Shicheng Xu
Luke
Circular Reasoning: Understanding Self-Reinforcing Loops in Large Reasoning Models
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Despite the success of test-time scaling, Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) frequently encounter repetitive loops that lead to computational waste and inference failure. In this paper, we identify a distinct failure mode termed Circular Reasoning. Unlike traditional model degeneration, this phenomenon manifests as a self-reinforcing trap where generated content acts as a logical premise for its own recurrence, compelling the reiteration of preceding text. To systematically analyze this phenomenon, we introduce LoopBench, a dataset designed to capture two distinct loop typologies: numerical loops and statement loops. Mechanistically, we characterize circular reasoning as a state collapse exhibiting distinct boundaries, where semantic repetition precedes textual repetition. We reveal that reasoning impasses trigger the loop onset, which subsequently persists as an inescapable cycle driven by a self-reinforcing V-shaped attention mechanism. Guided by these findings, we employ the Cumulative Sum (CUSUM) algorithm to capture these precursors for early loop prediction. Experiments across diverse LRMs validate its accuracy and elucidate the stability of long-chain reasoning.
Stop Spinning Wheels: Mitigating LLM Overthinking via Mining Patterns for Early Reasoning Exit
Aug 25, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) enhance complex reasoning tasks by scaling the individual thinking process. However, prior work shows that overthinking can degrade overall performance. Motivated by observed patterns in thinking length and content length, we categorize reasoning into three stages: insufficient exploration stage, compensatory reasoning stage, and reasoning convergence stage. Typically, LLMs produce correct answers in the compensatory reasoning stage, whereas reasoning convergence often triggers overthinking, causing increased resource usage or even infinite loops. Therefore, mitigating overthinking hinges on detecting the end of the compensatory reasoning stage, defined as the Reasoning Completion Point (RCP). RCP typically appears at the end of the first complete reasoning cycle and can be identified by querying the LLM sentence by sentence or monitoring the probability of an end-of-thinking token (e.g., \texttt{</think>}), though these methods lack an efficient and precise balance. To improve this, we mine more sensitive and consistent RCP patterns and develop a lightweight thresholding strategy based on heuristic rules. Experimental evaluations on benchmarks (AIME24, AIME25, GPQA-D) demonstrate that the proposed method reduces token consumption while preserving or enhancing reasoning accuracy.
Distilling the Implicit Multi-Branch Structure in LLMs' Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning
May 22, 2025Abstract:Distilling reasoning paths from teacher to student models via supervised fine-tuning (SFT) provides a shortcut for improving the reasoning ability of smaller Large Language Models (LLMs). However, the reasoning paths generated by teacher models often reflect only surface-level traces of their underlying authentic reasoning. Insights from cognitive neuroscience suggest that authentic reasoning involves a complex interweaving between meta-reasoning (which selects appropriate sub-problems from multiple candidates) and solving (which addresses the sub-problem). This implies authentic reasoning has an implicit multi-branch structure. Supervised fine-tuning collapses this rich structure into a flat sequence of token prediction in the teacher's reasoning path, preventing effective distillation of this structure to students. To address this limitation, we propose RLKD, a reinforcement learning (RL)-based distillation framework guided by a novel Generative Structure Reward Model (GSRM). Our GSRM converts reasoning paths into multiple meta-reasoning-solving steps and computes rewards to measure structural alignment between student and teacher reasoning. RLKD combines this reward with RL, enabling student LLMs to internalize the teacher's implicit multi-branch reasoning structure rather than merely mimicking fixed output paths. Experiments show RLKD surpasses standard SFT-RL pipelines even when trained on 0.1% of data under an RL-only regime, unlocking greater student reasoning potential than SFT-based distillation.
Generative Ghost: Investigating Ranking Bias Hidden in AI-Generated Videos
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:With the rapid development of AI-generated content (AIGC), the creation of high-quality AI-generated videos has become faster and easier, resulting in the Internet being flooded with all kinds of video content. However, the impact of these videos on the content ecosystem remains largely unexplored. Video information retrieval remains a fundamental approach for accessing video content. Building on the observation that retrieval models often favor AI-generated content in ad-hoc and image retrieval tasks, we investigate whether similar biases emerge in the context of challenging video retrieval, where temporal and visual factors may further influence model behavior. To explore this, we first construct a comprehensive benchmark dataset containing both real and AI-generated videos, along with a set of fair and rigorous metrics to assess bias. This benchmark consists of 13,000 videos generated by two state-of-the-art open-source video generation models. We meticulously design a suite of rigorous metrics to accurately measure this preference, accounting for potential biases arising from the limited frame rate and suboptimal quality of AIGC videos. We then applied three off-the-shelf video retrieval models to perform retrieval tasks on this hybrid dataset. Our findings reveal a clear preference for AI-generated videos in retrieval. Further investigation shows that incorporating AI-generated videos into the training set of retrieval models exacerbates this bias. Unlike the preference observed in image modalities, we find that video retrieval bias arises from both unseen visual and temporal information, making the root causes of video bias a complex interplay of these two factors. To mitigate this bias, we fine-tune the retrieval models using a contrastive learning approach. The results of this study highlight the potential implications of AI-generated videos on retrieval systems.
Cross-Modal Safety Mechanism Transfer in Large Vision-Language Models
Oct 16, 2024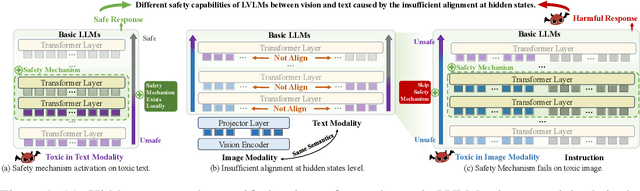
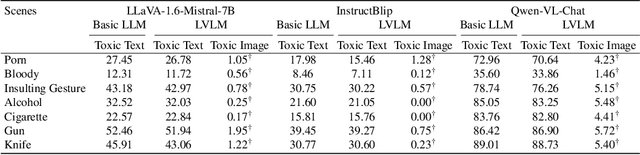
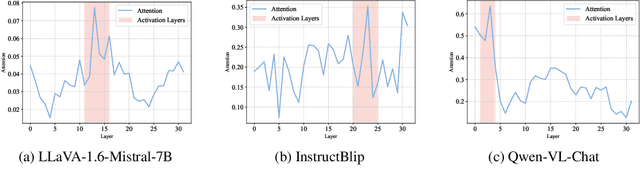
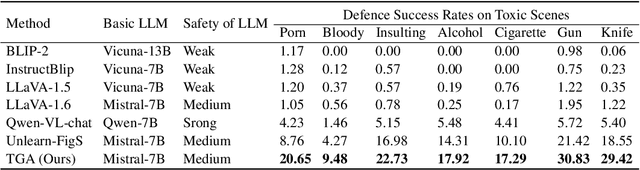
Abstract:Vision-language alignment in Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) successfully enables LLMs to understand visual input. However, we find that existing vision-language alignment methods fail to transfer the existing safety mechanism for text in LLMs to vision, which leads to vulnerabilities in toxic image. To explore the cause of this problem, we give the insightful explanation of where and how the safety mechanism of LVLMs operates and conduct comparative analysis between text and vision. We find that the hidden states at the specific transformer layers play a crucial role in the successful activation of safety mechanism, while the vision-language alignment at hidden states level in current methods is insufficient. This results in a semantic shift for input images compared to text in hidden states, therefore misleads the safety mechanism. To address this, we propose a novel Text-Guided vision-language Alignment method (TGA) for LVLMs. TGA retrieves the texts related to input vision and uses them to guide the projection of vision into the hidden states space in LLMs. Experiments show that TGA not only successfully transfers the safety mechanism for text in basic LLMs to vision in vision-language alignment for LVLMs without any safety fine-tuning on the visual modality but also maintains the general performance on various vision tasks (Safe and Good).
DC3DO: Diffusion Classifier for 3D Objects
Aug 13, 2024



Abstract:Inspired by Geoffrey Hinton emphasis on generative modeling, To recognize shapes, first learn to generate them, we explore the use of 3D diffusion models for object classification. Leveraging the density estimates from these models, our approach, the Diffusion Classifier for 3D Objects (DC3DO), enables zero-shot classification of 3D shapes without additional training. On average, our method achieves a 12.5 percent improvement compared to its multiview counterparts, demonstrating superior multimodal reasoning over discriminative approaches. DC3DO employs a class-conditional diffusion model trained on ShapeNet, and we run inferences on point clouds of chairs and cars. This work highlights the potential of generative models in 3D object classification.
Unveil the Duality of Retrieval-Augmented Generation: Theoretical Analysis and Practical Solution
Jun 03, 2024



Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) utilizes retrieved texts to enhance large language models (LLMs). However, studies show that RAG is not consistently effective and can even mislead LLMs due to noisy or incorrect retrieved texts. This suggests that RAG possesses a duality including both benefit and detriment. Although many existing methods attempt to address this issue, they lack a theoretical explanation for the duality in RAG. The benefit and detriment within this duality remain a black box that cannot be quantified or compared in an explainable manner. This paper takes the first step in theoretically giving the essential explanation of benefit and detriment in RAG by: (1) decoupling and formalizing them from RAG prediction, (2) approximating the gap between their values by representation similarity and (3) establishing the trade-off mechanism between them, to make them explainable, quantifiable, and comparable. We demonstrate that the distribution difference between retrieved texts and LLMs' knowledge acts as double-edged sword, bringing both benefit and detriment. We also prove that the actual effect of RAG can be predicted at token level. Based on our theory, we propose a practical novel method, X-RAG, which achieves collaborative generation between pure LLM and RAG at token level to preserve benefit and avoid detriment. Experiments in real-world tasks based on LLMs including OPT, LLaMA-2, and Mistral show the effectiveness of our method and support our theoretical results.
Unifying Bias and Unfairness in Information Retrieval: A Survey of Challenges and Opportunities with Large Language Models
Apr 17, 2024



Abstract:With the rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs), information retrieval (IR) systems, such as search engines and recommender systems, have undergone a significant paradigm shift. This evolution, while heralding new opportunities, introduces emerging challenges, particularly in terms of biases and unfairness, which may threaten the information ecosystem. In this paper, we present a comprehensive survey of existing works on emerging and pressing bias and unfairness issues in IR systems when the integration of LLMs. We first unify bias and unfairness issues as distribution mismatch problems, providing a groundwork for categorizing various mitigation strategies through distribution alignment. Subsequently, we systematically delve into the specific bias and unfairness issues arising from three critical stages of LLMs integration into IR systems: data collection, model development, and result evaluation. In doing so, we meticulously review and analyze recent literature, focusing on the definitions, characteristics, and corresponding mitigation strategies associated with these issues. Finally, we identify and highlight some open problems and challenges for future work, aiming to inspire researchers and stakeholders in the IR field and beyond to better understand and mitigate bias and unfairness issues of IR in this LLM era. We also consistently maintain a GitHub repository for the relevant papers and resources in this rising direction at https://github.com/KID-22/LLM-IR-Bias-Fairness-Survey.
Unsupervised Information Refinement Training of Large Language Models for Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Feb 28, 2024



Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) enhances large language models (LLMs) by incorporating additional information from retrieval. However, studies have shown that LLMs still face challenges in effectively using the retrieved information, even ignoring it or being misled by it. The key reason is that the training of LLMs does not clearly make LLMs learn how to utilize input retrieved texts with varied quality. In this paper, we propose a novel perspective that considers the role of LLMs in RAG as ``Information Refiner'', which means that regardless of correctness, completeness, or usefulness of retrieved texts, LLMs can consistently integrate knowledge within the retrieved texts and model parameters to generate the texts that are more concise, accurate, and complete than the retrieved texts. To this end, we propose an information refinement training method named InFO-RAG that optimizes LLMs for RAG in an unsupervised manner. InFO-RAG is low-cost and general across various tasks. Extensive experiments on zero-shot prediction of 11 datasets in diverse tasks including Question Answering, Slot-Filling, Language Modeling, Dialogue, and Code Generation show that InFO-RAG improves the performance of LLaMA2 by an average of 9.39\% relative points. InFO-RAG also shows advantages in in-context learning and robustness of RAG.
List-aware Reranking-Truncation Joint Model for Search and Retrieval-augmented Generation
Feb 05, 2024Abstract:The results of information retrieval (IR) are usually presented in the form of a ranked list of candidate documents, such as web search for humans and retrieval-augmented generation for large language models (LLMs). List-aware retrieval aims to capture the list-level contextual features to return a better list, mainly including reranking and truncation. Reranking finely re-scores the documents in the list. Truncation dynamically determines the cut-off point of the ranked list to achieve the trade-off between overall relevance and avoiding misinformation from irrelevant documents. Previous studies treat them as two separate tasks and model them separately. However, the separation is not optimal. First, it is hard to share the contextual information of the ranking list between the two tasks. Second, the separate pipeline usually meets the error accumulation problem, where the small error from the reranking stage can largely affect the truncation stage. To solve these problems, we propose a Reranking-Truncation joint model (GenRT) that can perform the two tasks concurrently. GenRT integrates reranking and truncation via generative paradigm based on encoder-decoder architecture. We also design the novel loss functions for joint optimization to make the model learn both tasks. Sharing parameters by the joint model is conducive to making full use of the common modeling information of the two tasks. Besides, the two tasks are performed concurrently and co-optimized to solve the error accumulation problem between separate stages. Experiments on public learning-to-rank benchmarks and open-domain Q\&A tasks show that our method achieves SOTA performance on both reranking and truncation tasks for web search and retrieval-augmented LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge