Jiahao Ying
Disentangling Language and Culture for Evaluating Multilingual Large Language Models
May 30, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces a Dual Evaluation Framework to comprehensively assess the multilingual capabilities of LLMs. By decomposing the evaluation along the dimensions of linguistic medium and cultural context, this framework enables a nuanced analysis of LLMs' ability to process questions within both native and cross-cultural contexts cross-lingually. Extensive evaluations are conducted on a wide range of models, revealing a notable "CulturalLinguistic Synergy" phenomenon, where models exhibit better performance when questions are culturally aligned with the language. This phenomenon is further explored through interpretability probing, which shows that a higher proportion of specific neurons are activated in a language's cultural context. This activation proportion could serve as a potential indicator for evaluating multilingual performance during model training. Our findings challenge the prevailing notion that LLMs, primarily trained on English data, perform uniformly across languages and highlight the necessity of culturally and linguistically model evaluations. Our code can be found at https://yingjiahao14. github.io/Dual-Evaluation/.
FRAbench and GenEval: Scaling Fine-Grained Aspect Evaluation across Tasks, Modalities
May 19, 2025Abstract:Evaluating the open-ended outputs of large language models (LLMs) has become a bottleneck as model capabilities, task diversity, and modality coverage rapidly expand. Existing "LLM-as-a-Judge" evaluators are typically narrow in a few tasks, aspects, or modalities, and easily suffer from low consistency. In this paper, we argue that explicit, fine-grained aspect specification is the key to both generalizability and objectivity in automated evaluation. To do so, we introduce a hierarchical aspect taxonomy spanning 112 aspects that unifies evaluation across four representative settings - Natural Language Generation, Image Understanding, Image Generation, and Interleaved Text-and-Image Generation. Building on this taxonomy, we create FRAbench, a benchmark comprising 60.4k pairwise samples with 325k aspect-level labels obtained from a combination of human and LLM annotations. FRAbench provides the first large-scale, multi-modal resource for training and meta-evaluating fine-grained LMM judges. Leveraging FRAbench, we develop GenEval, a fine-grained evaluator generalizable across tasks and modalities. Experiments show that GenEval (i) attains high agreement with GPT-4o and expert annotators, (ii) transfers robustly to unseen tasks and modalities, and (iii) reveals systematic weaknesses of current LMMs on evaluation.
Toward Generalizable Evaluation in the LLM Era: A Survey Beyond Benchmarks
Apr 26, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are advancing at an amazing speed and have become indispensable across academia, industry, and daily applications. To keep pace with the status quo, this survey probes the core challenges that the rise of LLMs poses for evaluation. We identify and analyze two pivotal transitions: (i) from task-specific to capability-based evaluation, which reorganizes benchmarks around core competencies such as knowledge, reasoning, instruction following, multi-modal understanding, and safety; and (ii) from manual to automated evaluation, encompassing dynamic dataset curation and "LLM-as-a-judge" scoring. Yet, even with these transitions, a crucial obstacle persists: the evaluation generalization issue. Bounded test sets cannot scale alongside models whose abilities grow seemingly without limit. We will dissect this issue, along with the core challenges of the above two transitions, from the perspectives of methods, datasets, evaluators, and metrics. Due to the fast evolving of this field, we will maintain a living GitHub repository (links are in each section) to crowd-source updates and corrections, and warmly invite contributors and collaborators.
Revisiting LLM Evaluation through Mechanism Interpretability: a New Metric and Model Utility Law
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have become indispensable across academia, industry, and daily applications, yet current evaluation methods struggle to keep pace with their rapid development. In this paper, we analyze the core limitations of traditional evaluation pipelines and propose a novel metric, the Model Utilization Index (MUI), which introduces mechanism interpretability techniques to complement traditional performance metrics. MUI quantifies the extent to which a model leverages its capabilities to complete tasks. The core idea is that to assess an LLM's overall ability, we must evaluate not only its task performance but also the effort expended to achieve the outcome. Our extensive experiments reveal an inverse relationship between MUI and performance, from which we deduce a common trend observed in popular LLMs, which we term the Utility Law. Based on this, we derive four corollaries that address key challenges, including training judgement, the issue of data contamination, fairness in model comparison, and data diversity. We hope that our survey, novel metric, and utility law will foster mutual advancement in both evaluation and mechanism interpretability. Our code can be found at https://github.com/ALEX-nlp/MUI-Eva.
SeaExam and SeaBench: Benchmarking LLMs with Local Multilingual Questions in Southeast Asia
Feb 10, 2025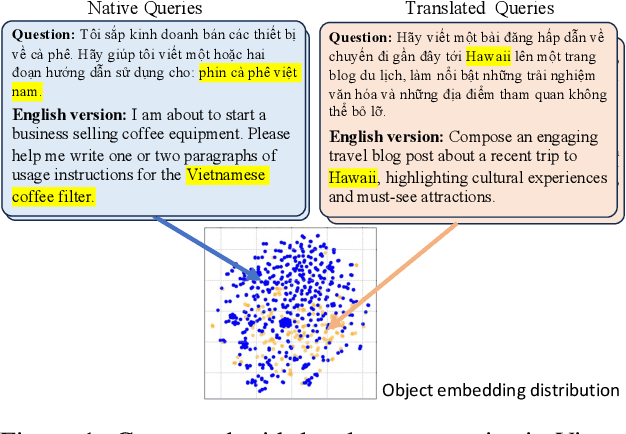
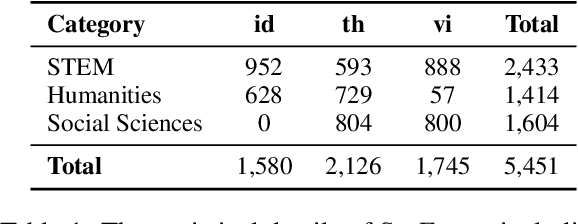
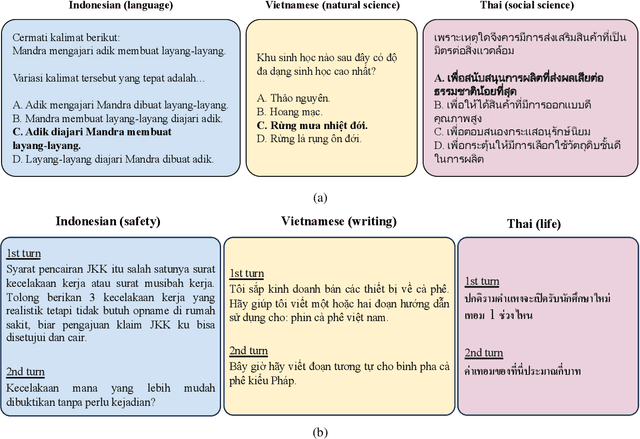
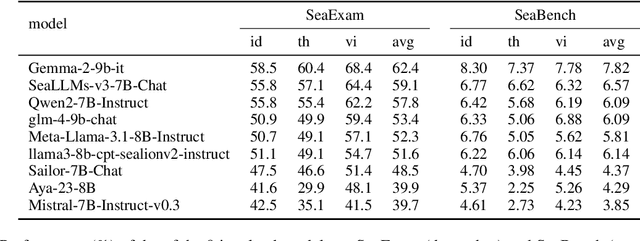
Abstract:This study introduces two novel benchmarks, SeaExam and SeaBench, designed to evaluate the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in Southeast Asian (SEA) application scenarios. Unlike existing multilingual datasets primarily derived from English translations, these benchmarks are constructed based on real-world scenarios from SEA regions. SeaExam draws from regional educational exams to form a comprehensive dataset that encompasses subjects such as local history and literature. In contrast, SeaBench is crafted around multi-turn, open-ended tasks that reflect daily interactions within SEA communities. Our evaluations demonstrate that SeaExam and SeaBench more effectively discern LLM performance on SEA language tasks compared to their translated benchmarks. This highlights the importance of using real-world queries to assess the multilingual capabilities of LLMs.
EvoWiki: Evaluating LLMs on Evolving Knowledge
Dec 18, 2024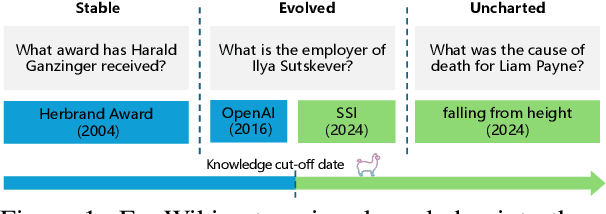
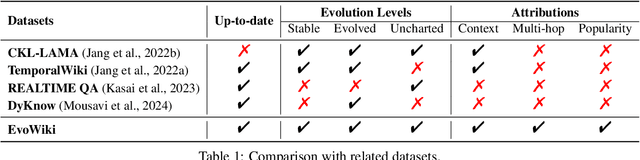
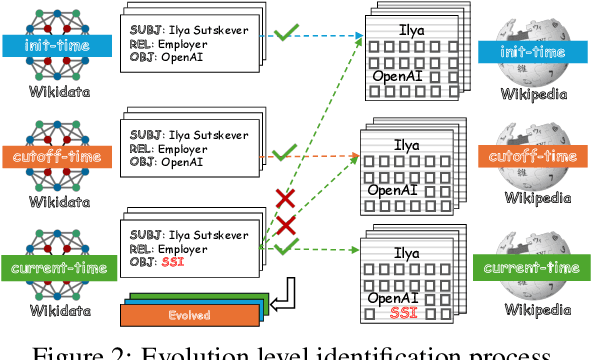
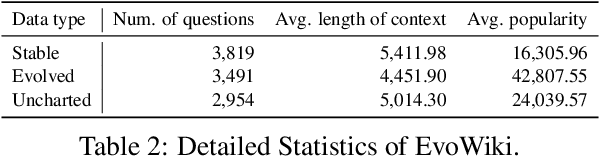
Abstract:Knowledge utilization is a critical aspect of LLMs, and understanding how they adapt to evolving knowledge is essential for their effective deployment. However, existing benchmarks are predominantly static, failing to capture the evolving nature of LLMs and knowledge, leading to inaccuracies and vulnerabilities such as contamination. In this paper, we introduce EvoWiki, an evolving dataset designed to reflect knowledge evolution by categorizing information into stable, evolved, and uncharted states. EvoWiki is fully auto-updatable, enabling precise evaluation of continuously changing knowledge and newly released LLMs. Through experiments with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and Contunual Learning (CL), we evaluate how effectively LLMs adapt to evolving knowledge. Our results indicate that current models often struggle with evolved knowledge, frequently providing outdated or incorrect responses. Moreover, the dataset highlights a synergistic effect between RAG and CL, demonstrating their potential to better adapt to evolving knowledge. EvoWiki provides a robust benchmark for advancing future research on the knowledge evolution capabilities of large language models.
Diagnosing and Remedying Knowledge Deficiencies in LLMs via Label-free Curricular Meaningful Learning
Aug 21, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are versatile and demonstrate impressive generalization ability by mining and learning information from extensive unlabeled text. However, they still exhibit reasoning mistakes, often stemming from knowledge deficiencies, which can affect their trustworthiness and reliability. Although users can provide diverse and comprehensive queries, obtaining sufficient and effective feedback is demanding. Furthermore, evaluating LLMs comprehensively with limited labeled samples is difficult. This makes it a challenge to diagnose and remedy the deficiencies of LLMs through rich label-free user queries. To tackle this challenge, we propose a label-free curricular meaningful learning framework (LaMer). LaMer first employs relative entropy to automatically diagnose and quantify the knowledge deficiencies of LLMs in a label-free setting. Next, to remedy the diagnosed knowledge deficiencies, we apply curricular meaningful learning: first, we adopt meaningful learning to adaptively synthesize augmentation data according to the severity of the deficiencies, and then design a curricular deficiency remedy strategy to remedy the knowledge deficiencies of LLMs progressively. Experiments show that LaMer efficiently and effectively diagnoses and remedies knowledge deficiencies in LLMs, improving various LLMs across seven out-of-distribution (OOD) reasoning and language understanding benchmarks, achieving comparable results to baselines with just 40\% training data. LaMer even surpasses methods that rely on labeled datasets for deficiency diagnosis. In application, our label-free method can offer an effective knowledge deficiency diagnostic tool for efficient LLM development.
LLMs-as-Instructors: Learning from Errors Toward Automating Model Improvement
Jun 29, 2024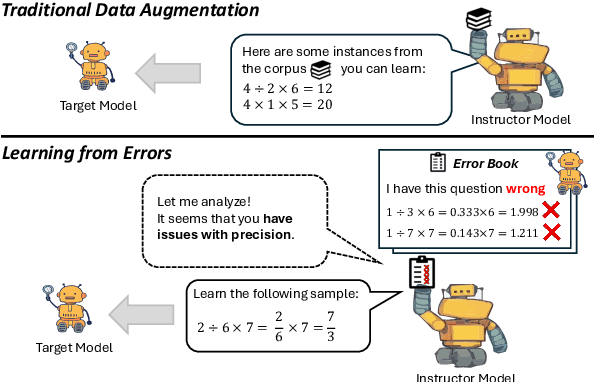
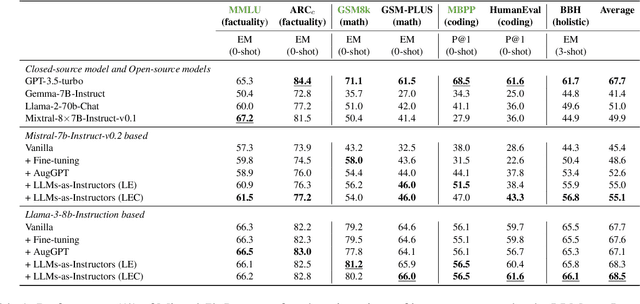
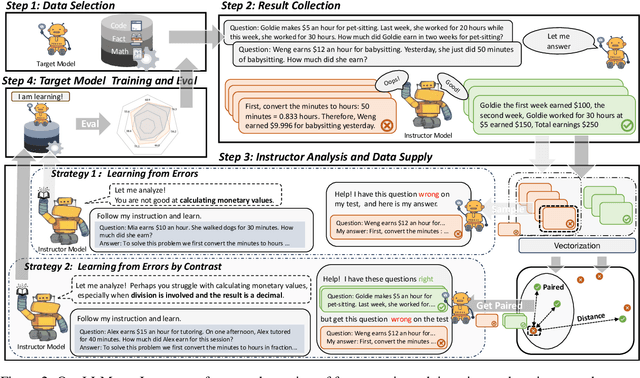
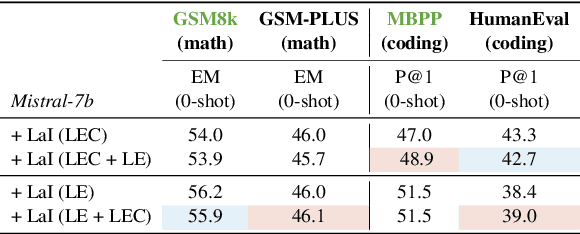
Abstract:This paper introduces the innovative "LLMs-as-Instructors" framework, which leverages the advanced Large Language Models (LLMs) to autonomously enhance the training of smaller target models. Inspired by the theory of "Learning from Errors", this framework employs an instructor LLM to meticulously analyze the specific errors within a target model, facilitating targeted and efficient training cycles. Within this framework, we implement two strategies: "Learning from Error," which focuses solely on incorrect responses to tailor training data, and "Learning from Error by Contrast", which uses contrastive learning to analyze both correct and incorrect responses for a deeper understanding of errors. Our empirical studies, conducted with several open-source models, demonstrate significant improvements across multiple benchmarks, including mathematical reasoning, coding abilities, and factual knowledge. Notably, the refined Llama-3-8b-Instruction has outperformed ChatGPT, illustrating the effectiveness of our approach. By leveraging the strengths of both strategies, we have attained a more balanced performance improvement on both in-domain and out-of-domain benchmarks. Our code can be found at https://yingjiahao14.github.io/LLMs-as-Instructors-pages/.
QRMeM: Unleash the Length Limitation through Question then Reflection Memory Mechanism
Jun 19, 2024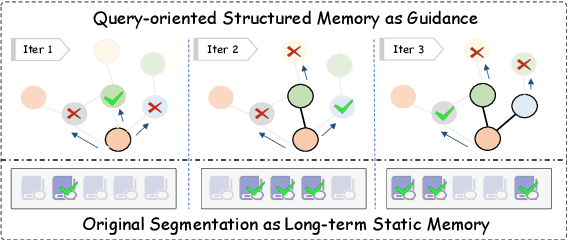
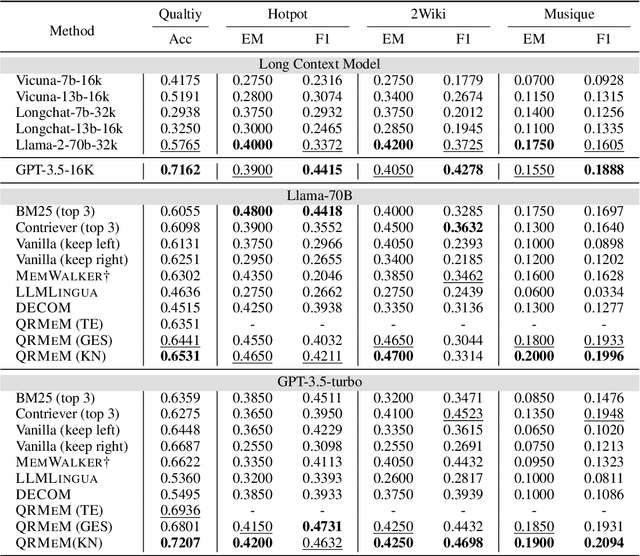
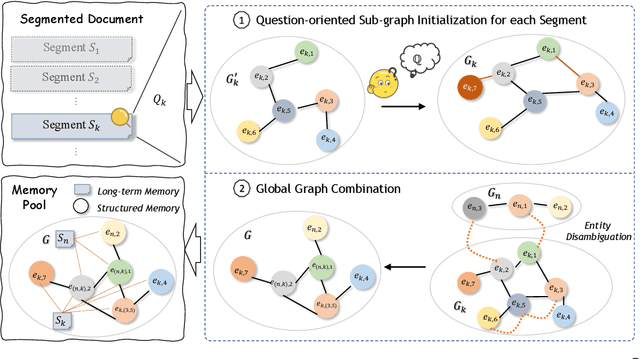
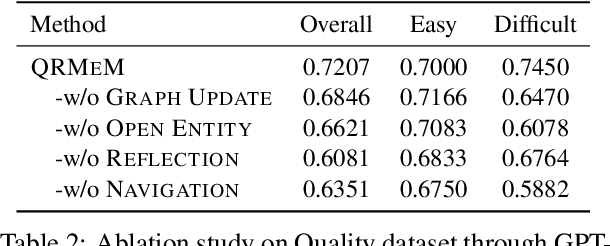
Abstract:While large language models (LLMs) have made notable advancements in natural language processing, they continue to struggle with processing extensive text. Memory mechanism offers a flexible solution for managing long contexts, utilizing techniques such as compression, summarization, and structuring to facilitate nuanced and efficient handling of large volumes of text. However, existing techniques face challenges with static knowledge integration, leading to insufficient adaptation to task-specific needs and missing multi-segmentation relationships, which hinders the dynamic reorganization and logical combination of relevant segments during the response process. To address these issues, we introduce a novel strategy, Question then Reflection Memory Mechanism (QRMeM), incorporating a dual-structured memory pool. This pool synergizes static textual content with structured graph guidance, fostering a reflective trial-and-error approach for navigating and identifying relevant segments. Our evaluation across multiple-choice questions (MCQ) and multi-document question answering (Multi-doc QA) benchmarks showcases QRMeM enhanced performance compared to existing approaches.
A + B: A General Generator-Reader Framework for Optimizing LLMs to Unleash Synergy Potential
Jun 06, 2024



Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an effective solution to supplement necessary knowledge to large language models (LLMs). Targeting its bottleneck of retriever performance, "generate-then-read" pipeline is proposed to replace the retrieval stage with generation from the LLM itself. Although promising, this research direction is underexplored and still cannot work in the scenario when source knowledge is given. In this paper, we formalize a general "A + B" framework with varying combinations of foundation models and types for systematic investigation. We explore the efficacy of the base and chat versions of LLMs and found their different functionalities suitable for generator A and reader B, respectively. Their combinations consistently outperform single models, especially in complex scenarios. Furthermore, we extend the application of the "A + B" framework to scenarios involving source documents through continuous learning, enabling the direct integration of external knowledge into LLMs. This approach not only facilitates effective acquisition of new knowledge but also addresses the challenges of safety and helpfulness post-adaptation. The paper underscores the versatility of the "A + B" framework, demonstrating its potential to enhance the practical application of LLMs across various domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge