Haojun Yu
DeformCL: Learning Deformable Centerline Representation for Vessel Extraction in 3D Medical Image
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:In the field of 3D medical imaging, accurately extracting and representing the blood vessels with curvilinear structures holds paramount importance for clinical diagnosis. Previous methods have commonly relied on discrete representation like mask, often resulting in local fractures or scattered fragments due to the inherent limitations of the per-pixel classification paradigm. In this work, we introduce DeformCL, a new continuous representation based on Deformable Centerlines, where centerline points act as nodes connected by edges that capture spatial relationships. Compared with previous representations, DeformCL offers three key advantages: natural connectivity, noise robustness, and interaction facility. We present a comprehensive training pipeline structured in a cascaded manner to fully exploit these favorable properties of DeformCL. Extensive experiments on four 3D vessel segmentation datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our method. Furthermore, the visualization of curved planar reformation images validates the clinical significance of the proposed framework. We release the code in https://github.com/barry664/DeformCL
LarvSeg: Exploring Image Classification Data For Large Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation via Category-wise Attentive Classifier
Jan 12, 2025



Abstract:Scaling up the vocabulary of semantic segmentation models is extremely challenging because annotating large-scale mask labels is labour-intensive and time-consuming. Recently, language-guided segmentation models have been proposed to address this challenge. However, their performance drops significantly when applied to out-of-distribution categories. In this paper, we propose a new large vocabulary semantic segmentation framework, called LarvSeg. Different from previous works, LarvSeg leverages image classification data to scale the vocabulary of semantic segmentation models as large-vocabulary classification datasets usually contain balanced categories and are much easier to obtain. However, for classification tasks, the category is image-level, while for segmentation we need to predict the label at pixel level. To address this issue, we first propose a general baseline framework to incorporate image-level supervision into the training process of a pixel-level segmentation model, making the trained network perform semantic segmentation on newly introduced categories in the classification data. We then observe that a model trained on segmentation data can group pixel features of categories beyond the training vocabulary. Inspired by this finding, we design a category-wise attentive classifier to apply supervision to the precise regions of corresponding categories to improve the model performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that LarvSeg significantly improves the large vocabulary semantic segmentation performance, especially in the categories without mask labels. For the first time, we provide a 21K-category semantic segmentation model with the help of ImageNet21K. The code is available at https://github.com/HaojunYu1998/large_voc_seg.
A Foundational Generative Model for Breast Ultrasound Image Analysis
Jan 12, 2025



Abstract:Foundational models have emerged as powerful tools for addressing various tasks in clinical settings. However, their potential development to breast ultrasound analysis remains untapped. In this paper, we present BUSGen, the first foundational generative model specifically designed for breast ultrasound image analysis. Pretrained on over 3.5 million breast ultrasound images, BUSGen has acquired extensive knowledge of breast structures, pathological features, and clinical variations. With few-shot adaptation, BUSGen can generate repositories of realistic and informative task-specific data, facilitating the development of models for a wide range of downstream tasks. Extensive experiments highlight BUSGen's exceptional adaptability, significantly exceeding real-data-trained foundational models in breast cancer screening, diagnosis, and prognosis. In breast cancer early diagnosis, our approach outperformed all board-certified radiologists (n=9), achieving an average sensitivity improvement of 16.5% (P-value<0.0001). Additionally, we characterized the scaling effect of using generated data which was as effective as the collected real-world data for training diagnostic models. Moreover, extensive experiments demonstrated that our approach improved the generalization ability of downstream models. Importantly, BUSGen protected patient privacy by enabling fully de-identified data sharing, making progress forward in secure medical data utilization. An online demo of BUSGen is available at https://aibus.bio.
Knowledge-driven AI-generated data for accurate and interpretable breast ultrasound diagnoses
Jul 23, 2024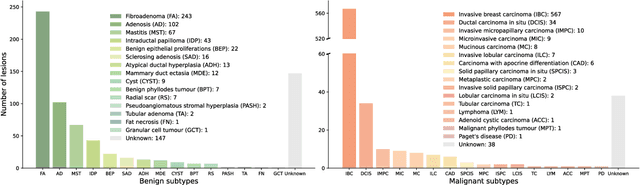
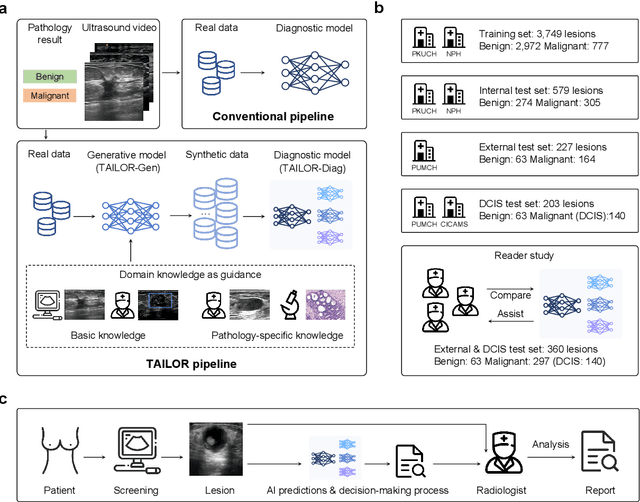
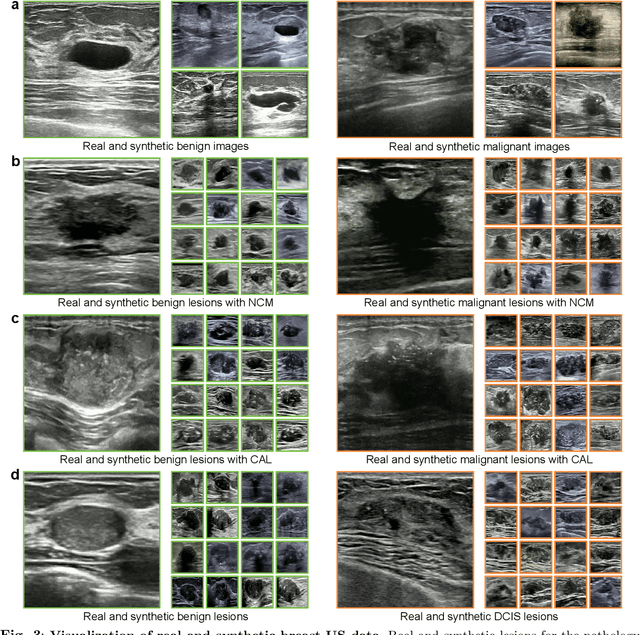
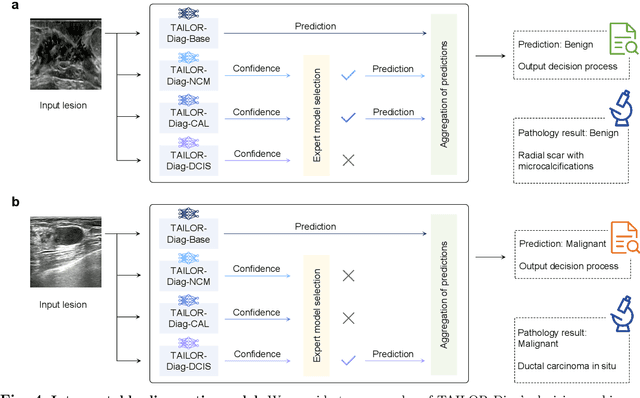
Abstract:Data-driven deep learning models have shown great capabilities to assist radiologists in breast ultrasound (US) diagnoses. However, their effectiveness is limited by the long-tail distribution of training data, which leads to inaccuracies in rare cases. In this study, we address a long-standing challenge of improving the diagnostic model performance on rare cases using long-tailed data. Specifically, we introduce a pipeline, TAILOR, that builds a knowledge-driven generative model to produce tailored synthetic data. The generative model, using 3,749 lesions as source data, can generate millions of breast-US images, especially for error-prone rare cases. The generated data can be further used to build a diagnostic model for accurate and interpretable diagnoses. In the prospective external evaluation, our diagnostic model outperforms the average performance of nine radiologists by 33.5% in specificity with the same sensitivity, improving their performance by providing predictions with an interpretable decision-making process. Moreover, on ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), our diagnostic model outperforms all radiologists by a large margin, with only 34 DCIS lesions in the source data. We believe that TAILOR can potentially be extended to various diseases and imaging modalities.
Mining Negative Temporal Contexts For False Positive Suppression In Real-Time Ultrasound Lesion Detection
May 29, 2023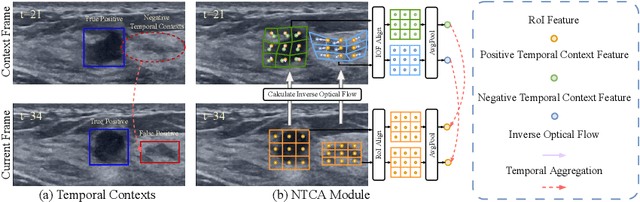
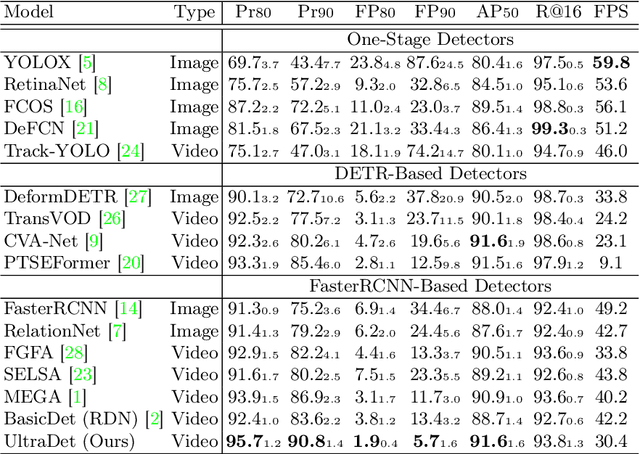
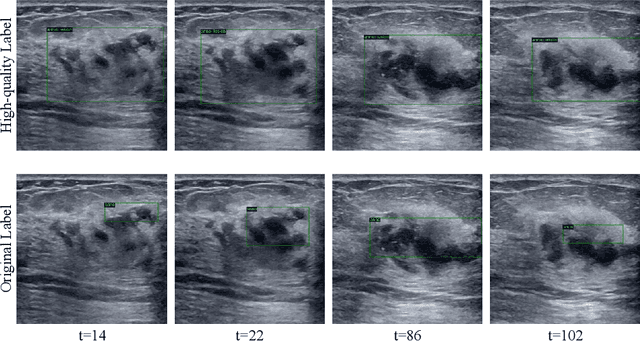
Abstract:During ultrasonic scanning processes, real-time lesion detection can assist radiologists in accurate cancer diagnosis. However, this essential task remains challenging and underexplored. General-purpose real-time object detection models can mistakenly report obvious false positives (FPs) when applied to ultrasound videos, potentially misleading junior radiologists. One key issue is their failure to utilize negative symptoms in previous frames, denoted as negative temporal contexts (NTC). To address this issue, we propose to extract contexts from previous frames, including NTC, with the guidance of inverse optical flow. By aggregating extracted contexts, we endow the model with the ability to suppress FPs by leveraging NTC. We call the resulting model UltraDet. The proposed UltraDet demonstrates significant improvement over previous state-of-the-arts and achieves real-time inference speed. To facilitate future research, we will release the code, checkpoints, and high-quality labels of the CVA-BUS dataset used in our experiments.
DETRs with Hybrid Matching
Jul 26, 2022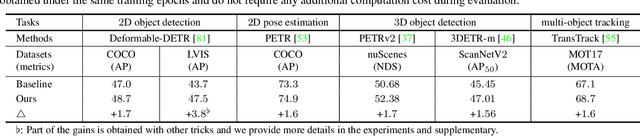
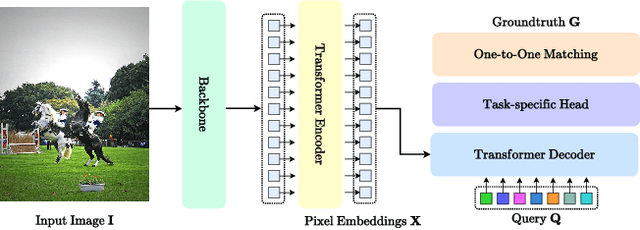
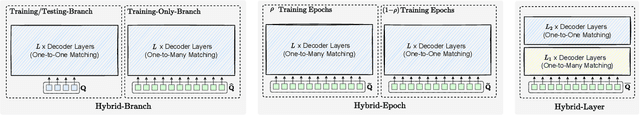
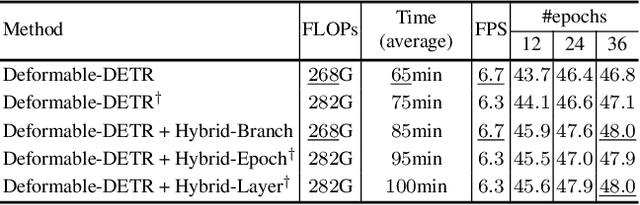
Abstract:One-to-one set matching is a key design for DETR to establish its end-to-end capability, so that object detection does not require a hand-crafted NMS (non-maximum suppression) method to remove duplicate detections. This end-to-end signature is important for the versatility of DETR, and it has been generalized to a wide range of visual problems, including instance/semantic segmentation, human pose estimation, and point cloud/multi-view-images based detection, etc. However, we note that because there are too few queries assigned as positive samples, the one-to-one set matching significantly reduces the training efficiency of positive samples. This paper proposes a simple yet effective method based on a hybrid matching scheme that combines the original one-to-one matching branch with auxiliary queries that use one-to-many matching loss during training. This hybrid strategy has been shown to significantly improve training efficiency and improve accuracy. In inference, only the original one-to-one match branch is used, thus maintaining the end-to-end merit and the same inference efficiency of DETR. The method is named $\mathcal{H}$-DETR, and it shows that a wide range of representative DETR methods can be consistently improved across a wide range of visual tasks, including Deformable-DETR, 3DETR/PETRv2, PETR, and TransTrack, among others. Code will be available at: https://github.com/HDETR
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge