Liang Pang
D-Models and E-Models: Diversity-Stability Trade-offs in the Sampling Behavior of Large Language Models
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:The predictive probability of the next token (P_token) in large language models (LLMs) is inextricably linked to the probability of relevance for the next piece of information, the purchase probability of the next product, and the execution probability of the next action-all of which fall under the scope of the task-level target distribution (P_task). While LLMs are known to generate samples that approximate real-world distributions, whether their fine-grained sampling probabilities faithfully align with task requirements remains an open question. Through controlled distribution-sampling simulations, we uncover a striking dichotomy in LLM behavior, distinguishing two model types: D-models (e.g. Qwen-2.5), whose P_token exhibits large step-to-step variability and poor alignment with P_task; and E-models (e.g. Mistral-Small), whose P_token is more stable and better aligned with P_task. We further evaluate these two model types in downstream tasks such as code generation and recommendation, revealing systematic trade-offs between diversity and stability that shape task outcomes. Finally, we analyze the internal properties of both model families to probe their underlying mechanisms. These findings offer foundational insights into the probabilistic sampling behavior of LLMs and provide practical guidance on when to favor D- versus E-models. For web-scale applications, including recommendation, search, and conversational agents, our results inform model selection and configuration to balance diversity with reliability under real-world uncertainty, providing a better level of interpretation.
Projecting Out the Malice: A Global Subspace Approach to LLM Detoxification
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) exhibit exceptional performance but pose inherent risks of generating toxic content, restricting their safe deployment. While traditional methods (e.g., alignment) adjust output preferences, they fail to eliminate underlying toxic regions in parameters, leaving models vulnerable to adversarial attacks. Prior mechanistic studies characterize toxic regions as "toxic vectors" or "layer-wise subspaces", yet our analysis identifies critical limitations: i) Removed toxic vectors can be reconstructed via linear combinations of non-toxic vectors, demanding targeting of entire toxic subspace; ii) Contrastive objective over limited samples inject noise into layer-wise subspaces, hindering stable extraction. These highlight the challenge of identifying robust toxic subspace and removing them. Therefore, we propose GLOSS (GLobal tOxic Subspace Suppression), a lightweight method that mitigates toxicity by identifying and eliminating this global subspace from FFN parameters. Experiments on LLMs (e.g., Qwen3) show GLOSS achieves SOTA detoxification while preserving general capabilities without requiring large-scale retraining. WARNING: This paper contains context which is toxic in nature.
Circular Reasoning: Understanding Self-Reinforcing Loops in Large Reasoning Models
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Despite the success of test-time scaling, Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) frequently encounter repetitive loops that lead to computational waste and inference failure. In this paper, we identify a distinct failure mode termed Circular Reasoning. Unlike traditional model degeneration, this phenomenon manifests as a self-reinforcing trap where generated content acts as a logical premise for its own recurrence, compelling the reiteration of preceding text. To systematically analyze this phenomenon, we introduce LoopBench, a dataset designed to capture two distinct loop typologies: numerical loops and statement loops. Mechanistically, we characterize circular reasoning as a state collapse exhibiting distinct boundaries, where semantic repetition precedes textual repetition. We reveal that reasoning impasses trigger the loop onset, which subsequently persists as an inescapable cycle driven by a self-reinforcing V-shaped attention mechanism. Guided by these findings, we employ the Cumulative Sum (CUSUM) algorithm to capture these precursors for early loop prediction. Experiments across diverse LRMs validate its accuracy and elucidate the stability of long-chain reasoning.
Stable-RAG: Mitigating Retrieval-Permutation-Induced Hallucinations in Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has become a key paradigm for reducing factual hallucinations in large language models (LLMs), yet little is known about how the order of retrieved documents affects model behavior. We empirically show that under Top-5 retrieval with the gold document included, LLM answers vary substantially across permutations of the retrieved set, even when the gold document is fixed in the first position. This reveals a previously underexplored sensitivity to retrieval permutations. Although robust RAG methods primarily focus on enhancing LLM robustness to low-quality retrieval and mitigating positional bias to distribute attention fairly over long contexts, neither approach directly addresses permutation sensitivity. In this paper, we propose Stable-RAG, which exploits permutation sensitivity estimation to mitigate permutation-induced hallucinations. Stable-RAG runs the generator under multiple retrieval orders, clusters hidden states, and decodes from a cluster-center representation that captures the dominant reasoning pattern. It then uses these reasoning results to align hallucinated outputs toward the correct answer, encouraging the model to produce consistent and accurate predictions across document permutations. Experiments on three QA datasets show that Stable-RAG significantly improves answer accuracy, reasoning consistency and robust generalization across datasets, retrievers, and input lengths compared with baselines.
Can Synthetic Query Rewrites Capture User Intent Better than Humans in Retrieval-Augmented Generation?
Sep 26, 2025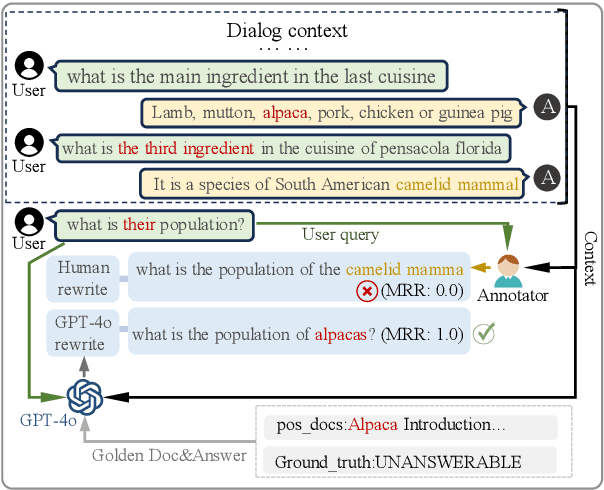



Abstract:Multi-turn RAG systems often face queries with colloquial omissions and ambiguous references, posing significant challenges for effective retrieval and generation. Traditional query rewriting relies on human annotators to clarify queries, but due to limitations in annotators' expressive ability and depth of understanding, manually rewritten queries often diverge from those needed in real-world RAG systems, resulting in a gap between user intent and system response. We observe that high-quality synthetic queries can better bridge this gap, achieving superior performance in both retrieval and generation compared to human rewrites. This raises an interesting question: Can rewriting models trained on synthetic queries better capture user intent than human annotators? In this paper, we propose SynRewrite, a synthetic data-driven query rewriting model to generate high-quality synthetic rewrites more aligned with user intent. To construct training data, we prompt GPT-4o with dialogue history, current queries, positive documents, and answers to synthesize high-quality rewrites. A Flan-T5 model is then finetuned on this dataset to map dialogue history and queries to synthetic rewrites. Finally, we further enhance the rewriter using the generator's feedback through the DPO algorithm to boost end-task performance. Experiments on TopiOCQA and QRECC datasets show that SynRewrite consistently outperforms human rewrites in both retrieval and generation tasks. Our results demonstrate that synthetic rewrites can serve as a scalable and effective alternative to human annotations.
Stop Spinning Wheels: Mitigating LLM Overthinking via Mining Patterns for Early Reasoning Exit
Aug 25, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) enhance complex reasoning tasks by scaling the individual thinking process. However, prior work shows that overthinking can degrade overall performance. Motivated by observed patterns in thinking length and content length, we categorize reasoning into three stages: insufficient exploration stage, compensatory reasoning stage, and reasoning convergence stage. Typically, LLMs produce correct answers in the compensatory reasoning stage, whereas reasoning convergence often triggers overthinking, causing increased resource usage or even infinite loops. Therefore, mitigating overthinking hinges on detecting the end of the compensatory reasoning stage, defined as the Reasoning Completion Point (RCP). RCP typically appears at the end of the first complete reasoning cycle and can be identified by querying the LLM sentence by sentence or monitoring the probability of an end-of-thinking token (e.g., \texttt{</think>}), though these methods lack an efficient and precise balance. To improve this, we mine more sensitive and consistent RCP patterns and develop a lightweight thresholding strategy based on heuristic rules. Experimental evaluations on benchmarks (AIME24, AIME25, GPQA-D) demonstrate that the proposed method reduces token consumption while preserving or enhancing reasoning accuracy.
Distilling the Implicit Multi-Branch Structure in LLMs' Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning
May 22, 2025Abstract:Distilling reasoning paths from teacher to student models via supervised fine-tuning (SFT) provides a shortcut for improving the reasoning ability of smaller Large Language Models (LLMs). However, the reasoning paths generated by teacher models often reflect only surface-level traces of their underlying authentic reasoning. Insights from cognitive neuroscience suggest that authentic reasoning involves a complex interweaving between meta-reasoning (which selects appropriate sub-problems from multiple candidates) and solving (which addresses the sub-problem). This implies authentic reasoning has an implicit multi-branch structure. Supervised fine-tuning collapses this rich structure into a flat sequence of token prediction in the teacher's reasoning path, preventing effective distillation of this structure to students. To address this limitation, we propose RLKD, a reinforcement learning (RL)-based distillation framework guided by a novel Generative Structure Reward Model (GSRM). Our GSRM converts reasoning paths into multiple meta-reasoning-solving steps and computes rewards to measure structural alignment between student and teacher reasoning. RLKD combines this reward with RL, enabling student LLMs to internalize the teacher's implicit multi-branch reasoning structure rather than merely mimicking fixed output paths. Experiments show RLKD surpasses standard SFT-RL pipelines even when trained on 0.1% of data under an RL-only regime, unlocking greater student reasoning potential than SFT-based distillation.
NExT-Search: Rebuilding User Feedback Ecosystem for Generative AI Search
May 20, 2025Abstract:Generative AI search is reshaping information retrieval by offering end-to-end answers to complex queries, reducing users' reliance on manually browsing and summarizing multiple web pages. However, while this paradigm enhances convenience, it disrupts the feedback-driven improvement loop that has historically powered the evolution of traditional Web search. Web search can continuously improve their ranking models by collecting large-scale, fine-grained user feedback (e.g., clicks, dwell time) at the document level. In contrast, generative AI search operates through a much longer search pipeline, spanning query decomposition, document retrieval, and answer generation, yet typically receives only coarse-grained feedback on the final answer. This introduces a feedback loop disconnect, where user feedback for the final output cannot be effectively mapped back to specific system components, making it difficult to improve each intermediate stage and sustain the feedback loop. In this paper, we envision NExT-Search, a next-generation paradigm designed to reintroduce fine-grained, process-level feedback into generative AI search. NExT-Search integrates two complementary modes: User Debug Mode, which allows engaged users to intervene at key stages; and Shadow User Mode, where a personalized user agent simulates user preferences and provides AI-assisted feedback for less interactive users. Furthermore, we envision how these feedback signals can be leveraged through online adaptation, which refines current search outputs in real-time, and offline update, which aggregates interaction logs to periodically fine-tune query decomposition, retrieval, and generation models. By restoring human control over key stages of the generative AI search pipeline, we believe NExT-Search offers a promising direction for building feedback-rich AI search systems that can evolve continuously alongside human feedback.
Understanding Accuracy-Fairness Trade-offs in Re-ranking through Elasticity in Economics
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:Fairness is an increasingly important factor in re-ranking tasks. Prior work has identified a trade-off between ranking accuracy and item fairness. However, the underlying mechanisms are still not fully understood. An analogy can be drawn between re-ranking and the dynamics of economic transactions. The accuracy-fairness trade-off parallels the coupling of the commodity tax transfer process. Fairness considerations in re-ranking, similar to a commodity tax on suppliers, ultimately translate into a cost passed on to consumers. Analogously, item-side fairness constraints result in a decline in user-side accuracy. In economics, the extent to which commodity tax on the supplier (item fairness) transfers to commodity tax on users (accuracy loss) is formalized using the notion of elasticity. The re-ranking fairness-accuracy trade-off is similarly governed by the elasticity of utility between item groups. This insight underscores the limitations of current fair re-ranking evaluations, which often rely solely on a single fairness metric, hindering comprehensive assessment of fair re-ranking algorithms. Centered around the concept of elasticity, this work presents two significant contributions. We introduce the Elastic Fairness Curve (EF-Curve) as an evaluation framework. This framework enables a comparative analysis of algorithm performance across different elasticity levels, facilitating the selection of the most suitable approach. Furthermore, we propose ElasticRank, a fair re-ranking algorithm that employs elasticity calculations to adjust inter-item distances within a curved space. Experiments on three widely used ranking datasets demonstrate its effectiveness and efficiency.
Learning to Erase Private Knowledge from Multi-Documents for Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Models
Apr 14, 2025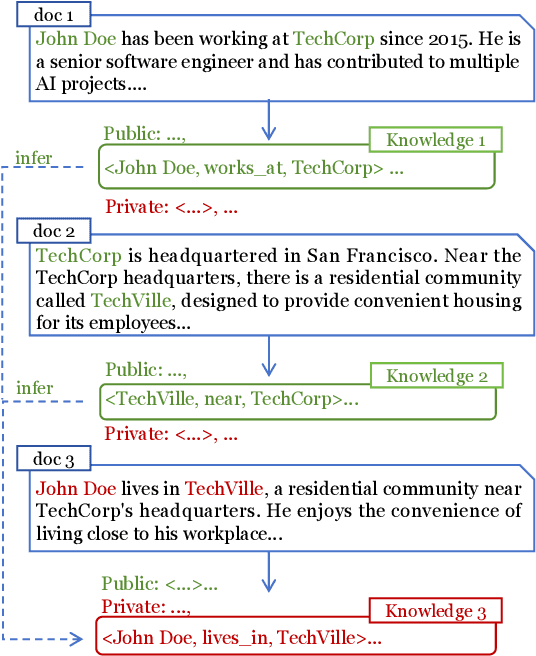



Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a promising technique for applying LLMs to proprietary domains. However, retrieved documents may contain sensitive knowledge, posing risks of privacy leakage in generative results. Thus, effectively erasing private information from retrieved documents is a key challenge for RAG. Unlike traditional text anonymization, RAG should consider: (1) the inherent multi-document reasoning may face de-anonymization attacks; (2) private knowledge varies by scenarios, so users should be allowed to customize which information to erase; (3) preserving sufficient publicly available knowledge for generation tasks. This paper introduces the privacy erasure task for RAG and proposes Eraser4RAG, a private knowledge eraser which effectively removes user-defined private knowledge from documents while preserving sufficient public knowledge for generation. Specifically, we first construct a global knowledge graph to identify potential knowledge across documents, aiming to defend against de-anonymization attacks. Then we randomly split it into private and public sub-graphs, and fine-tune Flan-T5 to rewrite the retrieved documents excluding private triples. Finally, PPO algorithm optimizes the rewriting model to minimize private triples and maximize public triples retention. Experiments on four QA datasets demonstrate that Eraser4RAG achieves superior erase performance than GPT-4o.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge