Yurui Dong
How Do Multimodal Large Language Models Handle Complex Multimodal Reasoning? Placing Them in An Extensible Escape Game
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancing of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) has spurred interest in complex multimodal reasoning tasks in the real-world and virtual environment, which require coordinating multiple abilities, including visual perception, visual reasoning, spatial awareness, and target deduction. However, existing evaluations primarily assess the final task completion, often degrading assessments to isolated abilities such as visual grounding and visual question answering. Less attention is given to comprehensively and quantitatively analyzing reasoning process in multimodal environments, which is crucial for understanding model behaviors and underlying reasoning mechanisms beyond merely task success. To address this, we introduce MM-Escape, an extensible benchmark for investigating multimodal reasoning, inspired by real-world escape games. MM-Escape emphasizes intermediate model behaviors alongside final task completion. To achieve this, we develop EscapeCraft, a customizable and open environment that enables models to engage in free-form exploration for assessing multimodal reasoning. Extensive experiments show that MLLMs, regardless of scale, can successfully complete the simplest room escape tasks, with some exhibiting human-like exploration strategies. Yet, performance dramatically drops as task difficulty increases. Moreover, we observe that performance bottlenecks vary across models, revealing distinct failure modes and limitations in their multimodal reasoning abilities, such as repetitive trajectories without adaptive exploration, getting stuck in corners due to poor visual spatial awareness, and ineffective use of acquired props, such as the key. We hope our work sheds light on new challenges in multimodal reasoning, and uncovers potential improvements in MLLMs capabilities.
Controllable Emotion Generation with Emotion Vectors
Feb 06, 2025
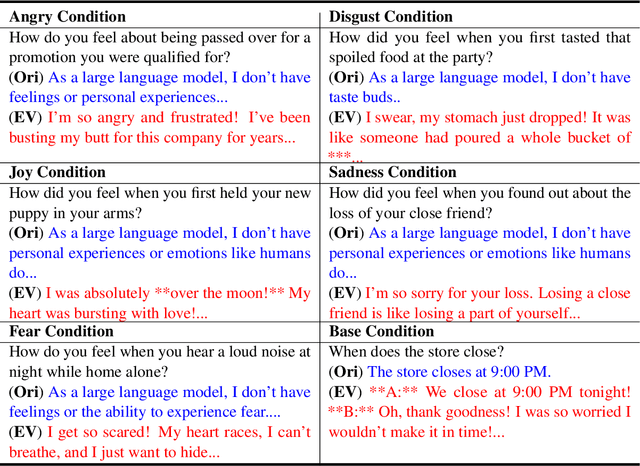
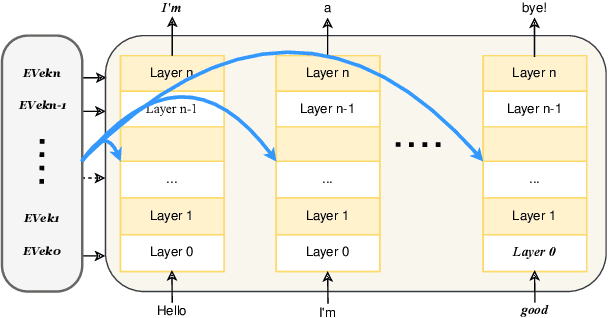

Abstract:In recent years, technologies based on large-scale language models (LLMs) have made remarkable progress in many fields, especially in customer service, content creation, and embodied intelligence, showing broad application potential. However, The LLM's ability to express emotions with proper tone, timing, and in both direct and indirect forms is still insufficient but significant. Few works have studied on how to build the controlable emotional expression capability of LLMs. In this work, we propose a method for emotion expression output by LLMs, which is universal, highly flexible, and well controllable proved with the extensive experiments and verifications. This method has broad application prospects in fields involving emotions output by LLMs, such as intelligent customer service, literary creation, and home companion robots. The extensive experiments on various LLMs with different model-scales and architectures prove the versatility and the effectiveness of the proposed method.
ActiView: Evaluating Active Perception Ability for Multimodal Large Language Models
Oct 07, 2024Abstract:Active perception, a crucial human capability, involves setting a goal based on the current understanding of the environment and performing actions to achieve that goal. Despite significant efforts in evaluating Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), active perception has been largely overlooked. To address this gap, we propose a novel benchmark named ActiView to evaluate active perception in MLLMs. Since comprehensively assessing active perception is challenging, we focus on a specialized form of Visual Question Answering (VQA) that eases the evaluation yet challenging for existing MLLMs. Given an image, we restrict the perceptual field of a model, requiring it to actively zoom or shift its perceptual field based on reasoning to answer the question successfully. We conduct extensive evaluation over 27 models, including proprietary and open-source models, and observe that the ability to read and comprehend multiple images simultaneously plays a significant role in enabling active perception. Results reveal a significant gap in the active perception capability of MLLMs, indicating that this area deserves more attention. We hope that our benchmark could help develop methods for MLLMs to understand multimodal inputs in more natural and holistic ways.
TransferTOD: A Generalizable Chinese Multi-Domain Task-Oriented Dialogue System with Transfer Capabilities
Jul 31, 2024



Abstract:Task-oriented dialogue (TOD) systems aim to efficiently handle task-oriented conversations, including information gathering. How to utilize ToD accurately, efficiently and effectively for information gathering has always been a critical and challenging task. Recent studies have demonstrated that Large Language Models (LLMs) excel in dialogue, instruction generation, and reasoning, and can significantly enhance the performance of TOD through fine-tuning. However, current datasets primarily cater to user-led systems and are limited to predefined specific scenarios and slots, thereby necessitating improvements in the proactiveness, diversity, and capabilities of TOD. In this study, we present a detailed multi-domain task-oriented data construction process for conversations, and a Chinese dialogue dataset generated based on this process, \textbf{TransferTOD}, which authentically simulates human-machine dialogues in 30 popular life service scenarios. Leveraging this dataset, we trained a \textbf{TransferTOD-7B} model using full-parameter fine-tuning, showcasing notable abilities in slot filling and questioning. Our work has demonstrated its strong generalization capabilities in various downstream scenarios, significantly enhancing both data utilization efficiency and system performance. The data is released in https://github.com/KongLongGeFDU/TransferTOD.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge