Jingyang Yuan
Identifying and Correcting Label Noise for Robust GNNs via Influence Contradiction
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have shown remarkable capabilities in learning from graph-structured data with various applications such as social analysis and bioinformatics. However, the presence of label noise in real scenarios poses a significant challenge in learning robust GNNs, and their effectiveness can be severely impacted when dealing with noisy labels on graphs, often stemming from annotation errors or inconsistencies. To address this, in this paper we propose a novel approach called ICGNN that harnesses the structure information of the graph to effectively alleviate the challenges posed by noisy labels. Specifically, we first design a novel noise indicator that measures the influence contradiction score (ICS) based on the graph diffusion matrix to quantify the credibility of nodes with clean labels, such that nodes with higher ICS values are more likely to be detected as having noisy labels. Then we leverage the Gaussian mixture model to precisely detect whether the label of a node is noisy or not. Additionally, we develop a soft strategy to combine the predictions from neighboring nodes on the graph to correct the detected noisy labels. At last, pseudo-labeling for abundant unlabeled nodes is incorporated to provide auxiliary supervision signals and guide the model optimization. Experiments on benchmark datasets show the superiority of our proposed approach.
mHC: Manifold-Constrained Hyper-Connections
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Recently, studies exemplified by Hyper-Connections (HC) have extended the ubiquitous residual connection paradigm established over the past decade by expanding the residual stream width and diversifying connectivity patterns. While yielding substantial performance gains, this diversification fundamentally compromises the identity mapping property intrinsic to the residual connection, which causes severe training instability and restricted scalability, and additionally incurs notable memory access overhead. To address these challenges, we propose Manifold-Constrained Hyper-Connections (mHC), a general framework that projects the residual connection space of HC onto a specific manifold to restore the identity mapping property, while incorporating rigorous infrastructure optimization to ensure efficiency. Empirical experiments demonstrate that mHC is effective for training at scale, offering tangible performance improvements and superior scalability. We anticipate that mHC, as a flexible and practical extension of HC, will contribute to a deeper understanding of topological architecture design and suggest promising directions for the evolution of foundational models.
A Survey on Efficient Large Language Model Training: From Data-centric Perspectives
Oct 29, 2025Abstract:Post-training of Large Language Models (LLMs) is crucial for unlocking their task generalization potential and domain-specific capabilities. However, the current LLM post-training paradigm faces significant data challenges, including the high costs of manual annotation and diminishing marginal returns on data scales. Therefore, achieving data-efficient post-training has become a key research question. In this paper, we present the first systematic survey of data-efficient LLM post-training from a data-centric perspective. We propose a taxonomy of data-efficient LLM post-training methods, covering data selection, data quality enhancement, synthetic data generation, data distillation and compression, and self-evolving data ecosystems. We summarize representative approaches in each category and outline future research directions. By examining the challenges in data-efficient LLM post-training, we highlight open problems and propose potential research avenues. We hope our work inspires further exploration into maximizing the potential of data utilization in large-scale model training. Paper List: https://github.com/luo-junyu/Awesome-Data-Efficient-LLM
Large Language Model Agent: A Survey on Methodology, Applications and Challenges
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:The era of intelligent agents is upon us, driven by revolutionary advancements in large language models. Large Language Model (LLM) agents, with goal-driven behaviors and dynamic adaptation capabilities, potentially represent a critical pathway toward artificial general intelligence. This survey systematically deconstructs LLM agent systems through a methodology-centered taxonomy, linking architectural foundations, collaboration mechanisms, and evolutionary pathways. We unify fragmented research threads by revealing fundamental connections between agent design principles and their emergent behaviors in complex environments. Our work provides a unified architectural perspective, examining how agents are constructed, how they collaborate, and how they evolve over time, while also addressing evaluation methodologies, tool applications, practical challenges, and diverse application domains. By surveying the latest developments in this rapidly evolving field, we offer researchers a structured taxonomy for understanding LLM agents and identify promising directions for future research. The collection is available at https://github.com/luo-junyu/Awesome-Agent-Papers.
Attention Bootstrapping for Multi-Modal Test-Time Adaptation
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:Test-time adaptation aims to adapt a well-trained model to potential distribution shifts at test time using only unlabeled test data, without access to the original training data. While previous efforts mainly focus on a single modality, test-time distribution shift in the multi-modal setting is more complex and calls for new solutions. This paper tackles the problem of multi-modal test-time adaptation by proposing a novel method named Attention Bootstrapping with Principal Entropy Minimization (ABPEM). We observe that test-time distribution shift causes misalignment across modalities, leading to a large gap between intra-modality discrepancies (measured by self-attention) and inter-modality discrepancies (measured by cross-attention). We name this the attention gap. This attention gap widens with more severe distribution shifts, hindering effective modality fusion. To mitigate this attention gap and encourage better modality fusion, we propose attention bootstrapping that promotes cross-attention with the guidance of self-attention. Moreover, to reduce the gradient noise in the commonly-used entropy minimization, we adopt principal entropy minimization, a refinement of entropy minimization that reduces gradient noise by focusing on the principal parts of entropy, excluding less reliable gradient information. Extensive experiments on the benchmarks validate the effectiveness of the proposed ABPEM in comparison with competing baselines.
DeepSeek-V3 Technical Report
Dec 27, 2024



Abstract:We present DeepSeek-V3, a strong Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) language model with 671B total parameters with 37B activated for each token. To achieve efficient inference and cost-effective training, DeepSeek-V3 adopts Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA) and DeepSeekMoE architectures, which were thoroughly validated in DeepSeek-V2. Furthermore, DeepSeek-V3 pioneers an auxiliary-loss-free strategy for load balancing and sets a multi-token prediction training objective for stronger performance. We pre-train DeepSeek-V3 on 14.8 trillion diverse and high-quality tokens, followed by Supervised Fine-Tuning and Reinforcement Learning stages to fully harness its capabilities. Comprehensive evaluations reveal that DeepSeek-V3 outperforms other open-source models and achieves performance comparable to leading closed-source models. Despite its excellent performance, DeepSeek-V3 requires only 2.788M H800 GPU hours for its full training. In addition, its training process is remarkably stable. Throughout the entire training process, we did not experience any irrecoverable loss spikes or perform any rollbacks. The model checkpoints are available at https://github.com/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-V3.
RobustFT: Robust Supervised Fine-tuning for Large Language Models under Noisy Response
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Supervised fine-tuning (SFT) plays a crucial role in adapting large language models (LLMs) to specific domains or tasks. However, as demonstrated by empirical experiments, the collected data inevitably contains noise in practical applications, which poses significant challenges to model performance on downstream tasks. Therefore, there is an urgent need for a noise-robust SFT framework to enhance model capabilities in downstream tasks. To address this challenge, we introduce a robust SFT framework (RobustFT) that performs noise detection and relabeling on downstream task data. For noise identification, our approach employs a multi-expert collaborative system with inference-enhanced models to achieve superior noise detection. In the denoising phase, we utilize a context-enhanced strategy, which incorporates the most relevant and confident knowledge followed by careful assessment to generate reliable annotations. Additionally, we introduce an effective data selection mechanism based on response entropy, ensuring only high-quality samples are retained for fine-tuning. Extensive experiments conducted on multiple LLMs across five datasets demonstrate RobustFT's exceptional performance in noisy scenarios.
GALA: Graph Diffusion-based Alignment with Jigsaw for Source-free Domain Adaptation
Oct 22, 2024



Abstract:Source-free domain adaptation is a crucial machine learning topic, as it contains numerous applications in the real world, particularly with respect to data privacy. Existing approaches predominantly focus on Euclidean data, such as images and videos, while the exploration of non-Euclidean graph data remains scarce. Recent graph neural network (GNN) approaches can suffer from serious performance decline due to domain shift and label scarcity in source-free adaptation scenarios. In this study, we propose a novel method named Graph Diffusion-based Alignment with Jigsaw (GALA), tailored for source-free graph domain adaptation. To achieve domain alignment, GALA employs a graph diffusion model to reconstruct source-style graphs from target data. Specifically, a score-based graph diffusion model is trained using source graphs to learn the generative source styles. Then, we introduce perturbations to target graphs via a stochastic differential equation instead of sampling from a prior, followed by the reverse process to reconstruct source-style graphs. We feed the source-style graphs into an off-the-shelf GNN and introduce class-specific thresholds with curriculum learning, which can generate accurate and unbiased pseudo-labels for target graphs. Moreover, we develop a simple yet effective graph-mixing strategy named graph jigsaw to combine confident graphs and unconfident graphs, which can enhance generalization capabilities and robustness via consistency learning. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets validate the effectiveness of GALA.
Rank and Align: Towards Effective Source-free Graph Domain Adaptation
Aug 22, 2024



Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) have achieved impressive performance in graph domain adaptation. However, extensive source graphs could be unavailable in real-world scenarios due to privacy and storage concerns. To this end, we investigate an underexplored yet practical problem of source-free graph domain adaptation, which transfers knowledge from source models instead of source graphs to a target domain. To solve this problem, we introduce a novel GNN-based approach called Rank and Align (RNA), which ranks graph similarities with spectral seriation for robust semantics learning, and aligns inharmonic graphs with harmonic graphs which close to the source domain for subgraph extraction. In particular, to overcome label scarcity, we employ the spectral seriation algorithm to infer the robust pairwise rankings, which can guide semantic learning using a similarity learning objective. To depict distribution shifts, we utilize spectral clustering and the silhouette coefficient to detect harmonic graphs, which the source model can easily classify. To reduce potential domain discrepancy, we extract domain-invariant subgraphs from inharmonic graphs by an adversarial edge sampling process, which guides the invariant learning of GNNs. Extensive experiments on several benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed RNA.
A Hybrid RAG System with Comprehensive Enhancement on Complex Reasoning
Aug 09, 2024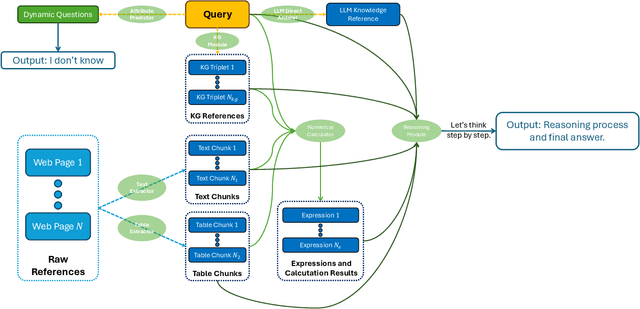
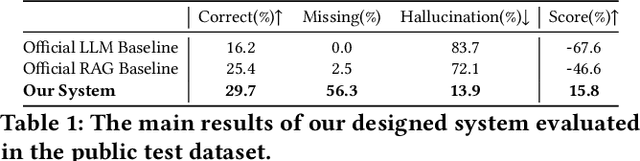
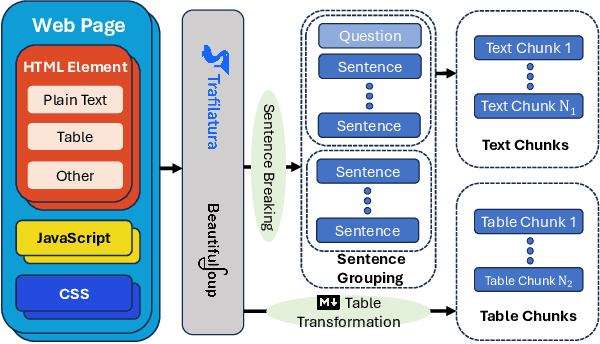
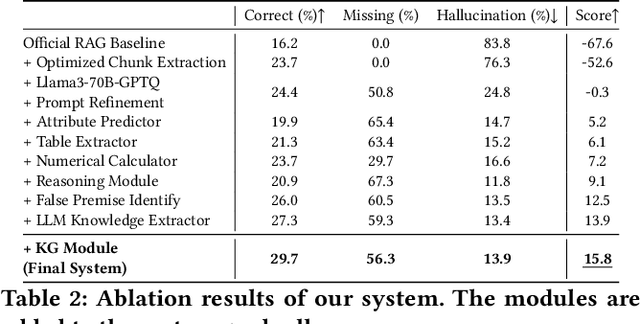
Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) is a framework enabling large language models (LLMs) to enhance their accuracy and reduce hallucinations by integrating external knowledge bases. In this paper, we introduce a hybrid RAG system enhanced through a comprehensive suite of optimizations that significantly improve retrieval quality, augment reasoning capabilities, and refine numerical computation ability. We refined the text chunks and tables in web pages, added attribute predictors to reduce hallucinations, conducted LLM Knowledge Extractor and Knowledge Graph Extractor, and finally built a reasoning strategy with all the references. We evaluated our system on the CRAG dataset through the Meta CRAG KDD Cup 2024 Competition. Both the local and online evaluations demonstrate that our system significantly enhances complex reasoning capabilities. In local evaluations, we have significantly improved accuracy and reduced error rates compared to the baseline model, achieving a notable increase in scores. In the meanwhile, we have attained outstanding results in online assessments, demonstrating the performance and generalization capabilities of the proposed system. The source code for our system is released in \url{https://gitlab.aicrowd.com/shizueyy/crag-new}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge