Zhi Liu
Department of Mathematical and Systems Engineering, Shizuoka University, Japan
Breaking Coordinate Overfitting: Geometry-Aware WiFi Sensing for Cross-Layout 3D Pose Estimation
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:WiFi-based 3D human pose estimation offers a low-cost and privacy-preserving alternative to vision-based systems for smart interaction. However, existing approaches rely on visual 3D poses as supervision and directly regress CSI to a camera-based coordinate system. We find that this practice leads to coordinate overfitting: models memorize deployment-specific WiFi transceiver layouts rather than only learning activity-relevant representations, resulting in severe generalization failures. To address this challenge, we present PerceptAlign, the first geometry-conditioned framework for WiFi-based cross-layout pose estimation. PerceptAlign introduces a lightweight coordinate unification procedure that aligns WiFi and vision measurements in a shared 3D space using only two checkerboards and a few photos. Within this unified space, it encodes calibrated transceiver positions into high-dimensional embeddings and fuses them with CSI features, making the model explicitly aware of device geometry as a conditional variable. This design forces the network to disentangle human motion from deployment layouts, enabling robust and, for the first time, layout-invariant WiFi pose estimation. To support systematic evaluation, we construct the largest cross-domain 3D WiFi pose estimation dataset to date, comprising 21 subjects, 5 scenes, 18 actions, and 7 device layouts. Experiments show that PerceptAlign reduces in-domain error by 12.3% and cross-domain error by more than 60% compared to state-of-the-art baselines. These results establish geometry-conditioned learning as a viable path toward scalable and practical WiFi sensing.
Beyond Physical Labels: Redefining Domains for Robust WiFi-based Gesture Recognition
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:In this paper, we propose GesFi, a novel WiFi-based gesture recognition system that introduces WiFi latent domain mining to redefine domains directly from the data itself. GesFi first processes raw sensing data collected from WiFi receivers using CSI-ratio denoising, Short-Time Fast Fourier Transform, and visualization techniques to generate standardized input representations. It then employs class-wise adversarial learning to suppress gesture semantic and leverages unsupervised clustering to automatically uncover latent domain factors responsible for distributional shifts. These latent domains are then aligned through adversarial learning to support robust cross-domain generalization. Finally, the system is applied to the target environment for robust gesture inference. We deployed GesFi under both single-pair and multi-pair settings using commodity WiFi transceivers, and evaluated it across multiple public datasets and real-world environments. Compared to state-of-the-art baselines, GesFi achieves up to 78% and 50% performance improvements over existing adversarial methods, and consistently outperforms prior generalization approaches across most cross-domain tasks.
Time-Scaling Is What Agents Need Now
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Early artificial intelligence paradigms exhibited separated cognitive functions: Neural Networks focused on "perception-representation," Reinforcement Learning on "decision-making-behavior," and Symbolic AI on "knowledge-reasoning." With Transformer-based large models and world models, these paradigms are converging into cognitive agents with closed-loop "perception-decision-action" capabilities. Humans solve complex problems under limited cognitive resources through temporalized sequential reasoning. Language relies on problem space search for deep semantic reasoning. While early large language models (LLMs) could generate fluent text, they lacked robust semantic reasoning capabilities. Prompting techniques like Chain-of-Thought (CoT) and Tree-of-Thought (ToT) extended reasoning paths by making intermediate steps explicit. Recent models like DeepSeek-R1 enhanced performance through explicit reasoning trajectories. However, these methods have limitations in search completeness and efficiency. This highlights the need for "Time-Scaling"--the systematic extension and optimization of an agent's ability to unfold reasoning over time. Time-Scaling refers to architectural design utilizing extended temporal pathways, enabling deeper problem space exploration, dynamic strategy adjustment, and enhanced metacognitive control, paralleling human sequential reasoning under cognitive constraints. It represents a critical frontier for enhancing deep reasoning and problem-solving without proportional increases in static model parameters. Advancing intelligent agent capabilities requires placing Time-Scaling principles at the forefront, positioning explicit temporal reasoning management as foundational.
ReMA: A Training-Free Plug-and-Play Mixing Augmentation for Video Behavior Recognition
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Video behavior recognition demands stable and discriminative representations under complex spatiotemporal variations. However, prevailing data augmentation strategies for videos remain largely perturbation-driven, often introducing uncontrolled variations that amplify non-discriminative factors, which finally weaken intra-class distributional structure and representation drift with inconsistent gains across temporal scales. To address these problems, we propose Representation-aware Mixing Augmentation (ReMA), a plug-and-play augmentation strategy that formulates mixing as a controlled replacement process to expand representations while preserving class-conditional stability. ReMA integrates two complementary mechanisms. Firstly, the Representation Alignment Mechanism (RAM) performs structured intra-class mixing under distributional alignment constraints, suppressing irrelevant intra-class drift while enhancing statistical reliability. Then, the Dynamic Selection Mechanism (DSM) generates motion-aware spatiotemporal masks to localize perturbations, guiding them away from discrimination-sensitive regions and promoting temporal coherence. By jointly controlling how and where mixing is applied, ReMA improves representation robustness without additional supervision or trainable parameters. Extensive experiments on diverse video behavior benchmarks demonstrate that ReMA consistently enhances generalization and robustness across different spatiotemporal granularities.
Generative Human-Object Interaction Detection via Differentiable Cognitive Steering of Multi-modal LLMs
Dec 19, 2025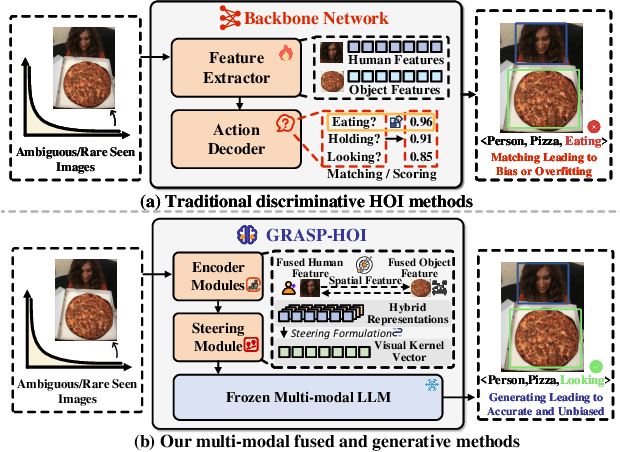
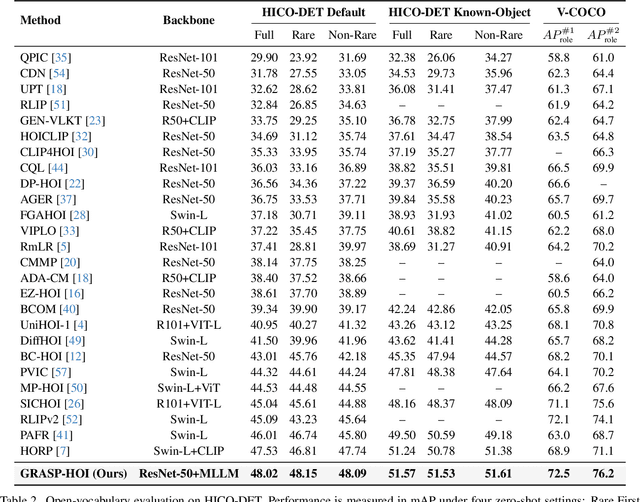
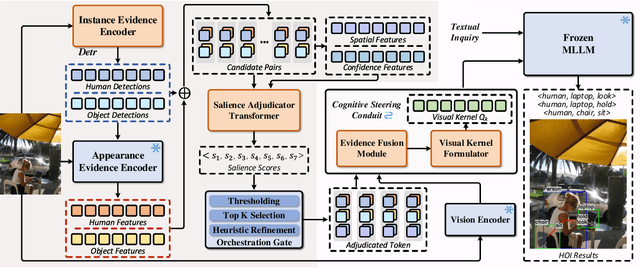
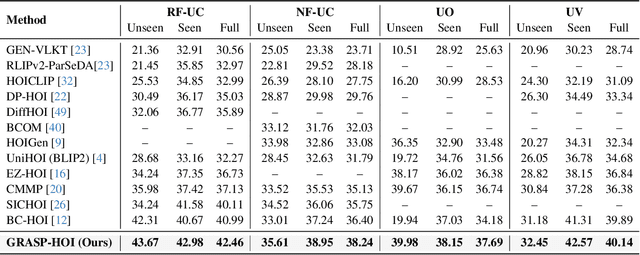
Abstract:Human-object interaction (HOI) detection aims to localize human-object pairs and the interactions between them. Existing methods operate under a closed-world assumption, treating the task as a classification problem over a small, predefined verb set, which struggles to generalize to the long-tail of unseen or ambiguous interactions in the wild. While recent multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) possess the rich world knowledge required for open-vocabulary understanding, they remain decoupled from existing HOI detectors since fine-tuning them is computationally prohibitive. To address these constraints, we propose \GRASP-HO}, a novel Generative Reasoning And Steerable Perception framework that reformulates HOI detection from the closed-set classification task to the open-vocabulary generation problem. To bridge the vision and cognitive, we first extract hybrid interaction representations, then design a lightweight learnable cognitive steering conduit (CSC) module to inject the fine-grained visual evidence into a frozen MLLM for effective reasoning. To address the supervision mismatch between classification-based HOI datasets and open-vocabulary generative models, we introduce a hybrid guidance strategy that coupling the language modeling loss and auxiliary classification loss, enabling discriminative grounding without sacrificing generative flexibility. Experiments demonstrate state-of-the-art closed-set performance and strong zero-shot generalization, achieving a unified paradigm that seamlessly bridges discriminative perception and generative reasoning for open-world HOI detection.
GeoDiffMM: Geometry-Guided Conditional Diffusion for Motion Magnification
Dec 09, 2025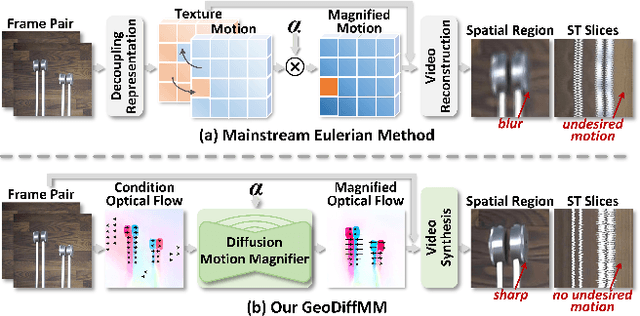
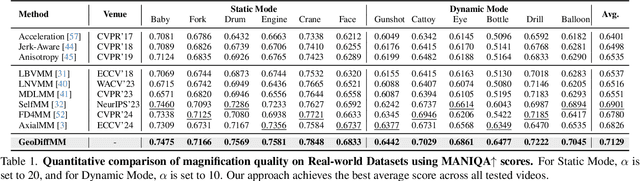
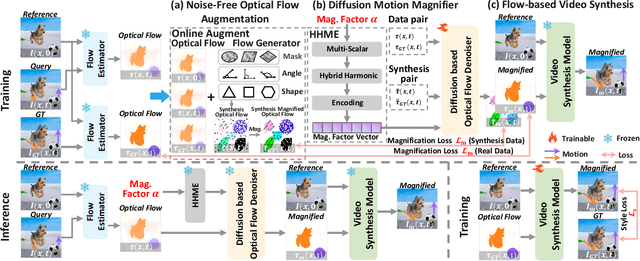
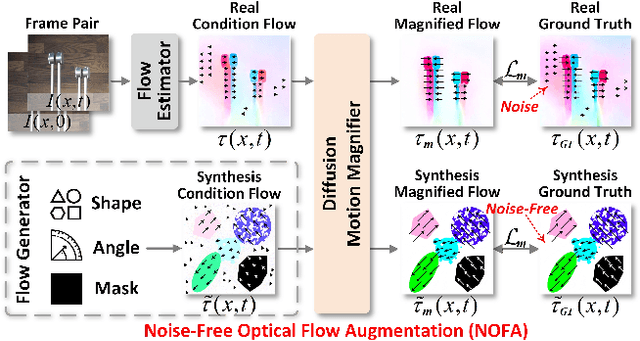
Abstract:Video Motion Magnification (VMM) amplifies subtle macroscopic motions to a perceptible level. Recently, existing mainstream Eulerian approaches address amplification-induced noise via decoupling representation learning such as texture, shape and frequancey schemes, but they still struggle to separate photon noise from true micro-motion when motion displacements are very small. We propose GeoDiffMM, a novel diffusion-based Lagrangian VMM framework conditioned on optical flow as a geometric cue, enabling structurally consistent motion magnification. Specifically, we design a Noise-free Optical Flow Augmentation strategy that synthesizes diverse nonrigid motion fields without photon noise as supervision, helping the model learn more accurate geometry-aware optial flow and generalize better. Next, we develop a Diffusion Motion Magnifier that conditions the denoising process on (i) optical flow as a geometry prior and (ii) a learnable magnification factor controlling magnitude, thereby selectively amplifying motion components consistent with scene semantics and structure while suppressing content-irrelevant perturbations. Finally, we perform Flow-based Video Synthesis to map the amplified motion back to the image domain with high fidelity. Extensive experiments on real and synthetic datasets show that GeoDiffMM outperforms state-of-the-art methods and significantly improves motion magnification.
SEMC: Structure-Enhanced Mixture-of-Experts Contrastive Learning for Ultrasound Standard Plane Recognition
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Ultrasound standard plane recognition is essential for clinical tasks such as disease screening, organ evaluation, and biometric measurement. However, existing methods fail to effectively exploit shallow structural information and struggle to capture fine-grained semantic differences through contrastive samples generated by image augmentations, ultimately resulting in suboptimal recognition of both structural and discriminative details in ultrasound standard planes. To address these issues, we propose SEMC, a novel Structure-Enhanced Mixture-of-Experts Contrastive learning framework that combines structure-aware feature fusion with expert-guided contrastive learning. Specifically, we first introduce a novel Semantic-Structure Fusion Module (SSFM) to exploit multi-scale structural information and enhance the model's ability to perceive fine-grained structural details by effectively aligning shallow and deep features. Then, a novel Mixture-of-Experts Contrastive Recognition Module (MCRM) is designed to perform hierarchical contrastive learning and classification across multi-level features using a mixture-of-experts (MoE) mechanism, further improving class separability and recognition performance. More importantly, we also curate a large-scale and meticulously annotated liver ultrasound dataset containing six standard planes. Extensive experimental results on our in-house dataset and two public datasets demonstrate that SEMC outperforms recent state-of-the-art methods across various metrics.
SAM-DAQ: Segment Anything Model with Depth-guided Adaptive Queries for RGB-D Video Salient Object Detection
Nov 13, 2025
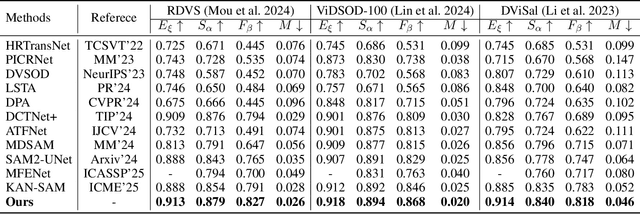
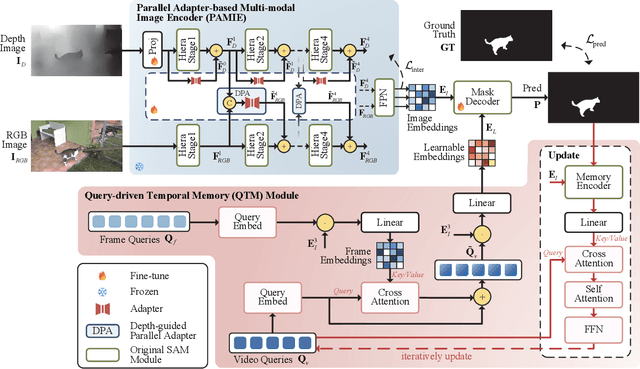
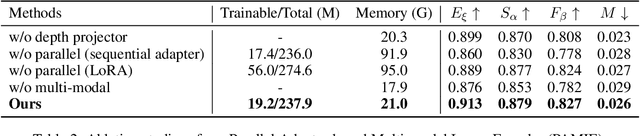
Abstract:Recently segment anything model (SAM) has attracted widespread concerns, and it is often treated as a vision foundation model for universal segmentation. Some researchers have attempted to directly apply the foundation model to the RGB-D video salient object detection (RGB-D VSOD) task, which often encounters three challenges, including the dependence on manual prompts, the high memory consumption of sequential adapters, and the computational burden of memory attention. To address the limitations, we propose a novel method, namely Segment Anything Model with Depth-guided Adaptive Queries (SAM-DAQ), which adapts SAM2 to pop-out salient objects from videos by seamlessly integrating depth and temporal cues within a unified framework. Firstly, we deploy a parallel adapter-based multi-modal image encoder (PAMIE), which incorporates several depth-guided parallel adapters (DPAs) in a skip-connection way. Remarkably, we fine-tune the frozen SAM encoder under prompt-free conditions, where the DPA utilizes depth cues to facilitate the fusion of multi-modal features. Secondly, we deploy a query-driven temporal memory (QTM) module, which unifies the memory bank and prompt embeddings into a learnable pipeline. Concretely, by leveraging both frame-level queries and video-level queries simultaneously, the QTM module can not only selectively extract temporal consistency features but also iteratively update the temporal representations of the queries. Extensive experiments are conducted on three RGB-D VSOD datasets, and the results show that the proposed SAM-DAQ consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of all evaluation metrics.
Information Bottleneck-based Causal Attention for Multi-label Medical Image Recognition
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Multi-label classification (MLC) of medical images aims to identify multiple diseases and holds significant clinical potential. A critical step is to learn class-specific features for accurate diagnosis and improved interpretability effectively. However, current works focus primarily on causal attention to learn class-specific features, yet they struggle to interpret the true cause due to the inadvertent attention to class-irrelevant features. To address this challenge, we propose a new structural causal model (SCM) that treats class-specific attention as a mixture of causal, spurious, and noisy factors, and a novel Information Bottleneck-based Causal Attention (IBCA) that is capable of learning the discriminative class-specific attention for MLC of medical images. Specifically, we propose learning Gaussian mixture multi-label spatial attention to filter out class-irrelevant information and capture each class-specific attention pattern. Then a contrastive enhancement-based causal intervention is proposed to gradually mitigate the spurious attention and reduce noise information by aligning multi-head attention with the Gaussian mixture multi-label spatial. Quantitative and ablation results on Endo and MuReD show that IBCA outperforms all methods. Compared to the second-best results for each metric, IBCA achieves improvements of 6.35\% in CR, 7.72\% in OR, and 5.02\% in mAP for MuReD, 1.47\% in CR, and 1.65\% in CF1, and 1.42\% in mAP for Endo.
Tianyi: A Traditional Chinese Medicine all-rounder language model and its Real-World Clinical Practice
May 19, 2025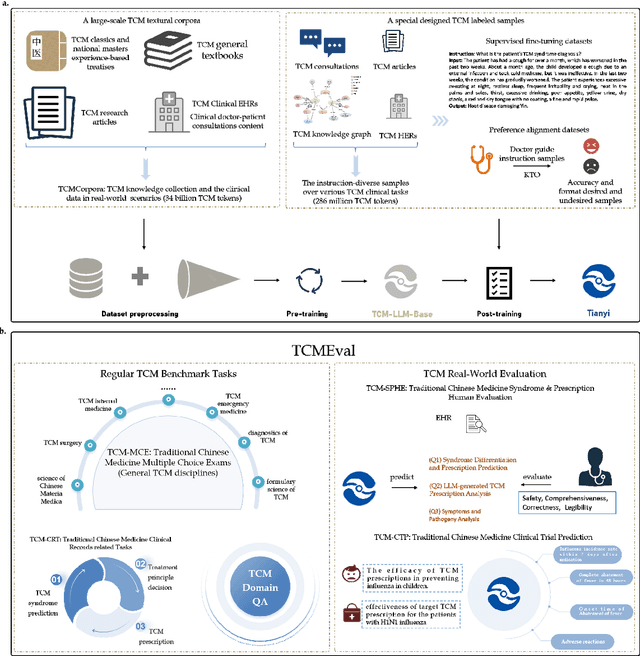
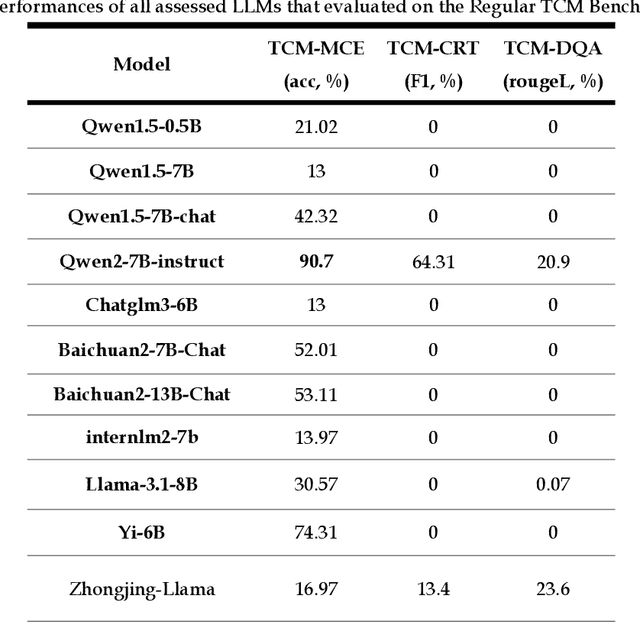

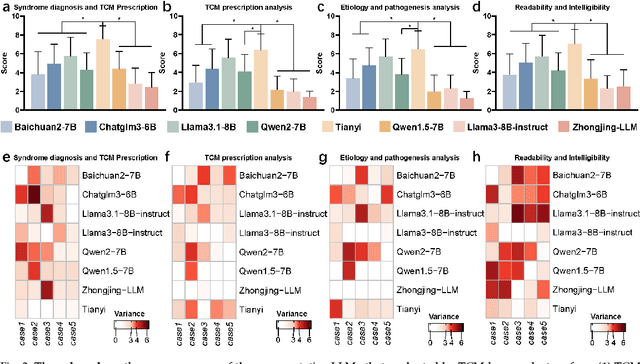
Abstract:Natural medicines, particularly Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), are gaining global recognition for their therapeutic potential in addressing human symptoms and diseases. TCM, with its systematic theories and extensive practical experience, provides abundant resources for healthcare. However, the effective application of TCM requires precise syndrome diagnosis, determination of treatment principles, and prescription formulation, which demand decades of clinical expertise. Despite advancements in TCM-based decision systems, machine learning, and deep learning research, limitations in data and single-objective constraints hinder their practical application. In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated potential in complex tasks, but lack specialization in TCM and face significant challenges, such as too big model scale to deploy and issues with hallucination. To address these challenges, we introduce Tianyi with 7.6-billion-parameter LLM, a model scale proper and specifically designed for TCM, pre-trained and fine-tuned on diverse TCM corpora, including classical texts, expert treatises, clinical records, and knowledge graphs. Tianyi is designed to assimilate interconnected and systematic TCM knowledge through a progressive learning manner. Additionally, we establish TCMEval, a comprehensive evaluation benchmark, to assess LLMs in TCM examinations, clinical tasks, domain-specific question-answering, and real-world trials. The extensive evaluations demonstrate the significant potential of Tianyi as an AI assistant in TCM clinical practice and research, bridging the gap between TCM knowledge and practical application.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge