Wenhang Ge
CamPilot: Improving Camera Control in Video Diffusion Model with Efficient Camera Reward Feedback
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in camera-controlled video diffusion models have significantly improved video-camera alignment. However, the camera controllability still remains limited. In this work, we build upon Reward Feedback Learning and aim to further improve camera controllability. However, directly borrowing existing ReFL approaches faces several challenges. First, current reward models lack the capacity to assess video-camera alignment. Second, decoding latent into RGB videos for reward computation introduces substantial computational overhead. Third, 3D geometric information is typically neglected during video decoding. To address these limitations, we introduce an efficient camera-aware 3D decoder that decodes video latent into 3D representations for reward quantization. Specifically, video latent along with the camera pose are decoded into 3D Gaussians. In this process, the camera pose not only acts as input, but also serves as a projection parameter. Misalignment between the video latent and camera pose will cause geometric distortions in the 3D structure, resulting in blurry renderings. Based on this property, we explicitly optimize pixel-level consistency between the rendered novel views and ground-truth ones as reward. To accommodate the stochastic nature, we further introduce a visibility term that selectively supervises only deterministic regions derived via geometric warping. Extensive experiments conducted on RealEstate10K and WorldScore benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method. Project page: \href{https://a-bigbao.github.io/CamPilot/}{CamPilot Page}.
A Mechanistic View on Video Generation as World Models: State and Dynamics
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Large-scale video generation models have demonstrated emergent physical coherence, positioning them as potential world models. However, a gap remains between contemporary "stateless" video architectures and classic state-centric world model theories. This work bridges this gap by proposing a novel taxonomy centered on two pillars: State Construction and Dynamics Modeling. We categorize state construction into implicit paradigms (context management) and explicit paradigms (latent compression), while dynamics modeling is analyzed through knowledge integration and architectural reformulation. Furthermore, we advocate for a transition in evaluation from visual fidelity to functional benchmarks, testing physical persistence and causal reasoning. We conclude by identifying two critical frontiers: enhancing persistence via data-driven memory and compressed fidelity, and advancing causality through latent factor decoupling and reasoning-prior integration. By addressing these challenges, the field can evolve from generating visually plausible videos to building robust, general-purpose world simulators.
StereoPilot: Learning Unified and Efficient Stereo Conversion via Generative Priors
Dec 18, 2025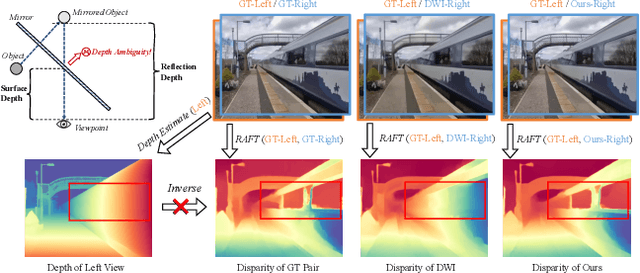
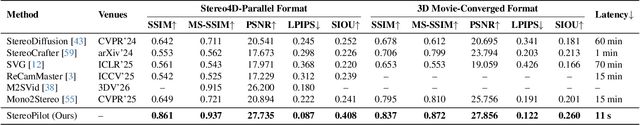
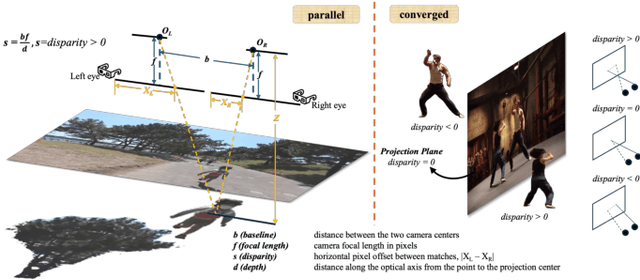

Abstract:The rapid growth of stereoscopic displays, including VR headsets and 3D cinemas, has led to increasing demand for high-quality stereo video content. However, producing 3D videos remains costly and complex, while automatic Monocular-to-Stereo conversion is hindered by the limitations of the multi-stage ``Depth-Warp-Inpaint'' (DWI) pipeline. This paradigm suffers from error propagation, depth ambiguity, and format inconsistency between parallel and converged stereo configurations. To address these challenges, we introduce UniStereo, the first large-scale unified dataset for stereo video conversion, covering both stereo formats to enable fair benchmarking and robust model training. Building upon this dataset, we propose StereoPilot, an efficient feed-forward model that directly synthesizes the target view without relying on explicit depth maps or iterative diffusion sampling. Equipped with a learnable domain switcher and a cycle consistency loss, StereoPilot adapts seamlessly to different stereo formats and achieves improved consistency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that StereoPilot significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both visual fidelity and computational efficiency. Project page: https://hit-perfect.github.io/StereoPilot/.
Matrix-3D: Omnidirectional Explorable 3D World Generation
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Explorable 3D world generation from a single image or text prompt forms a cornerstone of spatial intelligence. Recent works utilize video model to achieve wide-scope and generalizable 3D world generation. However, existing approaches often suffer from a limited scope in the generated scenes. In this work, we propose Matrix-3D, a framework that utilize panoramic representation for wide-coverage omnidirectional explorable 3D world generation that combines conditional video generation and panoramic 3D reconstruction. We first train a trajectory-guided panoramic video diffusion model that employs scene mesh renders as condition, to enable high-quality and geometrically consistent scene video generation. To lift the panorama scene video to 3D world, we propose two separate methods: (1) a feed-forward large panorama reconstruction model for rapid 3D scene reconstruction and (2) an optimization-based pipeline for accurate and detailed 3D scene reconstruction. To facilitate effective training, we also introduce the Matrix-Pano dataset, the first large-scale synthetic collection comprising 116K high-quality static panoramic video sequences with depth and trajectory annotations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed framework achieves state-of-the-art performance in panoramic video generation and 3D world generation. See more in https://matrix-3d.github.io.
DiMeR: Disentangled Mesh Reconstruction Model
Apr 24, 2025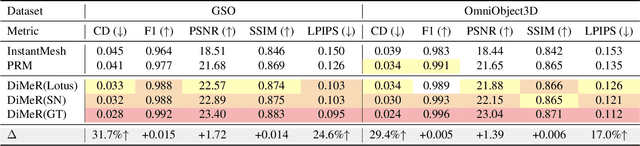
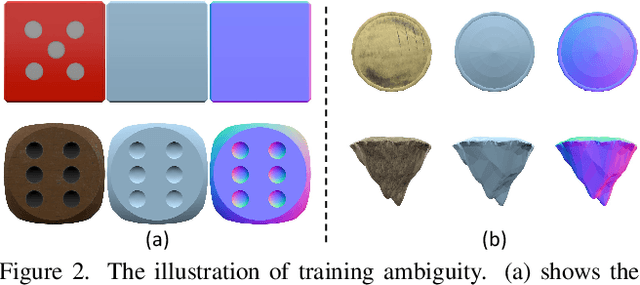
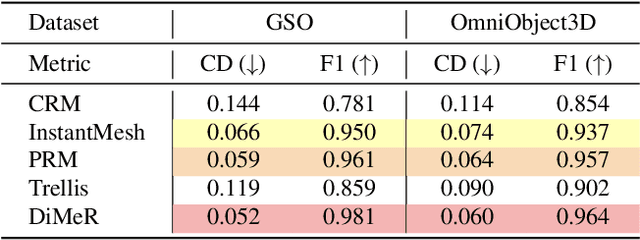
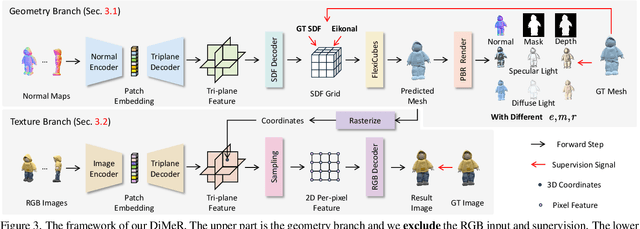
Abstract:With the advent of large-scale 3D datasets, feed-forward 3D generative models, such as the Large Reconstruction Model (LRM), have gained significant attention and achieved remarkable success. However, we observe that RGB images often lead to conflicting training objectives and lack the necessary clarity for geometry reconstruction. In this paper, we revisit the inductive biases associated with mesh reconstruction and introduce DiMeR, a novel disentangled dual-stream feed-forward model for sparse-view mesh reconstruction. The key idea is to disentangle both the input and framework into geometry and texture parts, thereby reducing the training difficulty for each part according to the Principle of Occam's Razor. Given that normal maps are strictly consistent with geometry and accurately capture surface variations, we utilize normal maps as exclusive input for the geometry branch to reduce the complexity between the network's input and output. Moreover, we improve the mesh extraction algorithm to introduce 3D ground truth supervision. As for texture branch, we use RGB images as input to obtain the textured mesh. Overall, DiMeR demonstrates robust capabilities across various tasks, including sparse-view reconstruction, single-image-to-3D, and text-to-3D. Numerous experiments show that DiMeR significantly outperforms previous methods, achieving over 30% improvement in Chamfer Distance on the GSO and OmniObject3D dataset.
Uni-Renderer: Unifying Rendering and Inverse Rendering Via Dual Stream Diffusion
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Rendering and inverse rendering are pivotal tasks in both computer vision and graphics. The rendering equation is the core of the two tasks, as an ideal conditional distribution transfer function from intrinsic properties to RGB images. Despite achieving promising results of existing rendering methods, they merely approximate the ideal estimation for a specific scene and come with a high computational cost. Additionally, the inverse conditional distribution transfer is intractable due to the inherent ambiguity. To address these challenges, we propose a data-driven method that jointly models rendering and inverse rendering as two conditional generation tasks within a single diffusion framework. Inspired by UniDiffuser, we utilize two distinct time schedules to model both tasks, and with a tailored dual streaming module, we achieve cross-conditioning of two pre-trained diffusion models. This unified approach, named Uni-Renderer, allows the two processes to facilitate each other through a cycle-consistent constrain, mitigating ambiguity by enforcing consistency between intrinsic properties and rendered images. Combined with a meticulously prepared dataset, our method effectively decomposition of intrinsic properties and demonstrates a strong capability to recognize changes during rendering. We will open-source our training and inference code to the public, fostering further research and development in this area.
GaussianProperty: Integrating Physical Properties to 3D Gaussians with LMMs
Dec 15, 2024Abstract:Estimating physical properties for visual data is a crucial task in computer vision, graphics, and robotics, underpinning applications such as augmented reality, physical simulation, and robotic grasping. However, this area remains under-explored due to the inherent ambiguities in physical property estimation. To address these challenges, we introduce GaussianProperty, a training-free framework that assigns physical properties of materials to 3D Gaussians. Specifically, we integrate the segmentation capability of SAM with the recognition capability of GPT-4V(ision) to formulate a global-local physical property reasoning module for 2D images. Then we project the physical properties from multi-view 2D images to 3D Gaussians using a voting strategy. We demonstrate that 3D Gaussians with physical property annotations enable applications in physics-based dynamic simulation and robotic grasping. For physics-based dynamic simulation, we leverage the Material Point Method (MPM) for realistic dynamic simulation. For robot grasping, we develop a grasping force prediction strategy that estimates a safe force range required for object grasping based on the estimated physical properties. Extensive experiments on material segmentation, physics-based dynamic simulation, and robotic grasping validate the effectiveness of our proposed method, highlighting its crucial role in understanding physical properties from visual data. Online demo, code, more cases and annotated datasets are available on \href{https://Gaussian-Property.github.io}{this https URL}.
PRM: Photometric Stereo based Large Reconstruction Model
Dec 10, 2024Abstract:We propose PRM, a novel photometric stereo based large reconstruction model to reconstruct high-quality meshes with fine-grained local details. Unlike previous large reconstruction models that prepare images under fixed and simple lighting as both input and supervision, PRM renders photometric stereo images by varying materials and lighting for the purposes, which not only improves the precise local details by providing rich photometric cues but also increases the model robustness to variations in the appearance of input images. To offer enhanced flexibility of images rendering, we incorporate a real-time physically-based rendering (PBR) method and mesh rasterization for online images rendering. Moreover, in employing an explicit mesh as our 3D representation, PRM ensures the application of differentiable PBR, which supports the utilization of multiple photometric supervisions and better models the specular color for high-quality geometry optimization. Our PRM leverages photometric stereo images to achieve high-quality reconstructions with fine-grained local details, even amidst sophisticated image appearances. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PRM significantly outperforms other models.
FlexGen: Flexible Multi-View Generation from Text and Image Inputs
Oct 14, 2024Abstract:In this work, we introduce FlexGen, a flexible framework designed to generate controllable and consistent multi-view images, conditioned on a single-view image, or a text prompt, or both. FlexGen tackles the challenges of controllable multi-view synthesis through additional conditioning on 3D-aware text annotations. We utilize the strong reasoning capabilities of GPT-4V to generate 3D-aware text annotations. By analyzing four orthogonal views of an object arranged as tiled multi-view images, GPT-4V can produce text annotations that include 3D-aware information with spatial relationship. By integrating the control signal with proposed adaptive dual-control module, our model can generate multi-view images that correspond to the specified text. FlexGen supports multiple controllable capabilities, allowing users to modify text prompts to generate reasonable and corresponding unseen parts. Additionally, users can influence attributes such as appearance and material properties, including metallic and roughness. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach offers enhanced multiple controllability, marking a significant advancement over existing multi-view diffusion models. This work has substantial implications for fields requiring rapid and flexible 3D content creation, including game development, animation, and virtual reality. Project page: https://xxu068.github.io/flexgen.github.io/.
LLM-Optic: Unveiling the Capabilities of Large Language Models for Universal Visual Grounding
May 28, 2024Abstract:Visual grounding is an essential tool that links user-provided text queries with query-specific regions within an image. Despite advancements in visual grounding models, their ability to comprehend complex queries remains limited. To overcome this limitation, we introduce LLM-Optic, an innovative method that utilizes Large Language Models (LLMs) as an optical lens to enhance existing visual grounding models in comprehending complex text queries involving intricate text structures, multiple objects, or object spatial relationships, situations that current models struggle with. LLM-Optic first employs an LLM as a Text Grounder to interpret complex text queries and accurately identify objects the user intends to locate. Then a pre-trained visual grounding model is used to generate candidate bounding boxes given the refined query by the Text Grounder. After that, LLM-Optic annotates the candidate bounding boxes with numerical marks to establish a connection between text and specific image regions, thereby linking two distinct modalities. Finally, it employs a Large Multimodal Model (LMM) as a Visual Grounder to select the marked candidate objects that best correspond to the original text query. Through LLM-Optic, we have achieved universal visual grounding, which allows for the detection of arbitrary objects specified by arbitrary human language input. Importantly, our method achieves this enhancement without requiring additional training or fine-tuning. Extensive experiments across various challenging benchmarks demonstrate that LLM-Optic achieves state-of-the-art zero-shot visual grounding capabilities. Project Page: https://haoyu-zhao.github.io/LLM-Optic.github.io/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge