Peiqi Wang
Inference Compute-Optimal Video Vision Language Models
May 24, 2025Abstract:This work investigates the optimal allocation of inference compute across three key scaling factors in video vision language models: language model size, frame count, and the number of visual tokens per frame. While prior works typically focuses on optimizing model efficiency or improving performance without considering resource constraints, we instead identify optimal model configuration under fixed inference compute budgets. We conduct large-scale training sweeps and careful parametric modeling of task performance to identify the inference compute-optimal frontier. Our experiments reveal how task performance depends on scaling factors and finetuning data size, as well as how changes in data size shift the compute-optimal frontier. These findings translate to practical tips for selecting these scaling factors.
Hunyuan-TurboS: Advancing Large Language Models through Mamba-Transformer Synergy and Adaptive Chain-of-Thought
May 21, 2025Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) rapidly advance, we introduce Hunyuan-TurboS, a novel large hybrid Transformer-Mamba Mixture of Experts (MoE) model. It synergistically combines Mamba's long-sequence processing efficiency with Transformer's superior contextual understanding. Hunyuan-TurboS features an adaptive long-short chain-of-thought (CoT) mechanism, dynamically switching between rapid responses for simple queries and deep "thinking" modes for complex problems, optimizing computational resources. Architecturally, this 56B activated (560B total) parameter model employs 128 layers (Mamba2, Attention, FFN) with an innovative AMF/MF block pattern. Faster Mamba2 ensures linear complexity, Grouped-Query Attention minimizes KV cache, and FFNs use an MoE structure. Pre-trained on 16T high-quality tokens, it supports a 256K context length and is the first industry-deployed large-scale Mamba model. Our comprehensive post-training strategy enhances capabilities via Supervised Fine-Tuning (3M instructions), a novel Adaptive Long-short CoT Fusion method, Multi-round Deliberation Learning for iterative improvement, and a two-stage Large-scale Reinforcement Learning process targeting STEM and general instruction-following. Evaluations show strong performance: overall top 7 rank on LMSYS Chatbot Arena with a score of 1356, outperforming leading models like Gemini-2.0-Flash-001 (1352) and o4-mini-2025-04-16 (1345). TurboS also achieves an average of 77.9% across 23 automated benchmarks. Hunyuan-TurboS balances high performance and efficiency, offering substantial capabilities at lower inference costs than many reasoning models, establishing a new paradigm for efficient large-scale pre-trained models.
Calibrating Expressions of Certainty
Oct 06, 2024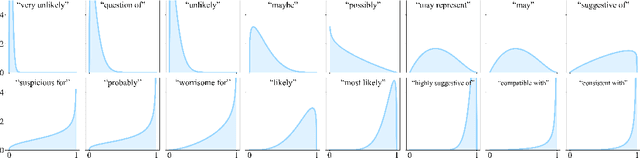
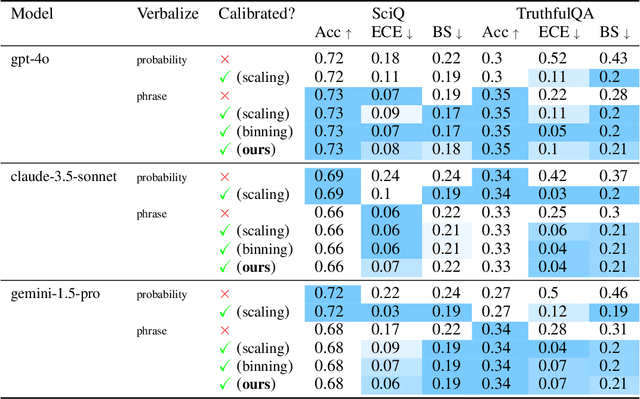
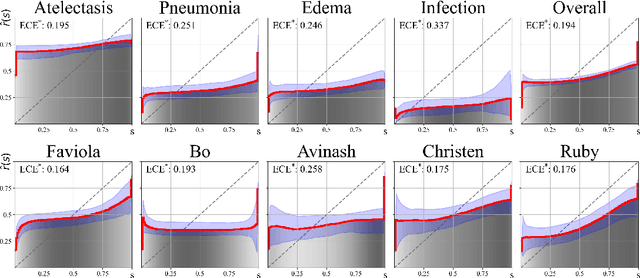
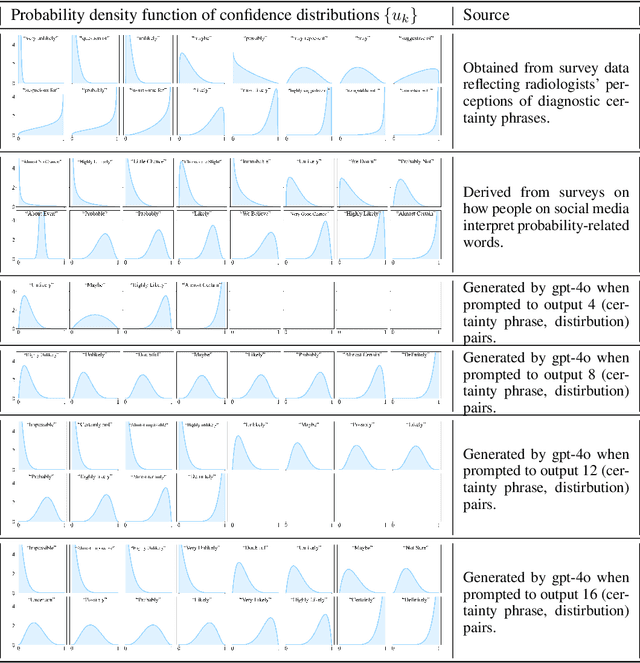
Abstract:We present a novel approach to calibrating linguistic expressions of certainty, e.g., "Maybe" and "Likely". Unlike prior work that assigns a single score to each certainty phrase, we model uncertainty as distributions over the simplex to capture their semantics more accurately. To accommodate this new representation of certainty, we generalize existing measures of miscalibration and introduce a novel post-hoc calibration method. Leveraging these tools, we analyze the calibration of both humans (e.g., radiologists) and computational models (e.g., language models) and provide interpretable suggestions to improve their calibration.
Diversity Measurement and Subset Selection for Instruction Tuning Datasets
Feb 04, 2024Abstract:We aim to select data subsets for the fine-tuning of large language models to more effectively follow instructions. Prior work has emphasized the importance of diversity in dataset curation but relied on heuristics such as the number of tasks. In this paper, we use determinantal point processes to capture the diversity and quality of instruction tuning datasets for subset selection. We propose to measure dataset diversity with log determinant distance that is the distance between the dataset of interest and a maximally diverse reference dataset. Our experiments demonstrate that the proposed diversity measure in the normalized weight gradient space is correlated with downstream instruction-following performance. Consequently, it can be used to inform when data selection is the most helpful and to analyze dataset curation strategies. We demonstrate the utility of our approach on various instruction tuning datasets.
Dr. LLaMA: Improving Small Language Models on PubMedQA via Generative Data Augmentation
May 17, 2023



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have made remarkable strides in natural language processing, but their expanding size poses challenges in terms of computational expense and inefficiency. Conversely, Small Language Models (SLMs) are known for their efficiency but often encounter difficulties in tasks with limited capacity and training data, particularly in domain-specific scenarios. In this paper, we introduce Dr. LLaMA, a method that improves SLMs in the medical domain through generative data augmentation utilizing LLMs. The objective is to develop more efficient and capable models tailored for specialized applications. Our preliminary results on the PubMedQA dataset demonstrate that LLMs effectively refine and diversify existing question-answer pairs, leading to improved performance of a significantly smaller model after fine-tuning. The best SLM surpasses few-shot GPT-4 with under 1.6 billion parameters on the PubMedQA. Our code and generated data are publicly available to facilitate further explorations.
Sample-Specific Debiasing for Better Image-Text Models
Apr 25, 2023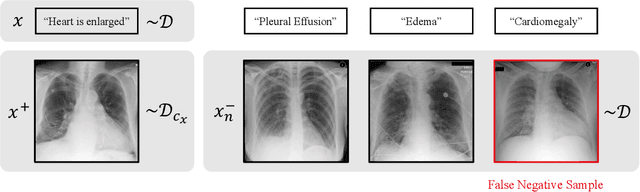
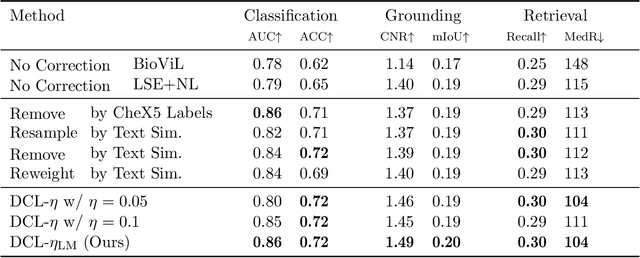
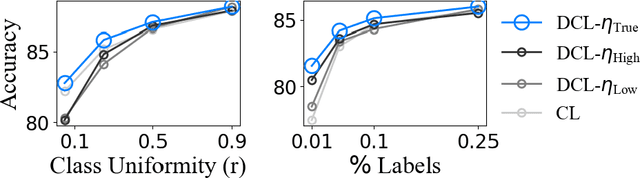

Abstract:Self-supervised representation learning on image-text data facilitates crucial medical applications, such as image classification, visual grounding, and cross-modal retrieval. One common approach involves contrasting semantically similar (positive) and dissimilar (negative) pairs of data points. Drawing negative samples uniformly from the training data set introduces false negatives, i.e., samples that are treated as dissimilar but belong to the same class. In healthcare data, the underlying class distribution is nonuniform, implying that false negatives occur at a highly variable rate. To improve the quality of learned representations, we develop a novel approach that corrects for false negatives. Our method can be viewed as a variant of debiased constrastive learning that uses estimated sample-specific class probabilities. We provide theoretical analysis of the objective function and demonstrate the proposed approach on both image and paired image-text data sets. Our experiments demonstrate empirical advantages of sample-specific debiasing.
Using Multiple Instance Learning to Build Multimodal Representations
Dec 11, 2022Abstract:Image-text multimodal representation learning aligns data across modalities and enables important medical applications, e.g., image classification, visual grounding, and cross-modal retrieval. In this work, we establish a connection between multimodal representation learning and multiple instance learning. Based on this connection, we propose a generic framework for constructing permutation-invariant score functions with many existing multimodal representation learning approaches as special cases. Furthermore, we use the framework to derive a novel contrastive learning approach and demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art results on a number of downstream tasks.
Image Classification with Consistent Supporting Evidence
Nov 13, 2021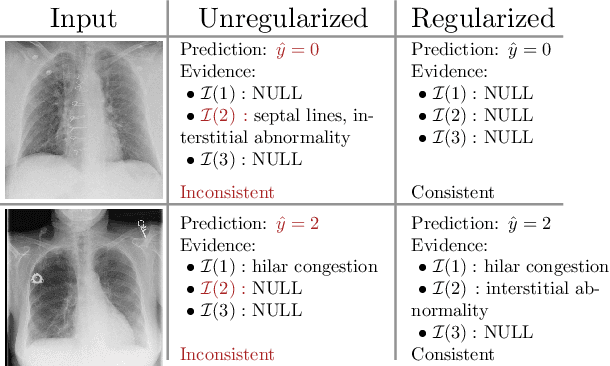
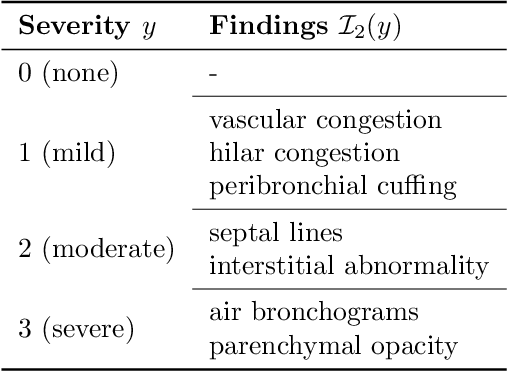
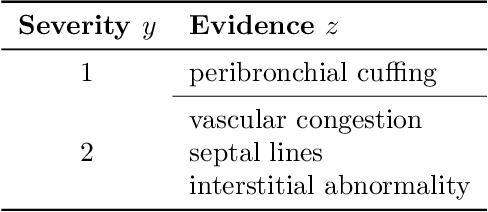
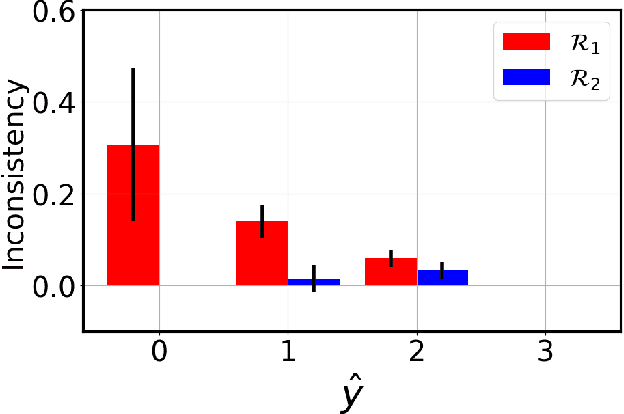
Abstract:Adoption of machine learning models in healthcare requires end users' trust in the system. Models that provide additional supportive evidence for their predictions promise to facilitate adoption. We define consistent evidence to be both compatible and sufficient with respect to model predictions. We propose measures of model inconsistency and regularizers that promote more consistent evidence. We demonstrate our ideas in the context of edema severity grading from chest radiographs. We demonstrate empirically that consistent models provide competitive performance while supporting interpretation.
FPSA: A Full System Stack Solution for Reconfigurable ReRAM-based NN Accelerator Architecture
Jan 28, 2019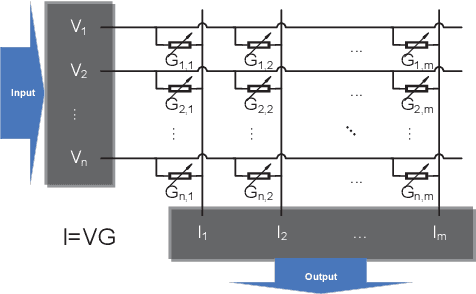
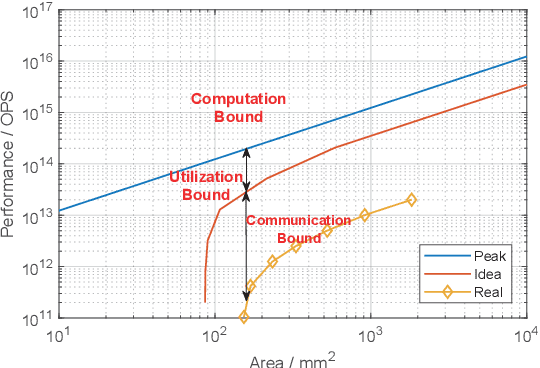
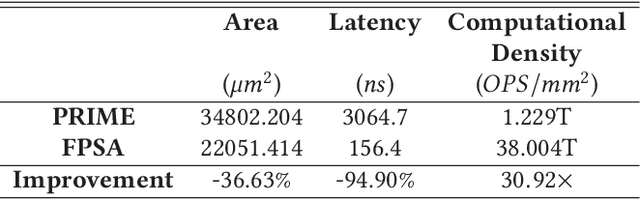
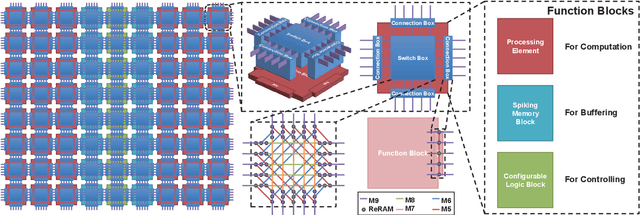
Abstract:Neural Network (NN) accelerators with emerging ReRAM (resistive random access memory) technologies have been investigated as one of the promising solutions to address the \textit{memory wall} challenge, due to the unique capability of \textit{processing-in-memory} within ReRAM-crossbar-based processing elements (PEs). However, the high efficiency and high density advantages of ReRAM have not been fully utilized due to the huge communication demands among PEs and the overhead of peripheral circuits. In this paper, we propose a full system stack solution, composed of a reconfigurable architecture design, Field Programmable Synapse Array (FPSA) and its software system including neural synthesizer, temporal-to-spatial mapper, and placement & routing. We highly leverage the software system to make the hardware design compact and efficient. To satisfy the high-performance communication demand, we optimize it with a reconfigurable routing architecture and the placement & routing tool. To improve the computational density, we greatly simplify the PE circuit with the spiking schema and then adopt neural synthesizer to enable the high density computation-resources to support different kinds of NN operations. In addition, we provide spiking memory blocks (SMBs) and configurable logic blocks (CLBs) in hardware and leverage the temporal-to-spatial mapper to utilize them to balance the storage and computation requirements of NN. Owing to the end-to-end software system, we can efficiently deploy existing deep neural networks to FPSA. Evaluations show that, compared to one of state-of-the-art ReRAM-based NN accelerators, PRIME, the computational density of FPSA improves by 31x; for representative NNs, its inference performance can achieve up to 1000x speedup.
QGAN: Quantized Generative Adversarial Networks
Jan 24, 2019
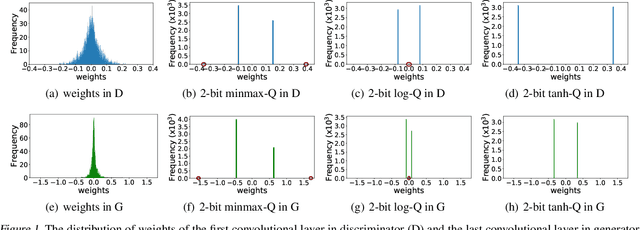
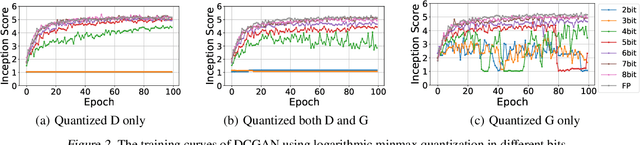
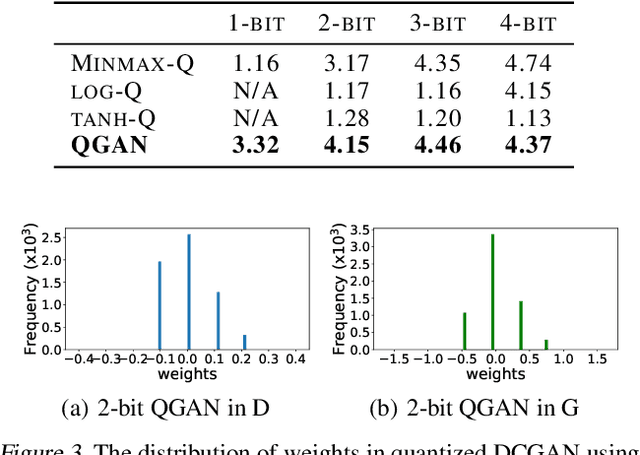
Abstract:The intensive computation and memory requirements of generative adversarial neural networks (GANs) hinder its real-world deployment on edge devices such as smartphones. Despite the success in model reduction of CNNs, neural network quantization methods have not yet been studied on GANs, which are mainly faced with the issues of both the effectiveness of quantization algorithms and the instability of training GAN models. In this paper, we start with an extensive study on applying existing successful methods to quantize GANs. Our observation reveals that none of them generates samples with reasonable quality because of the underrepresentation of quantized values in model weights, and the generator and discriminator networks show different sensitivities upon quantization methods. Motivated by these observations, we develop a novel quantization method for GANs based on EM algorithms, named as QGAN. We also propose a multi-precision algorithm to help find the optimal number of bits of quantized GAN models in conjunction with corresponding result qualities. Experiments on CIFAR-10 and CelebA show that QGAN can quantize GANs to even 1-bit or 2-bit representations with results of quality comparable to original models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge