Weizhi Zhang
Learning Query-Aware Budget-Tier Routing for Runtime Agent Memory
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Memory is increasingly central to Large Language Model (LLM) agents operating beyond a single context window, yet most existing systems rely on offline, query-agnostic memory construction that can be inefficient and may discard query-critical information. Although runtime memory utilization is a natural alternative, prior work often incurs substantial overhead and offers limited explicit control over the performance-cost trade-off. In this work, we present \textbf{BudgetMem}, a runtime agent memory framework for explicit, query-aware performance-cost control. BudgetMem structures memory processing as a set of memory modules, each offered in three budget tiers (i.e., \textsc{Low}/\textsc{Mid}/\textsc{High}). A lightweight router performs budget-tier routing across modules to balance task performance and memory construction cost, which is implemented as a compact neural policy trained with reinforcement learning. Using BudgetMem as a unified testbed, we study three complementary strategies for realizing budget tiers: implementation (method complexity), reasoning (inference behavior), and capacity (module model size). Across LoCoMo, LongMemEval, and HotpotQA, BudgetMem surpasses strong baselines when performance is prioritized (i.e., high-budget setting), and delivers better accuracy-cost frontiers under tighter budgets. Moreover, our analysis disentangles the strengths and weaknesses of different tiering strategies, clarifying when each axis delivers the most favorable trade-offs under varying budget regimes.
MemSkill: Learning and Evolving Memory Skills for Self-Evolving Agents
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Most Large Language Model (LLM) agent memory systems rely on a small set of static, hand-designed operations for extracting memory. These fixed procedures hard-code human priors about what to store and how to revise memory, making them rigid under diverse interaction patterns and inefficient on long histories. To this end, we present \textbf{MemSkill}, which reframes these operations as learnable and evolvable memory skills, structured and reusable routines for extracting, consolidating, and pruning information from interaction traces. Inspired by the design philosophy of agent skills, MemSkill employs a \emph{controller} that learns to select a small set of relevant skills, paired with an LLM-based \emph{executor} that produces skill-guided memories. Beyond learning skill selection, MemSkill introduces a \emph{designer} that periodically reviews hard cases where selected skills yield incorrect or incomplete memories, and evolves the skill set by proposing refinements and new skills. Together, MemSkill forms a closed-loop procedure that improves both the skill-selection policy and the skill set itself. Experiments on LoCoMo, LongMemEval, HotpotQA, and ALFWorld demonstrate that MemSkill improves task performance over strong baselines and generalizes well across settings. Further analyses shed light on how skills evolve, offering insights toward more adaptive, self-evolving memory management for LLM agents.
DREAM: Dual-Standard Semantic Homogeneity with Dynamic Optimization for Graph Learning with Label Noise
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) have been widely used in various graph machine learning scenarios. Existing literature primarily assumes well-annotated training graphs, while the reliability of labels is not guaranteed in real-world scenarios. Recently, efforts have been made to address the problem of graph learning with label noise. However, existing methods often (i) struggle to distinguish between reliable and unreliable nodes, and (ii) overlook the relational information embedded in the graph topology. To tackle this problem, this paper proposes a novel method, Dual-Standard Semantic Homogeneity with Dynamic Optimization (DREAM), for reliable, relation-informed optimization on graphs with label noise. Specifically, we design a relation-informed dynamic optimization framework that iteratively reevaluates the reliability of each labeled node in the graph during the optimization process according to the relation of the target node and other nodes. To measure this relation comprehensively, we propose a dual-standard selection strategy that selects a set of anchor nodes based on both node proximity and graph topology. Subsequently, we compute the semantic homogeneity between the target node and the anchor nodes, which serves as guidance for optimization. We also provide a rigorous theoretical analysis to justify the design of DREAM. Extensive experiments are performed on six graph datasets across various domains under three types of graph label noise against competing baselines, and the results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed DREAM.
DTRec: Learning Dynamic Reasoning Trajectories for Sequential Recommendation
Dec 16, 2025

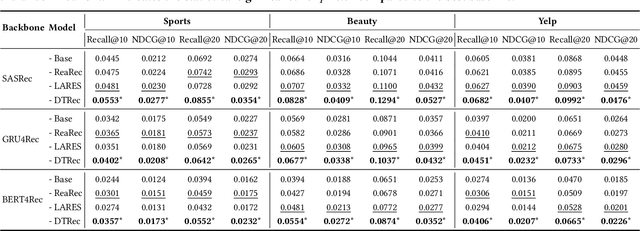

Abstract:Inspired by advances in LLMs, reasoning-enhanced sequential recommendation performs multi-step deliberation before making final predictions, unlocking greater potential for capturing user preferences. However, current methods are constrained by static reasoning trajectories that are ill-suited for the diverse complexity of user behaviors. They suffer from two key limitations: (1) a static reasoning direction, which uses flat supervision signals misaligned with human-like hierarchical reasoning, and (2) a fixed reasoning depth, which inefficiently applies the same computational effort to all users, regardless of pattern complexity. These rigidity lead to suboptimal performance and significant computational waste. To overcome these challenges, we propose DTRec, a novel and effective framework that explores the Dynamic reasoning Trajectory for Sequential Recommendation along both direction and depth. To guide the direction, we develop Hierarchical Process Supervision (HPS), which provides coarse-to-fine supervisory signals to emulate the natural, progressive refinement of human cognitive processes. To optimize the depth, we introduce the Adaptive Reasoning Halting (ARH) mechanism that dynamically adjusts the number of reasoning steps by jointly monitoring three indicators. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate the superiority of our approach, achieving up to a 24.5% performance improvement over strong baselines while simultaneously reducing computational cost by up to 41.6%.
LLM-MemCluster: Empowering Large Language Models with Dynamic Memory for Text Clustering
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are reshaping unsupervised learning by offering an unprecedented ability to perform text clustering based on their deep semantic understanding. However, their direct application is fundamentally limited by a lack of stateful memory for iterative refinement and the difficulty of managing cluster granularity. As a result, existing methods often rely on complex pipelines with external modules, sacrificing a truly end-to-end approach. We introduce LLM-MemCluster, a novel framework that reconceptualizes clustering as a fully LLM-native task. It leverages a Dynamic Memory to instill state awareness and a Dual-Prompt Strategy to enable the model to reason about and determine the number of clusters. Evaluated on several benchmark datasets, our tuning-free framework significantly and consistently outperforms strong baselines. LLM-MemCluster presents an effective, interpretable, and truly end-to-end paradigm for LLM-based text clustering.
SGCL: Unifying Self-Supervised and Supervised Learning for Graph Recommendation
Jul 17, 2025Abstract:Recommender systems (RecSys) are essential for online platforms, providing personalized suggestions to users within a vast sea of information. Self-supervised graph learning seeks to harness high-order collaborative filtering signals through unsupervised augmentation on the user-item bipartite graph, primarily leveraging a multi-task learning framework that includes both supervised recommendation loss and self-supervised contrastive loss. However, this separate design introduces additional graph convolution processes and creates inconsistencies in gradient directions due to disparate losses, resulting in prolonged training times and sub-optimal performance. In this study, we introduce a unified framework of Supervised Graph Contrastive Learning for recommendation (SGCL) to address these issues. SGCL uniquely combines the training of recommendation and unsupervised contrastive losses into a cohesive supervised contrastive learning loss, aligning both tasks within a single optimization direction for exceptionally fast training. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets show that SGCL outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving superior accuracy and efficiency.
From Web Search towards Agentic Deep Research: Incentivizing Search with Reasoning Agents
Jun 23, 2025Abstract:Information retrieval is a cornerstone of modern knowledge acquisition, enabling billions of queries each day across diverse domains. However, traditional keyword-based search engines are increasingly inadequate for handling complex, multi-step information needs. Our position is that Large Language Models (LLMs), endowed with reasoning and agentic capabilities, are ushering in a new paradigm termed Agentic Deep Research. These systems transcend conventional information search techniques by tightly integrating autonomous reasoning, iterative retrieval, and information synthesis into a dynamic feedback loop. We trace the evolution from static web search to interactive, agent-based systems that plan, explore, and learn. We also introduce a test-time scaling law to formalize the impact of computational depth on reasoning and search. Supported by benchmark results and the rise of open-source implementations, we demonstrate that Agentic Deep Research not only significantly outperforms existing approaches, but is also poised to become the dominant paradigm for future information seeking. All the related resources, including industry products, research papers, benchmark datasets, and open-source implementations, are collected for the community in https://github.com/DavidZWZ/Awesome-Deep-Research.
A Call for Collaborative Intelligence: Why Human-Agent Systems Should Precede AI Autonomy
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Recent improvements in large language models (LLMs) have led many researchers to focus on building fully autonomous AI agents. This position paper questions whether this approach is the right path forward, as these autonomous systems still have problems with reliability, transparency, and understanding the actual requirements of human. We suggest a different approach: LLM-based Human-Agent Systems (LLM-HAS), where AI works with humans rather than replacing them. By keeping human involved to provide guidance, answer questions, and maintain control, these systems can be more trustworthy and adaptable. Looking at examples from healthcare, finance, and software development, we show how human-AI teamwork can handle complex tasks better than AI working alone. We also discuss the challenges of building these collaborative systems and offer practical solutions. This paper argues that progress in AI should not be measured by how independent systems become, but by how well they can work with humans. The most promising future for AI is not in systems that take over human roles, but in those that enhance human capabilities through meaningful partnership.
PersonaAgent: When Large Language Model Agents Meet Personalization at Test Time
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM) empowered agents have recently emerged as advanced paradigms that exhibit impressive capabilities in a wide range of domains and tasks. Despite their potential, current LLM agents often adopt a one-size-fits-all approach, lacking the flexibility to respond to users' varying needs and preferences. This limitation motivates us to develop PersonaAgent, the first personalized LLM agent framework designed to address versatile personalization tasks. Specifically, PersonaAgent integrates two complementary components - a personalized memory module that includes episodic and semantic memory mechanisms; a personalized action module that enables the agent to perform tool actions tailored to the user. At the core, the persona (defined as unique system prompt for each user) functions as an intermediary: it leverages insights from personalized memory to control agent actions, while the outcomes of these actions in turn refine the memory. Based on the framework, we propose a test-time user-preference alignment strategy that simulate the latest n interactions to optimize the persona prompt, ensuring real-time user preference alignment through textual loss feedback between simulated and ground-truth responses. Experimental evaluations demonstrate that PersonaAgent significantly outperforms other baseline methods by not only personalizing the action space effectively but also scaling during test-time real-world applications. These results underscore the feasibility and potential of our approach in delivering tailored, dynamic user experiences.
Cold-Start Recommendation with Knowledge-Guided Retrieval-Augmented Generation
May 27, 2025Abstract:Cold-start items remain a persistent challenge in recommender systems due to their lack of historical user interactions, which collaborative models rely on. While recent zero-shot methods leverage large language models (LLMs) to address this, they often struggle with sparse metadata and hallucinated or incomplete knowledge. We propose ColdRAG, a retrieval-augmented generation approach that builds a domain-specific knowledge graph dynamically to enhance LLM-based recommendation in cold-start scenarios, without requiring task-specific fine-tuning. ColdRAG begins by converting structured item attributes into rich natural-language profiles, from which it extracts entities and relationships to construct a unified knowledge graph capturing item semantics. Given a user's interaction history, it scores edges in the graph using an LLM, retrieves candidate items with supporting evidence, and prompts the LLM to rank them. By enabling multi-hop reasoning over this graph, ColdRAG grounds recommendations in verifiable evidence, reducing hallucinations and strengthening semantic connections. Experiments on three public benchmarks demonstrate that ColdRAG surpasses existing zero-shot baselines in both Recall and NDCG. This framework offers a practical solution to cold-start recommendation by combining knowledge-graph reasoning with retrieval-augmented LLM generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge