Jin Dong
H2Tune: Federated Foundation Model Fine-Tuning with Hybrid Heterogeneity
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:Different from existing federated fine-tuning (FFT) methods for foundation models, hybrid heterogeneous federated fine-tuning (HHFFT) is an under-explored scenario where clients exhibit double heterogeneity in model architectures and downstream tasks. This hybrid heterogeneity introduces two significant challenges: 1) heterogeneous matrix aggregation, where clients adopt different large-scale foundation models based on their task requirements and resource limitations, leading to dimensional mismatches during LoRA parameter aggregation; and 2) multi-task knowledge interference, where local shared parameters, trained with both task-shared and task-specific knowledge, cannot ensure only task-shared knowledge is transferred between clients. To address these challenges, we propose H2Tune, a federated foundation model fine-tuning with hybrid heterogeneity. Our framework H2Tune consists of three key components: (i) sparsified triple matrix decomposition to align hidden dimensions across clients through constructing rank-consistent middle matrices, with adaptive sparsification based on client resources; (ii) relation-guided matrix layer alignment to handle heterogeneous layer structures and representation capabilities; and (iii) alternating task-knowledge disentanglement mechanism to decouple shared and specific knowledge of local model parameters through alternating optimization. Theoretical analysis proves a convergence rate of O(1/\sqrt{T}). Extensive experiments show our method achieves up to 15.4% accuracy improvement compared to state-of-the-art baselines. Our code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/H2Tune-1407.
Proto-EVFL: Enhanced Vertical Federated Learning via Dual Prototype with Extremely Unaligned Data
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:In vertical federated learning (VFL), multiple enterprises address aligned sample scarcity by leveraging massive locally unaligned samples to facilitate collaborative learning. However, unaligned samples across different parties in VFL can be extremely class-imbalanced, leading to insufficient feature representation and limited model prediction space. Specifically, class-imbalanced problems consist of intra-party class imbalance and inter-party class imbalance, which can further cause local model bias and feature contribution inconsistency issues, respectively. To address the above challenges, we propose Proto-EVFL, an enhanced VFL framework via dual prototypes. We first introduce class prototypes for each party to learn relationships between classes in the latent space, allowing the active party to predict unseen classes. We further design a probabilistic dual prototype learning scheme to dynamically select unaligned samples by conditional optimal transport cost with class prior probability. Moreover, a mixed prior guided module guides this selection process by combining local and global class prior probabilities. Finally, we adopt an \textit{adaptive gated feature aggregation strategy} to mitigate feature contribution inconsistency by dynamically weighting and aggregating local features across different parties. We proved that Proto-EVFL, as the first bi-level optimization framework in VFL, has a convergence rate of 1/\sqrt T. Extensive experiments on various datasets validate the superiority of our Proto-EVFL. Even in a zero-shot scenario with one unseen class, it outperforms baselines by at least 6.97%
A Federated Splitting Framework for LLMs: Security, Efficiency, and Adaptability
May 21, 2025Abstract:Private data is typically larger and of higher quality than public data, offering great potential to improve LLM. However, its scattered distribution across data silos and the high computational demands of LLMs limit their deployment in federated environments. To address this, the transformer-based split learning model has emerged, offloading most model parameters to the server while retaining only the embedding and output layers on clients to ensure privacy. However, it still faces significant challenges in security, efficiency, and adaptability: 1) embedding gradients are vulnerable to attacks, leading to reverse engineering of private data; 2) the autoregressive nature of LLMs means that federated split learning can only train and infer sequentially, causing high communication overhead; 3) fixed partition points lack adaptability to downstream tasks. In this paper, we introduce FL-LLaMA, a secure, efficient, and adaptive federated split framework based on LLaMA2. First, we place some input and output blocks on the local client and inject Gaussian noise into forward-pass hidden states, enabling secure end-to-end propagation. Second, we employ client-batch and server-hierarchical strategies to achieve parallel training, along with attention-mask compression and KV cache mechanisms to accelerate inference, reducing communication costs effectively. Third, we allow users to dynamically adjust the partition points for input/output blocks based on specific task requirements and hardware limitations. Experiments on NLU, summarization and conversational QA tasks show that FL-LLaMA maintains performance comparable to centralized LLaMA2, and achieves up to 2x train speedups and 8x inference speedups. Further analysis of privacy attacks and different partition points also demonstrates the effectiveness of FL-LLaMA in security and adaptability.
TinyAlign: Boosting Lightweight Vision-Language Models by Mitigating Modal Alignment Bottlenecks
May 19, 2025Abstract:Lightweight Vision-Language Models (VLMs) are indispensable for resource-constrained applications. The prevailing approach to aligning vision and language models involves freezing both the vision encoder and the language model while training small connector modules. However, this strategy heavily depends on the intrinsic capabilities of the language model, which can be suboptimal for lightweight models with limited representational capacity. In this work, we investigate this alignment bottleneck through the lens of mutual information, demonstrating that the constrained capacity of the language model inherently limits the Effective Mutual Information (EMI) between multimodal inputs and outputs, thereby compromising alignment quality. To address this challenge, we propose TinyAlign, a novel framework inspired by Retrieval-Augmented Generation, which strategically retrieves relevant context from a memory bank to enrich multimodal inputs and enhance their alignment. Extensive empirical evaluations reveal that TinyAlign significantly reduces training loss, accelerates convergence, and enhances task performance. Remarkably, it allows models to achieve baseline-level performance with only 40\% of the fine-tuning data, highlighting exceptional data efficiency. Our work thus offers a practical pathway for developing more capable lightweight VLMs while introducing a fresh theoretical lens to better understand and address alignment bottlenecks in constrained multimodal systems.
CodeBC: A More Secure Large Language Model for Smart Contract Code Generation in Blockchain
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) excel at generating code from natural language instructions, yet they often lack an understanding of security vulnerabilities. This limitation makes it difficult for LLMs to avoid security risks in generated code, particularly in high-security programming tasks such as smart contract development for blockchain. Researchers have attempted to enhance the vulnerability awareness of these models by training them to differentiate between vulnerable and fixed code snippets. However, this approach relies heavily on manually labeled vulnerability data, which is only available for popular languages like Python and C++. For low-resource languages like Solidity, used in smart contracts, large-scale annotated datasets are scarce and difficult to obtain. To address this challenge, we introduce CodeBC, a code generation model specifically designed for generating secure smart contracts in blockchain. CodeBC employs a three-stage fine-tuning approach based on CodeLlama, distinguishing itself from previous methods by not relying on pairwise vulnerability location annotations. Instead, it leverages vulnerability and security tags to teach the model the differences between vulnerable and secure code. During the inference phase, the model leverages security tags to generate secure and robust code. Experimental results demonstrate that CodeBC outperforms baseline models in terms of BLEU, CodeBLEU, and compilation pass rates, while significantly reducing vulnerability rates. These findings validate the effectiveness and cost-efficiency of our three-stage fine-tuning strategy, making CodeBC a promising solution for generating secure smart contract code.
Privacy-Preserving Federated Embedding Learning for Localized Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Apr 27, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has recently emerged as a promising solution for enhancing the accuracy and credibility of Large Language Models (LLMs), particularly in Question & Answer tasks. This is achieved by incorporating proprietary and private data from integrated databases. However, private RAG systems face significant challenges due to the scarcity of private domain data and critical data privacy issues. These obstacles impede the deployment of private RAG systems, as developing privacy-preserving RAG systems requires a delicate balance between data security and data availability. To address these challenges, we regard federated learning (FL) as a highly promising technology for privacy-preserving RAG services. We propose a novel framework called Federated Retrieval-Augmented Generation (FedE4RAG). This framework facilitates collaborative training of client-side RAG retrieval models. The parameters of these models are aggregated and distributed on a central-server, ensuring data privacy without direct sharing of raw data. In FedE4RAG, knowledge distillation is employed for communication between the server and client models. This technique improves the generalization of local RAG retrievers during the federated learning process. Additionally, we apply homomorphic encryption within federated learning to safeguard model parameters and mitigate concerns related to data leakage. Extensive experiments conducted on the real-world dataset have validated the effectiveness of FedE4RAG. The results demonstrate that our proposed framework can markedly enhance the performance of private RAG systems while maintaining robust data privacy protection.
Unveiling Hidden Vulnerabilities in Digital Human Generation via Adversarial Attacks
Apr 24, 2025



Abstract:Expressive human pose and shape estimation (EHPS) is crucial for digital human generation, especially in applications like live streaming. While existing research primarily focuses on reducing estimation errors, it largely neglects robustness and security aspects, leaving these systems vulnerable to adversarial attacks. To address this significant challenge, we propose the \textbf{Tangible Attack (TBA)}, a novel framework designed to generate adversarial examples capable of effectively compromising any digital human generation model. Our approach introduces a \textbf{Dual Heterogeneous Noise Generator (DHNG)}, which leverages Variational Autoencoders (VAE) and ControlNet to produce diverse, targeted noise tailored to the original image features. Additionally, we design a custom \textbf{adversarial loss function} to optimize the noise, ensuring both high controllability and potent disruption. By iteratively refining the adversarial sample through multi-gradient signals from both the noise and the state-of-the-art EHPS model, TBA substantially improves the effectiveness of adversarial attacks. Extensive experiments demonstrate TBA's superiority, achieving a remarkable 41.0\% increase in estimation error, with an average improvement of approximately 17.0\%. These findings expose significant security vulnerabilities in current EHPS models and highlight the need for stronger defenses in digital human generation systems.
GPMFS: Global Foundation and Personalized Optimization for Multi-Label Feature Selection
Apr 17, 2025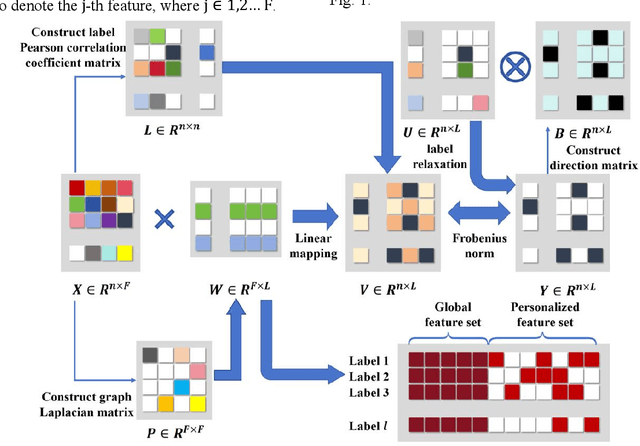
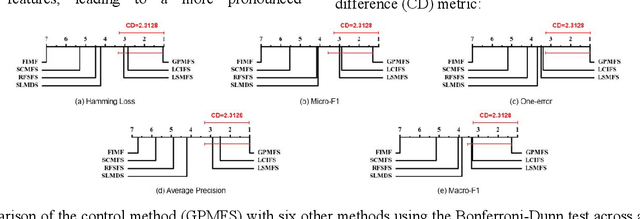
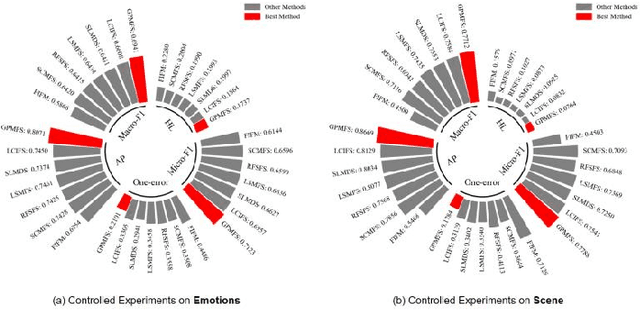
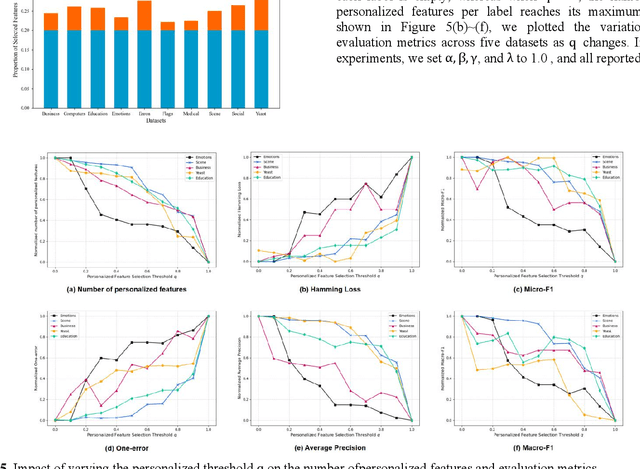
Abstract:As artificial intelligence methods are increasingly applied to complex task scenarios, high dimensional multi-label learning has emerged as a prominent research focus. At present, the curse of dimensionality remains one of the major bottlenecks in high-dimensional multi-label learning, which can be effectively addressed through multi-label feature selection methods. However, existing multi-label feature selection methods mostly focus on identifying global features shared across all labels, which overlooks personalized characteristics and specific requirements of individual labels. This global-only perspective may limit the ability to capture label-specific discriminative information, thereby affecting overall performance. In this paper, we propose a novel method called GPMFS (Global Foundation and Personalized Optimization for Multi-Label Feature Selection). GPMFS firstly identifies global features by exploiting label correlations, then adaptively supplements each label with a personalized subset of discriminative features using a threshold-controlled strategy. Experiments on multiple real-world datasets demonstrate that GPMFS achieves superior performance while maintaining strong interpretability and robustness. Furthermore, GPMFS provides insights into the label-specific strength across different multi-label datasets, thereby demonstrating the necessity and potential applicability of personalized feature selection approaches.
A Comprehensive Survey of Federated Transfer Learning: Challenges, Methods and Applications
Mar 03, 2024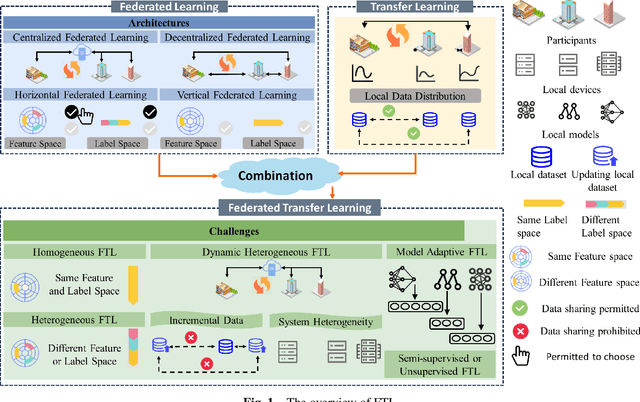
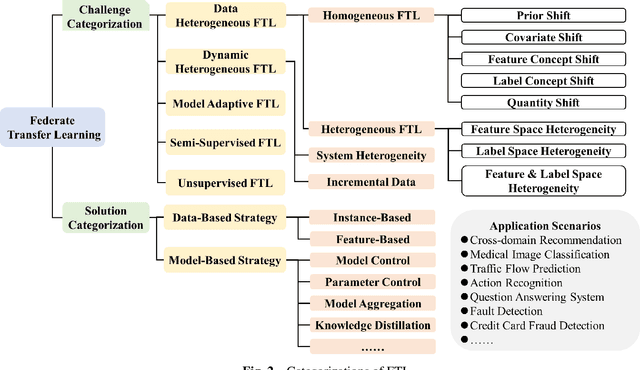
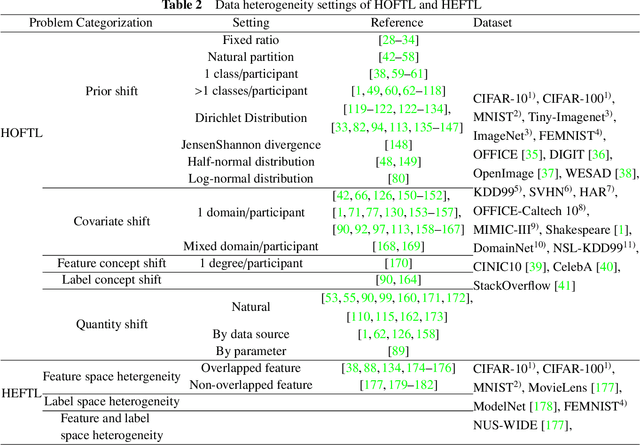
Abstract:Federated learning (FL) is a novel distributed machine learning paradigm that enables participants to collaboratively train a centralized model with privacy preservation by eliminating the requirement of data sharing. In practice, FL often involves multiple participants and requires the third party to aggregate global information to guide the update of the target participant. Therefore, many FL methods do not work well due to the training and test data of each participant may not be sampled from the same feature space and the same underlying distribution. Meanwhile, the differences in their local devices (system heterogeneity), the continuous influx of online data (incremental data), and labeled data scarcity may further influence the performance of these methods. To solve this problem, federated transfer learning (FTL), which integrates transfer learning (TL) into FL, has attracted the attention of numerous researchers. However, since FL enables a continuous share of knowledge among participants with each communication round while not allowing local data to be accessed by other participants, FTL faces many unique challenges that are not present in TL. In this survey, we focus on categorizing and reviewing the current progress on federated transfer learning, and outlining corresponding solutions and applications. Furthermore, the common setting of FTL scenarios, available datasets, and significant related research are summarized in this survey.
Knowledge-based Multiple Adaptive Spaces Fusion for Recommendation
Aug 29, 2023Abstract:Since Knowledge Graphs (KGs) contain rich semantic information, recently there has been an influx of KG-enhanced recommendation methods. Most of existing methods are entirely designed based on euclidean space without considering curvature. However, recent studies have revealed that a tremendous graph-structured data exhibits highly non-euclidean properties. Motivated by these observations, in this work, we propose a knowledge-based multiple adaptive spaces fusion method for recommendation, namely MCKG. Unlike existing methods that solely adopt a specific manifold, we introduce the unified space that is compatible with hyperbolic, euclidean and spherical spaces. Furthermore, we fuse the multiple unified spaces in an attention manner to obtain the high-quality embeddings for better knowledge propagation. In addition, we propose a geometry-aware optimization strategy which enables the pull and push processes benefited from both hyperbolic and spherical spaces. Specifically, in hyperbolic space, we set smaller margins in the area near to the origin, which is conducive to distinguishing between highly similar positive items and negative ones. At the same time, we set larger margins in the area far from the origin to ensure the model has sufficient error tolerance. The similar manner also applies to spherical spaces. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate that the MCKG has a significant improvement over state-of-the-art recommendation methods. Further ablation experiments verify the importance of multi-space fusion and geometry-aware optimization strategy, justifying the rationality and effectiveness of MCKG.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge