Letter-level Online Writer Identification
Paper and Code
Dec 06, 2021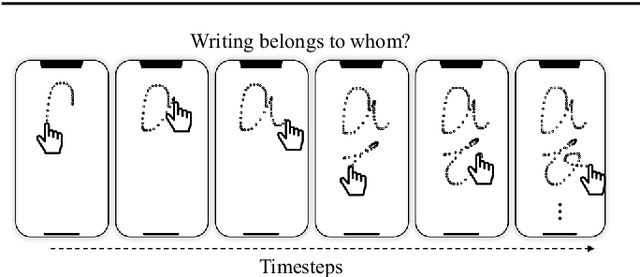
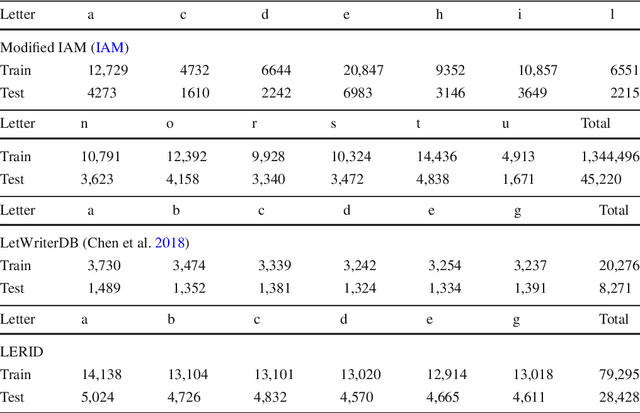
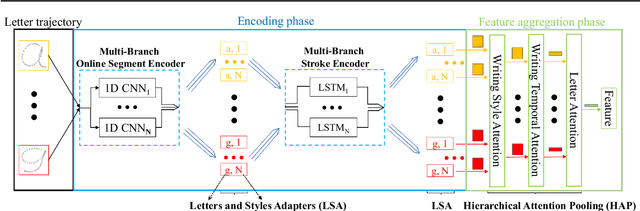
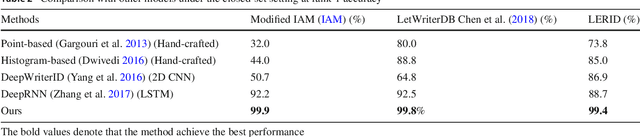
Writer identification (writer-id), an important field in biometrics, aims to identify a writer by their handwriting. Identification in existing writer-id studies requires a complete document or text, limiting the scalability and flexibility of writer-id in realistic applications. To make the application of writer-id more practical (e.g., on mobile devices), we focus on a novel problem, letter-level online writer-id, which requires only a few trajectories of written letters as identification cues. Unlike text-\ document-based writer-id which has rich context for identification, there are much fewer clues to recognize an author from only a few single letters. A main challenge is that a person often writes a letter in different styles from time to time. We refer to this problem as the variance of online writing styles (Var-O-Styles). We address the Var-O-Styles in a capture-normalize-aggregate fashion: Firstly, we extract different features of a letter trajectory by a carefully designed multi-branch encoder, in an attempt to capture different online writing styles. Then we convert all these style features to a reference style feature domain by a novel normalization layer. Finally, we aggregate the normalized features by a hierarchical attention pooling (HAP), which fuses all the input letters with multiple writing styles into a compact feature vector. In addition, we also contribute a large-scale LEtter-level online wRiter IDentification dataset (LERID) for evaluation. Extensive comparative experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge