Hongwei Zheng
Replacing Parameters with Preferences: Federated Alignment of Heterogeneous Vision-Language Models
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:VLMs have broad potential in privacy-sensitive domains such as healthcare and finance, yet strict data-sharing constraints render centralized training infeasible. FL mitigates this issue by enabling decentralized training, but practical deployments face challenges due to client heterogeneity in computational resources, application requirements, and model architectures. We argue that while replacing data with model parameters characterizes the present of FL, replacing parameters with preferences represents a more scalable and privacy-preserving future. Motivated by this perspective, we propose MoR, a federated alignment framework based on GRPO with Mixture-of-Rewards for heterogeneous VLMs. MoR initializes a visual foundation model as a KL-regularized reference, while each client locally trains a reward model from local preference annotations, capturing specific evaluation signals without exposing raw data. To reconcile heterogeneous rewards, we introduce a routing-based fusion mechanism that adaptively aggregates client reward signals. Finally, the server performs GRPO with this mixed reward to optimize the base VLM. Experiments on three public VQA benchmarks demonstrate that MoR consistently outperforms federated alignment baselines in generalization, robustness, and cross-client adaptability. Our approach provides a scalable solution for privacy-preserving alignment of heterogeneous VLMs under federated settings.
Stable-RAG: Mitigating Retrieval-Permutation-Induced Hallucinations in Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has become a key paradigm for reducing factual hallucinations in large language models (LLMs), yet little is known about how the order of retrieved documents affects model behavior. We empirically show that under Top-5 retrieval with the gold document included, LLM answers vary substantially across permutations of the retrieved set, even when the gold document is fixed in the first position. This reveals a previously underexplored sensitivity to retrieval permutations. Although robust RAG methods primarily focus on enhancing LLM robustness to low-quality retrieval and mitigating positional bias to distribute attention fairly over long contexts, neither approach directly addresses permutation sensitivity. In this paper, we propose Stable-RAG, which exploits permutation sensitivity estimation to mitigate permutation-induced hallucinations. Stable-RAG runs the generator under multiple retrieval orders, clusters hidden states, and decodes from a cluster-center representation that captures the dominant reasoning pattern. It then uses these reasoning results to align hallucinated outputs toward the correct answer, encouraging the model to produce consistent and accurate predictions across document permutations. Experiments on three QA datasets show that Stable-RAG significantly improves answer accuracy, reasoning consistency and robust generalization across datasets, retrievers, and input lengths compared with baselines.
CodeBC: A More Secure Large Language Model for Smart Contract Code Generation in Blockchain
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) excel at generating code from natural language instructions, yet they often lack an understanding of security vulnerabilities. This limitation makes it difficult for LLMs to avoid security risks in generated code, particularly in high-security programming tasks such as smart contract development for blockchain. Researchers have attempted to enhance the vulnerability awareness of these models by training them to differentiate between vulnerable and fixed code snippets. However, this approach relies heavily on manually labeled vulnerability data, which is only available for popular languages like Python and C++. For low-resource languages like Solidity, used in smart contracts, large-scale annotated datasets are scarce and difficult to obtain. To address this challenge, we introduce CodeBC, a code generation model specifically designed for generating secure smart contracts in blockchain. CodeBC employs a three-stage fine-tuning approach based on CodeLlama, distinguishing itself from previous methods by not relying on pairwise vulnerability location annotations. Instead, it leverages vulnerability and security tags to teach the model the differences between vulnerable and secure code. During the inference phase, the model leverages security tags to generate secure and robust code. Experimental results demonstrate that CodeBC outperforms baseline models in terms of BLEU, CodeBLEU, and compilation pass rates, while significantly reducing vulnerability rates. These findings validate the effectiveness and cost-efficiency of our three-stage fine-tuning strategy, making CodeBC a promising solution for generating secure smart contract code.
Learning to Erase Private Knowledge from Multi-Documents for Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Models
Apr 14, 2025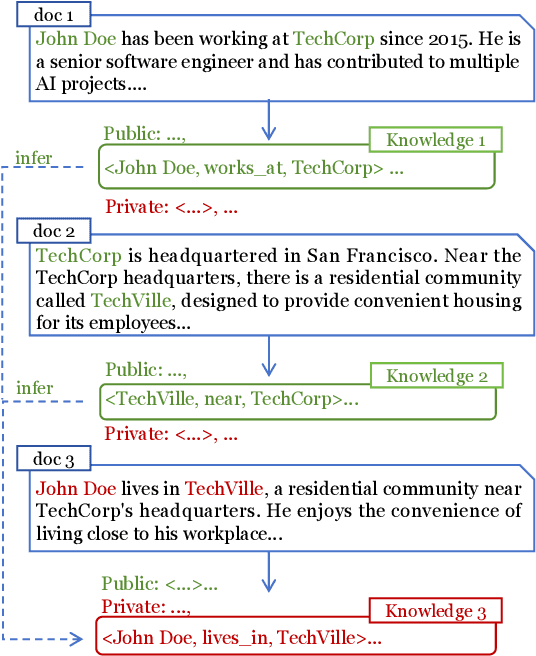



Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a promising technique for applying LLMs to proprietary domains. However, retrieved documents may contain sensitive knowledge, posing risks of privacy leakage in generative results. Thus, effectively erasing private information from retrieved documents is a key challenge for RAG. Unlike traditional text anonymization, RAG should consider: (1) the inherent multi-document reasoning may face de-anonymization attacks; (2) private knowledge varies by scenarios, so users should be allowed to customize which information to erase; (3) preserving sufficient publicly available knowledge for generation tasks. This paper introduces the privacy erasure task for RAG and proposes Eraser4RAG, a private knowledge eraser which effectively removes user-defined private knowledge from documents while preserving sufficient public knowledge for generation. Specifically, we first construct a global knowledge graph to identify potential knowledge across documents, aiming to defend against de-anonymization attacks. Then we randomly split it into private and public sub-graphs, and fine-tune Flan-T5 to rewrite the retrieved documents excluding private triples. Finally, PPO algorithm optimizes the rewriting model to minimize private triples and maximize public triples retention. Experiments on four QA datasets demonstrate that Eraser4RAG achieves superior erase performance than GPT-4o.
HiPART: Hierarchical Pose AutoRegressive Transformer for Occluded 3D Human Pose Estimation
Mar 30, 2025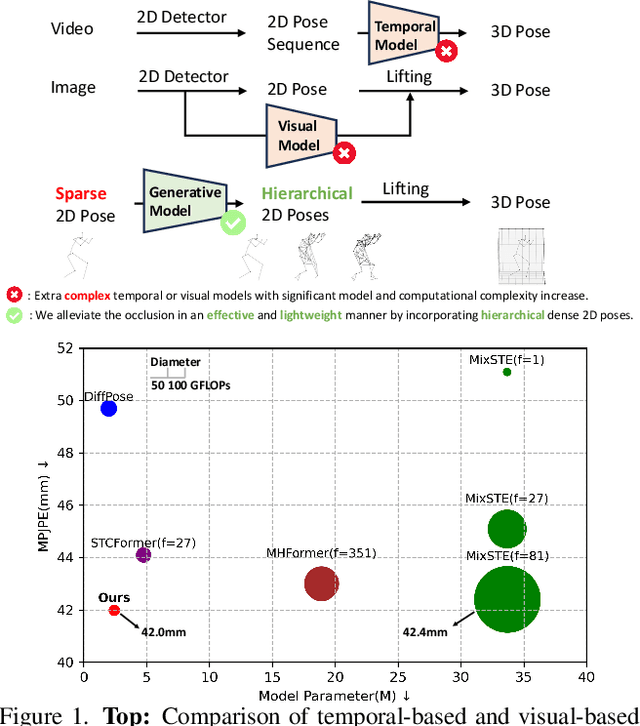
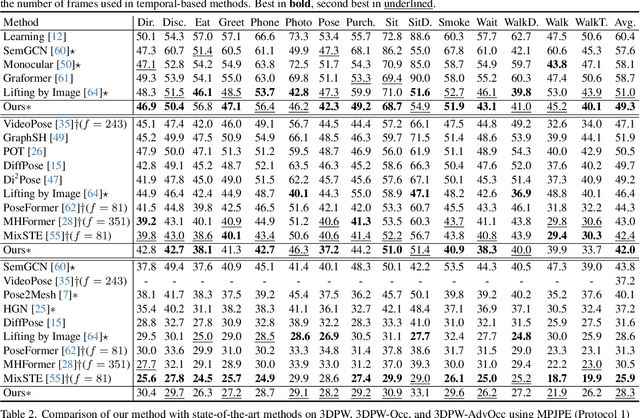
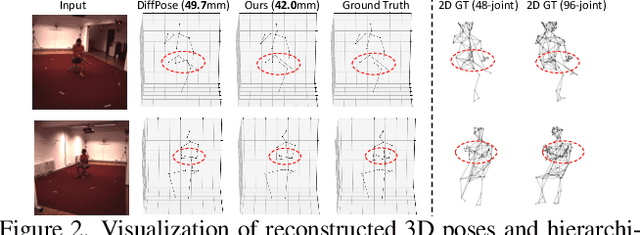
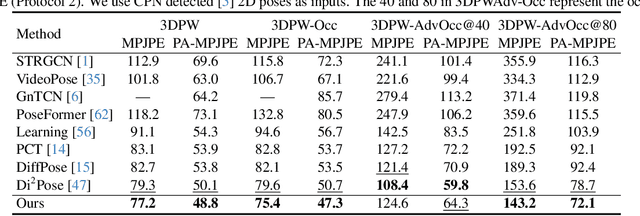
Abstract:Existing 2D-to-3D human pose estimation (HPE) methods struggle with the occlusion issue by enriching information like temporal and visual cues in the lifting stage. In this paper, we argue that these methods ignore the limitation of the sparse skeleton 2D input representation, which fundamentally restricts the 2D-to-3D lifting and worsens the occlusion issue. To address these, we propose a novel two-stage generative densification method, named Hierarchical Pose AutoRegressive Transformer (HiPART), to generate hierarchical 2D dense poses from the original sparse 2D pose. Specifically, we first develop a multi-scale skeleton tokenization module to quantize the highly dense 2D pose into hierarchical tokens and propose a Skeleton-aware Alignment to strengthen token connections. We then develop a Hierarchical AutoRegressive Modeling scheme for hierarchical 2D pose generation. With generated hierarchical poses as inputs for 2D-to-3D lifting, the proposed method shows strong robustness in occluded scenarios and achieves state-of-the-art performance on the single-frame-based 3D HPE. Moreover, it outperforms numerous multi-frame methods while reducing parameter and computational complexity and can also complement them to further enhance performance and robustness.
FineFilter: A Fine-grained Noise Filtering Mechanism for Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Models
Feb 18, 2025



Abstract:Retrieved documents containing noise will hinder Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) from detecting answer clues, necessitating noise filtering mechanisms to enhance accuracy. Existing methods use re-ranking or summarization to identify the most relevant sentences, but directly and accurately locating answer clues from these large-scale and complex documents remains challenging. Unlike these document-level operations, we treat noise filtering as a sentence-level MinMax optimization problem: first identifying the potential clues from multiple documents using contextual information, then ranking them by relevance, and finally retaining the least clues through truncation. In this paper, we propose FineFilter, a novel fine-grained noise filtering mechanism for RAG consisting of a clue extractor, a re-ranker, and a truncator. We optimize each module to tackle complex reasoning challenges: (1) Clue extractor firstly uses sentences containing the answer and similar ones as fine-tuned targets, aiming at extracting sufficient potential clues; (2) Re-ranker is trained to prioritize effective clues based on the real feedback from generation module, with clues capable of generating correct answer as positive samples and others as negative; (3) Truncator takes the minimum clues needed to answer the question (truncation point) as fine-tuned targets, and performs truncation on the re-ranked clues to achieve fine-grained noise filtering. Experiments on three QA datasets demonstrate that FineFilter significantly outperforms baselines in terms of performance and inference cost. Further analysis on each module shows the effectiveness of our optimizations for complex reasoning.
AdaComp: Extractive Context Compression with Adaptive Predictor for Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Models
Sep 03, 2024



Abstract:Retrieved documents containing noise will hinder RAG from detecting answer clues and make the inference process slow and expensive. Therefore, context compression is necessary to enhance its accuracy and efficiency. Existing context compression methods use extractive or generative models to retain the most query-relevant sentences or apply the information bottleneck theory to preserve sufficient information. However, these methods may face issues such as over-compression or high computational costs. We observe that the retriever often ranks relevant documents at the top, but the exact number of documents needed to answer the query is uncertain due to the impact of query complexity and retrieval quality: complex queries like multi-hop questions may require retaining more documents than simpler queries, and a low-quality retrieval may need to rely on more documents to generate accurate outputs. Therefore, determining the minimum number of required documents (compression rate) is still a challenge for RAG. In this paper, we introduce AdaComp, a low-cost extractive context compression method that adaptively determines the compression rate based on both query complexity and retrieval quality. Specifically, we first annotate the minimum top-k documents necessary for the RAG system to answer the current query as the compression rate and then construct triplets of the query, retrieved documents, and its compression rate. Then, we use this triplet dataset to train a compression-rate predictor. Experiments on three QA datasets and one conversational Muiti-doc QA dataset show that AdaComp significantly reduces inference costs while maintaining performance nearly identical to uncompressed models, achieving a balance between efficiency and performance.
MaFeRw: Query Rewriting with Multi-Aspect Feedbacks for Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Models
Aug 30, 2024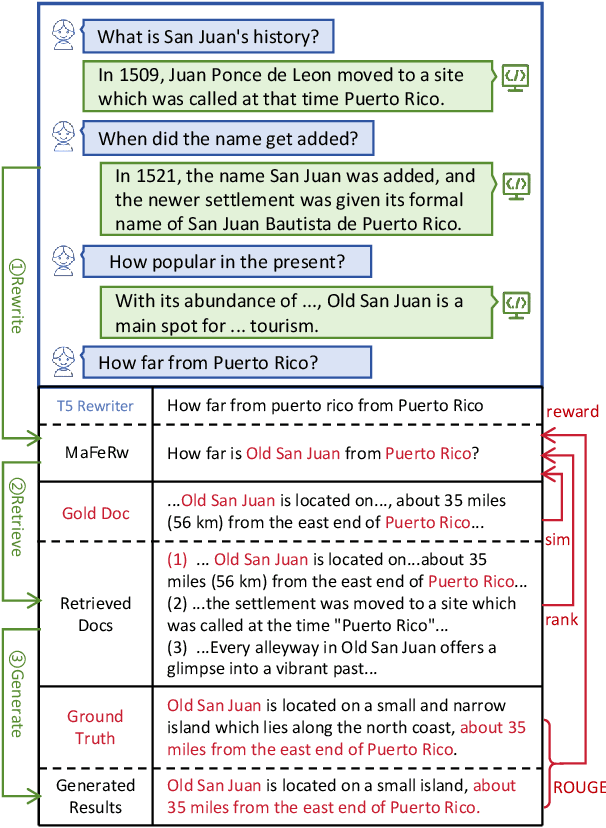

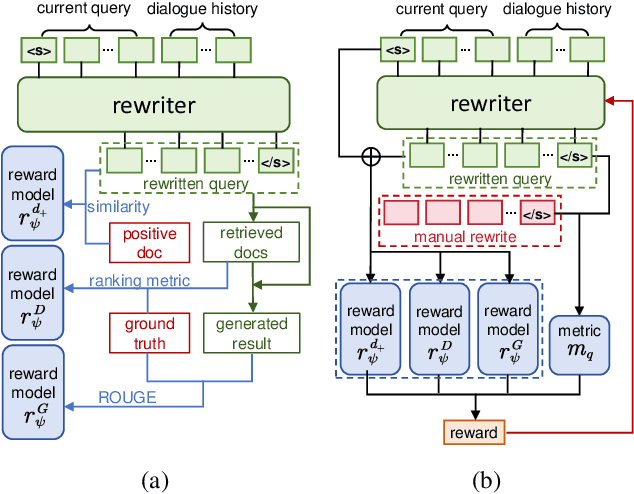

Abstract:In a real-world RAG system, the current query often involves spoken ellipses and ambiguous references from dialogue contexts, necessitating query rewriting to better describe user's information needs. However, traditional context-based rewriting has minimal enhancement on downstream generation tasks due to the lengthy process from query rewriting to response generation. Some researchers try to utilize reinforcement learning with generation feedback to assist the rewriter, but these sparse rewards provide little guidance in most cases, leading to unstable training and generation results. We find that user's needs are also reflected in the gold document, retrieved documents and ground truth. Therefore, by feeding back these multi-aspect dense rewards to query rewriting, more stable and satisfactory responses can be achieved. In this paper, we propose a novel query rewriting method MaFeRw, which improves RAG performance by integrating multi-aspect feedback from both the retrieval process and generated results. Specifically, we first use manual data to train a T5 model for the rewriter initialization. Next, we design three metrics as reinforcement learning feedback: the similarity between the rewritten query and the gold document, the ranking metrics, and ROUGE between the generation and the ground truth. Inspired by RLAIF, we train three kinds of reward models for the above metrics to achieve more efficient training. Finally, we combine the scores of these reward models as feedback, and use PPO algorithm to explore the optimal query rewriting strategy. Experimental results on two conversational RAG datasets demonstrate that MaFeRw achieves superior generation metrics and more stable training compared to baselines.
BEM: Balanced and Entropy-based Mix for Long-Tailed Semi-Supervised Learning
Apr 01, 2024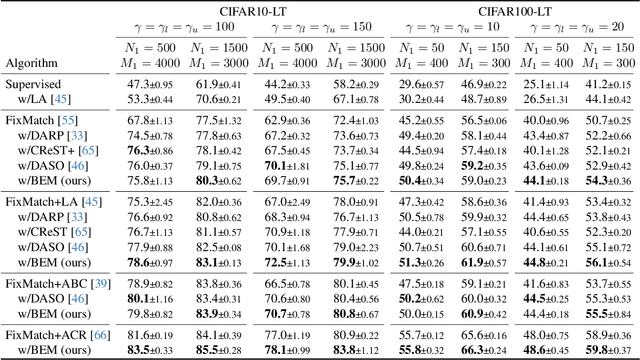
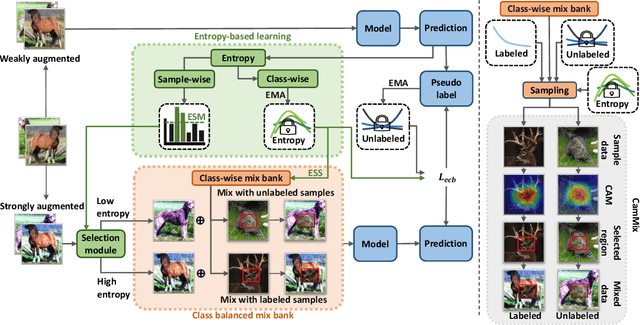
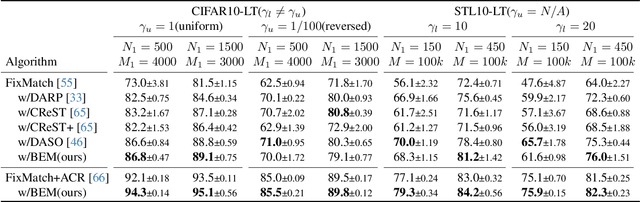
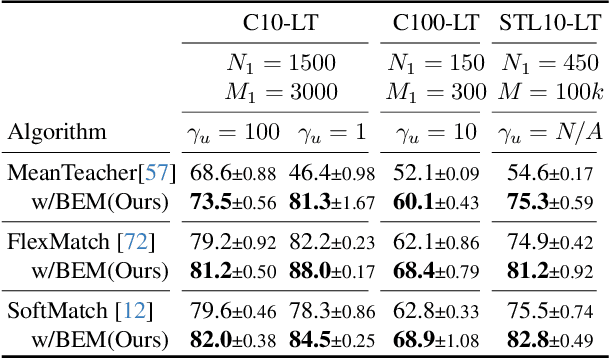
Abstract:Data mixing methods play a crucial role in semi-supervised learning (SSL), but their application is unexplored in long-tailed semi-supervised learning (LTSSL). The primary reason is that the in-batch mixing manner fails to address class imbalance. Furthermore, existing LTSSL methods mainly focus on re-balancing data quantity but ignore class-wise uncertainty, which is also vital for class balance. For instance, some classes with sufficient samples might still exhibit high uncertainty due to indistinguishable features. To this end, this paper introduces the Balanced and Entropy-based Mix (BEM), a pioneering mixing approach to re-balance the class distribution of both data quantity and uncertainty. Specifically, we first propose a class balanced mix bank to store data of each class for mixing. This bank samples data based on the estimated quantity distribution, thus re-balancing data quantity. Then, we present an entropy-based learning approach to re-balance class-wise uncertainty, including entropy-based sampling strategy, entropy-based selection module, and entropy-based class balanced loss. Our BEM first leverages data mixing for improving LTSSL, and it can also serve as a complement to the existing re-balancing methods. Experimental results show that BEM significantly enhances various LTSSL frameworks and achieves state-of-the-art performances across multiple benchmarks.
ActionPrompt: Action-Guided 3D Human Pose Estimation With Text and Pose Prompting
Jul 18, 2023
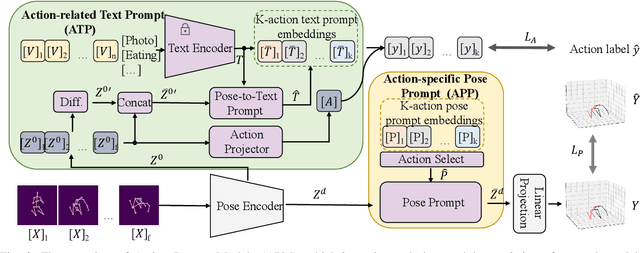
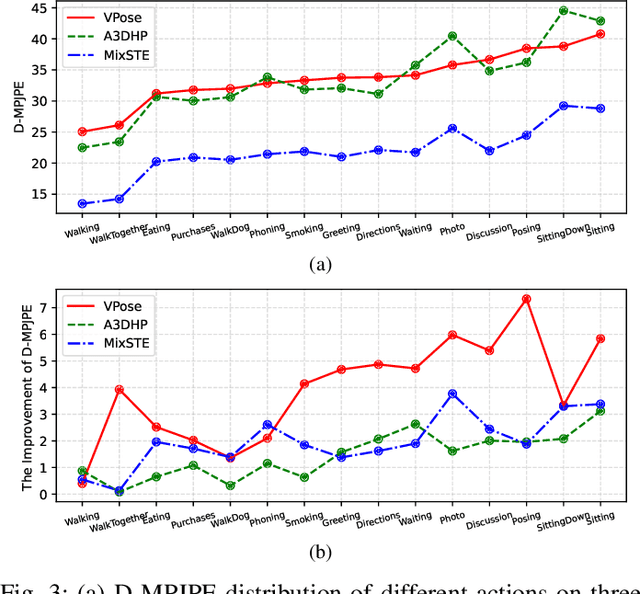
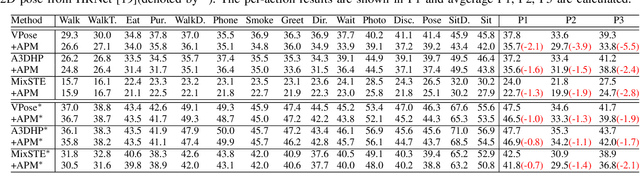
Abstract:Recent 2D-to-3D human pose estimation (HPE) utilizes temporal consistency across sequences to alleviate the depth ambiguity problem but ignore the action related prior knowledge hidden in the pose sequence. In this paper, we propose a plug-and-play module named Action Prompt Module (APM) that effectively mines different kinds of action clues for 3D HPE. The highlight is that, the mining scheme of APM can be widely adapted to different frameworks and bring consistent benefits. Specifically, we first present a novel Action-related Text Prompt module (ATP) that directly embeds action labels and transfers the rich language information in the label to the pose sequence. Besides, we further introduce Action-specific Pose Prompt module (APP) to mine the position-aware pose pattern of each action, and exploit the correlation between the mined patterns and input pose sequence for further pose refinement. Experiments show that APM can improve the performance of most video-based 2D-to-3D HPE frameworks by a large margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge