Congcong Li
Car-GS: Addressing Reflective and Transparent Surface Challenges in 3D Car Reconstruction
Jan 19, 2025



Abstract:3D car modeling is crucial for applications in autonomous driving systems, virtual and augmented reality, and gaming. However, due to the distinctive properties of cars, such as highly reflective and transparent surface materials, existing methods often struggle to achieve accurate 3D car reconstruction.To address these limitations, we propose Car-GS, a novel approach designed to mitigate the effects of specular highlights and the coupling of RGB and geometry in 3D geometric and shading reconstruction (3DGS). Our method incorporates three key innovations: First, we introduce view-dependent Gaussian primitives to effectively model surface reflections. Second, we identify the limitations of using a shared opacity parameter for both image rendering and geometric attributes when modeling transparent objects. To overcome this, we assign a learnable geometry-specific opacity to each 2D Gaussian primitive, dedicated solely to rendering depth and normals. Third, we observe that reconstruction errors are most prominent when the camera view is nearly orthogonal to glass surfaces. To address this issue, we develop a quality-aware supervision module that adaptively leverages normal priors from a pre-trained large-scale normal model.Experimental results demonstrate that Car-GS achieves precise reconstruction of car surfaces and significantly outperforms prior methods. The project page is available at https://lcc815.github.io/Car-GS.
STT: Stateful Tracking with Transformers for Autonomous Driving
Apr 30, 2024Abstract:Tracking objects in three-dimensional space is critical for autonomous driving. To ensure safety while driving, the tracker must be able to reliably track objects across frames and accurately estimate their states such as velocity and acceleration in the present. Existing works frequently focus on the association task while either neglecting the model performance on state estimation or deploying complex heuristics to predict the states. In this paper, we propose STT, a Stateful Tracking model built with Transformers, that can consistently track objects in the scenes while also predicting their states accurately. STT consumes rich appearance, geometry, and motion signals through long term history of detections and is jointly optimized for both data association and state estimation tasks. Since the standard tracking metrics like MOTA and MOTP do not capture the combined performance of the two tasks in the wider spectrum of object states, we extend them with new metrics called S-MOTA and MOTPS that address this limitation. STT achieves competitive real-time performance on the Waymo Open Dataset.
HiH: A Multi-modal Hierarchy in Hierarchy Network for Unconstrained Gait Recognition
Nov 19, 2023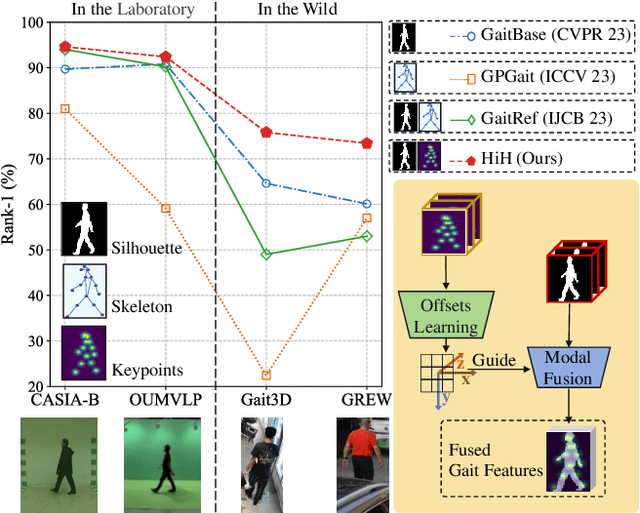
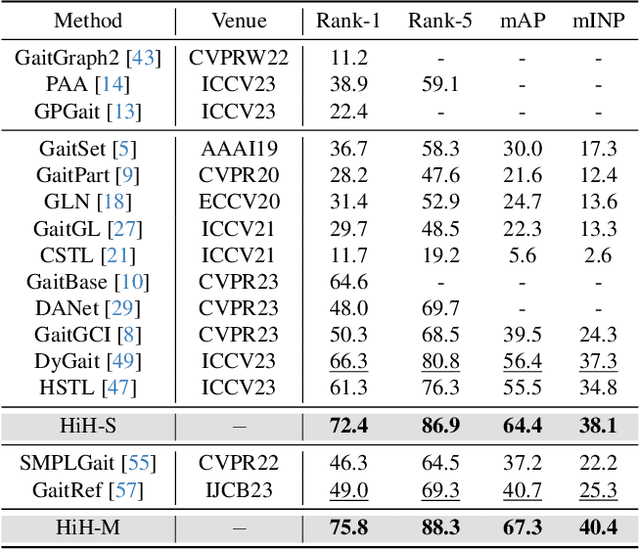
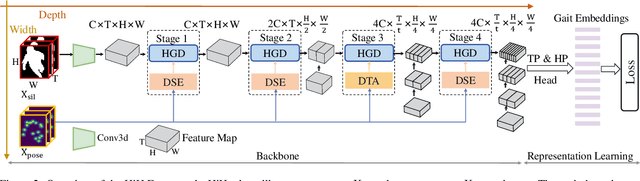
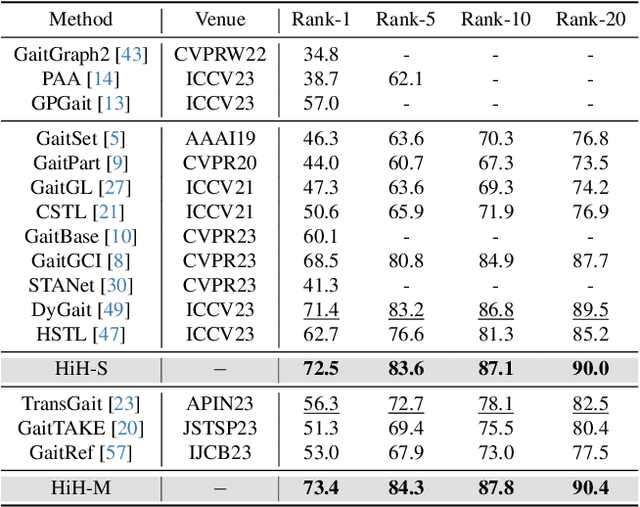
Abstract:Gait recognition has achieved promising advances in controlled settings, yet it significantly struggles in unconstrained environments due to challenges such as view changes, occlusions, and varying walking speeds. Additionally, efforts to fuse multiple modalities often face limited improvements because of cross-modality incompatibility, particularly in outdoor scenarios. To address these issues, we present a multi-modal Hierarchy in Hierarchy network (HiH) that integrates silhouette and pose sequences for robust gait recognition. HiH features a main branch that utilizes Hierarchical Gait Decomposer (HGD) modules for depth-wise and intra-module hierarchical examination of general gait patterns from silhouette data. This approach captures motion hierarchies from overall body dynamics to detailed limb movements, facilitating the representation of gait attributes across multiple spatial resolutions. Complementing this, an auxiliary branch, based on 2D joint sequences, enriches the spatial and temporal aspects of gait analysis. It employs a Deformable Spatial Enhancement (DSE) module for pose-guided spatial attention and a Deformable Temporal Alignment (DTA) module for aligning motion dynamics through learned temporal offsets. Extensive evaluations across diverse indoor and outdoor datasets demonstrate HiH's state-of-the-art performance, affirming a well-balanced trade-off between accuracy and efficiency.
Local Compressed Video Stream Learning for Generic Event Boundary Detection
Sep 27, 2023
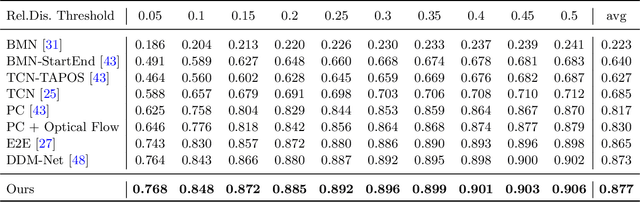
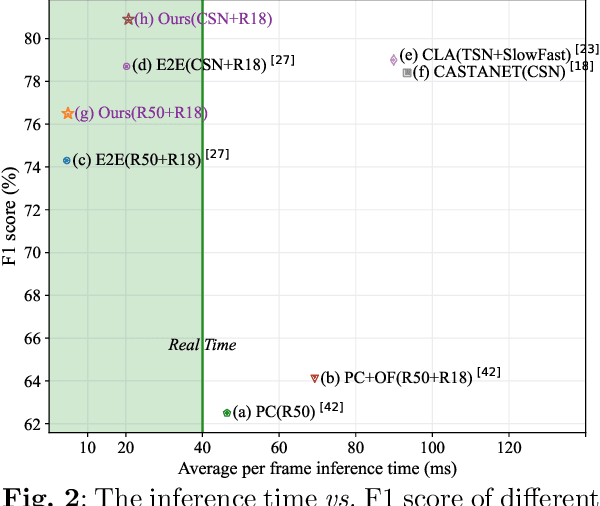
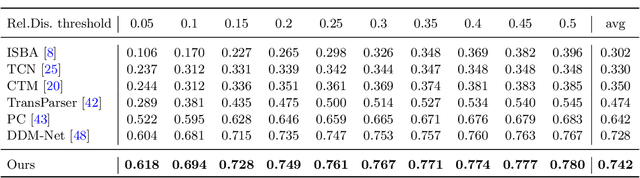
Abstract:Generic event boundary detection aims to localize the generic, taxonomy-free event boundaries that segment videos into chunks. Existing methods typically require video frames to be decoded before feeding into the network, which contains significant spatio-temporal redundancy and demands considerable computational power and storage space. To remedy these issues, we propose a novel compressed video representation learning method for event boundary detection that is fully end-to-end leveraging rich information in the compressed domain, i.e., RGB, motion vectors, residuals, and the internal group of pictures (GOP) structure, without fully decoding the video. Specifically, we use lightweight ConvNets to extract features of the P-frames in the GOPs and spatial-channel attention module (SCAM) is designed to refine the feature representations of the P-frames based on the compressed information with bidirectional information flow. To learn a suitable representation for boundary detection, we construct the local frames bag for each candidate frame and use the long short-term memory (LSTM) module to capture temporal relationships. We then compute frame differences with group similarities in the temporal domain. This module is only applied within a local window, which is critical for event boundary detection. Finally a simple classifier is used to determine the event boundaries of video sequences based on the learned feature representation. To remedy the ambiguities of annotations and speed up the training process, we use the Gaussian kernel to preprocess the ground-truth event boundaries. Extensive experiments conducted on the Kinetics-GEBD and TAPOS datasets demonstrate that the proposed method achieves considerable improvements compared to previous end-to-end approach while running at the same speed. The code is available at https://github.com/GX77/LCVSL.
Pedestrian Crossing Action Recognition and Trajectory Prediction with 3D Human Keypoints
Jun 01, 2023



Abstract:Accurate understanding and prediction of human behaviors are critical prerequisites for autonomous vehicles, especially in highly dynamic and interactive scenarios such as intersections in dense urban areas. In this work, we aim at identifying crossing pedestrians and predicting their future trajectories. To achieve these goals, we not only need the context information of road geometry and other traffic participants but also need fine-grained information of the human pose, motion and activity, which can be inferred from human keypoints. In this paper, we propose a novel multi-task learning framework for pedestrian crossing action recognition and trajectory prediction, which utilizes 3D human keypoints extracted from raw sensor data to capture rich information on human pose and activity. Moreover, we propose to apply two auxiliary tasks and contrastive learning to enable auxiliary supervisions to improve the learned keypoints representation, which further enhances the performance of major tasks. We validate our approach on a large-scale in-house dataset, as well as a public benchmark dataset, and show that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on a wide range of evaluation metrics. The effectiveness of each model component is validated in a detailed ablation study.
SC-Transformer++: Structured Context Transformer for Generic Event Boundary Detection
Jun 25, 2022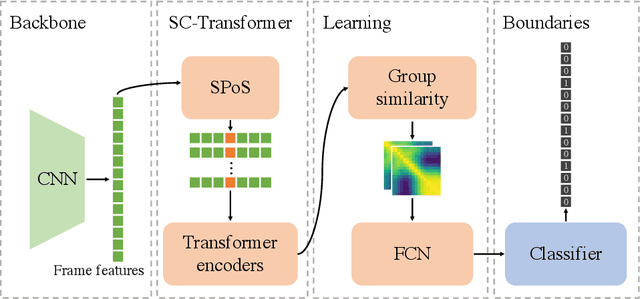
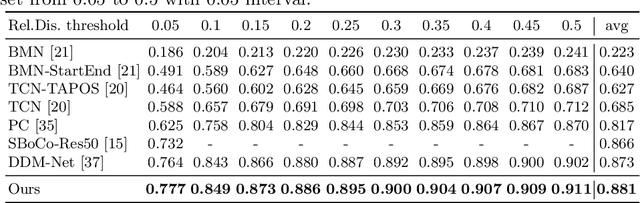
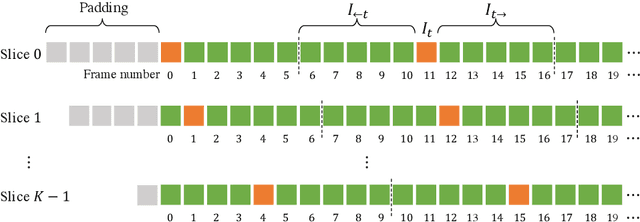
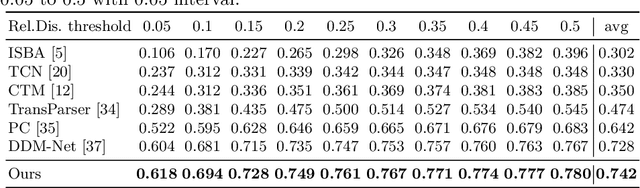
Abstract:This report presents the algorithm used in the submission of Generic Event Boundary Detection (GEBD) Challenge at CVPR 2022. In this work, we improve the existing Structured Context Transformer (SC-Transformer) method for GEBD. Specifically, a transformer decoder module is added after transformer encoders to extract high quality frame features. The final classification is performed jointly on the results of the original binary classifier and a newly introduced multi-class classifier branch. To enrich motion information, optical flow is introduced as a new modality. Finally, model ensemble is used to further boost performance. The proposed method achieves 86.49% F1 score on Kinetics-GEBD test set. which improves 2.86% F1 score compared to the previous SOTA method.
Depth Estimation Matters Most: Improving Per-Object Depth Estimation for Monocular 3D Detection and Tracking
Jun 08, 2022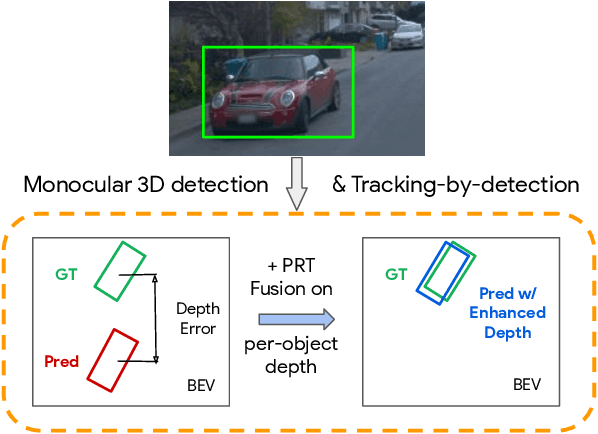
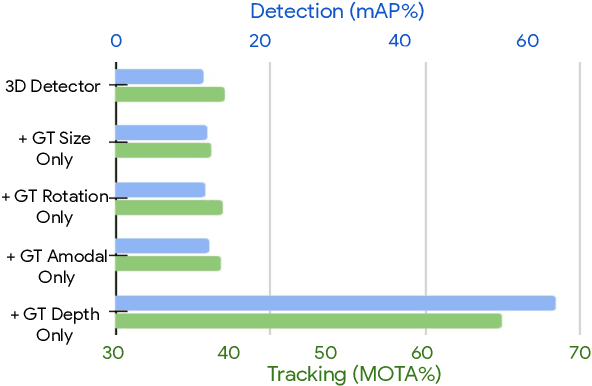
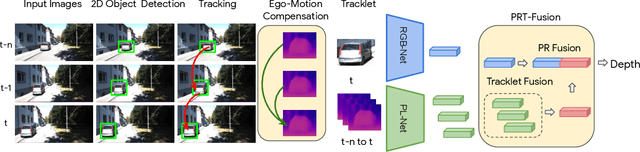
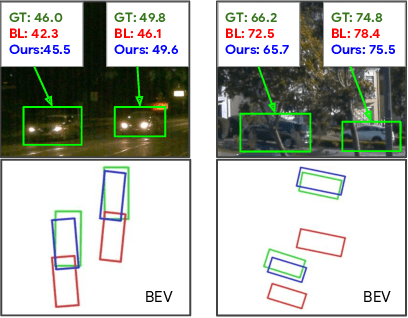
Abstract:Monocular image-based 3D perception has become an active research area in recent years owing to its applications in autonomous driving. Approaches to monocular 3D perception including detection and tracking, however, often yield inferior performance when compared to LiDAR-based techniques. Through systematic analysis, we identified that per-object depth estimation accuracy is a major factor bounding the performance. Motivated by this observation, we propose a multi-level fusion method that combines different representations (RGB and pseudo-LiDAR) and temporal information across multiple frames for objects (tracklets) to enhance per-object depth estimation. Our proposed fusion method achieves the state-of-the-art performance of per-object depth estimation on the Waymo Open Dataset, the KITTI detection dataset, and the KITTI MOT dataset. We further demonstrate that by simply replacing estimated depth with fusion-enhanced depth, we can achieve significant improvements in monocular 3D perception tasks, including detection and tracking.
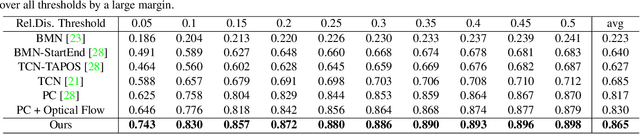
Structured Context Transformer for Generic Event Boundary Detection
Jun 07, 2022



Abstract:Generic Event Boundary Detection (GEBD) aims to detect moments where humans naturally perceive as event boundaries. In this paper, we present Structured Context Transformer (or SC-Transformer) to solve the GEBD task, which can be trained in an end-to-end fashion. Specifically, we use the backbone convolutional neural network (CNN) to extract the features of each video frame. To capture temporal context information of each frame, we design the structure context transformer (SC-Transformer) by re-partitioning input frame sequence. Note that, the overall computation complexity of SC-Transformer is linear to the video length. After that, the group similarities are computed to capture the differences between frames. Then, a lightweight fully convolutional network is used to determine the event boundaries based on the grouped similarity maps. To remedy the ambiguities of boundary annotations, the Gaussian kernel is adopted to preprocess the ground-truth event boundaries to further boost the accuracy. Extensive experiments conducted on the challenging Kinetics-GEBD and TAPOS datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method compared to the state-of-the-art methods.
End-to-End Compressed Video Representation Learning for Generic Event Boundary Detection
Mar 29, 2022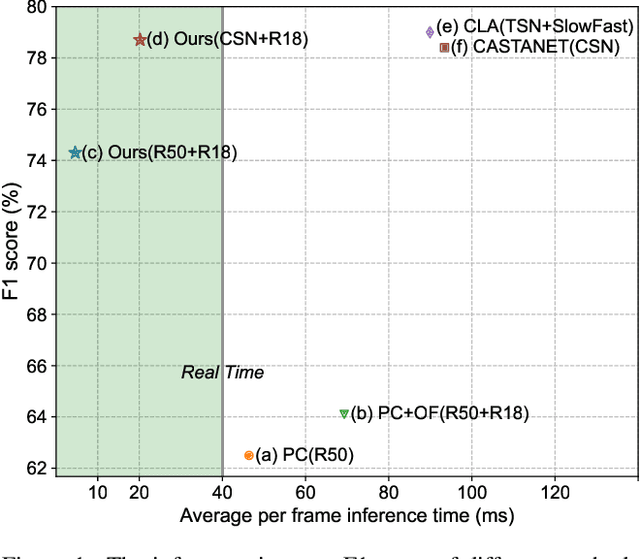
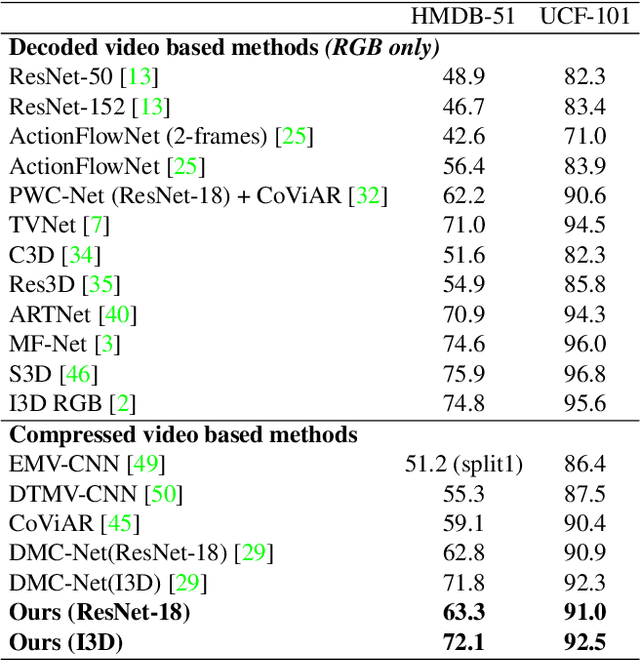
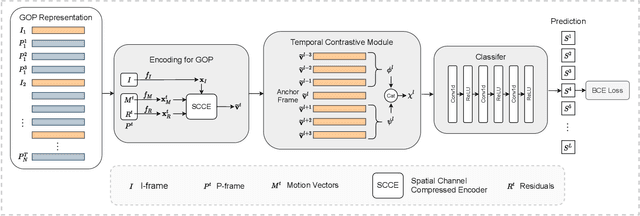
Abstract:Generic event boundary detection aims to localize the generic, taxonomy-free event boundaries that segment videos into chunks. Existing methods typically require video frames to be decoded before feeding into the network, which demands considerable computational power and storage space. To that end, we propose a new end-to-end compressed video representation learning for event boundary detection that leverages the rich information in the compressed domain, i.e., RGB, motion vectors, residuals, and the internal group of pictures (GOP) structure, without fully decoding the video. Specifically, we first use the ConvNets to extract features of the I-frames in the GOPs. After that, a light-weight spatial-channel compressed encoder is designed to compute the feature representations of the P-frames based on the motion vectors, residuals and representations of their dependent I-frames. A temporal contrastive module is proposed to determine the event boundaries of video sequences. To remedy the ambiguities of annotations and speed up the training process, we use the Gaussian kernel to preprocess the ground-truth event boundaries. Extensive experiments conducted on the Kinetics-GEBD dataset demonstrate that the proposed method achieves comparable results to the state-of-the-art methods with $4.5\times$ faster running speed.
Multi-modal 3D Human Pose Estimation with 2D Weak Supervision in Autonomous Driving
Dec 22, 2021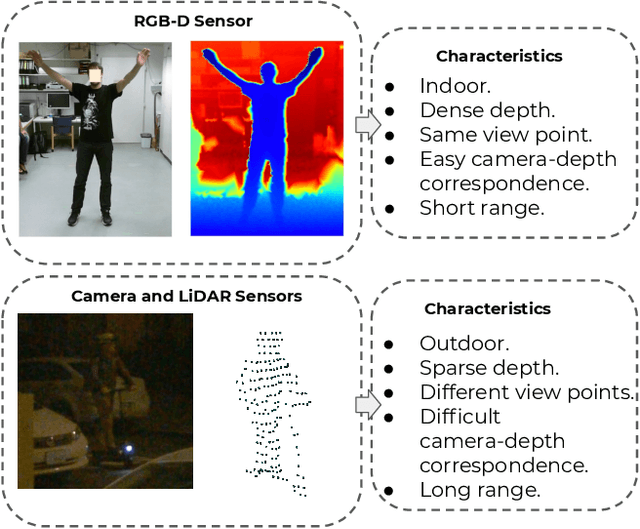
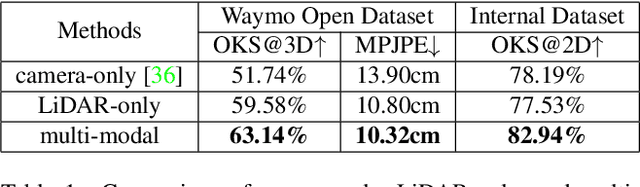
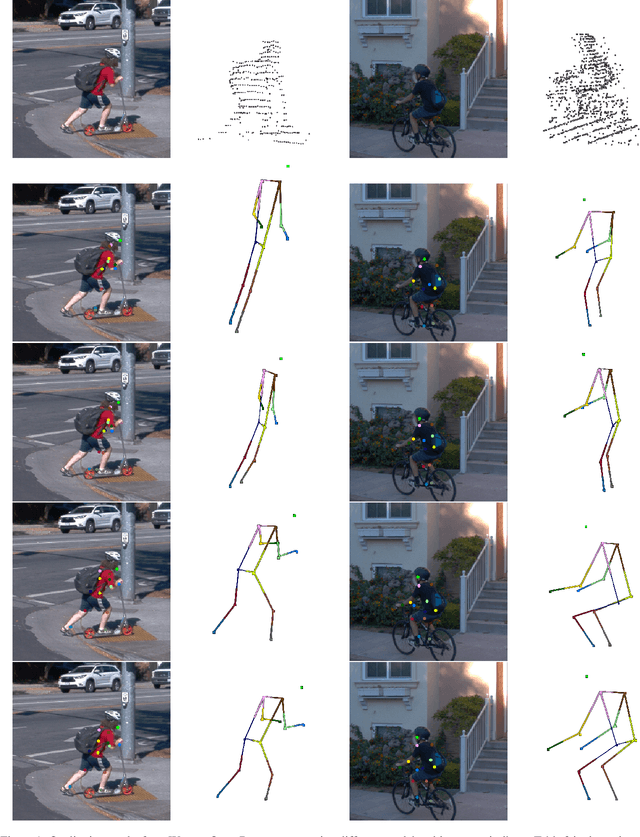
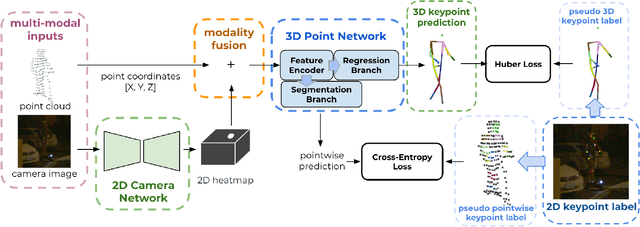
Abstract:3D human pose estimation (HPE) in autonomous vehicles (AV) differs from other use cases in many factors, including the 3D resolution and range of data, absence of dense depth maps, failure modes for LiDAR, relative location between the camera and LiDAR, and a high bar for estimation accuracy. Data collected for other use cases (such as virtual reality, gaming, and animation) may therefore not be usable for AV applications. This necessitates the collection and annotation of a large amount of 3D data for HPE in AV, which is time-consuming and expensive. In this paper, we propose one of the first approaches to alleviate this problem in the AV setting. Specifically, we propose a multi-modal approach which uses 2D labels on RGB images as weak supervision to perform 3D HPE. The proposed multi-modal architecture incorporates LiDAR and camera inputs with an auxiliary segmentation branch. On the Waymo Open Dataset, our approach achieves a 22% relative improvement over camera-only 2D HPE baseline, and 6% improvement over LiDAR-only model. Finally, careful ablation studies and parts based analysis illustrate the advantages of each of our contributions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge