Zhichao Yang
Fine-grained Image Aesthetic Assessment: Learning Discriminative Scores from Relative Ranks
Mar 04, 2026Abstract:Image aesthetic assessment (IAA) has extensive applications in content creation, album management, and recommendation systems, etc. In such applications, it is commonly needed to pick out the most aesthetically pleasing image from a series of images with subtle aesthetic variations, a topic we refer to as fine-grained IAA. Unfortunately, state-of-the-art IAA models are typically designed for coarse-grained evaluation, where images with notable aesthetic differences are evaluated independently on an absolute scale. These models are inherently limited in discriminating fine-grained aesthetic differences. To address the dilemma, we contribute FGAesthetics, a fine-grained IAA database with 32,217 images organized into 10,028 series, which are sourced from diverse categories including Natural, AIGC, and Cropping. Annotations are collected via pairwise comparisons within each series. We also devise Series Refinement and Rank Calibration to ensure the reliability of data and labels. Based on FGAesthetics, we further propose FGAesQ, a novel IAA framework that learns discriminative aesthetic scores from relative ranks through Difference-preserved Tokenization (DiffToken), Comparative Text-assisted Alignment (CTAlign), and Rank-aware Regression (RankReg). FGAesQ enables accurate aesthetic assessment in fine-grained scenarios while still maintains competitive performance in coarse-grained evaluation. Extensive experiments and comparisons demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method.
TARSE: Test-Time Adaptation via Retrieval of Skills and Experience for Reasoning Agents
Mar 01, 2026Abstract:Complex clinical decision making often fails not because a model lacks facts, but because it cannot reliably select and apply the right procedural knowledge and the right prior example at the right reasoning step. We frame clinical question answering as an agent problem with two explicit, retrievable resources: skills, reusable clinical procedures such as guidelines, protocols, and pharmacologic mechanisms; and experience, verified reasoning trajectories from previously solved cases (e.g., chain-of-thought solutions and their step-level decompositions). At test time, the agent retrieves both relevant skills and experiences from curated libraries and performs lightweight test-time adaptation to align the language model's intermediate reasoning with clinically valid logic. Concretely, we build (i) a skills library from guideline-style documents organized as executable decision rules, (ii) an experience library of exemplar clinical reasoning chains indexed by step-level transitions, and (iii) a step-aware retriever that selects the most useful skill and experience items for the current case. We then adapt the model on the retrieved items to reduce instance-step misalignment and to prevent reasoning from drifting toward unsupported shortcuts. Experiments on medical question-answering benchmarks show consistent gains over strong medical RAG baselines and prompting-only reasoning methods. Our results suggest that explicitly separating and retrieving clinical skills and experience, and then aligning the model at test time, is a practical approach to more reliable medical agents.
Fast and Effective On-policy Distillation from Reasoning Prefixes
Feb 16, 2026Abstract:On-policy distillation (OPD), which samples trajectories from the student model and supervises them with a teacher at the token level, avoids relying solely on verifiable terminal rewards and can yield better generalization than off-policy distillation. However, OPD requires expensive on-the-fly sampling of the student policy during training, which substantially increases training cost, especially for long responses. Our initial analysis shows that, during OPD, training signals are often concentrated in the prefix of each output, and that even a short teacher-generated prefix can significantly help the student produce the correct answer. Motivated by these observations, we propose a simple yet effective modification of OPD: we apply the distillation objective only to prefixes of student-generated outputs and terminate each sampling early during distillation. Experiments on a suite of AI-for-Math and out-of-domain benchmarks show that on-policy prefix distillation matches the performance of full OPD while reducing training FLOP by 2x-47x.
ESTAR: Early-Stopping Token-Aware Reasoning For Efficient Inference
Feb 10, 2026Abstract:Large reasoning models (LRMs) achieve state-of-the-art performance by generating long chains-of-thought, but often waste computation on redundant reasoning after the correct answer has already been reached. We introduce Early-Stopping for Token-Aware Reasoning (ESTAR), which detects and reduces such reasoning redundancy to improve efficiency without sacrificing accuracy. Our method combines (i) a trajectory-based classifier that identifies when reasoning can be safely stopped, (ii) supervised fine-tuning to teach LRMs to propose self-generated <stop> signals, and (iii) <stop>-aware reinforcement learning that truncates rollouts at self-generated stop points with compute-aware rewards. Experiments on four reasoning datasets show that ESTAR reduces reasoning length by about 3.7x (from 4,799 to 1,290) while preserving accuracy (74.9% vs. 74.2%), with strong cross-domain generalization. These results highlight early stopping as a simple yet powerful mechanism for improving reasoning efficiency in LRMs.
Health-SCORE: Towards Scalable Rubrics for Improving Health-LLMs
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Rubrics are essential for evaluating open-ended LLM responses, especially in safety-critical domains such as healthcare. However, creating high-quality and domain-specific rubrics typically requires significant human expertise time and development cost, making rubric-based evaluation and training difficult to scale. In this work, we introduce Health-SCORE, a generalizable and scalable rubric-based training and evaluation framework that substantially reduces rubric development costs without sacrificing performance. We show that Health-SCORE provides two practical benefits beyond standalone evaluation: it can be used as a structured reward signal to guide reinforcement learning with safety-aware supervision, and it can be incorporated directly into prompts to improve response quality through in-context learning. Across open-ended healthcare tasks, Health-SCORE achieves evaluation quality comparable to human-created rubrics while significantly lowering development effort, making rubric-based evaluation and training more scalable.
TransportAgents: a multi-agents LLM framework for traffic accident severity prediction
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Accurate prediction of traffic crash severity is critical for improving emergency response and public safety planning. Although recent large language models (LLMs) exhibit strong reasoning capabilities, their single-agent architectures often struggle with heterogeneous, domain-specific crash data and tend to generate biased or unstable predictions. To address these limitations, this paper proposes TransportAgents, a hybrid multi-agent framework that integrates category-specific LLM reasoning with a multilayer perceptron (MLP) integration module. Each specialized agent focuses on a particular subset of traffic information, such as demographics, environmental context, or incident details, to produce intermediate severity assessments that are subsequently fused into a unified prediction. Extensive experiments on two complementary U.S. datasets, the Consumer Product Safety Risk Management System (CPSRMS) and the National Electronic Injury Surveillance System (NEISS), demonstrate that TransportAgents consistently outperforms both traditional machine learning and advanced LLM-based baselines. Across three representative backbones, including closed-source models such as GPT-3.5 and GPT-4o, as well as open-source models such as LLaMA-3.3, the framework exhibits strong robustness, scalability, and cross-dataset generalizability. A supplementary distributional analysis further shows that TransportAgents produces more balanced and well-calibrated severity predictions than standard single-agent LLM approaches, highlighting its interpretability and reliability for safety-critical decision support applications.
LongT2IBench: A Benchmark for Evaluating Long Text-to-Image Generation with Graph-structured Annotations
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:The increasing popularity of long Text-to-Image (T2I) generation has created an urgent need for automatic and interpretable models that can evaluate the image-text alignment in long prompt scenarios. However, the existing T2I alignment benchmarks predominantly focus on short prompt scenarios and only provide MOS or Likert scale annotations. This inherent limitation hinders the development of long T2I evaluators, particularly in terms of the interpretability of alignment. In this study, we contribute LongT2IBench, which comprises 14K long text-image pairs accompanied by graph-structured human annotations. Given the detail-intensive nature of long prompts, we first design a Generate-Refine-Qualify annotation protocol to convert them into textual graph structures that encompass entities, attributes, and relations. Through this transformation, fine-grained alignment annotations are achieved based on these granular elements. Finally, the graph-structed annotations are converted into alignment scores and interpretations to facilitate the design of T2I evaluation models. Based on LongT2IBench, we further propose LongT2IExpert, a LongT2I evaluator that enables multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) to provide both quantitative scores and structured interpretations through an instruction-tuning process with Hierarchical Alignment Chain-of-Thought (CoT). Extensive experiments and comparisons demonstrate the superiority of the proposed LongT2IExpert in alignment evaluation and interpretation. Data and code have been released in https://welldky.github.io/LongT2IBench-Homepage/.
PRIME: Planning and Retrieval-Integrated Memory for Enhanced Reasoning
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Inspired by the dual-process theory of human cognition from \textit{Thinking, Fast and Slow}, we introduce \textbf{PRIME} (Planning and Retrieval-Integrated Memory for Enhanced Reasoning), a multi-agent reasoning framework that dynamically integrates \textbf{System 1} (fast, intuitive thinking) and \textbf{System 2} (slow, deliberate thinking). PRIME first employs a Quick Thinking Agent (System 1) to generate a rapid answer; if uncertainty is detected, it then triggers a structured System 2 reasoning pipeline composed of specialized agents for \textit{planning}, \textit{hypothesis generation}, \textit{retrieval}, \textit{information integration}, and \textit{decision-making}. This multi-agent design faithfully mimics human cognitive processes and enhances both efficiency and accuracy. Experimental results with LLaMA 3 models demonstrate that PRIME enables open-source LLMs to perform competitively with state-of-the-art closed-source models like GPT-4 and GPT-4o on benchmarks requiring multi-hop and knowledge-grounded reasoning. This research establishes PRIME as a scalable solution for improving LLMs in domains requiring complex, knowledge-intensive reasoning.
ChatThero: An LLM-Supported Chatbot for Behavior Change and Therapeutic Support in Addiction Recovery
Aug 28, 2025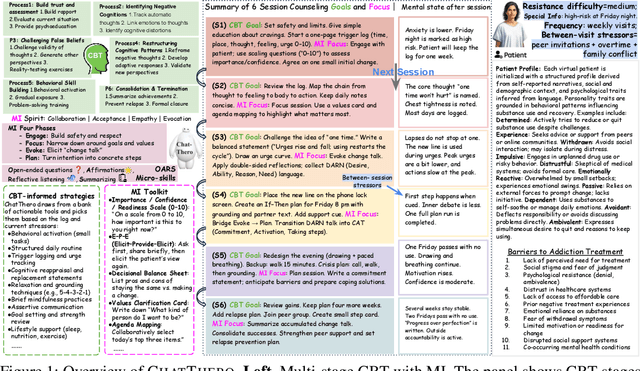
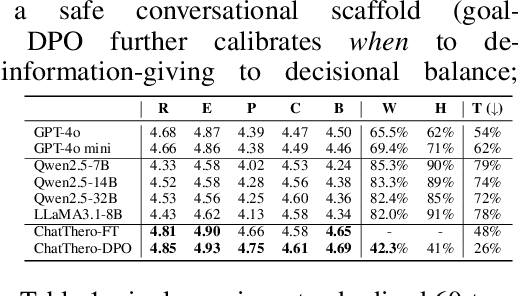
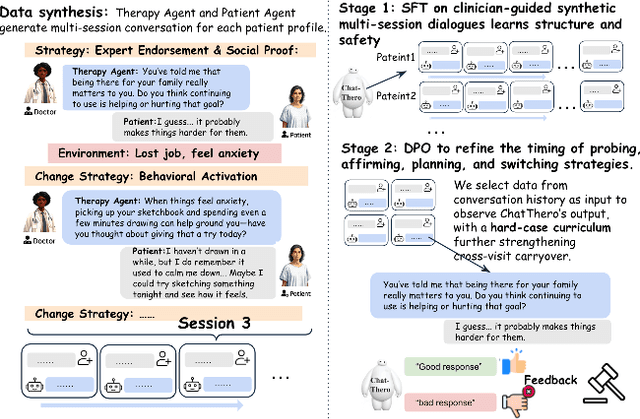
Abstract:Substance use disorders (SUDs) affect over 36 million people worldwide, yet few receive effective care due to stigma, motivational barriers, and limited personalized support. Although large language models (LLMs) show promise for mental-health assistance, most systems lack tight integration with clinically validated strategies, reducing effectiveness in addiction recovery. We present ChatThero, a multi-agent conversational framework that couples dynamic patient modeling with context-sensitive therapeutic dialogue and adaptive persuasive strategies grounded in cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and motivational interviewing (MI). We build a high-fidelity synthetic benchmark spanning Easy, Medium, and Hard resistance levels, and train ChatThero with a two-stage pipeline comprising supervised fine-tuning (SFT) followed by direct preference optimization (DPO). In evaluation, ChatThero yields a 41.5\% average gain in patient motivation, a 0.49\% increase in treatment confidence, and resolves hard cases with 26\% fewer turns than GPT-4o, and both automated and human clinical assessments rate it higher in empathy, responsiveness, and behavioral realism. The framework supports rigorous, privacy-preserving study of therapeutic conversation and provides a robust, replicable basis for research and clinical translation.
Can Structured Templates Facilitate LLMs in Tackling Harder Tasks? : An Exploration of Scaling Laws by Difficulty
Aug 26, 2025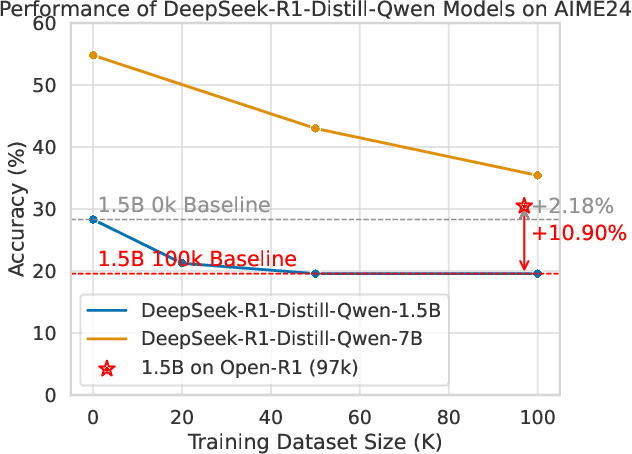
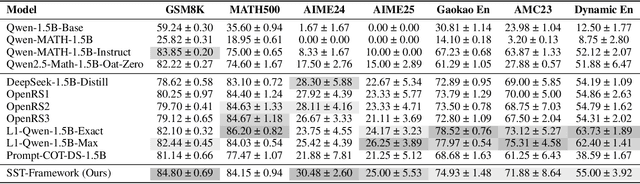
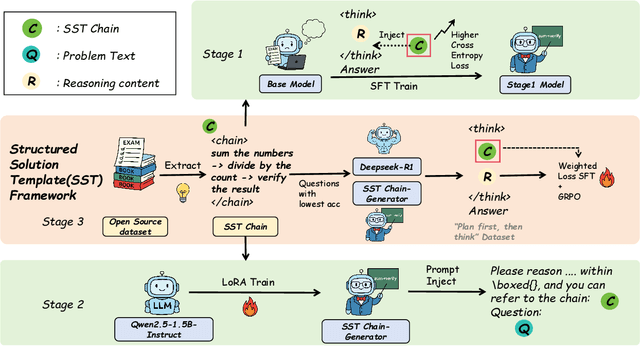

Abstract:Structured, procedural reasoning is essential for Large Language Models (LLMs), especially in mathematics. While post-training methods have improved LLM performance, they still fall short in capturing deep procedural logic on complex tasks. To tackle the issue, in this paper, we first investigate this limitation and uncover a novel finding: a Scaling Law by Difficulty, which reveals that model performance follows a U-shaped curve with respect to training data complexity -- excessive low-difficulty data impedes abstraction, while high-difficulty data significantly enhances reasoning ability. Motivated by this, we propose the Structured Solution Template (SST) framework, which uses solution templates and a curriculum of varied difficulty to explicitly teach procedural reasoning. Specifically, SST comprises (1) fine-tuning with structured solution-template chains and dynamically weighted loss to prioritize procedural logic, (2) prompt-time injection of solution templates as cognitive scaffolds to guide inference, and (3) integrated curriculum fine-tuning that explicitly teaches the model to self-plan - execute - self-correct. Experiments on GSM8K, AIME24, and new Dynamic En benchmark show that SST significantly improves both accuracy and efficiency, especially on harder problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge