Yipeng Gao
Envision: Embodied Visual Planning via Goal-Imagery Video Diffusion
Dec 27, 2025Abstract:Embodied visual planning aims to enable manipulation tasks by imagining how a scene evolves toward a desired goal and using the imagined trajectories to guide actions. Video diffusion models, through their image-to-video generation capability, provide a promising foundation for such visual imagination. However, existing approaches are largely forward predictive, generating trajectories conditioned on the initial observation without explicit goal modeling, thus often leading to spatial drift and goal misalignment. To address these challenges, we propose Envision, a diffusion-based framework that performs visual planning for embodied agents. By explicitly constraining the generation with a goal image, our method enforces physical plausibility and goal consistency throughout the generated trajectory. Specifically, Envision operates in two stages. First, a Goal Imagery Model identifies task-relevant regions, performs region-aware cross attention between the scene and the instruction, and synthesizes a coherent goal image that captures the desired outcome. Then, an Env-Goal Video Model, built upon a first-and-last-frame-conditioned video diffusion model (FL2V), interpolates between the initial observation and the goal image, producing smooth and physically plausible video trajectories that connect the start and goal states. Experiments on object manipulation and image editing benchmarks demonstrate that Envision achieves superior goal alignment, spatial consistency, and object preservation compared to baselines. The resulting visual plans can directly support downstream robotic planning and control, providing reliable guidance for embodied agents.
X-Dyna: Expressive Dynamic Human Image Animation
Jan 20, 2025Abstract:We introduce X-Dyna, a novel zero-shot, diffusion-based pipeline for animating a single human image using facial expressions and body movements derived from a driving video, that generates realistic, context-aware dynamics for both the subject and the surrounding environment. Building on prior approaches centered on human pose control, X-Dyna addresses key shortcomings causing the loss of dynamic details, enhancing the lifelike qualities of human video animations. At the core of our approach is the Dynamics-Adapter, a lightweight module that effectively integrates reference appearance context into the spatial attentions of the diffusion backbone while preserving the capacity of motion modules in synthesizing fluid and intricate dynamic details. Beyond body pose control, we connect a local control module with our model to capture identity-disentangled facial expressions, facilitating accurate expression transfer for enhanced realism in animated scenes. Together, these components form a unified framework capable of learning physical human motion and natural scene dynamics from a diverse blend of human and scene videos. Comprehensive qualitative and quantitative evaluations demonstrate that X-Dyna outperforms state-of-the-art methods, creating highly lifelike and expressive animations. The code is available at https://github.com/bytedance/X-Dyna.
Bridge Past and Future: Overcoming Information Asymmetry in Incremental Object Detection
Jul 16, 2024



Abstract:In incremental object detection, knowledge distillation has been proven to be an effective way to alleviate catastrophic forgetting. However, previous works focused on preserving the knowledge of old models, ignoring that images could simultaneously contain categories from past, present, and future stages. The co-occurrence of objects makes the optimization objectives inconsistent across different stages since the definition for foreground objects differs across various stages, which limits the model's performance greatly. To overcome this problem, we propose a method called ``Bridge Past and Future'' (BPF), which aligns models across stages, ensuring consistent optimization directions. In addition, we propose a novel Distillation with Future (DwF) loss, fully leveraging the background probability to mitigate the forgetting of old classes while ensuring a high level of adaptability in learning new classes. Extensive experiments are conducted on both Pascal VOC and MS COCO benchmarks. Without memory, BPF outperforms current state-of-the-art methods under various settings. The code is available at https://github.com/iSEE-Laboratory/BPF.
DreamView: Injecting View-specific Text Guidance into Text-to-3D Generation
Apr 09, 2024



Abstract:Text-to-3D generation, which synthesizes 3D assets according to an overall text description, has significantly progressed. However, a challenge arises when the specific appearances need customizing at designated viewpoints but referring solely to the overall description for generating 3D objects. For instance, ambiguity easily occurs when producing a T-shirt with distinct patterns on its front and back using a single overall text guidance. In this work, we propose DreamView, a text-to-image approach enabling multi-view customization while maintaining overall consistency by adaptively injecting the view-specific and overall text guidance through a collaborative text guidance injection module, which can also be lifted to 3D generation via score distillation sampling. DreamView is trained with large-scale rendered multi-view images and their corresponding view-specific texts to learn to balance the separate content manipulation in each view and the global consistency of the overall object, resulting in a dual achievement of customization and consistency. Consequently, DreamView empowers artists to design 3D objects creatively, fostering the creation of more innovative and diverse 3D assets. Code and model will be released at https://github.com/iSEE-Laboratory/DreamView.
MixCon3D: Synergizing Multi-View and Cross-Modal Contrastive Learning for Enhancing 3D Representation
Nov 03, 2023Abstract:Contrastive learning has emerged as a promising paradigm for 3D open-world understanding, jointly with text, image, and point cloud. In this paper, we introduce MixCon3D, which combines the complementary information between 2D images and 3D point clouds to enhance contrastive learning. With the further integration of multi-view 2D images, MixCon3D enhances the traditional tri-modal representation by offering a more accurate and comprehensive depiction of real-world 3D objects and bolstering text alignment. Additionally, we pioneer the first thorough investigation of various training recipes for the 3D contrastive learning paradigm, building a solid baseline with improved performance. Extensive experiments conducted on three representative benchmarks reveal that our method renders significant improvement over the baseline, surpassing the previous state-of-the-art performance on the challenging 1,156-category Objaverse-LVIS dataset by 5.7%. We further showcase the effectiveness of our approach in more applications, including text-to-3D retrieval and point cloud captioning. The code is available at https://github.com/UCSC-VLAA/MixCon3D.
Diversifying Spatial-Temporal Perception for Video Domain Generalization
Oct 27, 2023Abstract:Video domain generalization aims to learn generalizable video classification models for unseen target domains by training in a source domain. A critical challenge of video domain generalization is to defend against the heavy reliance on domain-specific cues extracted from the source domain when recognizing target videos. To this end, we propose to perceive diverse spatial-temporal cues in videos, aiming to discover potential domain-invariant cues in addition to domain-specific cues. We contribute a novel model named Spatial-Temporal Diversification Network (STDN), which improves the diversity from both space and time dimensions of video data. First, our STDN proposes to discover various types of spatial cues within individual frames by spatial grouping. Then, our STDN proposes to explicitly model spatial-temporal dependencies between video contents at multiple space-time scales by spatial-temporal relation modeling. Extensive experiments on three benchmarks of different types demonstrate the effectiveness and versatility of our approach.
ASAG: Building Strong One-Decoder-Layer Sparse Detectors via Adaptive Sparse Anchor Generation
Aug 18, 2023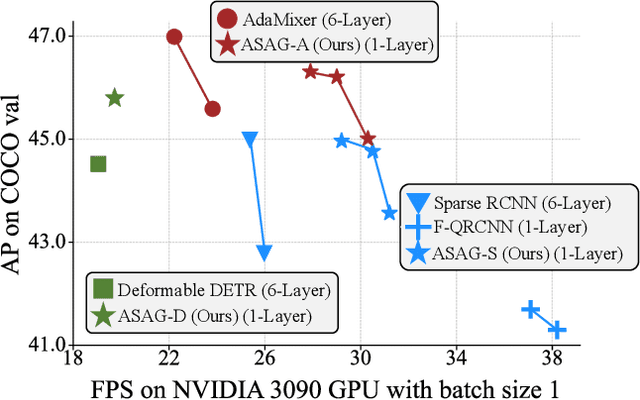

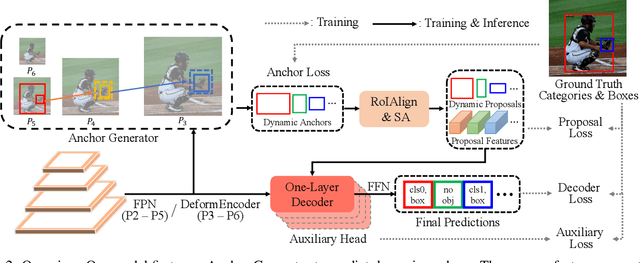

Abstract:Recent sparse detectors with multiple, e.g. six, decoder layers achieve promising performance but much inference time due to complex heads. Previous works have explored using dense priors as initialization and built one-decoder-layer detectors. Although they gain remarkable acceleration, their performance still lags behind their six-decoder-layer counterparts by a large margin. In this work, we aim to bridge this performance gap while retaining fast speed. We find that the architecture discrepancy between dense and sparse detectors leads to feature conflict, hampering the performance of one-decoder-layer detectors. Thus we propose Adaptive Sparse Anchor Generator (ASAG) which predicts dynamic anchors on patches rather than grids in a sparse way so that it alleviates the feature conflict problem. For each image, ASAG dynamically selects which feature maps and which locations to predict, forming a fully adaptive way to generate image-specific anchors. Further, a simple and effective Query Weighting method eases the training instability from adaptiveness. Extensive experiments show that our method outperforms dense-initialized ones and achieves a better speed-accuracy trade-off. The code is available at \url{https://github.com/iSEE-Laboratory/ASAG}.
DilateFormer: Multi-Scale Dilated Transformer for Visual Recognition
Feb 03, 2023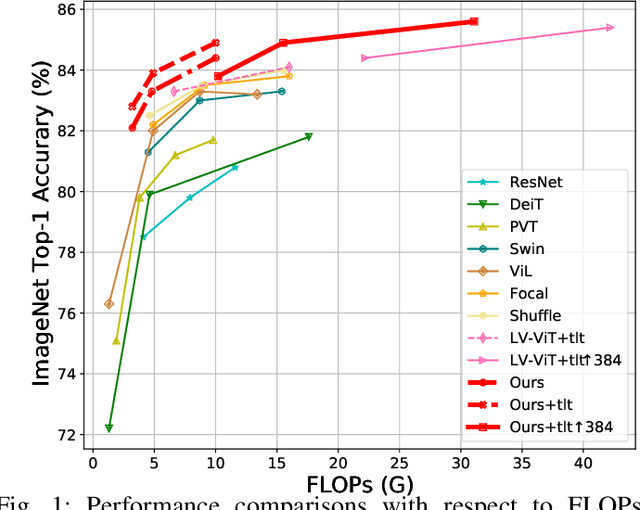

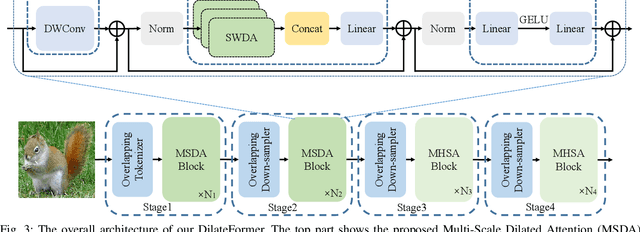
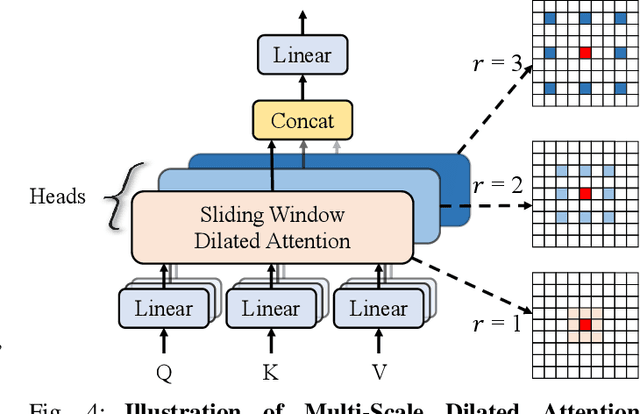
Abstract:As a de facto solution, the vanilla Vision Transformers (ViTs) are encouraged to model long-range dependencies between arbitrary image patches while the global attended receptive field leads to quadratic computational cost. Another branch of Vision Transformers exploits local attention inspired by CNNs, which only models the interactions between patches in small neighborhoods. Although such a solution reduces the computational cost, it naturally suffers from small attended receptive fields, which may limit the performance. In this work, we explore effective Vision Transformers to pursue a preferable trade-off between the computational complexity and size of the attended receptive field. By analyzing the patch interaction of global attention in ViTs, we observe two key properties in the shallow layers, namely locality and sparsity, indicating the redundancy of global dependency modeling in shallow layers of ViTs. Accordingly, we propose Multi-Scale Dilated Attention (MSDA) to model local and sparse patch interaction within the sliding window. With a pyramid architecture, we construct a Multi-Scale Dilated Transformer (DilateFormer) by stacking MSDA blocks at low-level stages and global multi-head self-attention blocks at high-level stages. Our experiment results show that our DilateFormer achieves state-of-the-art performance on various vision tasks. On ImageNet-1K classification task, DilateFormer achieves comparable performance with 70% fewer FLOPs compared with existing state-of-the-art models. Our DilateFormer-Base achieves 85.6% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet-1K classification task, 53.5% box mAP/46.1% mask mAP on COCO object detection/instance segmentation task and 51.1% MS mIoU on ADE20K semantic segmentation task.
AcroFOD: An Adaptive Method for Cross-domain Few-shot Object Detection
Sep 22, 2022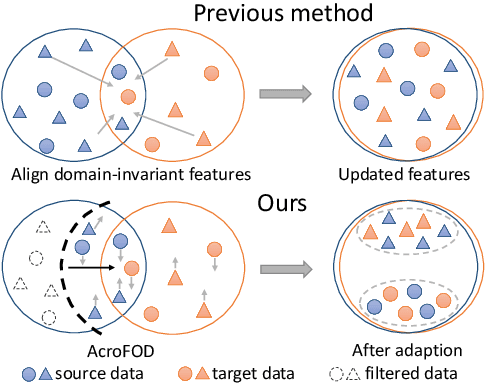
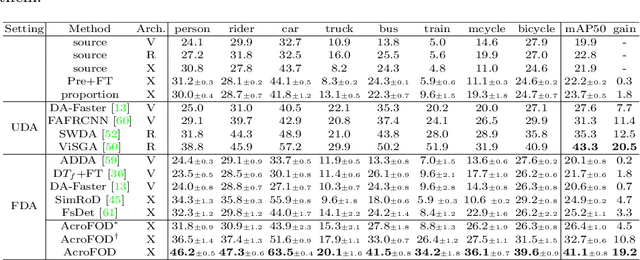
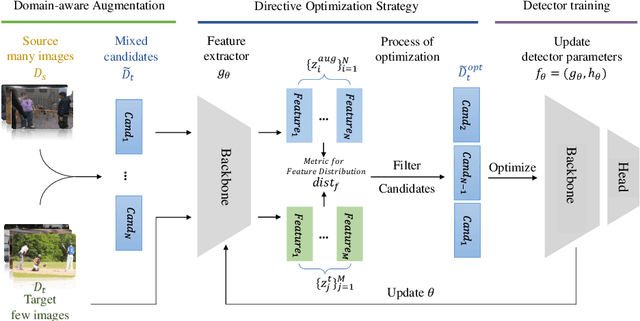
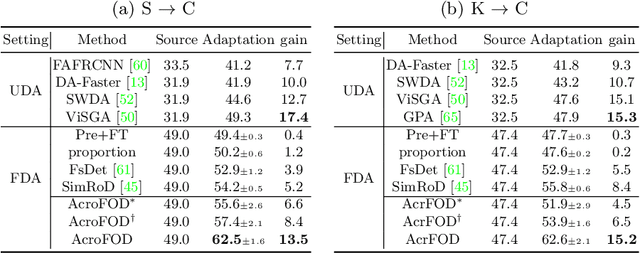
Abstract:Under the domain shift, cross-domain few-shot object detection aims to adapt object detectors in the target domain with a few annotated target data. There exists two significant challenges: (1) Highly insufficient target domain data; (2) Potential over-adaptation and misleading caused by inappropriately amplified target samples without any restriction. To address these challenges, we propose an adaptive method consisting of two parts. First, we propose an adaptive optimization strategy to select augmented data similar to target samples rather than blindly increasing the amount. Specifically, we filter the augmented candidates which significantly deviate from the target feature distribution in the very beginning. Second, to further relieve the data limitation, we propose the multi-level domain-aware data augmentation to increase the diversity and rationality of augmented data, which exploits the cross-image foreground-background mixture. Experiments show that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge