Pengyuan Zhou
GraphCheck: Breaking Long-Term Text Barriers with Extracted Knowledge Graph-Powered Fact-Checking
Feb 23, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are widely used, but they often generate subtle factual errors, especially in long-form text. These errors are fatal in some specialized domains such as medicine. Existing fact-checking with grounding documents methods face two main challenges: (1) they struggle to understand complex multihop relations in long documents, often overlooking subtle factual errors; (2) most specialized methods rely on pairwise comparisons, requiring multiple model calls, leading to high resource and computational costs. To address these challenges, we propose \textbf{\textit{GraphCheck}}, a fact-checking framework that uses extracted knowledge graphs to enhance text representation. Graph Neural Networks further process these graphs as a soft prompt, enabling LLMs to incorporate structured knowledge more effectively. Enhanced with graph-based reasoning, GraphCheck captures multihop reasoning chains which are often overlooked by existing methods, enabling precise and efficient fact-checking in a single inference call. Experimental results on seven benchmarks spanning both general and medical domains demonstrate a 6.1\% overall improvement over baseline models. Notably, GraphCheck outperforms existing specialized fact-checkers and achieves comparable performance with state-of-the-art LLMs, such as DeepSeek-V3 and OpenAI-o1, with significantly fewer parameters.
A + B: A General Generator-Reader Framework for Optimizing LLMs to Unleash Synergy Potential
Jun 06, 2024



Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an effective solution to supplement necessary knowledge to large language models (LLMs). Targeting its bottleneck of retriever performance, "generate-then-read" pipeline is proposed to replace the retrieval stage with generation from the LLM itself. Although promising, this research direction is underexplored and still cannot work in the scenario when source knowledge is given. In this paper, we formalize a general "A + B" framework with varying combinations of foundation models and types for systematic investigation. We explore the efficacy of the base and chat versions of LLMs and found their different functionalities suitable for generator A and reader B, respectively. Their combinations consistently outperform single models, especially in complex scenarios. Furthermore, we extend the application of the "A + B" framework to scenarios involving source documents through continuous learning, enabling the direct integration of external knowledge into LLMs. This approach not only facilitates effective acquisition of new knowledge but also addresses the challenges of safety and helpfulness post-adaptation. The paper underscores the versatility of the "A + B" framework, demonstrating its potential to enhance the practical application of LLMs across various domains.
360SFUDA++: Towards Source-free UDA for Panoramic Segmentation by Learning Reliable Category Prototypes
Apr 25, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we address the challenging source-free unsupervised domain adaptation (SFUDA) for pinhole-to-panoramic semantic segmentation, given only a pinhole image pre-trained model (i.e., source) and unlabeled panoramic images (i.e., target). Tackling this problem is non-trivial due to three critical challenges: 1) semantic mismatches from the distinct Field-of-View (FoV) between domains, 2) style discrepancies inherent in the UDA problem, and 3) inevitable distortion of the panoramic images. To tackle these problems, we propose 360SFUDA++ that effectively extracts knowledge from the source pinhole model with only unlabeled panoramic images and transfers the reliable knowledge to the target panoramic domain. Specifically, we first utilize Tangent Projection (TP) as it has less distortion and meanwhile slits the equirectangular projection (ERP) to patches with fixed FoV projection (FFP) to mimic the pinhole images. Both projections are shown effective in extracting knowledge from the source model. However, as the distinct projections make it less possible to directly transfer knowledge between domains, we then propose Reliable Panoramic Prototype Adaptation Module (RP2AM) to transfer knowledge at both prediction and prototype levels. RP$^2$AM selects the confident knowledge and integrates panoramic prototypes for reliable knowledge adaptation. Moreover, we introduce Cross-projection Dual Attention Module (CDAM), which better aligns the spatial and channel characteristics across projections at the feature level between domains. Both knowledge extraction and transfer processes are synchronously updated to reach the best performance. Extensive experiments on the synthetic and real-world benchmarks, including outdoor and indoor scenarios, demonstrate that our 360SFUDA++ achieves significantly better performance than prior SFUDA methods.
BotDGT: Dynamicity-aware Social Bot Detection with Dynamic Graph Transformers
Apr 24, 2024



Abstract:Detecting social bots has evolved into a pivotal yet intricate task, aimed at combating the dissemination of misinformation and preserving the authenticity of online interactions. While earlier graph-based approaches, which leverage topological structure of social networks, yielded notable outcomes, they overlooked the inherent dynamicity of social networks -- In reality, they largely depicted the social network as a static graph and solely relied on its most recent state. Due to the absence of dynamicity modeling, such approaches are vulnerable to evasion, particularly when advanced social bots interact with other users to camouflage identities and escape detection. To tackle these challenges, we propose BotDGT, a novel framework that not only considers the topological structure, but also effectively incorporates dynamic nature of social network. Specifically, we characterize a social network as a dynamic graph. A structural module is employed to acquire topological information from each historical snapshot. Additionally, a temporal module is proposed to integrate historical context and model the evolving behavior patterns exhibited by social bots and legitimate users. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of BotDGT against the leading methods that neglected the dynamic nature of social networks in terms of accuracy, recall, and F1-score.
DreamScene: 3D Gaussian-based Text-to-3D Scene Generation via Formation Pattern Sampling
Apr 04, 2024
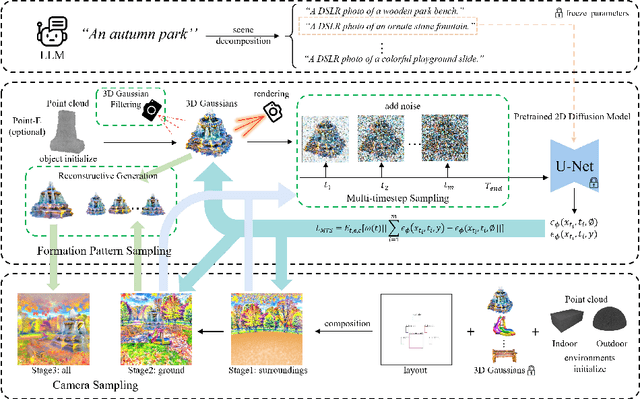
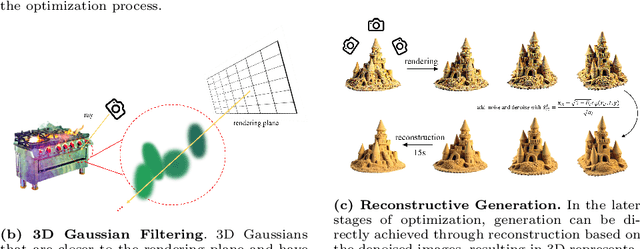
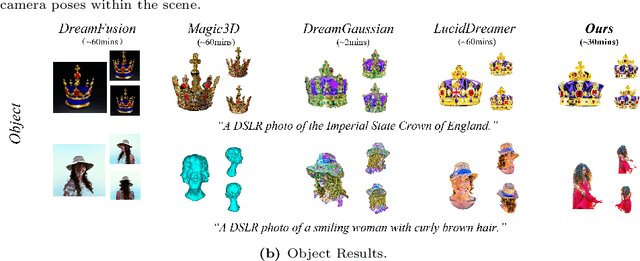
Abstract:Text-to-3D scene generation holds immense potential for the gaming, film, and architecture sectors. Despite significant progress, existing methods struggle with maintaining high quality, consistency, and editing flexibility. In this paper, we propose DreamScene, a 3D Gaussian-based novel text-to-3D scene generation framework, to tackle the aforementioned three challenges mainly via two strategies. First, DreamScene employs Formation Pattern Sampling (FPS), a multi-timestep sampling strategy guided by the formation patterns of 3D objects, to form fast, semantically rich, and high-quality representations. FPS uses 3D Gaussian filtering for optimization stability, and leverages reconstruction techniques to generate plausible textures. Second, DreamScene employs a progressive three-stage camera sampling strategy, specifically designed for both indoor and outdoor settings, to effectively ensure object-environment integration and scene-wide 3D consistency. Last, DreamScene enhances scene editing flexibility by integrating objects and environments, enabling targeted adjustments. Extensive experiments validate DreamScene's superiority over current state-of-the-art techniques, heralding its wide-ranging potential for diverse applications. Code and demos will be released at https://dreamscene-project.github.io .
Semantics, Distortion, and Style Matter: Towards Source-free UDA for Panoramic Segmentation
Mar 22, 2024



Abstract:This paper addresses an interesting yet challenging problem -- source-free unsupervised domain adaptation (SFUDA) for pinhole-to-panoramic semantic segmentation -- given only a pinhole image-trained model (i.e., source) and unlabeled panoramic images (i.e., target). Tackling this problem is nontrivial due to the semantic mismatches, style discrepancies, and inevitable distortion of panoramic images. To this end, we propose a novel method that utilizes Tangent Projection (TP) as it has less distortion and meanwhile slits the equirectangular projection (ERP) with a fixed FoV to mimic the pinhole images. Both projections are shown effective in extracting knowledge from the source model. However, the distinct projection discrepancies between source and target domains impede the direct knowledge transfer; thus, we propose a panoramic prototype adaptation module (PPAM) to integrate panoramic prototypes from the extracted knowledge for adaptation. We then impose the loss constraints on both predictions and prototypes and propose a cross-dual attention module (CDAM) at the feature level to better align the spatial and channel characteristics across the domains and projections. Both knowledge extraction and transfer processes are synchronously updated to reach the best performance. Extensive experiments on the synthetic and real-world benchmarks, including outdoor and indoor scenarios, demonstrate that our method achieves significantly better performance than prior SFUDA methods for pinhole-to-panoramic adaptation.
Dream360: Diverse and Immersive Outdoor Virtual Scene Creation via Transformer-Based 360 Image Outpainting
Jan 19, 2024



Abstract:360 images, with a field-of-view (FoV) of 180x360, provide immersive and realistic environments for emerging virtual reality (VR) applications, such as virtual tourism, where users desire to create diverse panoramic scenes from a narrow FoV photo they take from a viewpoint via portable devices. It thus brings us to a technical challenge: `How to allow the users to freely create diverse and immersive virtual scenes from a narrow FoV image with a specified viewport?' To this end, we propose a transformer-based 360 image outpainting framework called Dream360, which can generate diverse, high-fidelity, and high-resolution panoramas from user-selected viewports, considering the spherical properties of 360 images. Compared with existing methods, e.g., [3], which primarily focus on inputs with rectangular masks and central locations while overlooking the spherical property of 360 images, our Dream360 offers higher outpainting flexibility and fidelity based on the spherical representation. Dream360 comprises two key learning stages: (I) codebook-based panorama outpainting via Spherical-VQGAN (S-VQGAN), and (II) frequency-aware refinement with a novel frequency-aware consistency loss. Specifically, S-VQGAN learns a sphere-specific codebook from spherical harmonic (SH) values, providing a better representation of spherical data distribution for scene modeling. The frequency-aware refinement matches the resolution and further improves the semantic consistency and visual fidelity of the generated results. Our Dream360 achieves significantly lower Frechet Inception Distance (FID) scores and better visual fidelity than existing methods. We also conducted a user study involving 15 participants to interactively evaluate the quality of the generated results in VR, demonstrating the flexibility and superiority of our Dream360 framework.
Noise-NeRF: Hide Information in Neural Radiance Fields using Trainable Noise
Jan 02, 2024



Abstract:Neural radiance fields (NeRF) have been proposed as an innovative 3D representation method. While attracting lots of attention, NeRF faces critical issues such as information confidentiality and security. Steganography is a technique used to embed information in another object as a means of protecting information security. Currently, there are few related studies on NeRF steganography, facing challenges in low steganography quality, model weight damage, and a limited amount of steganographic information. This paper proposes a novel NeRF steganography method based on trainable noise: Noise-NeRF. Furthermore, we propose the Adaptive Pixel Selection strategy and Pixel Perturbation strategy to improve the steganography quality and efficiency. The extensive experiments on open-source datasets show that Noise-NeRF provides state-of-the-art performances in both steganography quality and rendering quality, as well as effectiveness in super-resolution image steganography.
2D-Guided 3D Gaussian Segmentation
Dec 26, 2023Abstract:Recently, 3D Gaussian, as an explicit 3D representation method, has demonstrated strong competitiveness over NeRF (Neural Radiance Fields) in terms of expressing complex scenes and training duration. These advantages signal a wide range of applications for 3D Gaussians in 3D understanding and editing. Meanwhile, the segmentation of 3D Gaussians is still in its infancy. The existing segmentation methods are not only cumbersome but also incapable of segmenting multiple objects simultaneously in a short amount of time. In response, this paper introduces a 3D Gaussian segmentation method implemented with 2D segmentation as supervision. This approach uses input 2D segmentation maps to guide the learning of the added 3D Gaussian semantic information, while nearest neighbor clustering and statistical filtering refine the segmentation results. Experiments show that our concise method can achieve comparable performances on mIOU and mAcc for multi-object segmentation as previous single-object segmentation methods.
FedMKGC: Privacy-Preserving Federated Multilingual Knowledge Graph Completion
Dec 17, 2023Abstract:Knowledge graph completion (KGC) aims to predict missing facts in knowledge graphs (KGs), which is crucial as modern KGs remain largely incomplete. While training KGC models on multiple aligned KGs can improve performance, previous methods that rely on transferring raw data among KGs raise privacy concerns. To address this challenge, we propose a new federated learning framework that implicitly aggregates knowledge from multiple KGs without demanding raw data exchange and entity alignment. We treat each KG as a client that trains a local language model through textbased knowledge representation learning. A central server then aggregates the model weights from clients. As natural language provides a universal representation, the same knowledge thus has similar semantic representations across KGs. As such, the aggregated language model can leverage complementary knowledge from multilingual KGs without demanding raw user data sharing. Extensive experiments on a benchmark dataset demonstrate that our method substantially improves KGC on multilingual KGs, achieving comparable performance to state-of-the-art alignment-based models without requiring any labeled alignments or raw user data sharing. Our codes will be publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge