Yao Tian
Low Rank Learning for Offline Query Optimization
Apr 08, 2025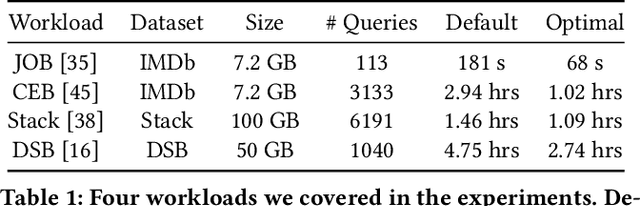
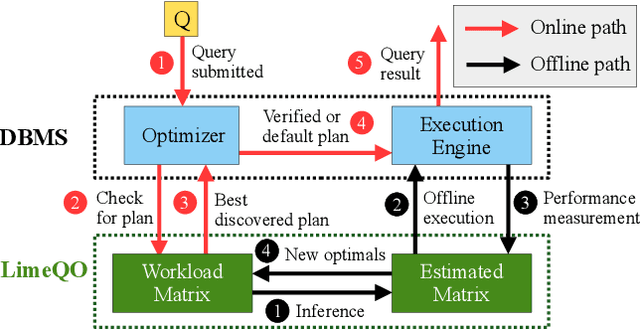
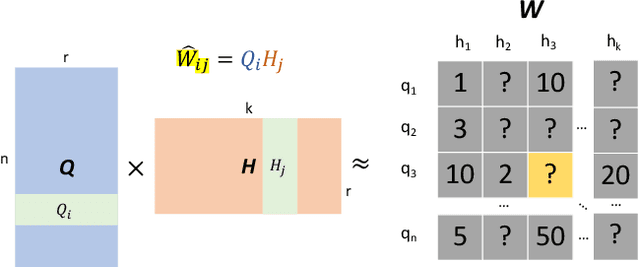
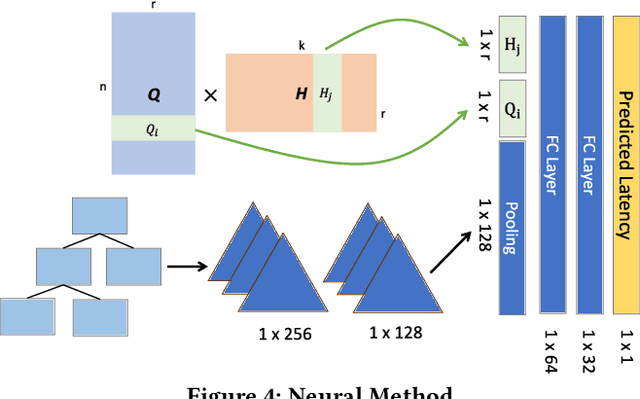
Abstract:Recent deployments of learned query optimizers use expensive neural networks and ad-hoc search policies. To address these issues, we introduce \textsc{LimeQO}, a framework for offline query optimization leveraging low-rank learning to efficiently explore alternative query plans with minimal resource usage. By modeling the workload as a partially observed, low-rank matrix, we predict unobserved query plan latencies using purely linear methods, significantly reducing computational overhead compared to neural networks. We formalize offline exploration as an active learning problem, and present simple heuristics that reduces a 3-hour workload to 1.5 hours after just 1.5 hours of exploration. Additionally, we propose a transductive Tree Convolutional Neural Network (TCNN) that, despite higher computational costs, achieves the same workload reduction with only 0.5 hours of exploration. Unlike previous approaches that place expensive neural networks directly in the query processing ``hot'' path, our approach offers a low-overhead solution and a no-regressions guarantee, all without making assumptions about the underlying DBMS. The code is available in \href{https://github.com/zixy17/LimeQO}{https://github.com/zixy17/LimeQO}.
Multimodal Large Models Are Effective Action Anticipators
Jan 01, 2025



Abstract:The task of long-term action anticipation demands solutions that can effectively model temporal dynamics over extended periods while deeply understanding the inherent semantics of actions. Traditional approaches, which primarily rely on recurrent units or Transformer layers to capture long-term dependencies, often fall short in addressing these challenges. Large Language Models (LLMs), with their robust sequential modeling capabilities and extensive commonsense knowledge, present new opportunities for long-term action anticipation. In this work, we introduce the ActionLLM framework, a novel approach that treats video sequences as successive tokens, leveraging LLMs to anticipate future actions. Our baseline model simplifies the LLM architecture by setting future tokens, incorporating an action tuning module, and reducing the textual decoder layer to a linear layer, enabling straightforward action prediction without the need for complex instructions or redundant descriptions. To further harness the commonsense reasoning of LLMs, we predict action categories for observed frames and use sequential textual clues to guide semantic understanding. In addition, we introduce a Cross-Modality Interaction Block, designed to explore the specificity within each modality and capture interactions between vision and textual modalities, thereby enhancing multimodal tuning. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of the proposed ActionLLM framework, encouraging a promising direction to explore LLMs in the context of action anticipation. Code is available at https://github.com/2tianyao1/ActionLLM.git.
LHPF: Look back the History and Plan for the Future in Autonomous Driving
Nov 26, 2024Abstract:Decision-making and planning in autonomous driving critically reflect the safety of the system, making effective planning imperative. Current imitation learning-based planning algorithms often merge historical trajectories with present observations to predict future candidate paths. However, these algorithms typically assess the current and historical plans independently, leading to discontinuities in driving intentions and an accumulation of errors with each step in a discontinuous plan. To tackle this challenge, this paper introduces LHPF, an imitation learning planner that integrates historical planning information. Our approach employs a historical intention aggregation module that pools historical planning intentions, which are then combined with a spatial query vector to decode the final planning trajectory. Furthermore, we incorporate a comfort auxiliary task to enhance the human-like quality of the driving behavior. Extensive experiments using both real-world and synthetic data demonstrate that LHPF not only surpasses existing advanced learning-based planners in planning performance but also marks the first instance of a purely learning-based planner outperforming the expert. Additionally, the application of the historical intention aggregation module across various backbones highlights the considerable potential of the proposed method. The code will be made publicly available.
A Dual-Path Framework with Frequency-and-Time Excited Network for Anomalous Sound Detection
Sep 05, 2024



Abstract:In contrast to human speech, machine-generated sounds of the same type often exhibit consistent frequency characteristics and discernible temporal periodicity. However, leveraging these dual attributes in anomaly detection remains relatively under-explored. In this paper, we propose an automated dual-path framework that learns prominent frequency and temporal patterns for diverse machine types. One pathway uses a novel Frequency-and-Time Excited Network (FTE-Net) to learn the salient features across frequency and time axes of the spectrogram. It incorporates a Frequency-and-Time Chunkwise Encoder (FTC-Encoder) and an excitation network. The other pathway uses a 1D convolutional network for utterance-level spectrum. Experimental results on the DCASE 2023 task 2 dataset show the state-of-the-art performance of our proposed method. Moreover, visualizations of the intermediate feature maps in the excitation network are provided to illustrate the effectiveness of our method.
Detect Depression from Social Networks with Sentiment Knowledge Sharing
Jun 13, 2023
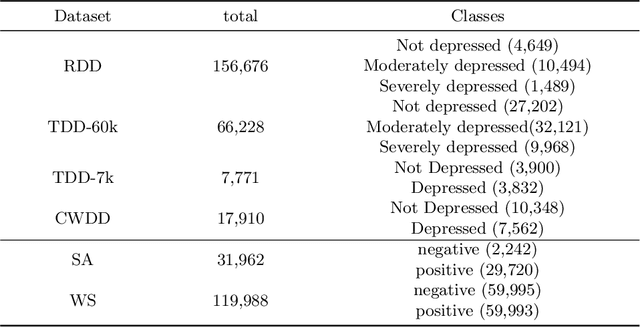

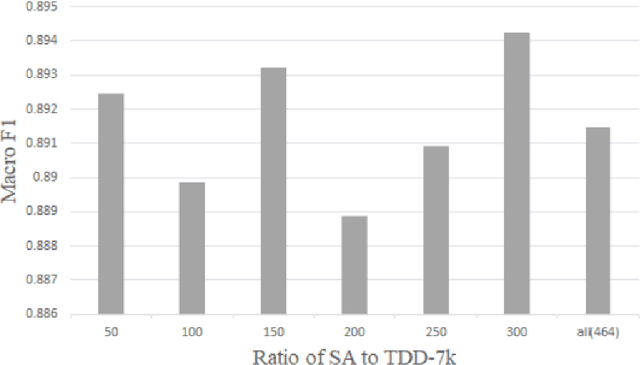
Abstract:Social network plays an important role in propagating people's viewpoints, emotions, thoughts, and fears. Notably, following lockdown periods during the COVID-19 pandemic, the issue of depression has garnered increasing attention, with a significant portion of individuals resorting to social networks as an outlet for expressing emotions. Using deep learning techniques to discern potential signs of depression from social network messages facilitates the early identification of mental health conditions. Current efforts in detecting depression through social networks typically rely solely on analyzing the textual content, overlooking other potential information. In this work, we conduct a thorough investigation that unveils a strong correlation between depression and negative emotional states. The integration of such associations as external knowledge can provide valuable insights for detecting depression. Accordingly, we propose a multi-task training framework, DeSK, which utilizes shared sentiment knowledge to enhance the efficacy of depression detection. Experiments conducted on both Chinese and English datasets demonstrate the cross-lingual effectiveness of DeSK.
A Learned Index for Exact Similarity Search in Metric Spaces
Apr 21, 2022



Abstract:Indexing is an effective way to support efficient query processing in large databases. Recently the concept of learned index has been explored actively to replace or supplement traditional index structures with machine learning models to reduce storage and search costs. However, accurate and efficient similarity query processing in high-dimensional metric spaces remains to be an open challenge. In this paper, a novel indexing approach called LIMS is proposed to use data clustering and pivot-based data transformation techniques to build learned indexes for efficient similarity query processing in metric spaces. The underlying data is partitioned into clusters such that each cluster follows a relatively uniform data distribution. Data redistribution is achieved by utilizing a small number of pivots for each cluster. Similar data are mapped into compact regions and the mapped values are totally ordinal. Machine learning models are developed to approximate the position of each data record on the disk. Efficient algorithms are designed for processing range queries and nearest neighbor queries based on LIMS, and for index maintenance with dynamic updates. Extensive experiments on real-world and synthetic datasets demonstrate the superiority of LIMS compared with traditional indexes and state-of-the-art learned indexes.
BiFSMN: Binary Neural Network for Keyword Spotting
Feb 15, 2022
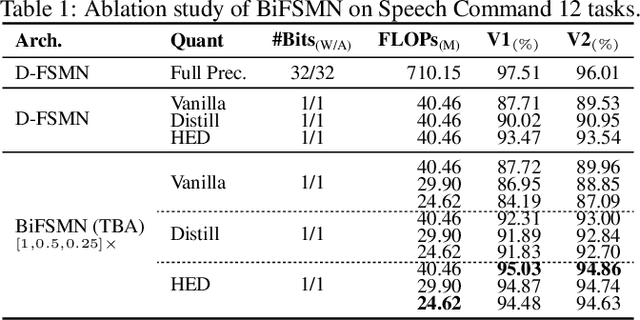

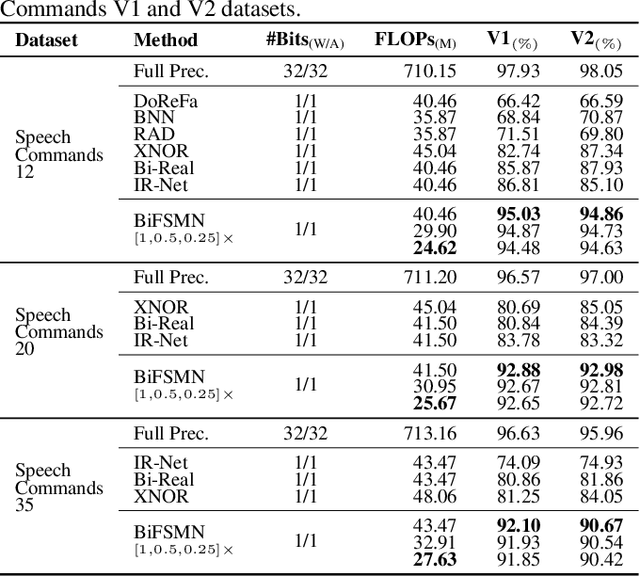
Abstract:The deep neural networks, such as the Deep-FSMN, have been widely studied for keyword spotting (KWS) applications. However, computational resources for these networks are significantly constrained since they usually run on-call on edge devices. In this paper, we present BiFSMN, an accurate and extreme-efficient binary neural network for KWS. We first construct a High-frequency Enhancement Distillation scheme for the binarization-aware training, which emphasizes the high-frequency information from the full-precision network's representation that is more crucial for the optimization of the binarized network. Then, to allow the instant and adaptive accuracy-efficiency trade-offs at runtime, we also propose a Thinnable Binarization Architecture to further liberate the acceleration potential of the binarized network from the topology perspective. Moreover, we implement a Fast Bitwise Computation Kernel for BiFSMN on ARMv8 devices which fully utilizes registers and increases instruction throughput to push the limit of deployment efficiency. Extensive experiments show that BiFSMN outperforms existing binarization methods by convincing margins on various datasets and is even comparable with the full-precision counterpart (e.g., less than 3% drop on Speech Commands V1-12). We highlight that benefiting from the thinnable architecture and the optimized 1-bit implementation, BiFSMN can achieve an impressive 22.3x speedup and 15.5x storage-saving on real-world edge hardware.
The Volcspeech system for the ICASSP 2022 multi-channel multi-party meeting transcription challenge
Feb 10, 2022



Abstract:This paper describes our submission to ICASSP 2022 Multi-channel Multi-party Meeting Transcription (M2MeT) Challenge. For Track 1, we propose several approaches to empower the clustering-based speaker diarization system to handle overlapped speech. Front-end dereverberation and the direction-of-arrival (DOA) estimation are used to improve the accuracy of speaker diarization. Multi-channel combination and overlap detection are applied to reduce the missed speaker error. A modified DOVER-Lap is also proposed to fuse the results of different systems. We achieve the final DER of 5.79% on the Eval set and 7.23% on the Test set. For Track 2, we develop our system using the Conformer model in a joint CTC-attention architecture. Serialized output training is adopted to multi-speaker overlapped speech recognition. We propose a neural front-end module to model multi-channel audio and train the model end-to-end. Various data augmentation methods are utilized to mitigate over-fitting in the multi-channel multi-speaker E2E system. Transformer language model fusion is developed to achieve better performance. The final CER is 19.2% on the Eval set and 20.8% on the Test set.
Comparison of Multiple Features and Modeling Methods for Text-dependent Speaker Verification
Sep 09, 2017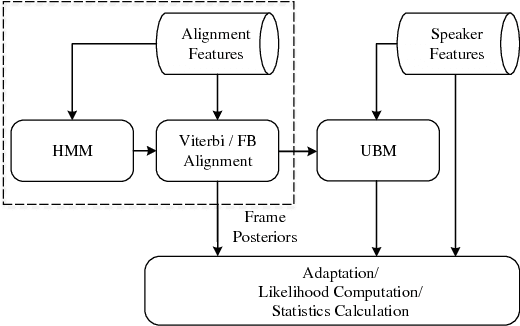
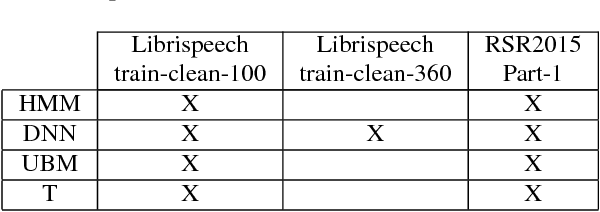
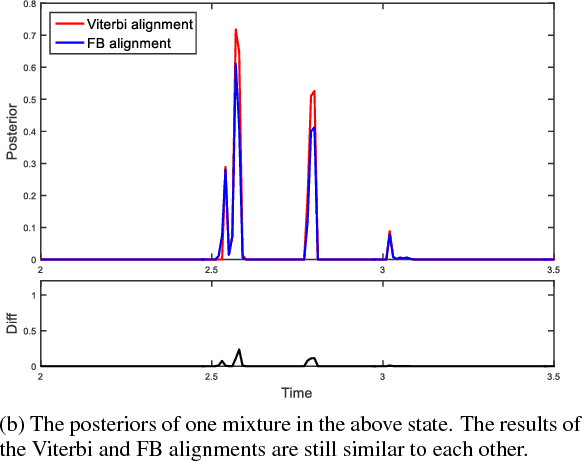
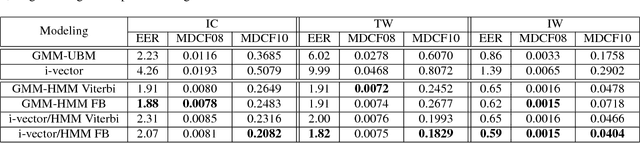
Abstract:Text-dependent speaker verification is becoming popular in the speaker recognition society. However, the conventional i-vector framework which has been successful for speaker identification and other similar tasks works relatively poorly in this task. Researchers have proposed several new methods to improve performance, but it is still unclear that which model is the best choice, especially when the pass-phrases are prompted during enrollment and test. In this paper, we introduce four modeling methods and compare their performance on the newly published RedDots dataset. To further explore the influence of different frame alignments, Viterbi and forward-backward algorithms are both used in the HMM-based models. Several bottleneck features are also investigated. Our experiments show that, by explicitly modeling the lexical content, the HMM-based modeling achieves good results in the fixed-phrase condition. In the prompted-phrase condition, GMM-HMM and i-vector/HMM are not as successful. In both conditions, the forward-backward algorithm brings more benefits to the i-vector/HMM system. Additionally, we also find that even though bottleneck features perform well for text-independent speaker verification, they do not outperform MFCCs on the most challenging Imposter-Correct trials on RedDots.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge