Ding Jia
GeminiFusion: Efficient Pixel-wise Multimodal Fusion for Vision Transformer
Jun 04, 2024



Abstract:Cross-modal transformers have demonstrated superiority in various vision tasks by effectively integrating different modalities. This paper first critiques prior token exchange methods which replace less informative tokens with inter-modal features, and demonstrate exchange based methods underperform cross-attention mechanisms, while the computational demand of the latter inevitably restricts its use with longer sequences. To surmount the computational challenges, we propose GeminiFusion, a pixel-wise fusion approach that capitalizes on aligned cross-modal representations. GeminiFusion elegantly combines intra-modal and inter-modal attentions, dynamically integrating complementary information across modalities. We employ a layer-adaptive noise to adaptively control their interplay on a per-layer basis, thereby achieving a harmonized fusion process. Notably, GeminiFusion maintains linear complexity with respect to the number of input tokens, ensuring this multimodal framework operates with efficiency comparable to unimodal networks. Comprehensive evaluations across multimodal image-to-image translation, 3D object detection and arbitrary-modal semantic segmentation tasks, including RGB, depth, LiDAR, event data, etc. demonstrate the superior performance of our GeminiFusion against leading-edge techniques. The PyTorch code is available at https://github.com/JiaDingCN/GeminiFusion
detrex: Benchmarking Detection Transformers
Jun 13, 2023



Abstract:The DEtection TRansformer (DETR) algorithm has received considerable attention in the research community and is gradually emerging as a mainstream approach for object detection and other perception tasks. However, the current field lacks a unified and comprehensive benchmark specifically tailored for DETR-based models. To address this issue, we develop a unified, highly modular, and lightweight codebase called detrex, which supports a majority of the mainstream DETR-based instance recognition algorithms, covering various fundamental tasks, including object detection, segmentation, and pose estimation. We conduct extensive experiments under detrex and perform a comprehensive benchmark for DETR-based models. Moreover, we enhance the performance of detection transformers through the refinement of training hyper-parameters, providing strong baselines for supported algorithms.We hope that detrex could offer research communities a standardized and unified platform to evaluate and compare different DETR-based models while fostering a deeper understanding and driving advancements in DETR-based instance recognition. Our code is available at https://github.com/IDEA-Research/detrex. The project is currently being actively developed. We encourage the community to use detrex codebase for further development and contributions.
Expediting Large-Scale Vision Transformer for Dense Prediction without Fine-tuning
Oct 03, 2022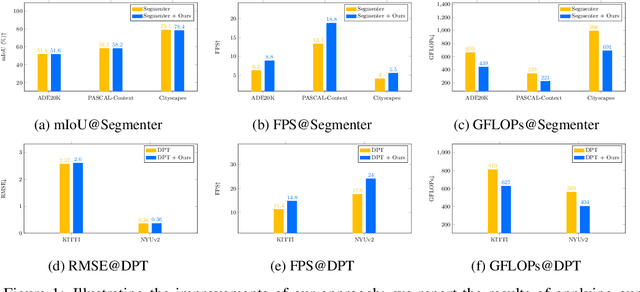

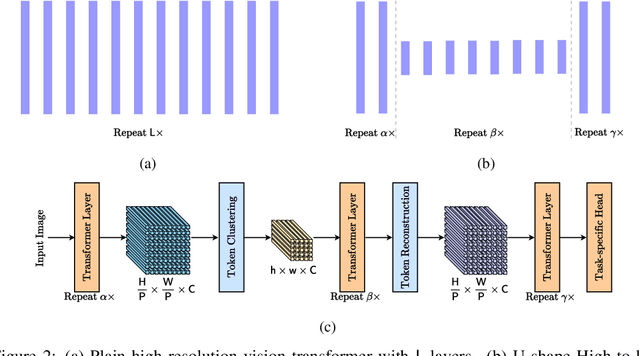
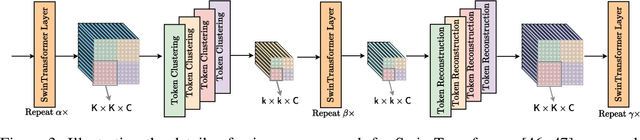
Abstract:Vision transformers have recently achieved competitive results across various vision tasks but still suffer from heavy computation costs when processing a large number of tokens. Many advanced approaches have been developed to reduce the total number of tokens in large-scale vision transformers, especially for image classification tasks. Typically, they select a small group of essential tokens according to their relevance with the class token, then fine-tune the weights of the vision transformer. Such fine-tuning is less practical for dense prediction due to the much heavier computation and GPU memory cost than image classification. In this paper, we focus on a more challenging problem, i.e., accelerating large-scale vision transformers for dense prediction without any additional re-training or fine-tuning. In response to the fact that high-resolution representations are necessary for dense prediction, we present two non-parametric operators, a token clustering layer to decrease the number of tokens and a token reconstruction layer to increase the number of tokens. The following steps are performed to achieve this: (i) we use the token clustering layer to cluster the neighboring tokens together, resulting in low-resolution representations that maintain the spatial structures; (ii) we apply the following transformer layers only to these low-resolution representations or clustered tokens; and (iii) we use the token reconstruction layer to re-create the high-resolution representations from the refined low-resolution representations. The results obtained by our method are promising on five dense prediction tasks, including object detection, semantic segmentation, panoptic segmentation, instance segmentation, and depth estimation.
DETRs with Hybrid Matching
Jul 26, 2022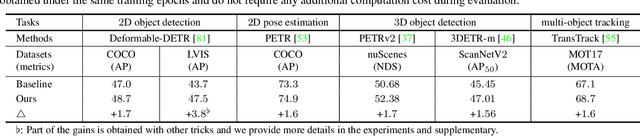
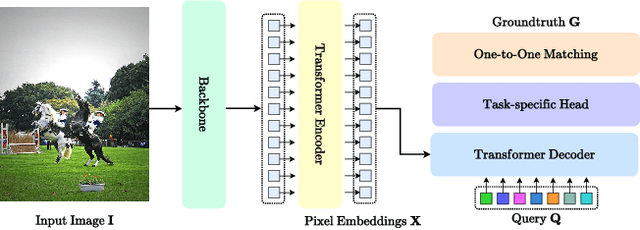
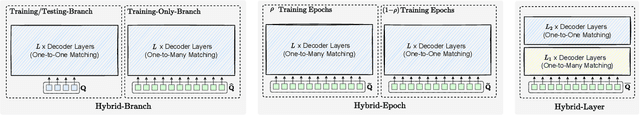
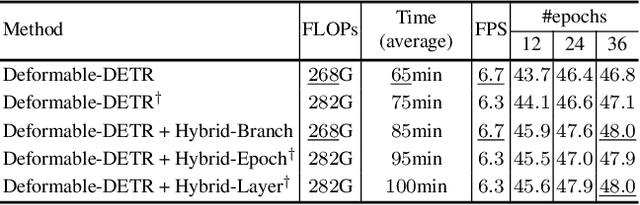
Abstract:One-to-one set matching is a key design for DETR to establish its end-to-end capability, so that object detection does not require a hand-crafted NMS (non-maximum suppression) method to remove duplicate detections. This end-to-end signature is important for the versatility of DETR, and it has been generalized to a wide range of visual problems, including instance/semantic segmentation, human pose estimation, and point cloud/multi-view-images based detection, etc. However, we note that because there are too few queries assigned as positive samples, the one-to-one set matching significantly reduces the training efficiency of positive samples. This paper proposes a simple yet effective method based on a hybrid matching scheme that combines the original one-to-one matching branch with auxiliary queries that use one-to-many matching loss during training. This hybrid strategy has been shown to significantly improve training efficiency and improve accuracy. In inference, only the original one-to-one match branch is used, thus maintaining the end-to-end merit and the same inference efficiency of DETR. The method is named $\mathcal{H}$-DETR, and it shows that a wide range of representative DETR methods can be consistently improved across a wide range of visual tasks, including Deformable-DETR, 3DETR/PETRv2, PETR, and TransTrack, among others. Code will be available at: https://github.com/HDETR
Efficient Vision Transformers via Fine-Grained Manifold Distillation
Jul 06, 2021



Abstract:This paper studies the model compression problem of vision transformers. Benefit from the self-attention module, transformer architectures have shown extraordinary performance on many computer vision tasks. Although the network performance is boosted, transformers are often required more computational resources including memory usage and the inference complexity. Compared with the existing knowledge distillation approaches, we propose to excavate useful information from the teacher transformer through the relationship between images and the divided patches. We then explore an efficient fine-grained manifold distillation approach that simultaneously calculates cross-images, cross-patch, and random-selected manifolds in teacher and student models. Experimental results conducted on several benchmarks demonstrate the superiority of the proposed algorithm for distilling portable transformer models with higher performance. For example, our approach achieves 75.06% Top-1 accuracy on the ImageNet-1k dataset for training a DeiT-Tiny model, which outperforms other ViT distillation methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge