Polina Golland
Fast Multi-Stack Slice-to-Volume Reconstruction via Multi-Scale Unrolled Optimization
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Fully convolutional networks have become the backbone of modern medical imaging due to their ability to learn multi-scale representations and perform end-to-end inference. Yet their potential for slice-to-volume reconstruction (SVR), the task of jointly estimating 3D anatomy and slice poses from misaligned 2D acquisitions, remains underexplored. We introduce a fast convolutional framework that fuses multiple orthogonal 2D slice stacks to recover coherent 3D structure and refines slice alignment through lightweight model-based optimization. Applied to fetal brain MRI, our approach reconstructs high-quality 3D volumes in under 10s, with 1s slice registration and accuracy on par with state-of-the-art iterative SVR pipelines, offering more than speedup. The framework uses non-rigid displacement fields to represent transformations, generalizing to other SVR problems like fetal body and placental MRI. Additionally, the fast inference time paves the way for real-time, scanner-side volumetric feedback during MRI acquisition.
Connecting Jensen-Shannon and Kullback-Leibler Divergences: A New Bound for Representation Learning
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:Mutual Information (MI) is a fundamental measure of statistical dependence widely used in representation learning. While direct optimization of MI via its definition as a Kullback-Leibler divergence (KLD) is often intractable, many recent methods have instead maximized alternative dependence measures, most notably, the Jensen-Shannon divergence (JSD) between joint and product of marginal distributions via discriminative losses. However, the connection between these surrogate objectives and MI remains poorly understood. In this work, we bridge this gap by deriving a new, tight, and tractable lower bound on KLD as a function of JSD in the general case. By specializing this bound to joint and marginal distributions, we demonstrate that maximizing the JSD-based information increases a guaranteed lower bound on mutual information. Furthermore, we revisit the practical implementation of JSD-based objectives and observe that minimizing the cross-entropy loss of a binary classifier trained to distinguish joint from marginal pairs recovers a known variational lower bound on the JSD. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our lower bound is tight when applied to MI estimation. We compared our lower bound to state-of-the-art neural estimators of variational lower bound across a range of established reference scenarios. Our lower bound estimator consistently provides a stable, low-variance estimate of a tight lower bound on MI. We also demonstrate its practical usefulness in the context of the Information Bottleneck framework. Taken together, our results provide new theoretical justifications and strong empirical evidence for using discriminative learning in MI-based representation learning.
PolyPose: Localizing Deformable Anatomy in 3D from Sparse 2D X-ray Images using Polyrigid Transforms
May 25, 2025Abstract:Determining the 3D pose of a patient from a limited set of 2D X-ray images is a critical task in interventional settings. While preoperative volumetric imaging (e.g., CT and MRI) provides precise 3D localization and visualization of anatomical targets, these modalities cannot be acquired during procedures, where fast 2D imaging (X-ray) is used instead. To integrate volumetric guidance into intraoperative procedures, we present PolyPose, a simple and robust method for deformable 2D/3D registration. PolyPose parameterizes complex 3D deformation fields as a composition of rigid transforms, leveraging the biological constraint that individual bones do not bend in typical motion. Unlike existing methods that either assume no inter-joint movement or fail outright in this under-determined setting, our polyrigid formulation enforces anatomically plausible priors that respect the piecewise rigid nature of human movement. This approach eliminates the need for expensive deformation regularizers that require patient- and procedure-specific hyperparameter optimization. Across extensive experiments on diverse datasets from orthopedic surgery and radiotherapy, we show that this strong inductive bias enables PolyPose to successfully align the patient's preoperative volume to as few as two X-ray images, thereby providing crucial 3D guidance in challenging sparse-view and limited-angle settings where current registration methods fail.
Rapid patient-specific neural networks for intraoperative X-ray to volume registration
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:The integration of artificial intelligence in image-guided interventions holds transformative potential, promising to extract 3D geometric and quantitative information from conventional 2D imaging modalities during complex procedures. Achieving this requires the rapid and precise alignment of 2D intraoperative images (e.g., X-ray) with 3D preoperative volumes (e.g., CT, MRI). However, current 2D/3D registration methods fail across the broad spectrum of procedures dependent on X-ray guidance: traditional optimization techniques require custom parameter tuning for each subject, whereas neural networks trained on small datasets do not generalize to new patients or require labor-intensive manual annotations, increasing clinical burden and precluding application to new anatomical targets. To address these challenges, we present xvr, a fully automated framework for training patient-specific neural networks for 2D/3D registration. xvr uses physics-based simulation to generate abundant high-quality training data from a patient's own preoperative volumetric imaging, thereby overcoming the inherently limited ability of supervised models to generalize to new patients and procedures. Furthermore, xvr requires only 5 minutes of training per patient, making it suitable for emergency interventions as well as planned procedures. We perform the largest evaluation of a 2D/3D registration algorithm on real X-ray data to date and find that xvr robustly generalizes across a diverse dataset comprising multiple anatomical structures, imaging modalities, and hospitals. Across surgical tasks, xvr achieves submillimeter-accurate registration at intraoperative speeds, improving upon existing methods by an order of magnitude. xvr is released as open-source software freely available at https://github.com/eigenvivek/xvr.
Spatial regularisation for improved accuracy and interpretability in keypoint-based registration
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:Unsupervised registration strategies bypass requirements in ground truth transforms or segmentations by optimising similarity metrics between fixed and moved volumes. Among these methods, a recent subclass of approaches based on unsupervised keypoint detection stand out as very promising for interpretability. Specifically, these methods train a network to predict feature maps for fixed and moving images, from which explainable centres of mass are computed to obtain point clouds, that are then aligned in closed-form. However, the features returned by the network often yield spatially diffuse patterns that are hard to interpret, thus undermining the purpose of keypoint-based registration. Here, we propose a three-fold loss to regularise the spatial distribution of the features. First, we use the KL divergence to model features as point spread functions that we interpret as probabilistic keypoints. Then, we sharpen the spatial distributions of these features to increase the precision of the detected landmarks. Finally, we introduce a new repulsive loss across keypoints to encourage spatial diversity. Overall, our loss considerably improves the interpretability of the features, which now correspond to precise and anatomically meaningful landmarks. We demonstrate our three-fold loss in foetal rigid motion tracking and brain MRI affine registration tasks, where it not only outperforms state-of-the-art unsupervised strategies, but also bridges the gap with state-of-the-art supervised methods. Our code is available at https://github.com/BenBillot/spatial_regularisation.
Differentiable Voxel-based X-ray Rendering Improves Sparse-View 3D CBCT Reconstruction
Dec 02, 2024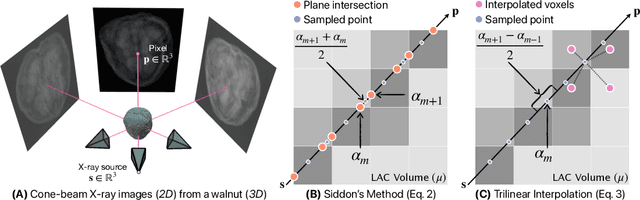
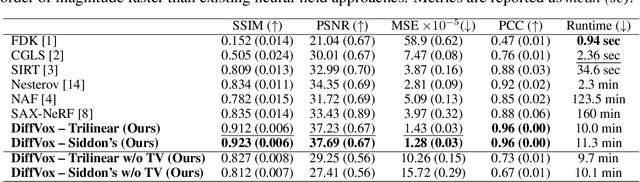
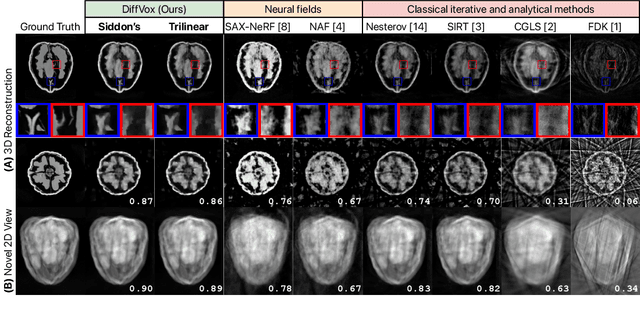
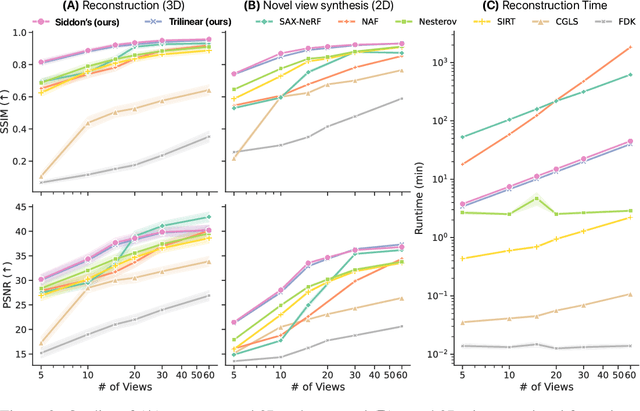
Abstract:We present DiffVox, a self-supervised framework for Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) reconstruction by directly optimizing a voxelgrid representation using physics-based differentiable X-ray rendering. Further, we investigate how the different implementations of the X-ray image formation model in the renderer affect the quality of 3D reconstruction and novel view synthesis. When combined with our regularized voxel-based learning framework, we find that using an exact implementation of the discrete Beer-Lambert law for X-ray attenuation in the renderer outperforms both widely used iterative CBCT reconstruction algorithms and modern neural field approaches, particularly when given only a few input views. As a result, we reconstruct high-fidelity 3D CBCT volumes from fewer X-rays, potentially reducing ionizing radiation exposure and improving diagnostic utility. Our implementation is available at https://github.com/hossein-momeni/DiffVox.
Learning General-Purpose Biomedical Volume Representations using Randomized Synthesis
Nov 04, 2024Abstract:Current volumetric biomedical foundation models struggle to generalize as public 3D datasets are small and do not cover the broad diversity of medical procedures, conditions, anatomical regions, and imaging protocols. We address this by creating a representation learning method that instead anticipates strong domain shifts at training time itself. We first propose a data engine that synthesizes highly variable training samples that enable generalization to new biomedical contexts. To then train a single 3D network for any voxel-level task, we develop a contrastive learning method that pretrains the network to be stable against nuisance imaging variation simulated by the data engine, a key inductive bias for generalization. This network's features can be used as robust representations of input images for downstream tasks and its weights provide a strong, dataset-agnostic initialization for finetuning on new datasets. As a result, we set new standards across both multimodality registration and few-shot segmentation, a first for any 3D biomedical vision model, all without (pre-)training on any existing dataset of real images.
Calibrating Expressions of Certainty
Oct 06, 2024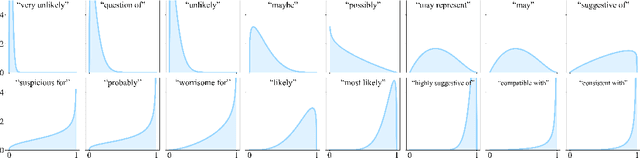
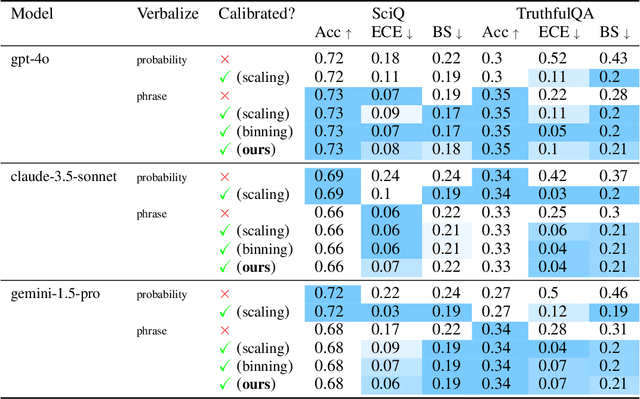
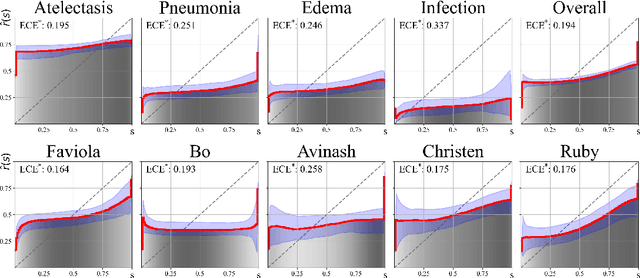
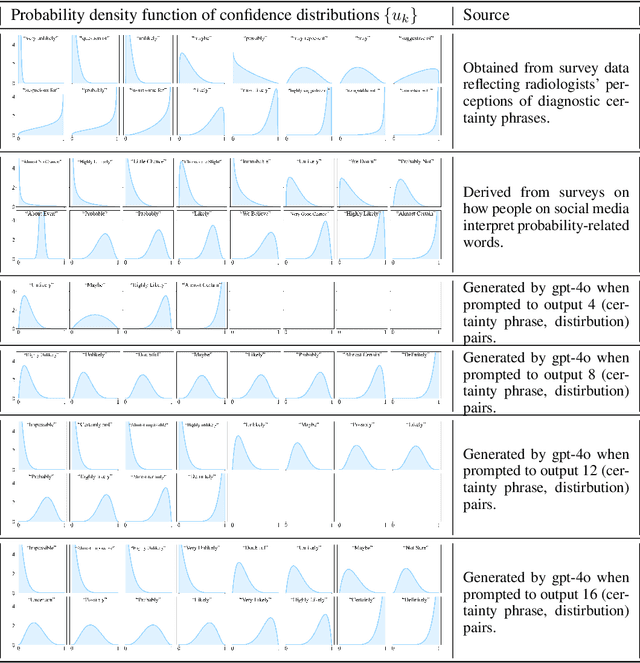
Abstract:We present a novel approach to calibrating linguistic expressions of certainty, e.g., "Maybe" and "Likely". Unlike prior work that assigns a single score to each certainty phrase, we model uncertainty as distributions over the simplex to capture their semantics more accurately. To accommodate this new representation of certainty, we generalize existing measures of miscalibration and introduce a novel post-hoc calibration method. Leveraging these tools, we analyze the calibration of both humans (e.g., radiologists) and computational models (e.g., language models) and provide interpretable suggestions to improve their calibration.
Deep-ER: Deep Learning ECCENTRIC Reconstruction for fast high-resolution neurometabolic imaging
Sep 26, 2024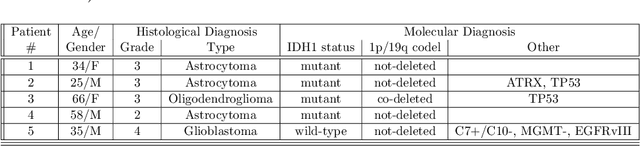
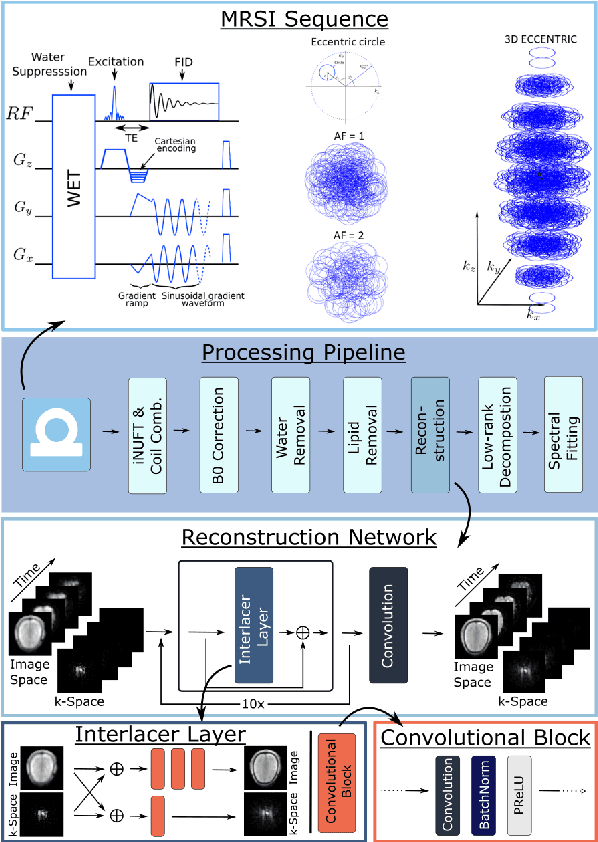
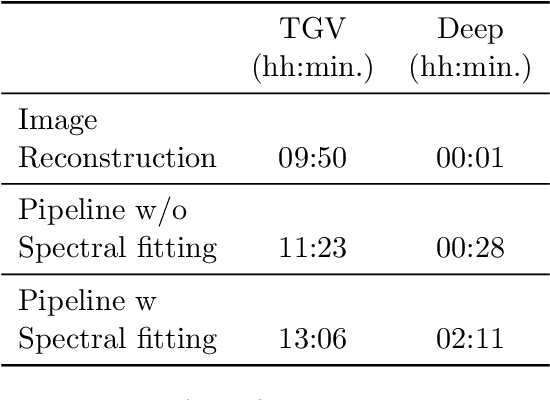

Abstract:Introduction: Altered neurometabolism is an important pathological mechanism in many neurological diseases and brain cancer, which can be mapped non-invasively by Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Imaging (MRSI). Advanced MRSI using non-cartesian compressed-sense acquisition enables fast high-resolution metabolic imaging but has lengthy reconstruction times that limits throughput and needs expert user interaction. Here, we present a robust and efficient Deep Learning reconstruction to obtain high-quality metabolic maps. Methods: Fast high-resolution whole-brain metabolic imaging was performed at 3.4 mm$^3$ isotropic resolution with acquisition times between 4:11-9:21 min:s using ECCENTRIC pulse sequence on a 7T MRI scanner. Data were acquired in a high-resolution phantom and 27 human participants, including 22 healthy volunteers and 5 glioma patients. A deep neural network using recurring interlaced convolutional layers with joint dual-space feature representation was developed for deep learning ECCENTRIC reconstruction (Deep-ER). 21 subjects were used for training and 6 subjects for testing. Deep-ER performance was compared to conventional iterative Total Generalized Variation reconstruction using image and spectral quality metrics. Results: Deep-ER demonstrated 600-fold faster reconstruction than conventional methods, providing improved spatial-spectral quality and metabolite quantification with 12%-45% (P<0.05) higher signal-to-noise and 8%-50% (P<0.05) smaller Cramer-Rao lower bounds. Metabolic images clearly visualize glioma tumor heterogeneity and boundary. Conclusion: Deep-ER provides efficient and robust reconstruction for sparse-sampled MRSI. The accelerated acquisition-reconstruction MRSI is compatible with high-throughput imaging workflow. It is expected that such improved performance will facilitate basic and clinical MRSI applications.
UniMo: Universal Motion Correction For Medical Images without Network Retraining
Sep 21, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a Universal Motion Correction (UniMo) framework, leveraging deep neural networks to tackle the challenges of motion correction across diverse imaging modalities. Our approach employs advanced neural network architectures with equivariant filters, overcoming the limitations of current models that require iterative inference or retraining for new image modalities. UniMo enables one-time training on a single modality while maintaining high stability and adaptability for inference across multiple unseen image modalities. We developed a joint learning framework that integrates multimodal knowledge from both shape and images that faithfully improve motion correction accuracy despite image appearance variations. UniMo features a geometric deformation augmenter that enhances the robustness of global motion correction by addressing any local deformations whether they are caused by object deformations or geometric distortions, and also generates augmented data to improve the training process. Our experimental results, conducted on various datasets with four different image modalities, demonstrate that UniMo surpasses existing motion correction methods in terms of accuracy. By offering a comprehensive solution to motion correction, UniMo marks a significant advancement in medical imaging, especially in challenging applications with wide ranges of motion, such as fetal imaging. The code for this work is available online, https://github.com/IntelligentImaging/UNIMO/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge