Zhao Zhang
Learning Adaptive Distribution Alignment with Neural Characteristic Function for Graph Domain Adaptation
Feb 11, 2026Abstract:Graph Domain Adaptation (GDA) transfers knowledge from labeled source graphs to unlabeled target graphs but is challenged by complex, multi-faceted distributional shifts. Existing methods attempt to reduce distributional shifts by aligning manually selected graph elements (e.g., node attributes or structural statistics), which typically require manually designed graph filters to extract relevant features before alignment. However, such approaches are inflexible: they rely on scenario-specific heuristics, and struggle when dominant discrepancies vary across transfer scenarios. To address these limitations, we propose \textbf{ADAlign}, an Adaptive Distribution Alignment framework for GDA. Unlike heuristic methods, ADAlign requires no manual specification of alignment criteria. It automatically identifies the most relevant discrepancies in each transfer and aligns them jointly, capturing the interplay between attributes, structures, and their dependencies. This makes ADAlign flexible, scenario-aware, and robust to diverse and dynamically evolving shifts. To enable this adaptivity, we introduce the Neural Spectral Discrepancy (NSD), a theoretically principled parametric distance that provides a unified view of cross-graph shifts. NSD leverages neural characteristic function in the spectral domain to encode feature-structure dependencies of all orders, while a learnable frequency sampler adaptively emphasizes the most informative spectral components for each task via minimax paradigm. Extensive experiments on 10 datasets and 16 transfer tasks show that ADAlign not only outperforms state-of-the-art baselines but also achieves efficiency gains with lower memory usage and faster training.
Learning Structure-Semantic Evolution Trajectories for Graph Domain Adaptation
Feb 11, 2026Abstract:Graph Domain Adaptation (GDA) aims to bridge distribution shifts between domains by transferring knowledge from well-labeled source graphs to given unlabeled target graphs. One promising recent approach addresses graph transfer by discretizing the adaptation process, typically through the construction of intermediate graphs or stepwise alignment procedures. However, such discrete strategies often fail in real-world scenarios, where graph structures evolve continuously and nonlinearly, making it difficult for fixed-step alignment to approximate the actual transformation process. To address these limitations, we propose \textbf{DiffGDA}, a \textbf{Diff}usion-based \textbf{GDA} method that models the domain adaptation process as a continuous-time generative process. We formulate the evolution from source to target graphs using stochastic differential equations (SDEs), enabling the joint modeling of structural and semantic transitions. To guide this evolution, a domain-aware network is introduced to steer the generative process toward the target domain, encouraging the diffusion trajectory to follow an optimal adaptation path. We theoretically show that the diffusion process converges to the optimal solution bridging the source and target domains in the latent space. Extensive experiments on 14 graph transfer tasks across 8 real-world datasets demonstrate DiffGDA consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines.
Reasoning over Precedents Alongside Statutes: Case-Augmented Deliberative Alignment for LLM Safety
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Ensuring that Large Language Models (LLMs) adhere to safety principles without refusing benign requests remains a significant challenge. While OpenAI introduces deliberative alignment (DA) to enhance the safety of its o-series models through reasoning over detailed ``code-like'' safety rules, the effectiveness of this approach in open-source LLMs, which typically lack advanced reasoning capabilities, is understudied. In this work, we systematically evaluate the impact of explicitly specifying extensive safety codes versus demonstrating them through illustrative cases. We find that referencing explicit codes inconsistently improves harmlessness and systematically degrades helpfulness, whereas training on case-augmented simple codes yields more robust and generalized safety behaviors. By guiding LLMs with case-augmented reasoning instead of extensive code-like safety rules, we avoid rigid adherence to narrowly enumerated rules and enable broader adaptability. Building on these insights, we propose CADA, a case-augmented deliberative alignment method for LLMs utilizing reinforcement learning on self-generated safety reasoning chains. CADA effectively enhances harmlessness, improves robustness against attacks, and reduces over-refusal while preserving utility across diverse benchmarks, offering a practical alternative to rule-only DA for improving safety while maintaining helpfulness.
Multi-Aspect Cross-modal Quantization for Generative Recommendation
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Generative Recommendation (GR) has emerged as a new paradigm in recommender systems. This approach relies on quantized representations to discretize item features, modeling users' historical interactions as sequences of discrete tokens. Based on these tokenized sequences, GR predicts the next item by employing next-token prediction methods. The challenges of GR lie in constructing high-quality semantic identifiers (IDs) that are hierarchically organized, minimally conflicting, and conducive to effective generative model training. However, current approaches remain limited in their ability to harness multimodal information and to capture the deep and intricate interactions among diverse modalities, both of which are essential for learning high-quality semantic IDs and for effectively training GR models. To address this, we propose Multi-Aspect Cross-modal quantization for generative Recommendation (MACRec), which introduces multimodal information and incorporates it into both semantic ID learning and generative model training from different aspects. Specifically, we first introduce cross-modal quantization during the ID learning process, which effectively reduces conflict rates and thus improves codebook usability through the complementary integration of multimodal information. In addition, to further enhance the generative ability of our GR model, we incorporate multi-aspect cross-modal alignments, including the implicit and explicit alignments. Finally, we conduct extensive experiments on three well-known recommendation datasets to demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
Benchmarking LLMs for Fine-Grained Code Review with Enriched Context in Practice
Nov 10, 2025



Abstract:Code review is a cornerstone of software quality assurance, and recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in automating this process. However, existing benchmarks for LLM-based code review face three major limitations. (1) Lack of semantic context: most benchmarks provide only code diffs without textual information such as issue descriptions, which are crucial for understanding developer intent. (2) Data quality issues: without rigorous validation, many samples are noisy-e.g., reviews on outdated or irrelevant code-reducing evaluation reliability. (3) Coarse granularity: most benchmarks operate at the file or commit level, overlooking the fine-grained, line-level reasoning essential for precise review. We introduce ContextCRBench, a high-quality, context-rich benchmark for fine-grained LLM evaluation in code review. Our construction pipeline comprises: (1) Raw Data Crawling, collecting 153.7K issues and pull requests from top-tier repositories; (2) Comprehensive Context Extraction, linking issue-PR pairs for textual context and extracting the full surrounding function or class for code context; and (3) Multi-stage Data Filtering, combining rule-based and LLM-based validation to remove outdated, malformed, or low-value samples, resulting in 67,910 context-enriched entries. ContextCRBench supports three evaluation scenarios aligned with the review workflow: (1) hunk-level quality assessment, (2) line-level defect localization, and (3) line-level comment generation. Evaluating eight leading LLMs (four closed-source and four open-source) reveals that textual context yields greater performance gains than code context alone, while current LLMs remain far from human-level review ability. Deployed at ByteDance, ContextCRBench drives a self-evolving code review system, improving performance by 61.98% and demonstrating its robustness and industrial utility.
Embodied Arena: A Comprehensive, Unified, and Evolving Evaluation Platform for Embodied AI
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Embodied AI development significantly lags behind large foundation models due to three critical challenges: (1) lack of systematic understanding of core capabilities needed for Embodied AI, making research lack clear objectives; (2) absence of unified and standardized evaluation systems, rendering cross-benchmark evaluation infeasible; and (3) underdeveloped automated and scalable acquisition methods for embodied data, creating critical bottlenecks for model scaling. To address these obstacles, we present Embodied Arena, a comprehensive, unified, and evolving evaluation platform for Embodied AI. Our platform establishes a systematic embodied capability taxonomy spanning three levels (perception, reasoning, task execution), seven core capabilities, and 25 fine-grained dimensions, enabling unified evaluation with systematic research objectives. We introduce a standardized evaluation system built upon unified infrastructure supporting flexible integration of 22 diverse benchmarks across three domains (2D/3D Embodied Q&A, Navigation, Task Planning) and 30+ advanced models from 20+ worldwide institutes. Additionally, we develop a novel LLM-driven automated generation pipeline ensuring scalable embodied evaluation data with continuous evolution for diversity and comprehensiveness. Embodied Arena publishes three real-time leaderboards (Embodied Q&A, Navigation, Task Planning) with dual perspectives (benchmark view and capability view), providing comprehensive overviews of advanced model capabilities. Especially, we present nine findings summarized from the evaluation results on the leaderboards of Embodied Arena. This helps to establish clear research veins and pinpoint critical research problems, thereby driving forward progress in the field of Embodied AI.
NTIRE 2025 Image Shadow Removal Challenge Report
Jun 18, 2025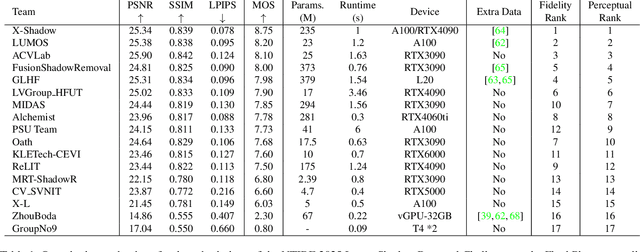

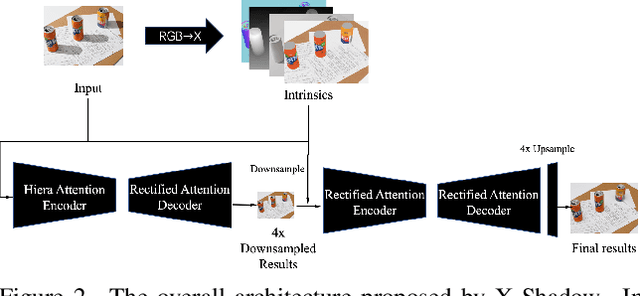
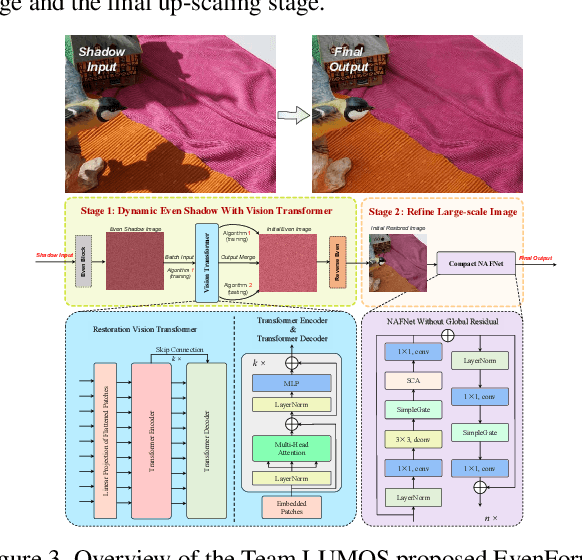
Abstract:This work examines the findings of the NTIRE 2025 Shadow Removal Challenge. A total of 306 participants have registered, with 17 teams successfully submitting their solutions during the final evaluation phase. Following the last two editions, this challenge had two evaluation tracks: one focusing on reconstruction fidelity and the other on visual perception through a user study. Both tracks were evaluated with images from the WSRD+ dataset, simulating interactions between self- and cast-shadows with a large number of diverse objects, textures, and materials.
CreatiPoster: Towards Editable and Controllable Multi-Layer Graphic Design Generation
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Graphic design plays a crucial role in both commercial and personal contexts, yet creating high-quality, editable, and aesthetically pleasing graphic compositions remains a time-consuming and skill-intensive task, especially for beginners. Current AI tools automate parts of the workflow, but struggle to accurately incorporate user-supplied assets, maintain editability, and achieve professional visual appeal. Commercial systems, like Canva Magic Design, rely on vast template libraries, which are impractical for replicate. In this paper, we introduce CreatiPoster, a framework that generates editable, multi-layer compositions from optional natural-language instructions or assets. A protocol model, an RGBA large multimodal model, first produces a JSON specification detailing every layer (text or asset) with precise layout, hierarchy, content and style, plus a concise background prompt. A conditional background model then synthesizes a coherent background conditioned on this rendered foreground layers. We construct a benchmark with automated metrics for graphic-design generation and show that CreatiPoster surpasses leading open-source approaches and proprietary commercial systems. To catalyze further research, we release a copyright-free corpus of 100,000 multi-layer designs. CreatiPoster supports diverse applications such as canvas editing, text overlay, responsive resizing, multilingual adaptation, and animated posters, advancing the democratization of AI-assisted graphic design. Project homepage: https://github.com/graphic-design-ai/creatiposter
DeformCL: Learning Deformable Centerline Representation for Vessel Extraction in 3D Medical Image
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:In the field of 3D medical imaging, accurately extracting and representing the blood vessels with curvilinear structures holds paramount importance for clinical diagnosis. Previous methods have commonly relied on discrete representation like mask, often resulting in local fractures or scattered fragments due to the inherent limitations of the per-pixel classification paradigm. In this work, we introduce DeformCL, a new continuous representation based on Deformable Centerlines, where centerline points act as nodes connected by edges that capture spatial relationships. Compared with previous representations, DeformCL offers three key advantages: natural connectivity, noise robustness, and interaction facility. We present a comprehensive training pipeline structured in a cascaded manner to fully exploit these favorable properties of DeformCL. Extensive experiments on four 3D vessel segmentation datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our method. Furthermore, the visualization of curved planar reformation images validates the clinical significance of the proposed framework. We release the code in https://github.com/barry664/DeformCL
FCKT: Fine-Grained Cross-Task Knowledge Transfer with Semantic Contrastive Learning for Targeted Sentiment Analysis
May 28, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we address the task of targeted sentiment analysis (TSA), which involves two sub-tasks, i.e., identifying specific aspects from reviews and determining their corresponding sentiments. Aspect extraction forms the foundation for sentiment prediction, highlighting the critical dependency between these two tasks for effective cross-task knowledge transfer. While most existing studies adopt a multi-task learning paradigm to align task-specific features in the latent space, they predominantly rely on coarse-grained knowledge transfer. Such approaches lack fine-grained control over aspect-sentiment relationships, often assuming uniform sentiment polarity within related aspects. This oversimplification neglects contextual cues that differentiate sentiments, leading to negative transfer. To overcome these limitations, we propose FCKT, a fine-grained cross-task knowledge transfer framework tailored for TSA. By explicitly incorporating aspect-level information into sentiment prediction, FCKT achieves fine-grained knowledge transfer, effectively mitigating negative transfer and enhancing task performance. Experiments on three datasets, including comparisons with various baselines and large language models (LLMs), demonstrate the effectiveness of FCKT. The source code is available on https://github.com/cwei01/FCKT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge