Parth Vashisht
UMass-BioNLP at MEDIQA-M3G 2024: DermPrompt -- A Systematic Exploration of Prompt Engineering with GPT-4V for Dermatological Diagnosis
Apr 27, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents our team's participation in the MEDIQA-ClinicalNLP2024 shared task B. We present a novel approach to diagnosing clinical dermatology cases by integrating large multimodal models, specifically leveraging the capabilities of GPT-4V under a retriever and a re-ranker framework. Our investigation reveals that GPT-4V, when used as a retrieval agent, can accurately retrieve the correct skin condition 85% of the time using dermatological images and brief patient histories. Additionally, we empirically show that Naive Chain-of-Thought (CoT) works well for retrieval while Medical Guidelines Grounded CoT is required for accurate dermatological diagnosis. Further, we introduce a Multi-Agent Conversation (MAC) framework and show its superior performance and potential over the best CoT strategy. The experiments suggest that using naive CoT for retrieval and multi-agent conversation for critique-based diagnosis, GPT-4V can lead to an early and accurate diagnosis of dermatological conditions. The implications of this work extend to improving diagnostic workflows, supporting dermatological education, and enhancing patient care by providing a scalable, accessible, and accurate diagnostic tool.
SYNFAC-EDIT: Synthetic Imitation Edit Feedback for Factual Alignment in Clinical Summarization
Feb 21, 2024
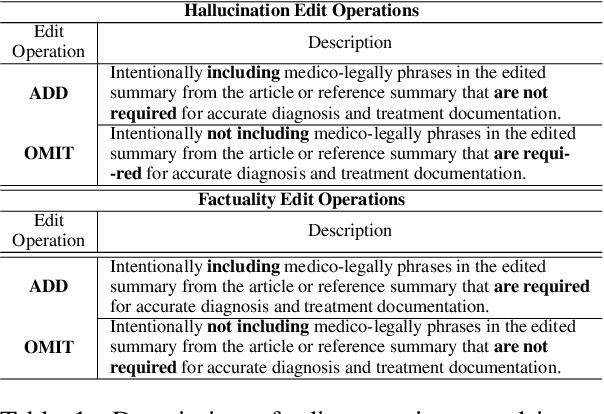
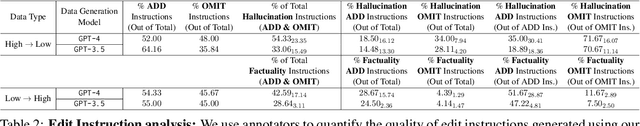
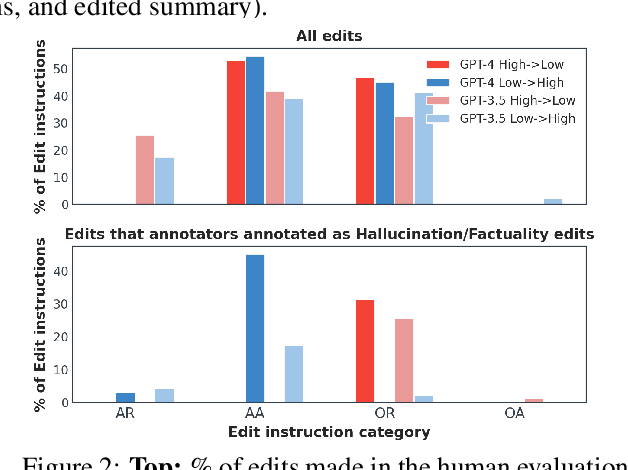
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) such as GPT and Llama have demonstrated significant achievements in summarization tasks but struggle with factual inaccuracies, a critical issue in clinical NLP applications where errors could lead to serious consequences. To counter the high costs and limited availability of expert-annotated data for factual alignment, this study introduces an innovative pipeline that utilizes GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 to generate high-quality feedback aimed at enhancing factual consistency in clinical note summarization. Our research primarily focuses on edit feedback, mirroring the practical scenario in which medical professionals refine AI system outputs without the need for additional annotations. Despite GPT's proven expertise in various clinical NLP tasks, such as the Medical Licensing Examination, there is scant research on its capacity to deliver expert-level edit feedback for improving weaker LMs or LLMs generation quality. This work leverages GPT's advanced capabilities in clinical NLP to offer expert-level edit feedback. Through the use of two distinct alignment algorithms (DPO and SALT) based on GPT edit feedback, our goal is to reduce hallucinations and align closely with medical facts, endeavoring to narrow the divide between AI-generated content and factual accuracy. This highlights the substantial potential of GPT edits in enhancing the alignment of clinical factuality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge