Chanwoo Kim
An Effective Energy Mask-based Adversarial Evasion Attacks against Misclassification in Speaker Recognition Systems
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Evasion attacks pose significant threats to AI systems, exploiting vulnerabilities in machine learning models to bypass detection mechanisms. The widespread use of voice data, including deepfakes, in promising future industries is currently hindered by insufficient legal frameworks. Adversarial attack methods have emerged as the most effective countermeasure against the indiscriminate use of such data. This research introduces masked energy perturbation (MEP), a novel approach using power spectrum for energy masking of original voice data. MEP applies masking to small energy regions in the frequency domain before generating adversarial perturbations, targeting areas less noticeable to the human auditory model. The study primarily employs advanced speaker recognition models, including ECAPA-TDNN and ResNet34, which have shown remarkable performance in speaker verification tasks. The proposed MEP method demonstrated strong performance in both audio quality and evasion effectiveness. The energy masking approach effectively minimizes the perceptual evaluation of speech quality (PESQ) degradation, indicating that minimal perceptual distortion occurs to the human listener despite the adversarial perturbations. Specifically, in the PESQ evaluation, the relative performance of the MEP method was 26.68% when compared to the fast gradient sign method (FGSM) and iterative FGSM.
SurrogateSHAP: Training-Free Contributor Attribution for Text-to-Image (T2I) Models
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:As Text-to-Image (T2I) diffusion models are increasingly used in real-world creative workflows, a principled framework for valuing contributors who provide a collection of data is essential for fair compensation and sustainable data marketplaces. While the Shapley value offers a theoretically grounded approach to attribution, it faces a dual computational bottleneck: (i) the prohibitive cost of exhaustive model retraining for each sampled subset of players (i.e., data contributors) and (ii) the combinatorial number of subsets needed to estimate marginal contributions due to contributor interactions. To this end, we propose SurrogateSHAP, a retraining-free framework that approximates the expensive retraining game through inference from a pretrained model. To further improve efficiency, we employ a gradient-boosted tree to approximate the utility function and derive Shapley values analytically from the tree-based model. We evaluate SurrogateSHAP across three diverse attribution tasks: (i) image quality for DDPM-CFG on CIFAR-20, (ii) aesthetics for Stable Diffusion on Post-Impressionist artworks, and (iii) product diversity for FLUX.1 on Fashion-Product data. Across settings, SurrogateSHAP outperforms prior methods while substantially reducing computational overhead, consistently identifying influential contributors across multiple utility metrics. Finally, we demonstrate that SurrogateSHAP effectively localizes data sources responsible for spurious correlations in clinical images, providing a scalable path toward auditing safety-critical generative models.
OleSpeech-IV: A Large-Scale Multispeaker and Multilingual Conversational Speech Dataset with Diverse Topics
Sep 04, 2025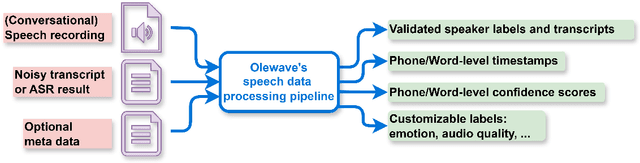
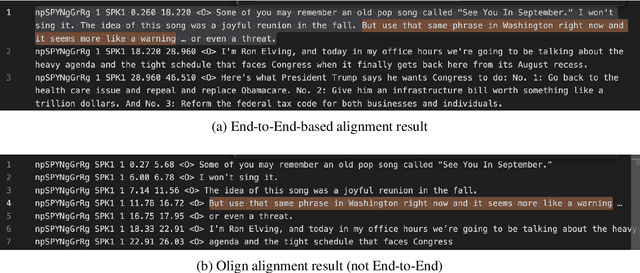
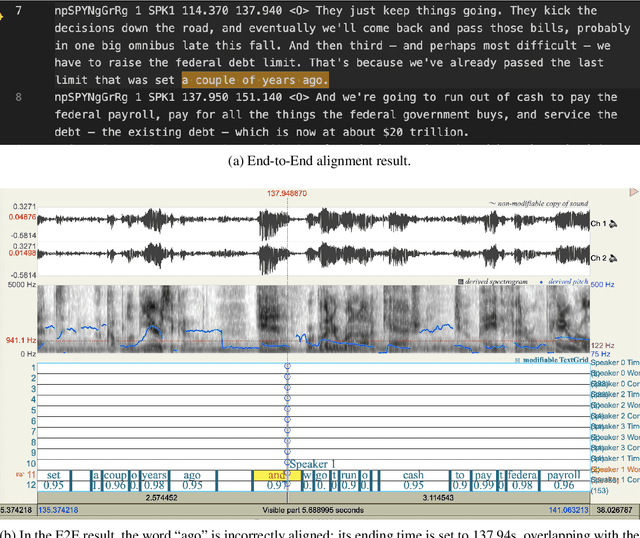
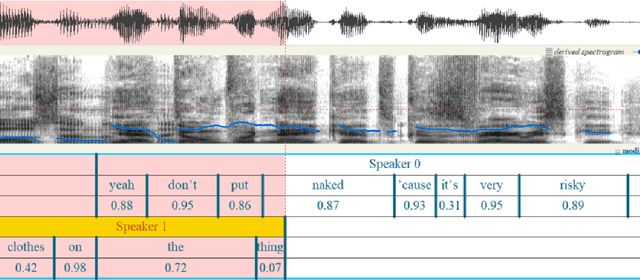
Abstract:OleSpeech-IV dataset is a large-scale multispeaker and multilingual conversational speech dataset with diverse topics. The audio content comes from publicly-available English podcasts, talk shows, teleconferences, and other conversations. Speaker names, turns, and transcripts are human-sourced and refined by a proprietary pipeline, while additional information such as timestamps and confidence scores is derived from the pipeline. The IV denotes its position as Tier IV in the Olewave dataset series. In addition, we have open-sourced a subset, OleSpeech-IV-2025-EN-AR-100, for non-commercial research use.
Graph Spectral Filtering with Chebyshev Interpolation for Recommendation
May 01, 2025Abstract:Graph convolutional networks have recently gained prominence in collaborative filtering (CF) for recommendations. However, we identify potential bottlenecks in two foundational components. First, the embedding layer leads to a latent space with limited capacity, overlooking locally observed but potentially valuable preference patterns. Also, the widely-used neighborhood aggregation is limited in its ability to leverage diverse preference patterns in a fine-grained manner. Building on spectral graph theory, we reveal that these limitations stem from graph filtering with a cut-off in the frequency spectrum and a restricted linear form. To address these issues, we introduce ChebyCF, a CF framework based on graph spectral filtering. Instead of a learned embedding, it takes a user's raw interaction history to utilize the full spectrum of signals contained in it. Also, it adopts Chebyshev interpolation to effectively approximate a flexible non-linear graph filter, and further enhances it by using an additional ideal pass filter and degree-based normalization. Through extensive experiments, we verify that ChebyCF overcomes the aforementioned bottlenecks and achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple benchmarks and reasonably fast inference. Our code is available at https://github.com/chanwoo0806/ChebyCF.
HyperFlow: Gradient-Free Emulation of Few-Shot Fine-Tuning
Apr 21, 2025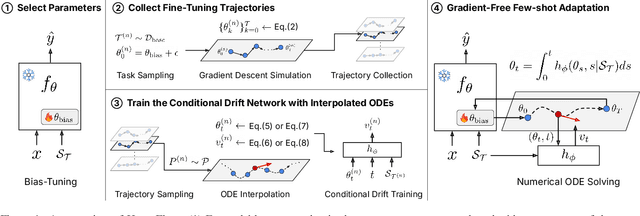
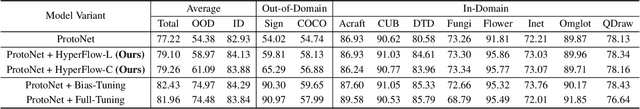
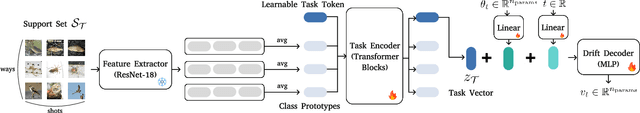
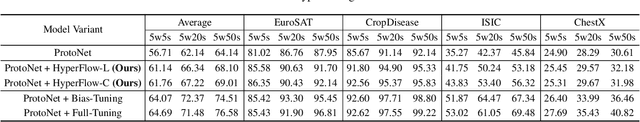
Abstract:While test-time fine-tuning is beneficial in few-shot learning, the need for multiple backpropagation steps can be prohibitively expensive in real-time or low-resource scenarios. To address this limitation, we propose an approach that emulates gradient descent without computing gradients, enabling efficient test-time adaptation. Specifically, we formulate gradient descent as an Euler discretization of an ordinary differential equation (ODE) and train an auxiliary network to predict the task-conditional drift using only the few-shot support set. The adaptation then reduces to a simple numerical integration (e.g., via the Euler method), which requires only a few forward passes of the auxiliary network -- no gradients or forward passes of the target model are needed. In experiments on cross-domain few-shot classification using the Meta-Dataset and CDFSL benchmarks, our method significantly improves out-of-domain performance over the non-fine-tuned baseline while incurring only 6\% of the memory cost and 0.02\% of the computation time of standard fine-tuning, thus establishing a practical middle ground between direct transfer and fully fine-tuned approaches.
AV-Surf: Surface-Enhanced Geometry-Aware Novel-View Acoustic Synthesis
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Accurately modeling sound propagation with complex real-world environments is essential for Novel View Acoustic Synthesis (NVAS). While previous studies have leveraged visual perception to estimate spatial acoustics, the combined use of surface normal and structural details from 3D representations in acoustic modeling has been underexplored. Given their direct impact on sound wave reflections and propagation, surface normals should be jointly modeled with structural details to achieve accurate spatial acoustics. In this paper, we propose a surface-enhanced geometry-aware approach for NVAS to improve spatial acoustic modeling. To achieve this, we exploit geometric priors, such as image, depth map, surface normals, and point clouds obtained using a 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) based framework. We introduce a dual cross-attention-based transformer integrating geometrical constraints into frequency query to understand the surroundings of the emitter. Additionally, we design a ConvNeXt-based spectral features processing network called Spectral Refinement Network (SRN) to synthesize realistic binaural audio. Experimental results on the RWAVS and SoundSpace datasets highlight the necessity of our approach, as it surpasses existing methods in novel view acoustic synthesis.
Learning-based Dynamic Robot-to-Human Handover
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a novel learning-based approach to dynamic robot-to-human handover, addressing the challenges of delivering objects to a moving receiver. We hypothesize that dynamic handover, where the robot adjusts to the receiver's movements, results in more efficient and comfortable interaction compared to static handover, where the receiver is assumed to be stationary. To validate this, we developed a nonparametric method for generating continuous handover motion, conditioned on the receiver's movements, and trained the model using a dataset of 1,000 human-to-human handover demonstrations. We integrated preference learning for improved handover effectiveness and applied impedance control to ensure user safety and adaptiveness. The approach was evaluated in both simulation and real-world settings, with user studies demonstrating that dynamic handover significantly reduces handover time and improves user comfort compared to static methods. Videos and demonstrations of our approach are available at https://zerotohero7886.github.io/dyn-r2h-handover .
Leveraging 2D Masked Reconstruction for Domain Adaptation of 3D Pose Estimation
Jan 14, 2025Abstract:RGB-based 3D pose estimation methods have been successful with the development of deep learning and the emergence of high-quality 3D pose datasets. However, most existing methods do not operate well for testing images whose distribution is far from that of training data. However, most existing methods do not operate well for testing images whose distribution is far from that of training data. This problem might be alleviated by involving diverse data during training, however it is non-trivial to collect such diverse data with corresponding labels (i.e. 3D pose). In this paper, we introduced an unsupervised domain adaptation framework for 3D pose estimation that utilizes the unlabeled data in addition to labeled data via masked image modeling (MIM) framework. Foreground-centric reconstruction and attention regularization are further proposed to increase the effectiveness of unlabeled data usage. Experiments are conducted on the various datasets in human and hand pose estimation tasks, especially using the cross-domain scenario. We demonstrated the effectiveness of ours by achieving the state-of-the-art accuracy on all datasets.
Physics Informed Distillation for Diffusion Models
Nov 13, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion models have recently emerged as a potent tool in generative modeling. However, their inherent iterative nature often results in sluggish image generation due to the requirement for multiple model evaluations. Recent progress has unveiled the intrinsic link between diffusion models and Probability Flow Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs), thus enabling us to conceptualize diffusion models as ODE systems. Simultaneously, Physics Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) have substantiated their effectiveness in solving intricate differential equations through implicit modeling of their solutions. Building upon these foundational insights, we introduce Physics Informed Distillation (PID), which employs a student model to represent the solution of the ODE system corresponding to the teacher diffusion model, akin to the principles employed in PINNs. Through experiments on CIFAR 10 and ImageNet 64x64, we observe that PID achieves performance comparable to recent distillation methods. Notably, it demonstrates predictable trends concerning method-specific hyperparameters and eliminates the need for synthetic dataset generation during the distillation process. Both of which contribute to its easy-to-use nature as a distillation approach for Diffusion Models. Our code and pre-trained checkpoint are publicly available at: https://github.com/pantheon5100/pid_diffusion.git.
Wave-U-Mamba: An End-To-End Framework For High-Quality And Efficient Speech Super Resolution
Sep 17, 2024



Abstract:Speech Super-Resolution (SSR) is a task of enhancing low-resolution speech signals by restoring missing high-frequency components. Conventional approaches typically reconstruct log-mel features, followed by a vocoder that generates high-resolution speech in the waveform domain. However, as log-mel features lack phase information, this can result in performance degradation during the reconstruction phase. Motivated by recent advances with Selective State Spaces Models (SSMs), we propose a method, referred to as Wave-U-Mamba that directly performs SSR in time domain. In our comparative study, including models such as WSRGlow, NU-Wave 2, and AudioSR, Wave-U-Mamba demonstrates superior performance, achieving the lowest Log-Spectral Distance (LSD) across various low-resolution sampling rates, ranging from 8 kHz to 24 kHz. Additionally, subjective human evaluations, scored using Mean Opinion Score (MOS) reveal that our method produces SSR with natural and human-like quality. Furthermore, Wave-U-Mamba achieves these results while generating high-resolution speech over nine times faster than baseline models on a single A100 GPU, with parameter sizes less than 2% of those in the baseline models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge