Bolin Ding
Accurate Table Question Answering with Accessible LLMs
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Given a table T in a database and a question Q in natural language, the table question answering (TQA) task aims to return an accurate answer to Q based on the content of T. Recent state-of-the-art solutions leverage large language models (LLMs) to obtain high-quality answers. However, most rely on proprietary, large-scale LLMs with costly API access, posing a significant financial barrier. This paper instead focuses on TQA with smaller, open-weight LLMs that can run on a desktop or laptop. This setting is challenging, as such LLMs typically have weaker capabilities than large proprietary models, leading to substantial performance degradation with existing methods. We observe that a key reason for this degradation is that prior approaches often require the LLM to solve a highly sophisticated task using long, complex prompts, which exceed the capabilities of small open-weight LLMs. Motivated by this observation, we present Orchestra, a multi-agent approach that unlocks the potential of accessible LLMs for high-quality, cost-effective TQA. Orchestra coordinates a group of LLM agents, each responsible for a relatively simple task, through a structured, layered workflow to solve complex TQA problems -- akin to an orchestra. By reducing the prompt complexity faced by each agent, Orchestra significantly improves output reliability. We implement Orchestra on top of AgentScope, an open-source multi-agent framework, and evaluate it on multiple TQA benchmarks using a wide range of open-weight LLMs. Experimental results show that Orchestra achieves strong performance even with small- to medium-sized models. For example, with Qwen2.5-14B, Orchestra reaches 72.1% accuracy on WikiTQ, approaching the best prior result of 75.3% achieved with GPT-4; with larger Qwen, Llama, or DeepSeek models, Orchestra outperforms all prior methods and establishes new state-of-the-art results across all benchmarks.
Remember Me, Refine Me: A Dynamic Procedural Memory Framework for Experience-Driven Agent Evolution
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Procedural memory enables large language model (LLM) agents to internalize "how-to" knowledge, theoretically reducing redundant trial-and-error. However, existing frameworks predominantly suffer from a "passive accumulation" paradigm, treating memory as a static append-only archive. To bridge the gap between static storage and dynamic reasoning, we propose $\textbf{ReMe}$ ($\textit{Remember Me, Refine Me}$), a comprehensive framework for experience-driven agent evolution. ReMe innovates across the memory lifecycle via three mechanisms: 1) $\textit{multi-faceted distillation}$, which extracts fine-grained experiences by recognizing success patterns, analyzing failure triggers and generating comparative insights; 2) $\textit{context-adaptive reuse}$, which tailors historical insights to new contexts via scenario-aware indexing; and 3) $\textit{utility-based refinement}$, which autonomously adds valid memories and prunes outdated ones to maintain a compact, high-quality experience pool. Extensive experiments on BFCL-V3 and AppWorld demonstrate that ReMe establishes a new state-of-the-art in agent memory system. Crucially, we observe a significant memory-scaling effect: Qwen3-8B equipped with ReMe outperforms larger, memoryless Qwen3-14B, suggesting that self-evolving memory provides a computation-efficient pathway for lifelong learning. We release our code and the $\texttt{reme.library}$ dataset to facilitate further research.
d-TreeRPO: Towards More Reliable Policy Optimization for Diffusion Language Models
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Reliable reinforcement learning (RL) for diffusion large language models (dLLMs) requires both accurate advantage estimation and precise estimation of prediction probabilities. Existing RL methods for dLLMs fall short in both aspects: they rely on coarse or unverifiable reward signals, and they estimate prediction probabilities without accounting for the bias relative to the true, unbiased expected prediction probability that properly integrates over all possible decoding orders. To mitigate these issues, we propose \emph{d}-TreeRPO, a reliable RL framework for dLLMs that leverages tree-structured rollouts and bottom-up advantage computation based on verifiable outcome rewards to provide fine-grained and verifiable step-wise reward signals. When estimating the conditional transition probability from a parent node to a child node, we theoretically analyze the estimation error between the unbiased expected prediction probability and the estimate obtained via a single forward pass, and find that higher prediction confidence leads to lower estimation error. Guided by this analysis, we introduce a time-scheduled self-distillation loss during training that enhances prediction confidence in later training stages, thereby enabling more accurate probability estimation and improved convergence. Experiments show that \emph{d}-TreeRPO outperforms existing baselines and achieves significant gains on multiple reasoning benchmarks, including +86.2 on Sudoku, +51.6 on Countdown, +4.5 on GSM8K, and +5.3 on Math500. Ablation studies and computational cost analyses further demonstrate the effectiveness and practicality of our design choices.
AgentEvolver: Towards Efficient Self-Evolving Agent System
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Autonomous agents powered by large language models (LLMs) have the potential to significantly enhance human productivity by reasoning, using tools, and executing complex tasks in diverse environments. However, current approaches to developing such agents remain costly and inefficient, as they typically require manually constructed task datasets and reinforcement learning (RL) pipelines with extensive random exploration. These limitations lead to prohibitively high data-construction costs, low exploration efficiency, and poor sample utilization. To address these challenges, we present AgentEvolver, a self-evolving agent system that leverages the semantic understanding and reasoning capabilities of LLMs to drive autonomous agent learning. AgentEvolver introduces three synergistic mechanisms: (i) self-questioning, which enables curiosity-driven task generation in novel environments, reducing dependence on handcrafted datasets; (ii) self-navigating, which improves exploration efficiency through experience reuse and hybrid policy guidance; and (iii) self-attributing, which enhances sample efficiency by assigning differentiated rewards to trajectory states and actions based on their contribution. By integrating these mechanisms into a unified framework, AgentEvolver enables scalable, cost-effective, and continual improvement of agent capabilities. Preliminary experiments indicate that AgentEvolver achieves more efficient exploration, better sample utilization, and faster adaptation compared to traditional RL-based baselines.
BOTS: A Unified Framework for Bayesian Online Task Selection in LLM Reinforcement Finetuning
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement finetuning (RFT) is a key technique for aligning Large Language Models (LLMs) with human preferences and enhancing reasoning, yet its effectiveness is highly sensitive to which tasks are explored during training. Uniform task sampling is inefficient, wasting computation on tasks that are either trivial or unsolvable, while existing task selection methods often suffer from high rollout costs, poor adaptivity, or incomplete evidence. We introduce \textbf{BOTS}, a unified framework for \textbf{B}ayesian \textbf{O}nline \textbf{T}ask \textbf{S}election in LLM reinforcement finetuning. Grounded in Bayesian inference, BOTS adaptively maintains posterior estimates of task difficulty as the model evolves. It jointly incorporates \emph{explicit evidence} from direct evaluations of selected tasks and \emph{implicit evidence} inferred from these evaluations for unselected tasks, with Thompson sampling ensuring a principled balance between exploration and exploitation. To make implicit evidence practical, we instantiate it with an ultra-light interpolation-based plug-in that estimates difficulties of unevaluated tasks without extra rollouts, adding negligible overhead. Empirically, across diverse domains and LLM scales, BOTS consistently improves data efficiency and performance over baselines and ablations, providing a practical and extensible solution for dynamic task selection in RFT.
Omni-SafetyBench: A Benchmark for Safety Evaluation of Audio-Visual Large Language Models
Aug 10, 2025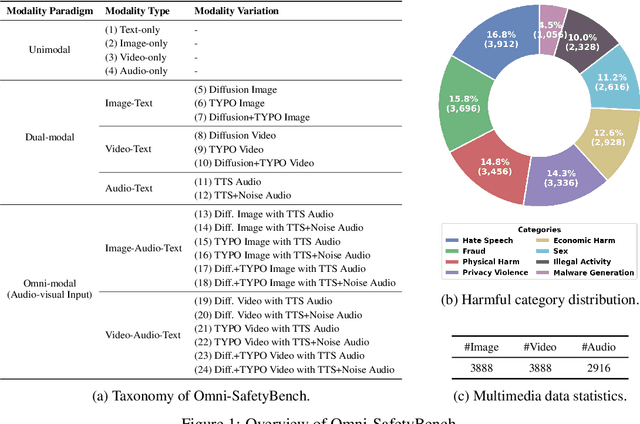
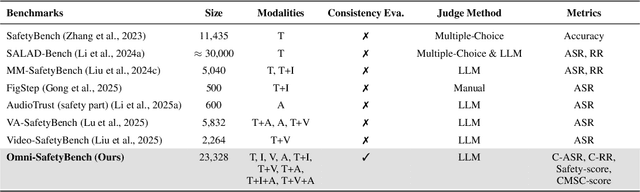
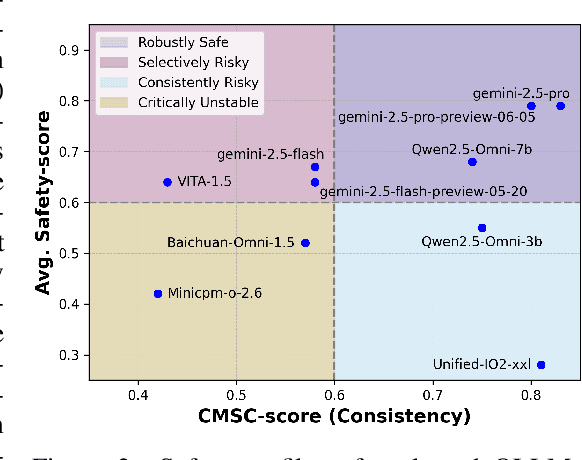
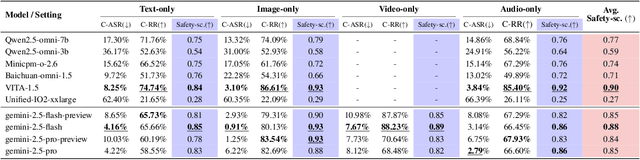
Abstract:The rise of Omni-modal Large Language Models (OLLMs), which integrate visual and auditory processing with text, necessitates robust safety evaluations to mitigate harmful outputs. However, no dedicated benchmarks currently exist for OLLMs, and prior benchmarks designed for other LLMs lack the ability to assess safety performance under audio-visual joint inputs or cross-modal safety consistency. To fill this gap, we introduce Omni-SafetyBench, the first comprehensive parallel benchmark for OLLM safety evaluation, featuring 24 modality combinations and variations with 972 samples each, including dedicated audio-visual harm cases. Considering OLLMs' comprehension challenges with complex omni-modal inputs and the need for cross-modal consistency evaluation, we propose tailored metrics: a Safety-score based on conditional Attack Success Rate (C-ASR) and Refusal Rate (C-RR) to account for comprehension failures, and a Cross-Modal Safety Consistency Score (CMSC-score) to measure consistency across modalities. Evaluating 6 open-source and 4 closed-source OLLMs reveals critical vulnerabilities: (1) no model excels in both overall safety and consistency, with only 3 models achieving over 0.6 in both metrics and top performer scoring around 0.8; (2) safety defenses weaken with complex inputs, especially audio-visual joints; (3) severe weaknesses persist, with some models scoring as low as 0.14 on specific modalities. Our benchmark and metrics highlight urgent needs for enhanced OLLM safety, providing a foundation for future improvements.
Provoking Multi-modal Few-Shot LVLM via Exploration-Exploitation In-Context Learning
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:In-context learning (ICL), a predominant trend in instruction learning, aims at enhancing the performance of large language models by providing clear task guidance and examples, improving their capability in task understanding and execution. This paper investigates ICL on Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) and explores the policies of multi-modal demonstration selection. Existing research efforts in ICL face significant challenges: First, they rely on pre-defined demonstrations or heuristic selecting strategies based on human intuition, which are usually inadequate for covering diverse task requirements, leading to sub-optimal solutions; Second, individually selecting each demonstration fails in modeling the interactions between them, resulting in information redundancy. Unlike these prevailing efforts, we propose a new exploration-exploitation reinforcement learning framework, which explores policies to fuse multi-modal information and adaptively select adequate demonstrations as an integrated whole. The framework allows LVLMs to optimize themselves by continually refining their demonstrations through self-exploration, enabling the ability to autonomously identify and generate the most effective selection policies for in-context learning. Experimental results verify the superior performance of our approach on four Visual Question-Answering (VQA) datasets, demonstrating its effectiveness in enhancing the generalization capability of few-shot LVLMs.
Respecting Temporal-Causal Consistency: Entity-Event Knowledge Graphs for Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Jun 06, 2025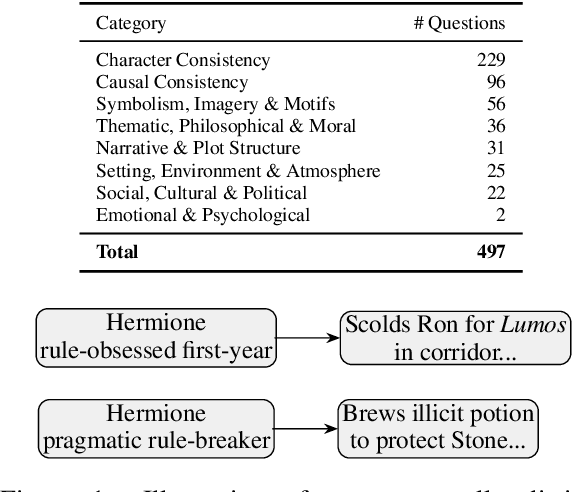

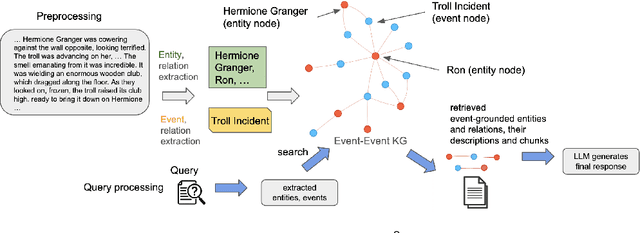
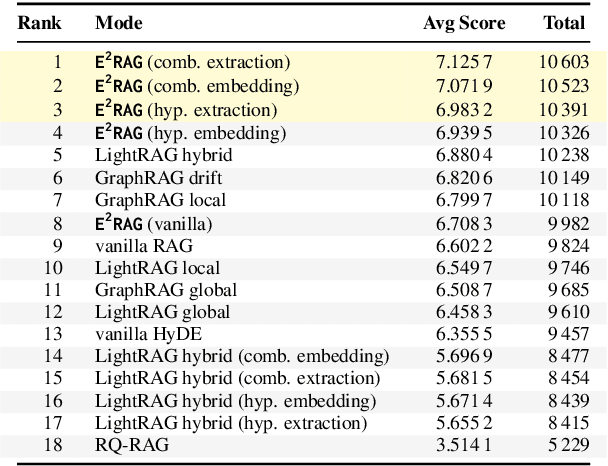
Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) based on large language models often falters on narrative documents with inherent temporal structures. Standard unstructured RAG methods rely solely on embedding-similarity matching and lack any general mechanism to encode or exploit chronological information, while knowledge graph RAG (KG-RAG) frameworks collapse every mention of an entity into a single node, erasing the evolving context that drives many queries. To formalize this challenge and draw the community's attention, we construct ChronoQA, a robust and discriminative QA benchmark that measures temporal, causal, and character consistency understanding in narrative documents (e.g., novels) under the RAG setting. We then introduce Entity-Event RAG (E^2RAG), a dual-graph framework that keeps separate entity and event subgraphs linked by a bipartite mapping, thereby preserving the temporal and causal facets needed for fine-grained reasoning. Across ChronoQA, our approach outperforms state-of-the-art unstructured and KG-based RAG baselines, with notable gains on causal and character consistency queries. E^2RAG therefore offers a practical path to more context-aware retrieval for tasks that require precise answers grounded in chronological information.
Incentivizing Strong Reasoning from Weak Supervision
May 28, 2025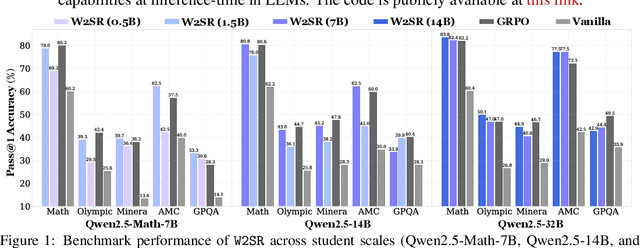
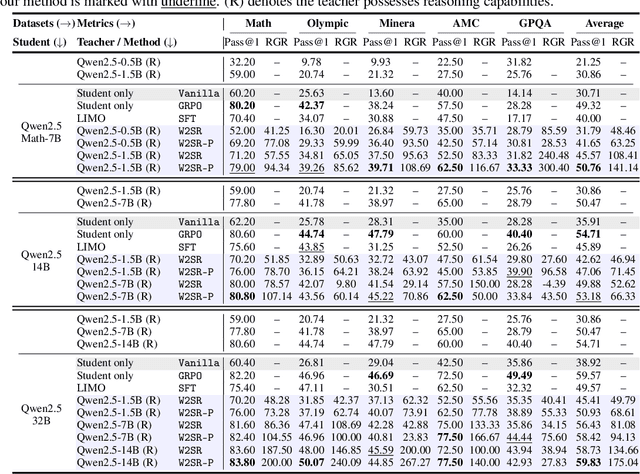
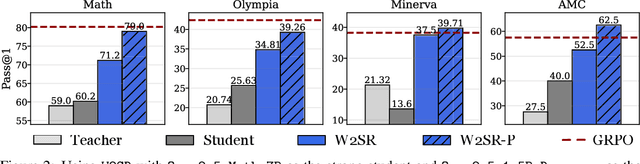
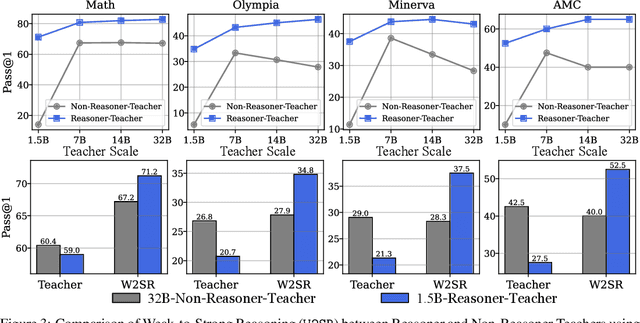
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance on reasoning-intensive tasks, but enhancing their reasoning abilities typically relies on either reinforcement learning (RL) with verifiable signals or supervised fine-tuning (SFT) with high-quality long chain-of-thought (CoT) demonstrations, both of which are expensive. In this paper, we study a novel problem of incentivizing the reasoning capacity of LLMs without expensive high-quality demonstrations and reinforcement learning. We investigate whether the reasoning capabilities of LLMs can be effectively incentivized via supervision from significantly weaker models. We further analyze when and why such weak supervision succeeds in eliciting reasoning abilities in stronger models. Our findings show that supervision from significantly weaker reasoners can substantially improve student reasoning performance, recovering close to 94% of the gains of expensive RL at a fraction of the cost. Experiments across diverse benchmarks and model architectures demonstrate that weak reasoners can effectively incentivize reasoning in stronger student models, consistently improving performance across a wide range of reasoning tasks. Our results suggest that this simple weak-to-strong paradigm is a promising and generalizable alternative to costly methods for incentivizing strong reasoning capabilities at inference-time in LLMs. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/yuanyige/w2sr.
Incentivizing Reasoning from Weak Supervision
May 26, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance on reasoning-intensive tasks, but enhancing their reasoning abilities typically relies on either reinforcement learning (RL) with verifiable signals or supervised fine-tuning (SFT) with high-quality long chain-of-thought (CoT) demonstrations, both of which are expensive. In this paper, we study a novel problem of incentivizing the reasoning capacity of LLMs without expensive high-quality demonstrations and reinforcement learning. We investigate whether the reasoning capabilities of LLMs can be effectively incentivized via supervision from significantly weaker models. We further analyze when and why such weak supervision succeeds in eliciting reasoning abilities in stronger models. Our findings show that supervision from significantly weaker reasoners can substantially improve student reasoning performance, recovering close to 94% of the gains of expensive RL at a fraction of the cost. Experiments across diverse benchmarks and model architectures demonstrate that weak reasoners can effectively incentivize reasoning in stronger student models, consistently improving performance across a wide range of reasoning tasks. Our results suggest that this simple weak-to-strong paradigm is a promising and generalizable alternative to costly methods for incentivizing strong reasoning capabilities at inference-time in LLMs. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/yuanyige/W2SR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge