Dexiang Hong
EmoVerse: A MLLMs-Driven Emotion Representation Dataset for Interpretable Visual Emotion Analysis
Nov 16, 2025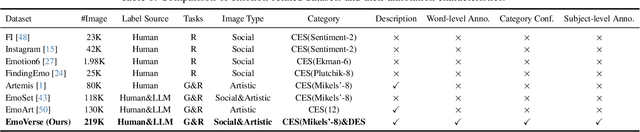
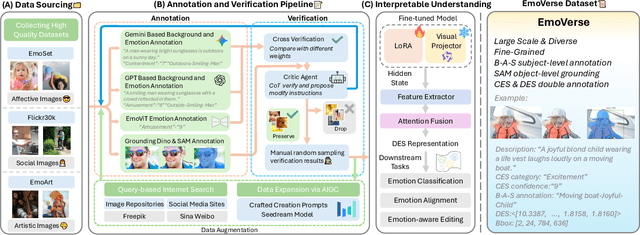
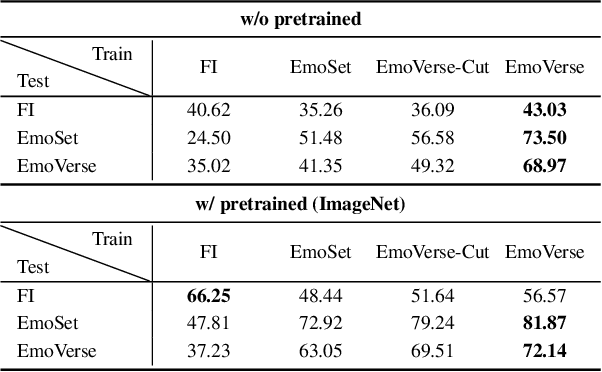
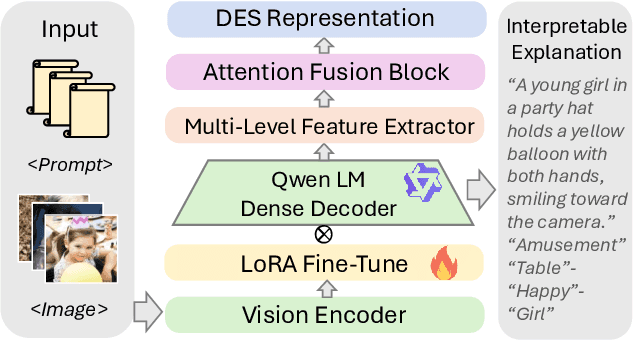
Abstract:Visual Emotion Analysis (VEA) aims to bridge the affective gap between visual content and human emotional responses. Despite its promise, progress in this field remains limited by the lack of open-source and interpretable datasets. Most existing studies assign a single discrete emotion label to an entire image, offering limited insight into how visual elements contribute to emotion. In this work, we introduce EmoVerse, a large-scale open-source dataset that enables interpretable visual emotion analysis through multi-layered, knowledge-graph-inspired annotations. By decomposing emotions into Background-Attribute-Subject (B-A-S) triplets and grounding each element to visual regions, EmoVerse provides word-level and subject-level emotional reasoning. With over 219k images, the dataset further includes dual annotations in Categorical Emotion States (CES) and Dimensional Emotion Space (DES), facilitating unified discrete and continuous emotion representation. A novel multi-stage pipeline ensures high annotation reliability with minimal human effort. Finally, we introduce an interpretable model that maps visual cues into DES representations and provides detailed attribution explanations. Together, the dataset, pipeline, and model form a comprehensive foundation for advancing explainable high-level emotion understanding.
CreatiPoster: Towards Editable and Controllable Multi-Layer Graphic Design Generation
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Graphic design plays a crucial role in both commercial and personal contexts, yet creating high-quality, editable, and aesthetically pleasing graphic compositions remains a time-consuming and skill-intensive task, especially for beginners. Current AI tools automate parts of the workflow, but struggle to accurately incorporate user-supplied assets, maintain editability, and achieve professional visual appeal. Commercial systems, like Canva Magic Design, rely on vast template libraries, which are impractical for replicate. In this paper, we introduce CreatiPoster, a framework that generates editable, multi-layer compositions from optional natural-language instructions or assets. A protocol model, an RGBA large multimodal model, first produces a JSON specification detailing every layer (text or asset) with precise layout, hierarchy, content and style, plus a concise background prompt. A conditional background model then synthesizes a coherent background conditioned on this rendered foreground layers. We construct a benchmark with automated metrics for graphic-design generation and show that CreatiPoster surpasses leading open-source approaches and proprietary commercial systems. To catalyze further research, we release a copyright-free corpus of 100,000 multi-layer designs. CreatiPoster supports diverse applications such as canvas editing, text overlay, responsive resizing, multilingual adaptation, and animated posters, advancing the democratization of AI-assisted graphic design. Project homepage: https://github.com/graphic-design-ai/creatiposter
CreatiDesign: A Unified Multi-Conditional Diffusion Transformer for Creative Graphic Design
May 25, 2025Abstract:Graphic design plays a vital role in visual communication across advertising, marketing, and multimedia entertainment. Prior work has explored automated graphic design generation using diffusion models, aiming to streamline creative workflows and democratize design capabilities. However, complex graphic design scenarios require accurately adhering to design intent specified by multiple heterogeneous user-provided elements (\eg images, layouts, and texts), which pose multi-condition control challenges for existing methods. Specifically, previous single-condition control models demonstrate effectiveness only within their specialized domains but fail to generalize to other conditions, while existing multi-condition methods often lack fine-grained control over each sub-condition and compromise overall compositional harmony. To address these limitations, we introduce CreatiDesign, a systematic solution for automated graphic design covering both model architecture and dataset construction. First, we design a unified multi-condition driven architecture that enables flexible and precise integration of heterogeneous design elements with minimal architectural modifications to the base diffusion model. Furthermore, to ensure that each condition precisely controls its designated image region and to avoid interference between conditions, we propose a multimodal attention mask mechanism. Additionally, we develop a fully automated pipeline for constructing graphic design datasets, and introduce a new dataset with 400K samples featuring multi-condition annotations, along with a comprehensive benchmark. Experimental results show that CreatiDesign outperforms existing models by a clear margin in faithfully adhering to user intent.
CreatiLayout: Siamese Multimodal Diffusion Transformer for Creative Layout-to-Image Generation
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion models have been recognized for their ability to generate images that are not only visually appealing but also of high artistic quality. As a result, Layout-to-Image (L2I) generation has been proposed to leverage region-specific positions and descriptions to enable more precise and controllable generation. However, previous methods primarily focus on UNet-based models (e.g., SD1.5 and SDXL), and limited effort has explored Multimodal Diffusion Transformers (MM-DiTs), which have demonstrated powerful image generation capabilities. Enabling MM-DiT for layout-to-image generation seems straightforward but is challenging due to the complexity of how layout is introduced, integrated, and balanced among multiple modalities. To this end, we explore various network variants to efficiently incorporate layout guidance into MM-DiT, and ultimately present SiamLayout. To Inherit the advantages of MM-DiT, we use a separate set of network weights to process the layout, treating it as equally important as the image and text modalities. Meanwhile, to alleviate the competition among modalities, we decouple the image-layout interaction into a siamese branch alongside the image-text one and fuse them in the later stage. Moreover, we contribute a large-scale layout dataset, named LayoutSAM, which includes 2.7 million image-text pairs and 10.7 million entities. Each entity is annotated with a bounding box and a detailed description. We further construct the LayoutSAM-Eval benchmark as a comprehensive tool for evaluating the L2I generation quality. Finally, we introduce the Layout Designer, which taps into the potential of large language models in layout planning, transforming them into experts in layout generation and optimization. Our code, model, and dataset will be available at https://creatilayout.github.io.
Multi-Attention Network for Compressed Video Referring Object Segmentation
Jul 26, 2022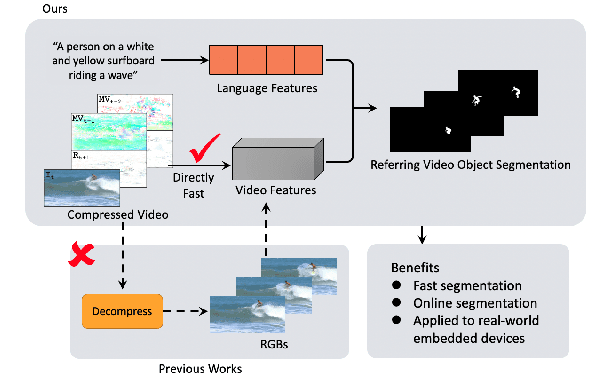
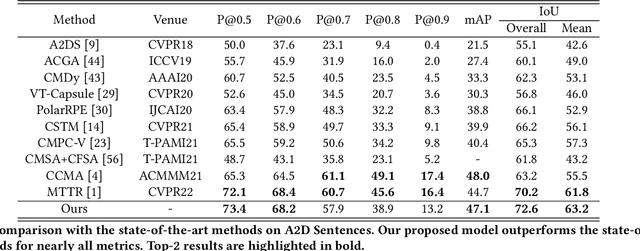
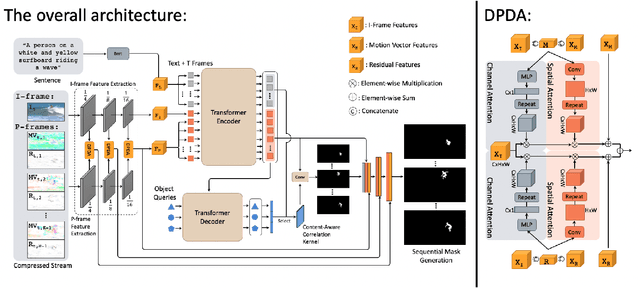
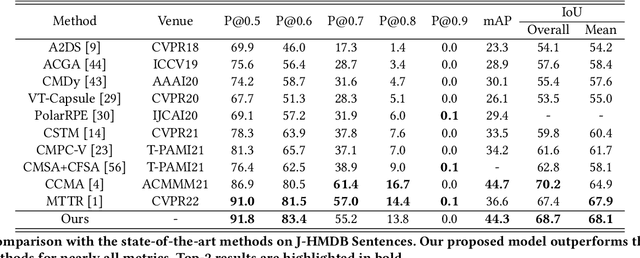
Abstract:Referring video object segmentation aims to segment the object referred by a given language expression. Existing works typically require compressed video bitstream to be decoded to RGB frames before being segmented, which increases computation and storage requirements and ultimately slows the inference down. This may hamper its application in real-world computing resource limited scenarios, such as autonomous cars and drones. To alleviate this problem, in this paper, we explore the referring object segmentation task on compressed videos, namely on the original video data flow. Besides the inherent difficulty of the video referring object segmentation task itself, obtaining discriminative representation from compressed video is also rather challenging. To address this problem, we propose a multi-attention network which consists of dual-path dual-attention module and a query-based cross-modal Transformer module. Specifically, the dual-path dual-attention module is designed to extract effective representation from compressed data in three modalities, i.e., I-frame, Motion Vector and Residual. The query-based cross-modal Transformer firstly models the correlation between linguistic and visual modalities, and then the fused multi-modality features are used to guide object queries to generate a content-aware dynamic kernel and to predict final segmentation masks. Different from previous works, we propose to learn just one kernel, which thus removes the complicated post mask-matching procedure of existing methods. Extensive promising experimental results on three challenging datasets show the effectiveness of our method compared against several state-of-the-art methods which are proposed for processing RGB data. Source code is available at: https://github.com/DexiangHong/MANet.
SC-Transformer++: Structured Context Transformer for Generic Event Boundary Detection
Jun 25, 2022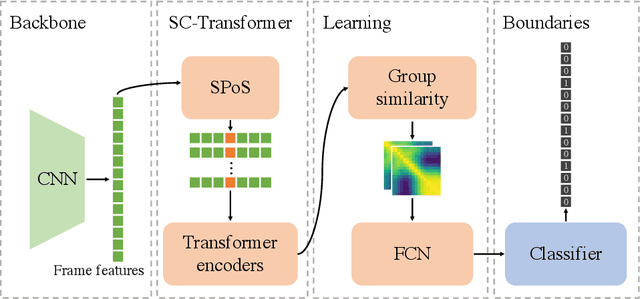
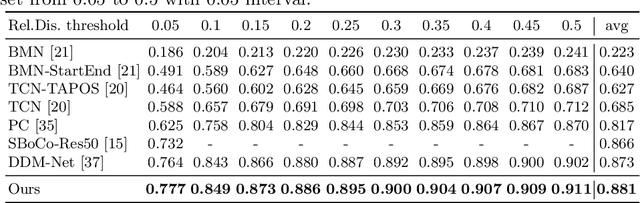
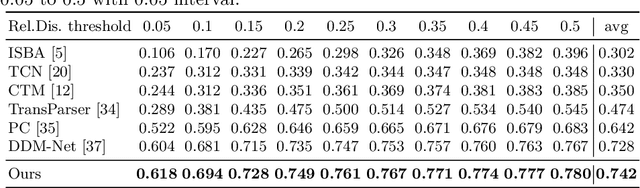
Abstract:This report presents the algorithm used in the submission of Generic Event Boundary Detection (GEBD) Challenge at CVPR 2022. In this work, we improve the existing Structured Context Transformer (SC-Transformer) method for GEBD. Specifically, a transformer decoder module is added after transformer encoders to extract high quality frame features. The final classification is performed jointly on the results of the original binary classifier and a newly introduced multi-class classifier branch. To enrich motion information, optical flow is introduced as a new modality. Finally, model ensemble is used to further boost performance. The proposed method achieves 86.49% F1 score on Kinetics-GEBD test set. which improves 2.86% F1 score compared to the previous SOTA method.
Structured Context Transformer for Generic Event Boundary Detection
Jun 07, 2022



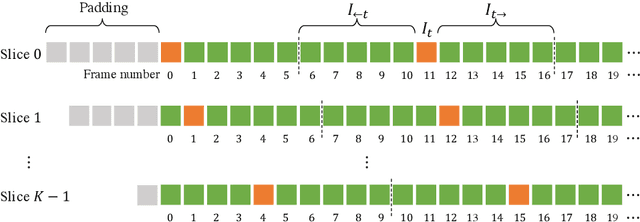
Abstract:Generic Event Boundary Detection (GEBD) aims to detect moments where humans naturally perceive as event boundaries. In this paper, we present Structured Context Transformer (or SC-Transformer) to solve the GEBD task, which can be trained in an end-to-end fashion. Specifically, we use the backbone convolutional neural network (CNN) to extract the features of each video frame. To capture temporal context information of each frame, we design the structure context transformer (SC-Transformer) by re-partitioning input frame sequence. Note that, the overall computation complexity of SC-Transformer is linear to the video length. After that, the group similarities are computed to capture the differences between frames. Then, a lightweight fully convolutional network is used to determine the event boundaries based on the grouped similarity maps. To remedy the ambiguities of boundary annotations, the Gaussian kernel is adopted to preprocess the ground-truth event boundaries to further boost the accuracy. Extensive experiments conducted on the challenging Kinetics-GEBD and TAPOS datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method compared to the state-of-the-art methods.
End-to-End Compressed Video Representation Learning for Generic Event Boundary Detection
Mar 29, 2022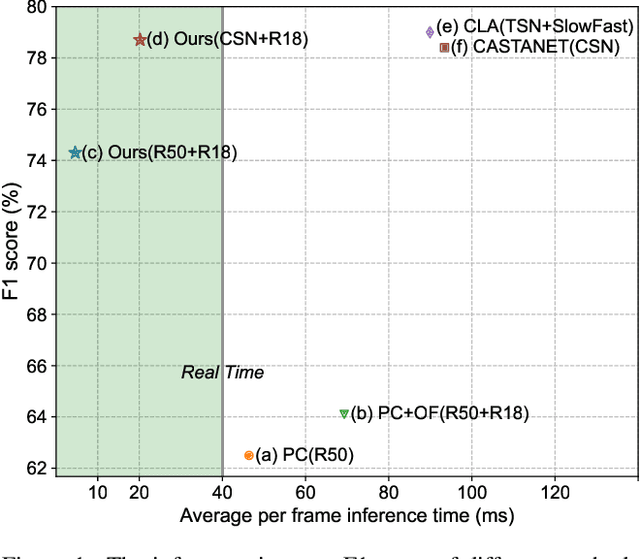
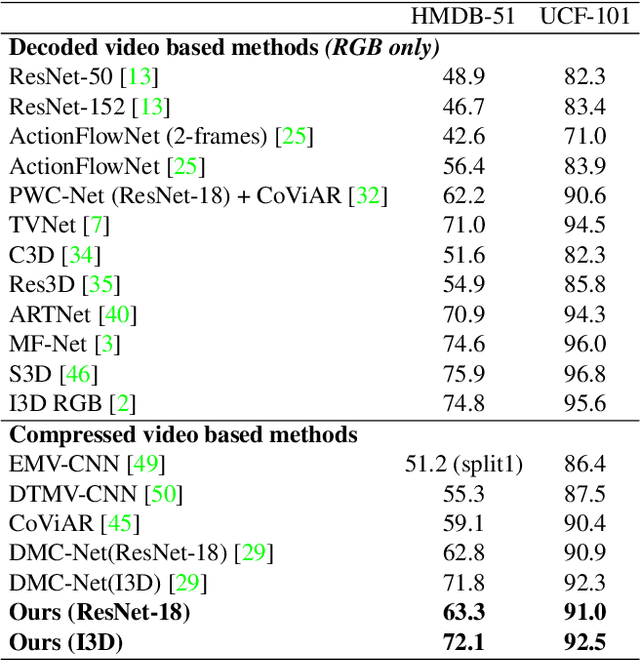
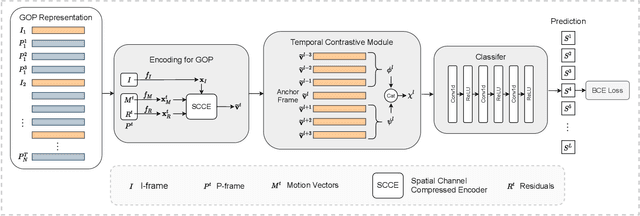
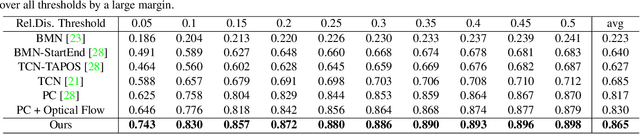
Abstract:Generic event boundary detection aims to localize the generic, taxonomy-free event boundaries that segment videos into chunks. Existing methods typically require video frames to be decoded before feeding into the network, which demands considerable computational power and storage space. To that end, we propose a new end-to-end compressed video representation learning for event boundary detection that leverages the rich information in the compressed domain, i.e., RGB, motion vectors, residuals, and the internal group of pictures (GOP) structure, without fully decoding the video. Specifically, we first use the ConvNets to extract features of the I-frames in the GOPs. After that, a light-weight spatial-channel compressed encoder is designed to compute the feature representations of the P-frames based on the motion vectors, residuals and representations of their dependent I-frames. A temporal contrastive module is proposed to determine the event boundaries of video sequences. To remedy the ambiguities of annotations and speed up the training process, we use the Gaussian kernel to preprocess the ground-truth event boundaries. Extensive experiments conducted on the Kinetics-GEBD dataset demonstrate that the proposed method achieves comparable results to the state-of-the-art methods with $4.5\times$ faster running speed.
Generic Event Boundary Detection Challenge at CVPR 2021 Technical Report: Cascaded Temporal Attention Network (CASTANET)
Jul 01, 2021



Abstract:This report presents the approach used in the submission of Generic Event Boundary Detection (GEBD) Challenge at CVPR21. In this work, we design a Cascaded Temporal Attention Network (CASTANET) for GEBD, which is formed by three parts, the backbone network, the temporal attention module, and the classification module. Specifically, the Channel-Separated Convolutional Network (CSN) is used as the backbone network to extract features, and the temporal attention module is designed to enforce the network to focus on the discriminative features. After that, the cascaded architecture is used in the classification module to generate more accurate boundaries. In addition, the ensemble strategy is used to further improve the performance of the proposed method. The proposed method achieves 83.30% F1 score on Kinetics-GEBD test set, which improves 20.5% F1 score compared to the baseline method. Code is available at https://github.com/DexiangHong/Cascade-PC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge