Qingyuan Liang
Grammar-Based Code Representation: Is It a Worthy Pursuit for LLMs?
Mar 07, 2025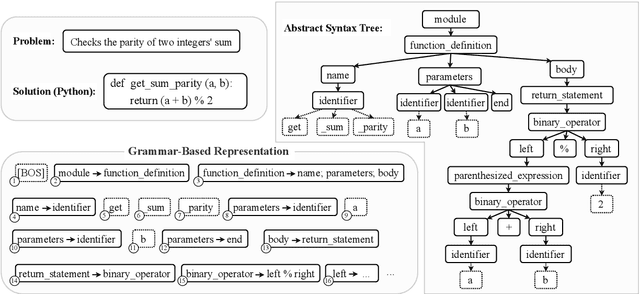
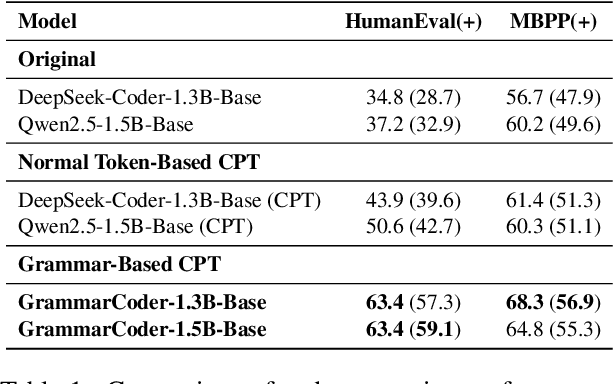
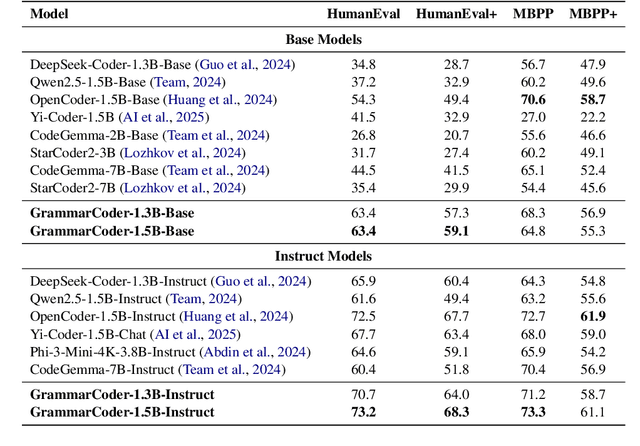
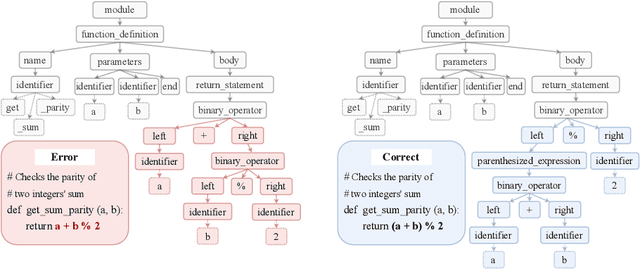
Abstract:Grammar serves as a cornerstone in programming languages and software engineering, providing frameworks to define the syntactic space and program structure. Existing research demonstrates the effectiveness of grammar-based code representations in small-scale models, showing their ability to reduce syntax errors and enhance performance. However, as language models scale to the billion level or beyond, syntax-level errors become rare, making it unclear whether grammar information still provides performance benefits. To explore this, we develop a series of billion-scale GrammarCoder models, incorporating grammar rules in the code generation process. Experiments on HumanEval (+) and MBPP (+) demonstrate a notable improvement in code generation accuracy. Further analysis shows that grammar-based representations enhance LLMs' ability to discern subtle code differences, reducing semantic errors caused by minor variations. These findings suggest that grammar-based code representations remain valuable even in billion-scale models, not only by maintaining syntax correctness but also by improving semantic differentiation.
Lyra: A Benchmark for Turducken-Style Code Generation
Aug 27, 2021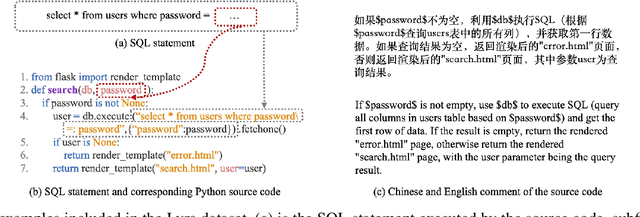
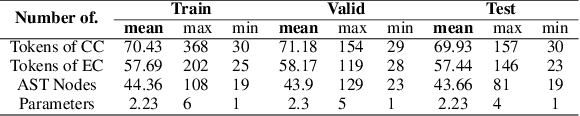
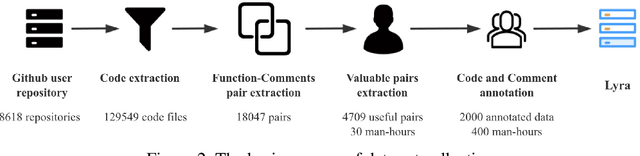
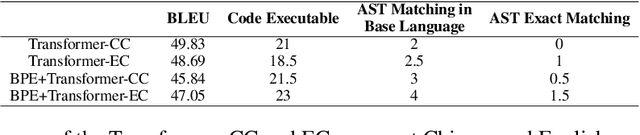
Abstract:Code generation is crucial to reduce manual software development efforts. Recently, neural techniques have been used to generate source code automatically. While promising, these approaches are evaluated on tasks for generating code in single programming languages. However, in actual development, one programming language is often embedded in another. For example, SQL statements are often embedded as strings in base programming languages such as Python and Java, and JavaScript programs are often embedded in sever-side programming languages, such as PHP, Java, and Python. We call this a turducken-style programming. In this paper, we define a new code generation task: given a natural language comment, this task aims to generate a program in a base language with an embedded language. To our knowledge, this is the first turducken-style code generation task. For this task, we present Lyra: a dataset in Python with embedded SQL. This dataset contains 2,000 carefully annotated database manipulation programs from real usage projects. Each program is paired with both a Chinese comment and an English comment. In our experiment, we adopted Transformer, a state-of-the-art technique, as the baseline. In the best setting, Transformer achieves 0.5% and 1.5% AST exact matching accuracy using Chinese and English comments, respectively. Therefore, we believe that Lyra provides a new challenge for code generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge