Weizhong Huang
QuoTA: Query-oriented Token Assignment via CoT Query Decouple for Long Video Comprehension
Mar 11, 2025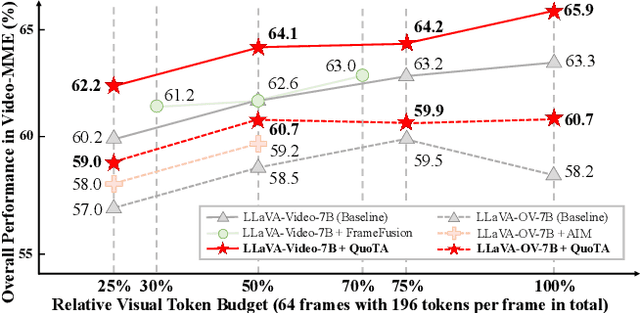
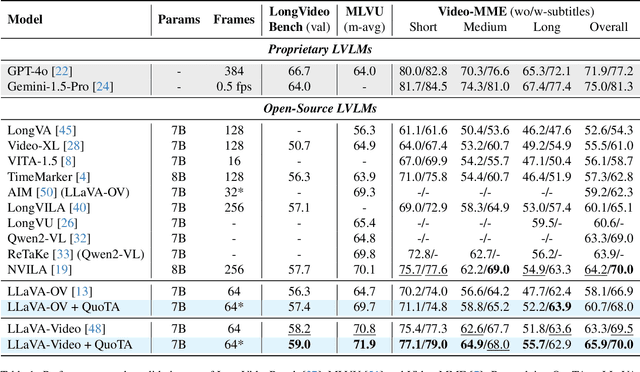
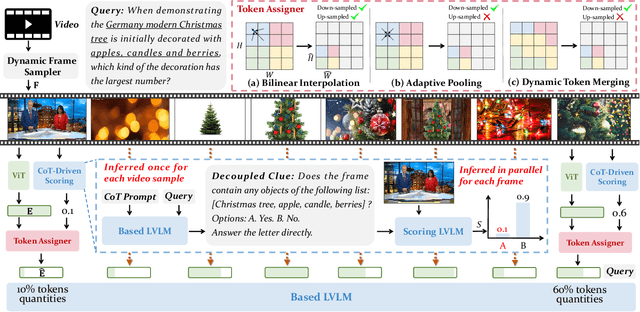
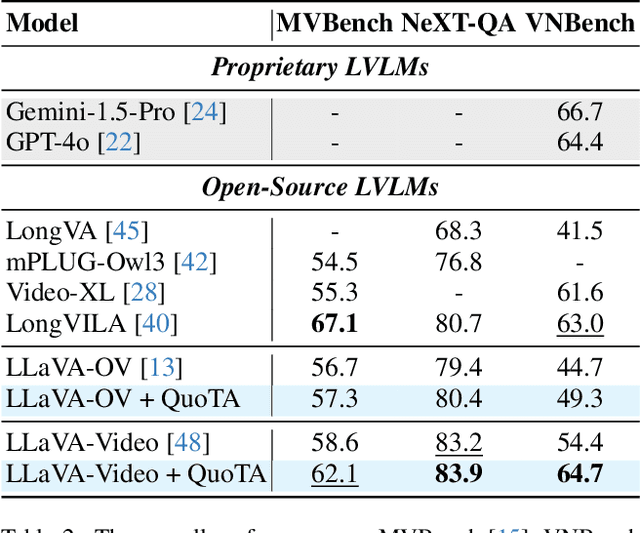
Abstract:Recent advances in long video understanding typically mitigate visual redundancy through visual token pruning based on attention distribution. However, while existing methods employ post-hoc low-response token pruning in decoder layers, they overlook the input-level semantic correlation between visual tokens and instructions (query). In this paper, we propose QuoTA, an ante-hoc training-free modular that extends existing large video-language models (LVLMs) for visual token assignment based on query-oriented frame-level importance assessment. The query-oriented token selection is crucial as it aligns visual processing with task-specific requirements, optimizing token budget utilization while preserving semantically relevant content. Specifically, (i) QuoTA strategically allocates frame-level importance scores based on query relevance, enabling one-time visual token assignment before cross-modal interactions in decoder layers, (ii) we decouple the query through Chain-of-Thoughts reasoning to facilitate more precise LVLM-based frame importance scoring, and (iii) QuoTA offers a plug-and-play functionality that extends to existing LVLMs. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that implementing QuoTA with LLaVA-Video-7B yields an average performance improvement of 3.2% across six benchmarks (including Video-MME and MLVU) while operating within an identical visual token budget as the baseline. Codes are open-sourced at https://github.com/MAC-AutoML/QuoTA.
Freezing chaos without synaptic plasticity
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Chaos is ubiquitous in high-dimensional neural dynamics. A strong chaotic fluctuation may be harmful to information processing. A traditional way to mitigate this issue is to introduce Hebbian plasticity, which can stabilize the dynamics. Here, we introduce another distinct way without synaptic plasticity. An Onsager reaction term due to the feedback of the neuron itself is added to the vanilla recurrent dynamics, making the driving force a gradient form. The original unstable fixed points supporting the chaotic fluctuation can then be approached by further decreasing the kinetic energy of the dynamics. We show that this freezing effect also holds in more biologically realistic networks, such as those composed of excitatory and inhibitory neurons. The gradient dynamics are also useful for computational tasks such as recalling or predicting external time-dependent stimuli.
Towards Efficient Automatic Self-Pruning of Large Language Models
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Despite exceptional capabilities, Large Language Models (LLMs) still face deployment challenges due to their enormous size. Post-training structured pruning is a promising solution that prunes LLMs without the need for retraining, reducing computational overhead, and it is hardware-deployment friendly. However, the training-free nature of post-training structured pruning leads to significant performance degradation. We argue that the key to mitigating this issue lies in accurately determining the pruning rate for each layer. Meanwhile, we find that LLMs may have prior knowledge about their own redundancy. Based on this insight, we introduce $\textbf{Self-Pruner}$ an end-to-end automatic self-pruning framework for LLMs, which efficiently search layer-wise pruning rates. Specifically, $\textbf{Self-Pruner}$ leverages LLMs to autonomously execute the entire evolutionary search process to search for pruning rate configurations. In this process, LLMs are used to generate populations, select parent solutions from the current population, and perform crossover and mutation operations to produce offspring solutions. In this way, LLMs automatically generate and evaluate a large number of candidate solutions, effectively converging to find the pruning rate configurations with minimal human intervention. Extensive experiments demonstrate $\textbf{Self-Pruner}$'s better performance compared to existing state-of-the-art methods. Notably, $\textbf{Self-Pruner}$ prunes LLaMA-2-70B to 49B level with only 0.80$\%$ drop in accuracy across seven commonsense reasoning tasks, achieving a 1.39$\times$ speedup on NVIDIA A100 80GB GPU. Further pruning to 35B level resulted in only a 3.80$\%$ decrease in accuracy while obtaining a 1.70$\times$ speedup.
Dynamic Low-Rank Sparse Adaptation for Large Language Models
Feb 20, 2025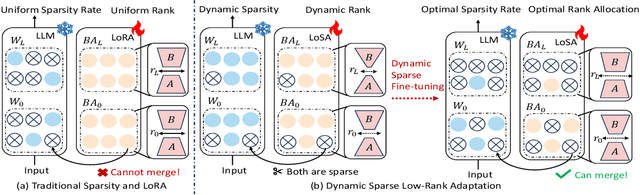
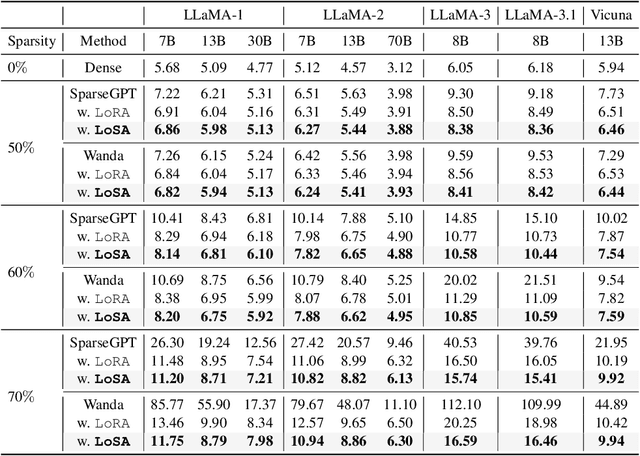
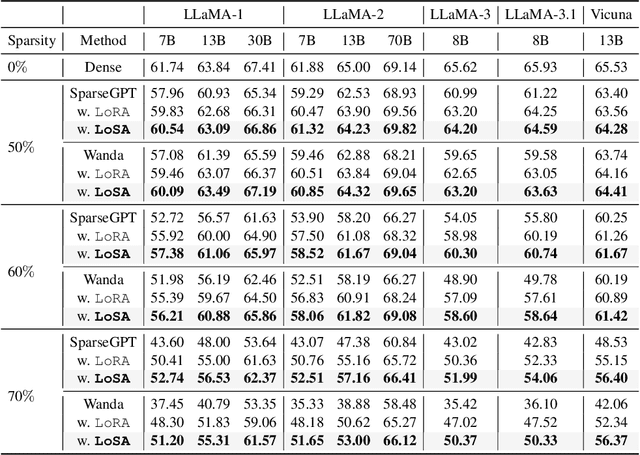
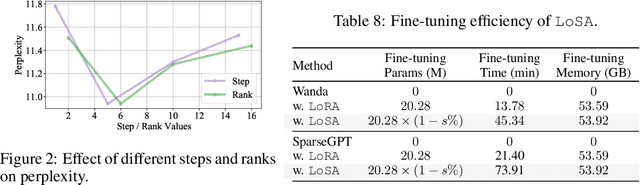
Abstract:Despite the efficacy of network sparsity in alleviating the deployment strain of Large Language Models (LLMs), it endures significant performance degradation. Applying Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) to fine-tune the sparse LLMs offers an intuitive approach to counter this predicament, while it holds shortcomings include: 1) The inability to integrate LoRA weights into sparse LLMs post-training, and 2) Insufficient performance recovery at high sparsity ratios. In this paper, we introduce dynamic Low-rank Sparse Adaptation (LoSA), a novel method that seamlessly integrates low-rank adaptation into LLM sparsity within a unified framework, thereby enhancing the performance of sparse LLMs without increasing the inference latency. In particular, LoSA dynamically sparsifies the LoRA outcomes based on the corresponding sparse weights during fine-tuning, thus guaranteeing that the LoRA module can be integrated into the sparse LLMs post-training. Besides, LoSA leverages Representation Mutual Information (RMI) as an indicator to determine the importance of layers, thereby efficiently determining the layer-wise sparsity rates during fine-tuning. Predicated on this, LoSA adjusts the rank of the LoRA module based on the variability in layer-wise reconstruction errors, allocating an appropriate fine-tuning for each layer to reduce the output discrepancies between dense and sparse LLMs. Extensive experiments tell that LoSA can efficiently boost the efficacy of sparse LLMs within a few hours, without introducing any additional inferential burden. For example, LoSA reduced the perplexity of sparse LLaMA-2-7B by 68.73 and increased zero-shot accuracy by 16.32$\%$, achieving a 2.60$\times$ speedup on CPU and 2.23$\times$ speedup on GPU, requiring only 45 minutes of fine-tuning on a single NVIDIA A100 80GB GPU. Code is available at https://github.com/wzhuang-xmu/LoSA.
Determining Layer-wise Sparsity for Large Language Models Through a Theoretical Perspective
Feb 20, 2025
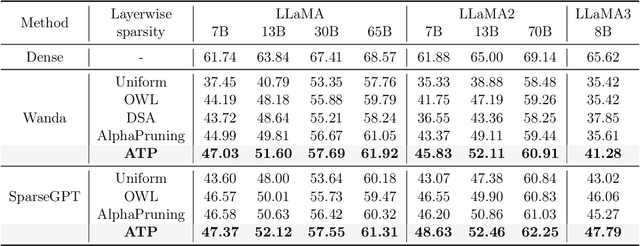
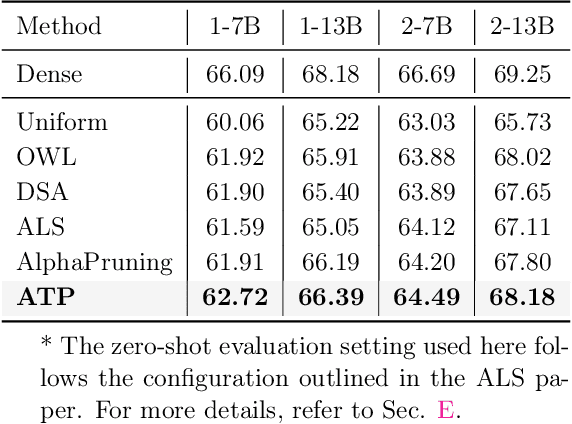
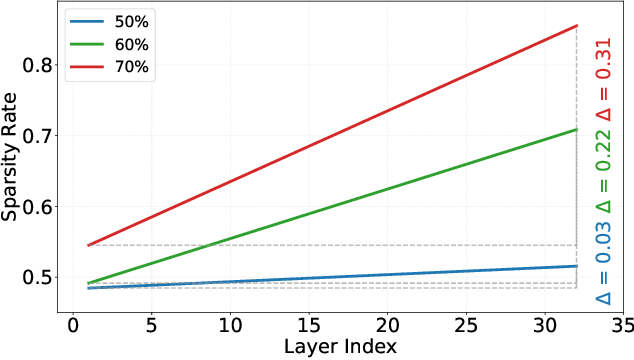
Abstract:In this paper, we address the challenge of determining the layer-wise sparsity rates of large language models (LLMs) through a theoretical perspective. Specifically, we identify a critical issue of ''$\textbf{reconstruction error explosion}$'' in existing LLMs sparsification methods. This refers to the cumulative effect of reconstruction errors throughout the sparsification process, where errors from earlier layers propagate and amplify in subsequent layers. As a result, the overall reconstruction error increases significantly, leading to a substantial degradation in model performance. Through theoretical analysis, we derive a simple yet effective approach to layer-wise sparsity allocation that mitigates this issue. Our method uses a monotonically increasing arithmetic progression, reducing the process of determining sparsity rates for multiple layers to the determination of a single common difference hyperparameter. Remarkably, this allows for the optimal layer-wise sparsity rates to be identified with just a few trials. Both our theoretical analysis and experimental results demonstrate that this sparsity allocation scheme is near optimal. Extensive experiments show that our method significantly improves the performance of sparse LLMs across various architectures, outperforming existing layer-wise sparsity methods. Furthermore, it enhances the performance of various compression techniques and is applicable to vision and multimodal models. Notably, our method achieves a reduction of 52.10 in perplexity for the 70$\%$ sparse LLaMA2-7B model obtained via Wanda, improves average zero-shot accuracy by 10.50$\%$, and delivers speedups of 2.63$\times$ and 2.23$\times$ on CPU and GPU, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge