Xiao Luo
Celine
InstructDiff: Domain-Adaptive Data Selection via Differential Entropy for Efficient LLM Fine-Tuning
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Supervised fine-tuning (SFT) is fundamental to adapting large language models, yet training on complete datasets incurs prohibitive costs with diminishing returns. Existing data selection methods suffer from severe domain specificity: techniques optimized for general instruction-following fail on reasoning tasks, and vice versa. We observe that measuring entropy differences between base models and minimally instruction-tuned calibrated models reveals a pattern -- samples with the lowest differential entropy consistently yield optimal performance across domains, yet this principle manifests domain-adaptively: reasoning tasks favor entropy increase (cognitive expansion), while general tasks favor entropy decrease (cognitive compression). We introduce InstructDiff, a unified framework that operationalizes differential entropy as a domain-adaptive selection criterion through warmup calibration, bi-directional NLL filtering, and entropy-based ranking. Extensive experiments show that InstructDiff achieves 17\% relative improvement over full data training on mathematical reasoning and 52\% for general instruction-following, outperforming prior baselines while using only 10\% of the data.
DREAM: Dual-Standard Semantic Homogeneity with Dynamic Optimization for Graph Learning with Label Noise
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) have been widely used in various graph machine learning scenarios. Existing literature primarily assumes well-annotated training graphs, while the reliability of labels is not guaranteed in real-world scenarios. Recently, efforts have been made to address the problem of graph learning with label noise. However, existing methods often (i) struggle to distinguish between reliable and unreliable nodes, and (ii) overlook the relational information embedded in the graph topology. To tackle this problem, this paper proposes a novel method, Dual-Standard Semantic Homogeneity with Dynamic Optimization (DREAM), for reliable, relation-informed optimization on graphs with label noise. Specifically, we design a relation-informed dynamic optimization framework that iteratively reevaluates the reliability of each labeled node in the graph during the optimization process according to the relation of the target node and other nodes. To measure this relation comprehensively, we propose a dual-standard selection strategy that selects a set of anchor nodes based on both node proximity and graph topology. Subsequently, we compute the semantic homogeneity between the target node and the anchor nodes, which serves as guidance for optimization. We also provide a rigorous theoretical analysis to justify the design of DREAM. Extensive experiments are performed on six graph datasets across various domains under three types of graph label noise against competing baselines, and the results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed DREAM.
DeepEra: A Deep Evidence Reranking Agent for Scientific Retrieval-Augmented Generated Question Answering
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:With the rapid growth of scientific literature, scientific question answering (SciQA) has become increasingly critical for exploring and utilizing scientific knowledge. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) enhances LLMs by incorporating knowledge from external sources, thereby providing credible evidence for scientific question answering. But existing retrieval and reranking methods remain vulnerable to passages that are semantically similar but logically irrelevant, often reducing factual reliability and amplifying hallucinations.To address this challenge, we propose a Deep Evidence Reranking Agent (DeepEra) that integrates step-by-step reasoning, enabling more precise evaluation of candidate passages beyond surface-level semantics. To support systematic evaluation, we construct SciRAG-SSLI (Scientific RAG - Semantically Similar but Logically Irrelevant), a large-scale dataset comprising about 300K SciQA instances across 10 subjects, constructed from 10M scientific corpus. The dataset combines naturally retrieved contexts with systematically generated distractors to test logical robustness and factual grounding. Comprehensive evaluations confirm that our approach achieves superior retrieval performance compared to leading rerankers. To our knowledge, this work is the first to comprehensively study and empirically validate innegligible SSLI issues in two-stage RAG frameworks.
Simulator and Experience Enhanced Diffusion Model for Comprehensive ECG Generation
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a leading cause of mortality worldwide. Electrocardiograms (ECGs) are the most widely used non-invasive tool for cardiac assessment, yet large, well-annotated ECG corpora are scarce due to cost, privacy, and workflow constraints. Generating ECGs can be beneficial for the mechanistic understanding of cardiac electrical activity, enable the construction of large, heterogeneous, and unbiased datasets, and facilitate privacy-preserving data sharing. Generating realistic ECG signals from clinical context is important yet underexplored. Recent work has leveraged diffusion models for text-to-ECG generation, but two challenges remain: (i) existing methods often overlook the physiological simulator knowledge of cardiac activity; and (ii) they ignore broader, experience-based clinical knowledge grounded in real-world practice. To address these gaps, we propose SE-Diff, a novel physiological simulator and experience enhanced diffusion model for comprehensive ECG generation. SE-Diff integrates a lightweight ordinary differential equation (ODE)-based ECG simulator into the diffusion process via a beat decoder and simulator-consistent constraints, injecting mechanistic priors that promote physiologically plausible waveforms. In parallel, we design an LLM-powered experience retrieval-augmented strategy to inject clinical knowledge, providing more guidance for ECG generation. Extensive experiments on real-world ECG datasets demonstrate that SE-Diff improves both signal fidelity and text-ECG semantic alignment over baselines, proving its superiority for text-to-ECG generation. We further show that the simulator-based and experience-based knowledge also benefit downstream ECG classification.
Conditional Neural ODE for Longitudinal Parkinson's Disease Progression Forecasting
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Parkinson's disease (PD) shows heterogeneous, evolving brain-morphometry patterns. Modeling these longitudinal trajectories enables mechanistic insight, treatment development, and individualized 'digital-twin' forecasting. However, existing methods usually adopt recurrent neural networks and transformer architectures, which rely on discrete, regularly sampled data while struggling to handle irregular and sparse magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in PD cohorts. Moreover, these methods have difficulty capturing individual heterogeneity including variations in disease onset, progression rate, and symptom severity, which is a hallmark of PD. To address these challenges, we propose CNODE (Conditional Neural ODE), a novel framework for continuous, individualized PD progression forecasting. The core of CNODE is to model morphological brain changes as continuous temporal processes using a neural ODE model. In addition, we jointly learn patient-specific initial time and progress speed to align individual trajectories into a shared progression trajectory. We validate CNODE on the Parkinson's Progression Markers Initiative (PPMI) dataset. Experimental results show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in forecasting longitudinal PD progression.
A Survey on Efficient Large Language Model Training: From Data-centric Perspectives
Oct 29, 2025Abstract:Post-training of Large Language Models (LLMs) is crucial for unlocking their task generalization potential and domain-specific capabilities. However, the current LLM post-training paradigm faces significant data challenges, including the high costs of manual annotation and diminishing marginal returns on data scales. Therefore, achieving data-efficient post-training has become a key research question. In this paper, we present the first systematic survey of data-efficient LLM post-training from a data-centric perspective. We propose a taxonomy of data-efficient LLM post-training methods, covering data selection, data quality enhancement, synthetic data generation, data distillation and compression, and self-evolving data ecosystems. We summarize representative approaches in each category and outline future research directions. By examining the challenges in data-efficient LLM post-training, we highlight open problems and propose potential research avenues. We hope our work inspires further exploration into maximizing the potential of data utilization in large-scale model training. Paper List: https://github.com/luo-junyu/Awesome-Data-Efficient-LLM
Monte Carlo Tree Diffusion with Multiple Experts for Protein Design
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:The goal of protein design is to generate amino acid sequences that fold into functional structures with desired properties. Prior methods combining autoregressive language models with Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) struggle with long-range dependencies and suffer from an impractically large search space. We propose MCTD-ME, Monte Carlo Tree Diffusion with Multiple Experts, which integrates masked diffusion models with tree search to enable multi-token planning and efficient exploration. Unlike autoregressive planners, MCTD-ME uses biophysical-fidelity-enhanced diffusion denoising as the rollout engine, jointly revising multiple positions and scaling to large sequence spaces. It further leverages experts of varying capacities to enrich exploration, guided by a pLDDT-based masking schedule that targets low-confidence regions while preserving reliable residues. We propose a novel multi-expert selection rule (PH-UCT-ME) extends predictive-entropy UCT to expert ensembles. On the inverse folding task (CAMEO and PDB benchmarks), MCTD-ME outperforms single-expert and unguided baselines in both sequence recovery (AAR) and structural similarity (scTM), with gains increasing for longer proteins and benefiting from multi-expert guidance. More generally, the framework is model-agnostic and applicable beyond inverse folding, including de novo protein engineering and multi-objective molecular generation.
SciRerankBench: Benchmarking Rerankers Towards Scientific Retrieval-Augmented Generated LLMs
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Scientific literature question answering is a pivotal step towards new scientific discoveries. Recently, \textit{two-stage} retrieval-augmented generated large language models (RAG-LLMs) have shown impressive advancements in this domain. Such a two-stage framework, especially the second stage (reranker), is particularly essential in the scientific domain, where subtle differences in terminology may have a greatly negative impact on the final factual-oriented or knowledge-intensive answers. Despite this significant progress, the potential and limitations of these works remain unexplored. In this work, we present a Scientific Rerank-oriented RAG Benchmark (SciRerankBench), for evaluating rerankers within RAG-LLMs systems, spanning five scientific subjects. To rigorously assess the reranker performance in terms of noise resilience, relevance disambiguation, and factual consistency, we develop three types of question-context-answer (Q-C-A) pairs, i.e., Noisy Contexts (NC), Semantically Similar but Logically Irrelevant Contexts (SSLI), and Counterfactual Contexts (CC). Through systematic evaluation of 13 widely used rerankers on five families of LLMs, we provide detailed insights into their relative strengths and limitations. To the best of our knowledge, SciRerankBench is the first benchmark specifically developed to evaluate rerankers within RAG-LLMs, which provides valuable observations and guidance for their future development.
Fewer Denoising Steps or Cheaper Per-Step Inference: Towards Compute-Optimal Diffusion Model Deployment
Aug 08, 2025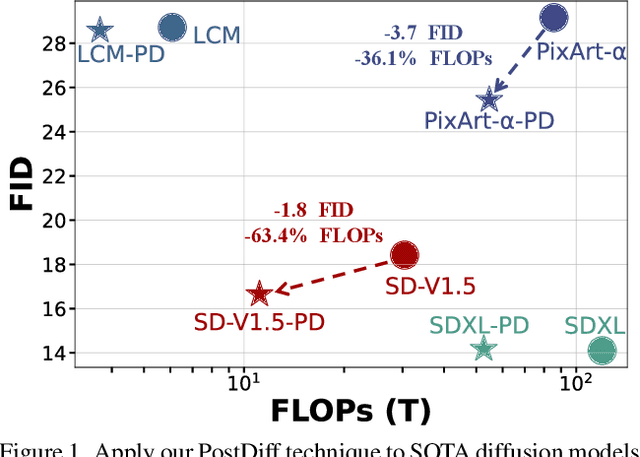
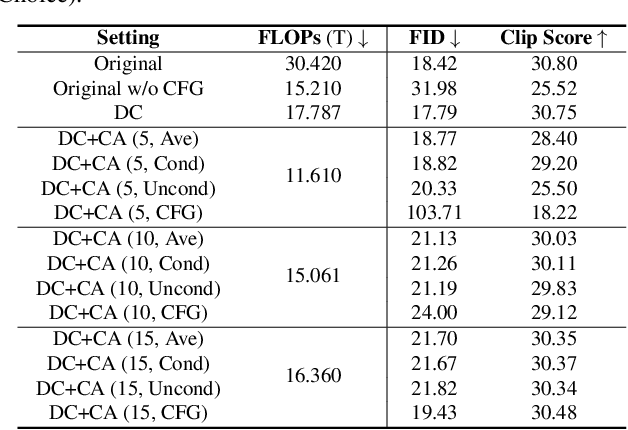
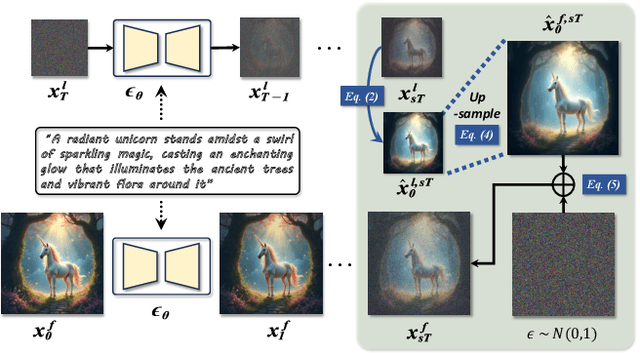
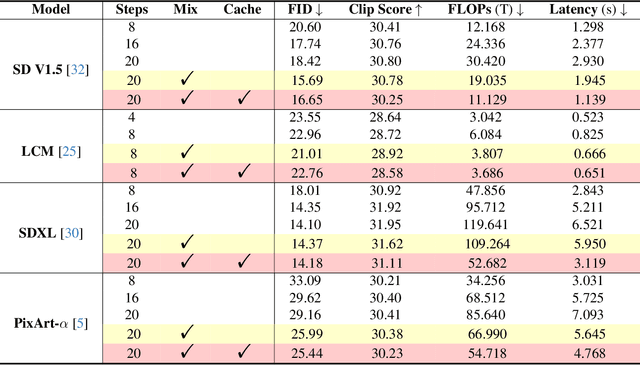
Abstract:Diffusion models have shown remarkable success across generative tasks, yet their high computational demands challenge deployment on resource-limited platforms. This paper investigates a critical question for compute-optimal diffusion model deployment: Under a post-training setting without fine-tuning, is it more effective to reduce the number of denoising steps or to use a cheaper per-step inference? Intuitively, reducing the number of denoising steps increases the variability of the distributions across steps, making the model more sensitive to compression. In contrast, keeping more denoising steps makes the differences smaller, preserving redundancy, and making post-training compression more feasible. To systematically examine this, we propose PostDiff, a training-free framework for accelerating pre-trained diffusion models by reducing redundancy at both the input level and module level in a post-training manner. At the input level, we propose a mixed-resolution denoising scheme based on the insight that reducing generation resolution in early denoising steps can enhance low-frequency components and improve final generation fidelity. At the module level, we employ a hybrid module caching strategy to reuse computations across denoising steps. Extensive experiments and ablation studies demonstrate that (1) PostDiff can significantly improve the fidelity-efficiency trade-off of state-of-the-art diffusion models, and (2) to boost efficiency while maintaining decent generation fidelity, reducing per-step inference cost is often more effective than reducing the number of denoising steps. Our code is available at https://github.com/GATECH-EIC/PostDiff.
Sparse Causal Discovery with Generative Intervention for Unsupervised Graph Domain Adaptation
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Unsupervised Graph Domain Adaptation (UGDA) leverages labeled source domain graphs to achieve effective performance in unlabeled target domains despite distribution shifts. However, existing methods often yield suboptimal results due to the entanglement of causal-spurious features and the failure of global alignment strategies. We propose SLOGAN (Sparse Causal Discovery with Generative Intervention), a novel approach that achieves stable graph representation transfer through sparse causal modeling and dynamic intervention mechanisms. Specifically, SLOGAN first constructs a sparse causal graph structure, leveraging mutual information bottleneck constraints to disentangle sparse, stable causal features while compressing domain-dependent spurious correlations through variational inference. To address residual spurious correlations, we innovatively design a generative intervention mechanism that breaks local spurious couplings through cross-domain feature recombination while maintaining causal feature semantic consistency via covariance constraints. Furthermore, to mitigate error accumulation in target domain pseudo-labels, we introduce a category-adaptive dynamic calibration strategy, ensuring stable discriminative learning. Extensive experiments on multiple real-world datasets demonstrate that SLOGAN significantly outperforms existing baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge