can achieve speaker disentanglement without severe loss of content. Our approach is adapted from the HuBERT framework, and incorporates disentangling mechanisms to regularize both the teacher labels and the learned representations. We evaluate the benefit of speaker disentanglement on a set of content-related downstream tasks, and observe a consistent and notable performance advantage of our speaker-disentangled representations.
WAVPROMPT: Towards Few-Shot Spoken Language Understanding with Frozen Language Models
Apr 14, 2022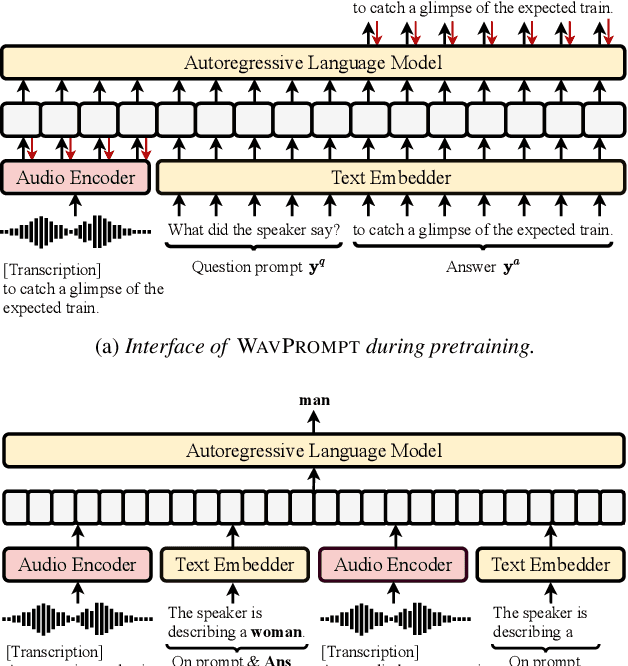
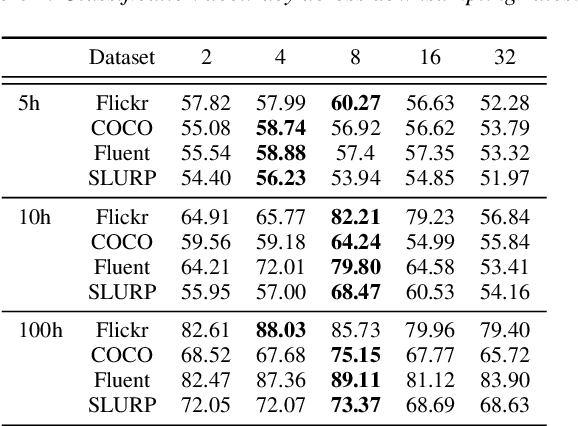
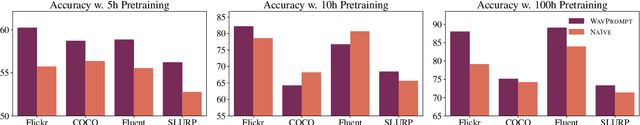
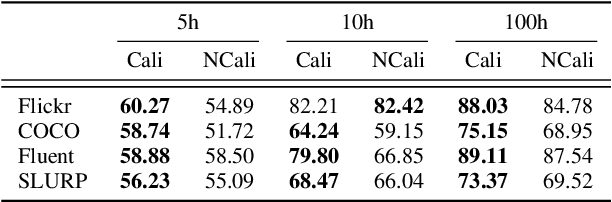
Abstract:Large-scale auto-regressive language models pretrained on massive text have demonstrated their impressive ability to perform new natural language tasks with only a few text examples, without the need for fine-tuning. Recent studies further show that such a few-shot learning ability can be extended to the text-image setting by training an encoder to encode the images into embeddings functioning like the text embeddings of the language model. Interested in exploring the possibility of transferring the few-shot learning ability to the audio-text setting, we propose a novel speech understanding framework, WavPrompt, where we finetune a wav2vec model to generate a sequence of audio embeddings understood by the language model. We show that WavPrompt is a few-shot learner that can perform speech understanding tasks better than a naive text baseline. We conduct detailed ablation studies on different components and hyperparameters to empirically identify the best model configuration. In addition, we conduct a non-speech understanding experiment to show WavPrompt can extract more information than just the transcriptions. Code is available at https://github.com/Hertin/WavPrompt
Unsupervised Text-to-Speech Synthesis by Unsupervised Automatic Speech Recognition
Mar 29, 2022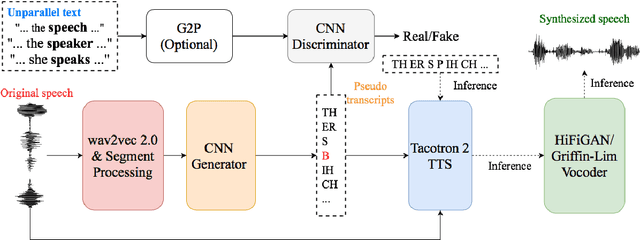

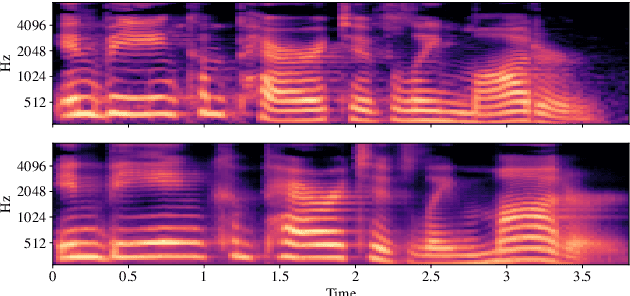
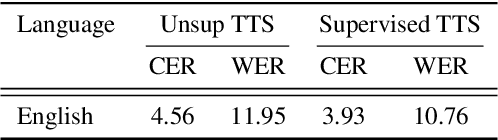
Abstract:An unsupervised text-to-speech synthesis (TTS) system learns to generate the speech waveform corresponding to any written sentence in a language by observing: 1) a collection of untranscribed speech waveforms in that language; 2) a collection of texts written in that language without access to any transcribed speech. Developing such a system can significantly improve the availability of speech technology to languages without a large amount of parallel speech and text data. This paper proposes an unsupervised TTS system by leveraging recent advances in unsupervised automatic speech recognition (ASR). Our unsupervised system can achieve comparable performance to the supervised system in seven languages with about 10-20 hours of speech each. A careful study on the effect of text units and vocoders has also been conducted to better understand what factors may affect unsupervised TTS performance. The samples generated by our models can be found at https://cactuswiththoughts.github.io/UnsupTTS-Demo.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge