Yingcheng Liu
Calibrating Expressions of Certainty
Oct 06, 2024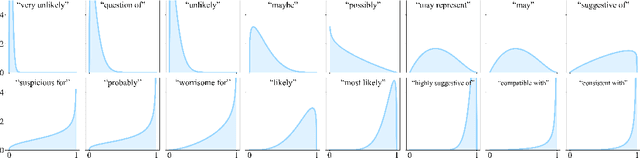
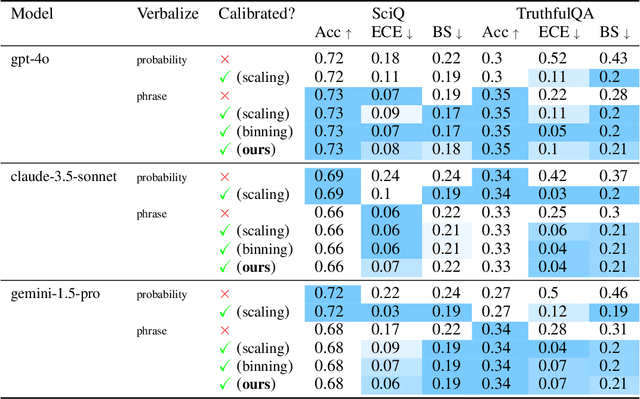
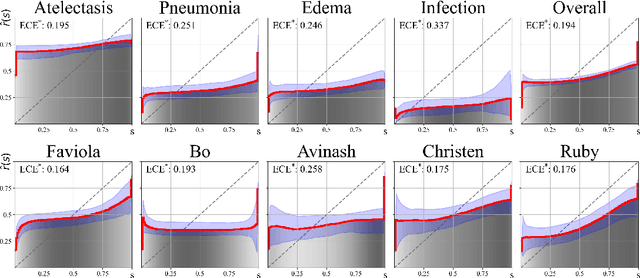
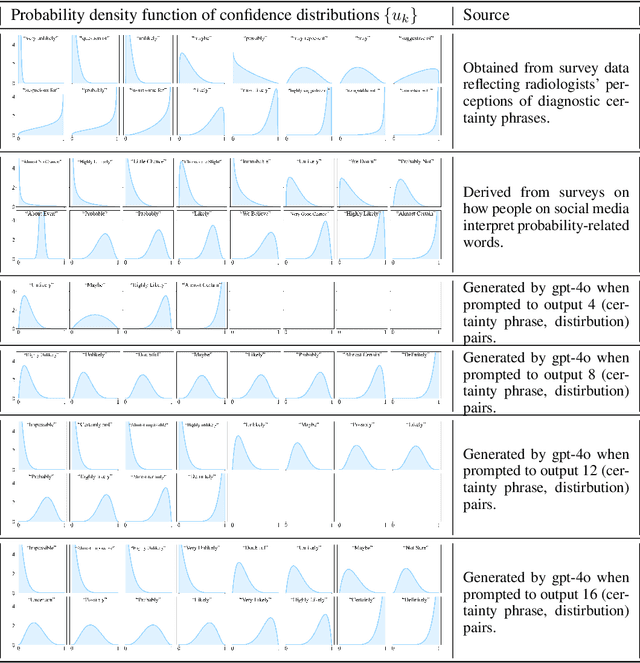
Abstract:We present a novel approach to calibrating linguistic expressions of certainty, e.g., "Maybe" and "Likely". Unlike prior work that assigns a single score to each certainty phrase, we model uncertainty as distributions over the simplex to capture their semantics more accurately. To accommodate this new representation of certainty, we generalize existing measures of miscalibration and introduce a novel post-hoc calibration method. Leveraging these tools, we analyze the calibration of both humans (e.g., radiologists) and computational models (e.g., language models) and provide interpretable suggestions to improve their calibration.
Dynamic Neural Fields for Learning Atlases of 4D Fetal MRI Time-series
Nov 06, 2023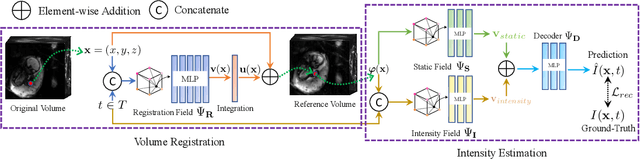
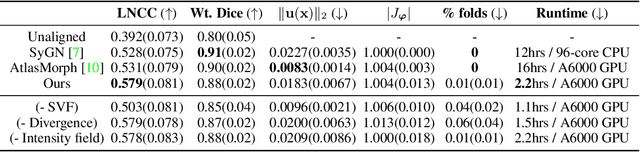
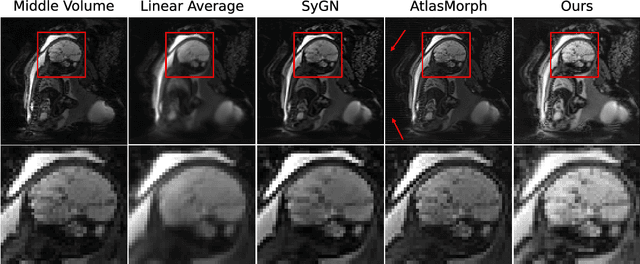
Abstract:We present a method for fast biomedical image atlas construction using neural fields. Atlases are key to biomedical image analysis tasks, yet conventional and deep network estimation methods remain time-intensive. In this preliminary work, we frame subject-specific atlas building as learning a neural field of deformable spatiotemporal observations. We apply our method to learning subject-specific atlases and motion stabilization of dynamic BOLD MRI time-series of fetuses in utero. Our method yields high-quality atlases of fetal BOLD time-series with $\sim$5-7$\times$ faster convergence compared to existing work. While our method slightly underperforms well-tuned baselines in terms of anatomical overlap, it estimates templates significantly faster, thus enabling rapid processing and stabilization of large databases of 4D dynamic MRI acquisitions. Code is available at https://github.com/Kidrauh/neural-atlasing
Consistency Regularization Improves Placenta Segmentation in Fetal EPI MRI Time Series
Oct 16, 2023Abstract:The placenta plays a crucial role in fetal development. Automated 3D placenta segmentation from fetal EPI MRI holds promise for advancing prenatal care. This paper proposes an effective semi-supervised learning method for improving placenta segmentation in fetal EPI MRI time series. We employ consistency regularization loss that promotes consistency under spatial transformation of the same image and temporal consistency across nearby images in a time series. The experimental results show that the method improves the overall segmentation accuracy and provides better performance for outliers and hard samples. The evaluation also indicates that our method improves the temporal coherency of the prediction, which could lead to more accurate computation of temporal placental biomarkers. This work contributes to the study of the placenta and prenatal clinical decision-making. Code is available at https://github.com/firstmover/cr-seg.
Sample-Specific Debiasing for Better Image-Text Models
Apr 25, 2023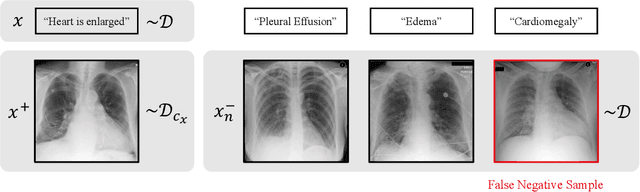
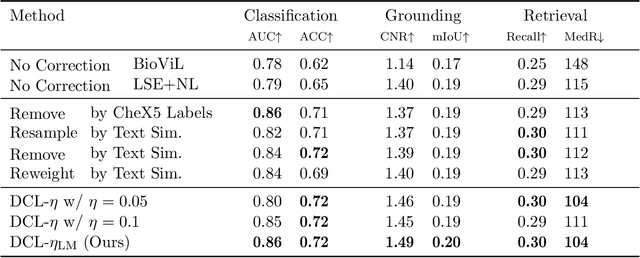
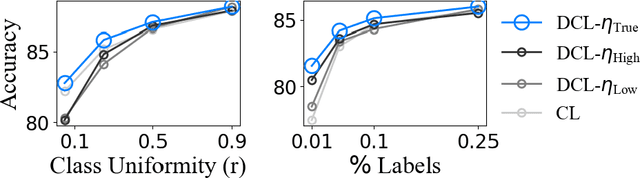

Abstract:Self-supervised representation learning on image-text data facilitates crucial medical applications, such as image classification, visual grounding, and cross-modal retrieval. One common approach involves contrasting semantically similar (positive) and dissimilar (negative) pairs of data points. Drawing negative samples uniformly from the training data set introduces false negatives, i.e., samples that are treated as dissimilar but belong to the same class. In healthcare data, the underlying class distribution is nonuniform, implying that false negatives occur at a highly variable rate. To improve the quality of learned representations, we develop a novel approach that corrects for false negatives. Our method can be viewed as a variant of debiased constrastive learning that uses estimated sample-specific class probabilities. We provide theoretical analysis of the objective function and demonstrate the proposed approach on both image and paired image-text data sets. Our experiments demonstrate empirical advantages of sample-specific debiasing.
Making the Invisible Visible: Action Recognition Through Walls and Occlusions
Sep 20, 2019



Abstract:Understanding people's actions and interactions typically depends on seeing them. Automating the process of action recognition from visual data has been the topic of much research in the computer vision community. But what if it is too dark, or if the person is occluded or behind a wall? In this paper, we introduce a neural network model that can detect human actions through walls and occlusions, and in poor lighting conditions. Our model takes radio frequency (RF) signals as input, generates 3D human skeletons as an intermediate representation, and recognizes actions and interactions of multiple people over time. By translating the input to an intermediate skeleton-based representation, our model can learn from both vision-based and RF-based datasets, and allow the two tasks to help each other. We show that our model achieves comparable accuracy to vision-based action recognition systems in visible scenarios, yet continues to work accurately when people are not visible, hence addressing scenarios that are beyond the limit of today's vision-based action recognition.
Unified Perceptual Parsing for Scene Understanding
Jul 26, 2018



Abstract:Humans recognize the visual world at multiple levels: we effortlessly categorize scenes and detect objects inside, while also identifying the textures and surfaces of the objects along with their different compositional parts. In this paper, we study a new task called Unified Perceptual Parsing, which requires the machine vision systems to recognize as many visual concepts as possible from a given image. A multi-task framework called UPerNet and a training strategy are developed to learn from heterogeneous image annotations. We benchmark our framework on Unified Perceptual Parsing and show that it is able to effectively segment a wide range of concepts from images. The trained networks are further applied to discover visual knowledge in natural scenes. Models are available at \url{https://github.com/CSAILVision/unifiedparsing}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge