Ancong Wu
Progressive Human Motion Generation Based on Text and Few Motion Frames
Mar 17, 2025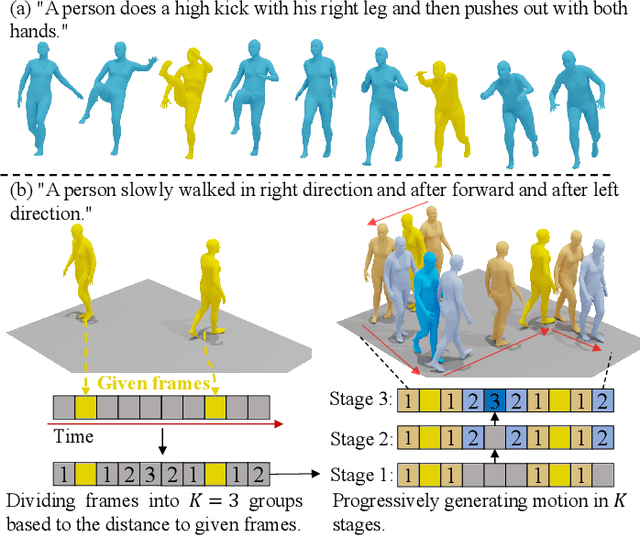



Abstract:Although existing text-to-motion (T2M) methods can produce realistic human motion from text description, it is still difficult to align the generated motion with the desired postures since using text alone is insufficient for precisely describing diverse postures. To achieve more controllable generation, an intuitive way is to allow the user to input a few motion frames describing precise desired postures. Thus, we explore a new Text-Frame-to-Motion (TF2M) generation task that aims to generate motions from text and very few given frames. Intuitively, the closer a frame is to a given frame, the lower the uncertainty of this frame is when conditioned on this given frame. Hence, we propose a novel Progressive Motion Generation (PMG) method to progressively generate a motion from the frames with low uncertainty to those with high uncertainty in multiple stages. During each stage, new frames are generated by a Text-Frame Guided Generator conditioned on frame-aware semantics of the text, given frames, and frames generated in previous stages. Additionally, to alleviate the train-test gap caused by multi-stage accumulation of incorrectly generated frames during testing, we propose a Pseudo-frame Replacement Strategy for training. Experimental results show that our PMG outperforms existing T2M generation methods by a large margin with even one given frame, validating the effectiveness of our PMG. Code will be released.
MaintaAvatar: A Maintainable Avatar Based on Neural Radiance Fields by Continual Learning
Feb 04, 2025



Abstract:The generation of a virtual digital avatar is a crucial research topic in the field of computer vision. Many existing works utilize Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) to address this issue and have achieved impressive results. However, previous works assume the images of the training person are available and fixed while the appearances and poses of a subject could constantly change and increase in real-world scenarios. How to update the human avatar but also maintain the ability to render the old appearance of the person is a practical challenge. One trivial solution is to combine the existing virtual avatar models based on NeRF with continual learning methods. However, there are some critical issues in this approach: learning new appearances and poses can cause the model to forget past information, which in turn leads to a degradation in the rendering quality of past appearances, especially color bleeding issues, and incorrect human body poses. In this work, we propose a maintainable avatar (MaintaAvatar) based on neural radiance fields by continual learning, which resolves the issues by utilizing a Global-Local Joint Storage Module and a Pose Distillation Module. Overall, our model requires only limited data collection to quickly fine-tune the model while avoiding catastrophic forgetting, thus achieving a maintainable virtual avatar. The experimental results validate the effectiveness of our MaintaAvatar model.
PixelFade: Privacy-preserving Person Re-identification with Noise-guided Progressive Replacement
Aug 10, 2024Abstract:Online person re-identification services face privacy breaches from potential data leakage and recovery attacks, exposing cloud-stored images to malicious attackers and triggering public concern. The privacy protection of pedestrian images is crucial. Previous privacy-preserving person re-identification methods are unable to resist recovery attacks and compromise accuracy. In this paper, we propose an iterative method (PixelFade) to optimize pedestrian images into noise-like images to resist recovery attacks. We first give an in-depth study of protected images from previous privacy methods, which reveal that the chaos of protected images can disrupt the learning of recovery models. Accordingly, Specifically, we propose Noise-guided Objective Function with the feature constraints of a specific authorization model, optimizing pedestrian images to normal-distributed noise images while preserving their original identity information as per the authorization model. To solve the above non-convex optimization problem, we propose a heuristic optimization algorithm that alternately performs the Constraint Operation and the Partial Replacement Operation. This strategy not only safeguards that original pixels are replaced with noises to protect privacy, but also guides the images towards an improved optimization direction to effectively preserve discriminative features. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our PixelFade outperforms previous methods in resisting recovery attacks and Re-ID performance. The code is available at https://github.com/iSEE-Laboratory/PixelFade.
Bridge Past and Future: Overcoming Information Asymmetry in Incremental Object Detection
Jul 16, 2024



Abstract:In incremental object detection, knowledge distillation has been proven to be an effective way to alleviate catastrophic forgetting. However, previous works focused on preserving the knowledge of old models, ignoring that images could simultaneously contain categories from past, present, and future stages. The co-occurrence of objects makes the optimization objectives inconsistent across different stages since the definition for foreground objects differs across various stages, which limits the model's performance greatly. To overcome this problem, we propose a method called ``Bridge Past and Future'' (BPF), which aligns models across stages, ensuring consistent optimization directions. In addition, we propose a novel Distillation with Future (DwF) loss, fully leveraging the background probability to mitigate the forgetting of old classes while ensuring a high level of adaptability in learning new classes. Extensive experiments are conducted on both Pascal VOC and MS COCO benchmarks. Without memory, BPF outperforms current state-of-the-art methods under various settings. The code is available at https://github.com/iSEE-Laboratory/BPF.
DreamView: Injecting View-specific Text Guidance into Text-to-3D Generation
Apr 09, 2024



Abstract:Text-to-3D generation, which synthesizes 3D assets according to an overall text description, has significantly progressed. However, a challenge arises when the specific appearances need customizing at designated viewpoints but referring solely to the overall description for generating 3D objects. For instance, ambiguity easily occurs when producing a T-shirt with distinct patterns on its front and back using a single overall text guidance. In this work, we propose DreamView, a text-to-image approach enabling multi-view customization while maintaining overall consistency by adaptively injecting the view-specific and overall text guidance through a collaborative text guidance injection module, which can also be lifted to 3D generation via score distillation sampling. DreamView is trained with large-scale rendered multi-view images and their corresponding view-specific texts to learn to balance the separate content manipulation in each view and the global consistency of the overall object, resulting in a dual achievement of customization and consistency. Consequently, DreamView empowers artists to design 3D objects creatively, fostering the creation of more innovative and diverse 3D assets. Code and model will be released at https://github.com/iSEE-Laboratory/DreamView.
Shape-Erased Feature Learning for Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification
Apr 09, 2023Abstract:Due to the modality gap between visible and infrared images with high visual ambiguity, learning \textbf{diverse} modality-shared semantic concepts for visible-infrared person re-identification (VI-ReID) remains a challenging problem. Body shape is one of the significant modality-shared cues for VI-ReID. To dig more diverse modality-shared cues, we expect that erasing body-shape-related semantic concepts in the learned features can force the ReID model to extract more and other modality-shared features for identification. To this end, we propose shape-erased feature learning paradigm that decorrelates modality-shared features in two orthogonal subspaces. Jointly learning shape-related feature in one subspace and shape-erased features in the orthogonal complement achieves a conditional mutual information maximization between shape-erased feature and identity discarding body shape information, thus enhancing the diversity of the learned representation explicitly. Extensive experiments on SYSU-MM01, RegDB, and HITSZ-VCM datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
Text-Adaptive Multiple Visual Prototype Matching for Video-Text Retrieval
Sep 27, 2022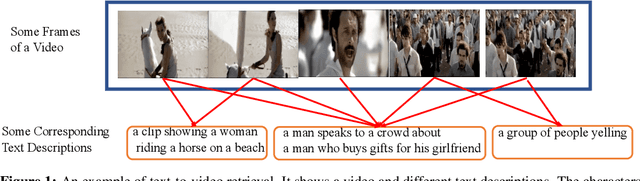
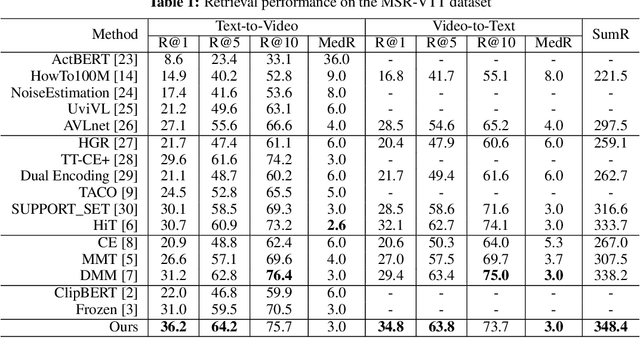
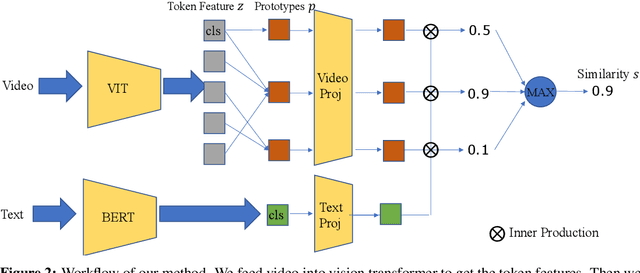
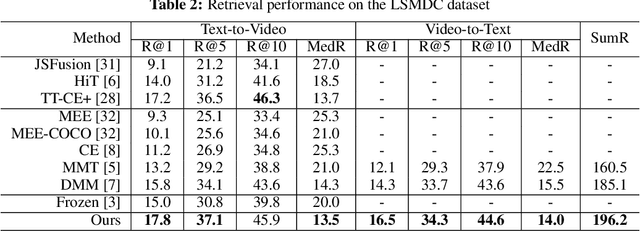
Abstract:Cross-modal retrieval between videos and texts has gained increasing research interest due to the rapid emergence of videos on the web. Generally, a video contains rich instance and event information and the query text only describes a part of the information. Thus, a video can correspond to multiple different text descriptions and queries. We call this phenomenon the ``Video-Text Correspondence Ambiguity'' problem. Current techniques mostly concentrate on mining local or multi-level alignment between contents of a video and text (\textit{e.g.}, object to entity and action to verb). It is difficult for these methods to alleviate the video-text correspondence ambiguity by describing a video using only one single feature, which is required to be matched with multiple different text features at the same time. To address this problem, we propose a Text-Adaptive Multiple Visual Prototype Matching model, which automatically captures multiple prototypes to describe a video by adaptive aggregation of video token features. Given a query text, the similarity is determined by the most similar prototype to find correspondence in the video, which is termed text-adaptive matching. To learn diverse prototypes for representing the rich information in videos, we propose a variance loss to encourage different prototypes to attend to different contents of the video. Our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods on four public video retrieval datasets.
* NIPS2022
Camera-Conditioned Stable Feature Generation for Isolated Camera Supervised Person Re-IDentification
Apr 04, 2022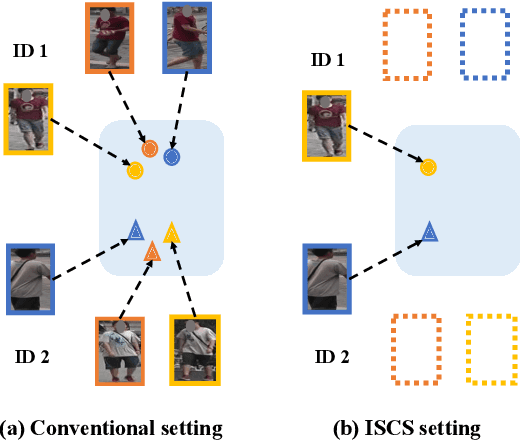
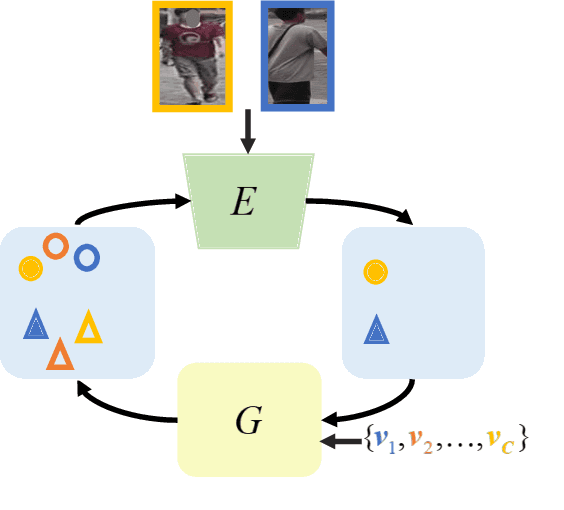
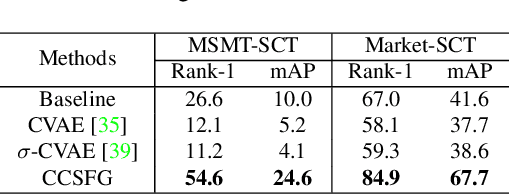
Abstract:To learn camera-view invariant features for person Re-IDentification (Re-ID), the cross-camera image pairs of each person play an important role. However, such cross-view training samples could be unavailable under the ISolated Camera Supervised (ISCS) setting, e.g., a surveillance system deployed across distant scenes. To handle this challenging problem, a new pipeline is introduced by synthesizing the cross-camera samples in the feature space for model training. Specifically, the feature encoder and generator are end-to-end optimized under a novel method, Camera-Conditioned Stable Feature Generation (CCSFG). Its joint learning procedure raises concern on the stability of generative model training. Therefore, a new feature generator, $\sigma$-Regularized Conditional Variational Autoencoder ($\sigma$-Reg.~CVAE), is proposed with theoretical and experimental analysis on its robustness. Extensive experiments on two ISCS person Re-ID datasets demonstrate the superiority of our CCSFG to the competitors.
Letter-level Online Writer Identification
Dec 06, 2021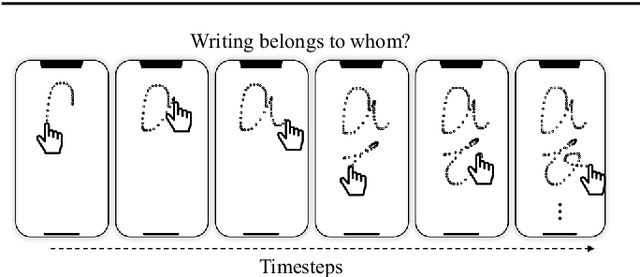
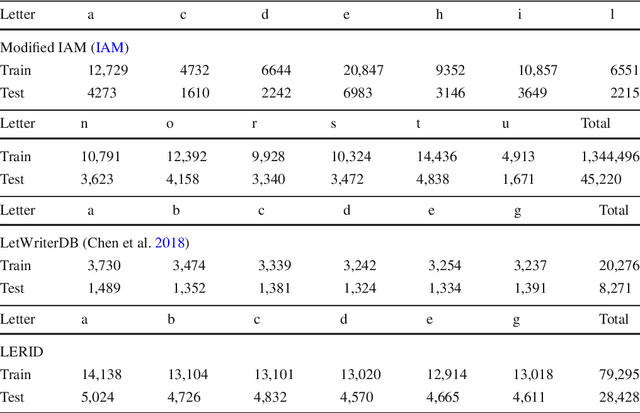
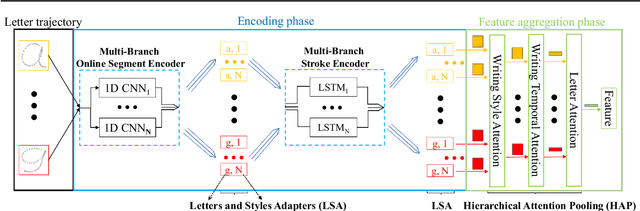
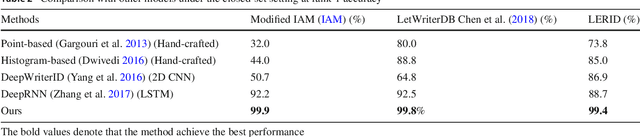
Abstract:Writer identification (writer-id), an important field in biometrics, aims to identify a writer by their handwriting. Identification in existing writer-id studies requires a complete document or text, limiting the scalability and flexibility of writer-id in realistic applications. To make the application of writer-id more practical (e.g., on mobile devices), we focus on a novel problem, letter-level online writer-id, which requires only a few trajectories of written letters as identification cues. Unlike text-\ document-based writer-id which has rich context for identification, there are much fewer clues to recognize an author from only a few single letters. A main challenge is that a person often writes a letter in different styles from time to time. We refer to this problem as the variance of online writing styles (Var-O-Styles). We address the Var-O-Styles in a capture-normalize-aggregate fashion: Firstly, we extract different features of a letter trajectory by a carefully designed multi-branch encoder, in an attempt to capture different online writing styles. Then we convert all these style features to a reference style feature domain by a novel normalization layer. Finally, we aggregate the normalized features by a hierarchical attention pooling (HAP), which fuses all the input letters with multiple writing styles into a compact feature vector. In addition, we also contribute a large-scale LEtter-level online wRiter IDentification dataset (LERID) for evaluation. Extensive comparative experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework.
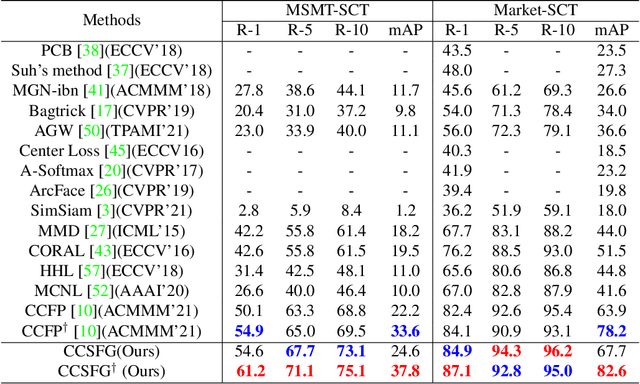
Cross-Camera Feature Prediction for Intra-Camera Supervised Person Re-identification across Distant Scenes
Jul 29, 2021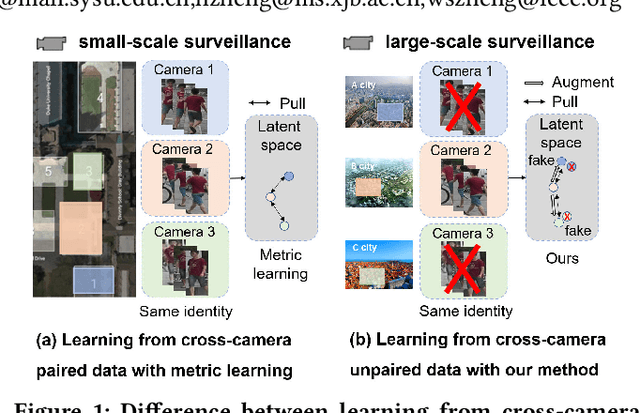
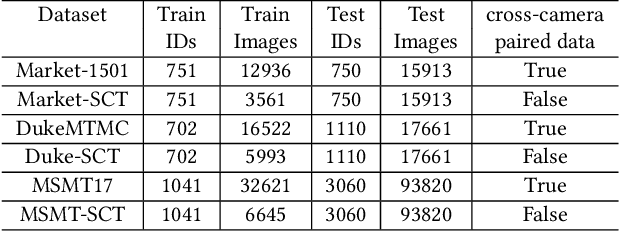
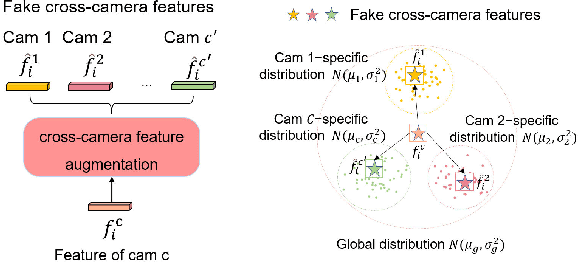
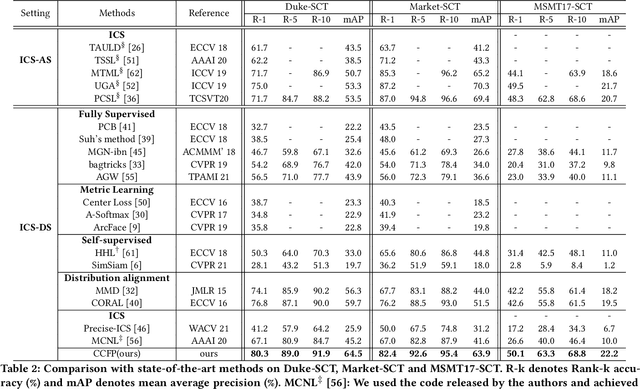
Abstract:Person re-identification (Re-ID) aims to match person images across non-overlapping camera views. The majority of Re-ID methods focus on small-scale surveillance systems in which each pedestrian is captured in different camera views of adjacent scenes. However, in large-scale surveillance systems that cover larger areas, it is required to track a pedestrian of interest across distant scenes (e.g., a criminal suspect escapes from one city to another). Since most pedestrians appear in limited local areas, it is difficult to collect training data with cross-camera pairs of the same person. In this work, we study intra-camera supervised person re-identification across distant scenes (ICS-DS Re-ID), which uses cross-camera unpaired data with intra-camera identity labels for training. It is challenging as cross-camera paired data plays a crucial role for learning camera-invariant features in most existing Re-ID methods. To learn camera-invariant representation from cross-camera unpaired training data, we propose a cross-camera feature prediction method to mine cross-camera self supervision information from camera-specific feature distribution by transforming fake cross-camera positive feature pairs and minimize the distances of the fake pairs. Furthermore, we automatically localize and extract local-level feature by a transformer. Joint learning of global-level and local-level features forms a global-local cross-camera feature prediction scheme for mining fine-grained cross-camera self supervision information. Finally, cross-camera self supervision and intra-camera supervision are aggregated in a framework. The experiments are conducted in the ICS-DS setting on Market-SCT, Duke-SCT and MSMT17-SCT datasets. The evaluation results demonstrate the superiority of our method, which gains significant improvements of 15.4 Rank-1 and 22.3 mAP on Market-SCT as compared to the second best method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge