Kun-Yu Lin
ProEdit: Inversion-based Editing From Prompts Done Right
Dec 26, 2025



Abstract:Inversion-based visual editing provides an effective and training-free way to edit an image or a video based on user instructions. Existing methods typically inject source image information during the sampling process to maintain editing consistency. However, this sampling strategy overly relies on source information, which negatively affects the edits in the target image (e.g., failing to change the subject's atributes like pose, number, or color as instructed). In this work, we propose ProEdit to address this issue both in the attention and the latent aspects. In the attention aspect, we introduce KV-mix, which mixes KV features of the source and the target in the edited region, mitigating the influence of the source image on the editing region while maintaining background consistency. In the latent aspect, we propose Latents-Shift, which perturbs the edited region of the source latent, eliminating the influence of the inverted latent on the sampling. Extensive experiments on several image and video editing benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves SOTA performance. In addition, our design is plug-and-play, which can be seamlessly integrated into existing inversion and editing methods, such as RF-Solver, FireFlow and UniEdit.
From Watch to Imagine: Steering Long-horizon Manipulation via Human Demonstration and Future Envisionment
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Generalizing to long-horizon manipulation tasks in a zero-shot setting remains a central challenge in robotics. Current multimodal foundation based approaches, despite their capabilities, typically fail to decompose high-level commands into executable action sequences from static visual input alone. To address this challenge, we introduce Super-Mimic, a hierarchical framework that enables zero-shot robotic imitation by directly inferring procedural intent from unscripted human demonstration videos. Our framework is composed of two sequential modules. First, a Human Intent Translator (HIT) parses the input video using multimodal reasoning to produce a sequence of language-grounded subtasks. These subtasks then condition a Future Dynamics Predictor (FDP), which employs a generative model that synthesizes a physically plausible video rollout for each step. The resulting visual trajectories are dynamics-aware, explicitly modeling crucial object interactions and contact points to guide the low-level controller. We validate this approach through extensive experiments on a suite of long-horizon manipulation tasks, where Super-Mimic significantly outperforms state-of-the-art zero-shot methods by over 20\%. These results establish that coupling video-driven intent parsing with prospective dynamics modeling is a highly effective strategy for developing general-purpose robotic systems.
CoopDiff: Anticipating 3D Human-object Interactions via Contact-consistent Decoupled Diffusion
Aug 10, 2025Abstract:3D human-object interaction (HOI) anticipation aims to predict the future motion of humans and their manipulated objects, conditioned on the historical context. Generally, the articulated humans and rigid objects exhibit different motion patterns, due to their distinct intrinsic physical properties. However, this distinction is ignored by most of the existing works, which intend to capture the dynamics of both humans and objects within a single prediction model. In this work, we propose a novel contact-consistent decoupled diffusion framework CoopDiff, which employs two distinct branches to decouple human and object motion modeling, with the human-object contact points as shared anchors to bridge the motion generation across branches. The human dynamics branch is aimed to predict highly structured human motion, while the object dynamics branch focuses on the object motion with rigid translations and rotations. These two branches are bridged by a series of shared contact points with consistency constraint for coherent human-object motion prediction. To further enhance human-object consistency and prediction reliability, we propose a human-driven interaction module to guide object motion modeling. Extensive experiments on the BEHAVE and Human-object Interaction datasets demonstrate that our CoopDiff outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
Panoptic Captioning: Seeking An Equivalency Bridge for Image and Text
May 22, 2025Abstract:This work introduces panoptic captioning, a novel task striving to seek the minimum text equivalence of images. We take the first step towards panoptic captioning by formulating it as a task of generating a comprehensive textual description for an image, which encapsulates all entities, their respective locations and attributes, relationships among entities, as well as global image state.Through an extensive evaluation, our work reveals that state-of-the-art Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have limited performance in solving panoptic captioning. To address this, we propose an effective data engine named PancapEngine to produce high-quality data and a novel method named PancapChain to improve panoptic captioning. Specifically, our PancapEngine first detects diverse categories of entities in images by an elaborate detection suite, and then generates required panoptic captions using entity-aware prompts. Additionally, our PancapChain explicitly decouples the challenging panoptic captioning task into multiple stages and generates panoptic captions step by step. More importantly, we contribute a comprehensive metric named PancapScore and a human-curated test set for reliable model evaluation.Experiments show that our PancapChain-13B model can beat state-of-the-art open-source MLLMs like InternVL-2.5-78B and even surpass proprietary models like GPT-4o and Gemini-2.0-Pro, demonstrating the effectiveness of our data engine and method. Project page: https://visual-ai.github.io/pancap/
Exploring the Limits of Vision-Language-Action Manipulations in Cross-task Generalization
May 21, 2025Abstract:The generalization capabilities of vision-language-action (VLA) models to unseen tasks are crucial to achieving general-purpose robotic manipulation in open-world settings. However, the cross-task generalization capabilities of existing VLA models remain significantly underexplored. To address this gap, we introduce AGNOSTOS, a novel simulation benchmark designed to rigorously evaluate cross-task zero-shot generalization in manipulation. AGNOSTOS comprises 23 unseen manipulation tasks for testing, distinct from common training task distributions, and incorporates two levels of generalization difficulty to assess robustness. Our systematic evaluation reveals that current VLA models, despite being trained on diverse datasets, struggle to generalize effectively to these unseen tasks. To overcome this limitation, we propose Cross-Task In-Context Manipulation (X-ICM), a method that conditions large language models (LLMs) on in-context demonstrations from seen tasks to predict action sequences for unseen tasks. Additionally, we introduce a dynamics-guided sample selection strategy that identifies relevant demonstrations by capturing cross-task dynamics. On AGNOSTOS, X-ICM significantly improves cross-task zero-shot generalization performance over leading VLAs. We believe AGNOSTOS and X-ICM will serve as valuable tools for advancing general-purpose robotic manipulation.
ActionArt: Advancing Multimodal Large Models for Fine-Grained Human-Centric Video Understanding
Apr 25, 2025
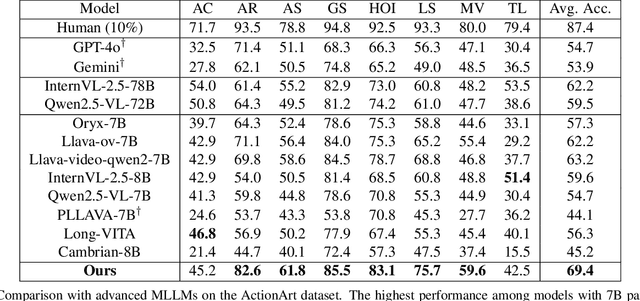
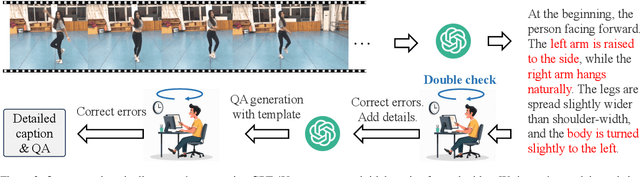
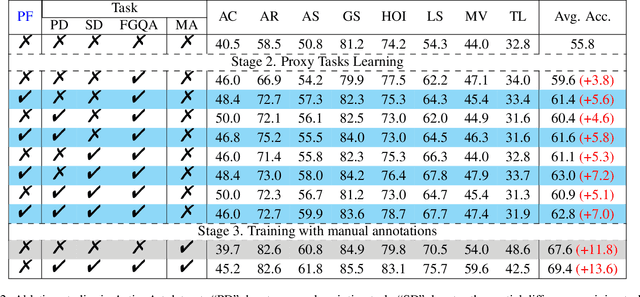
Abstract:Fine-grained understanding of human actions and poses in videos is essential for human-centric AI applications. In this work, we introduce ActionArt, a fine-grained video-caption dataset designed to advance research in human-centric multimodal understanding. Our dataset comprises thousands of videos capturing a broad spectrum of human actions, human-object interactions, and diverse scenarios, each accompanied by detailed annotations that meticulously label every limb movement. We develop eight sub-tasks to evaluate the fine-grained understanding capabilities of existing large multimodal models across different dimensions. Experimental results indicate that, while current large multimodal models perform commendably on various tasks, they often fall short in achieving fine-grained understanding. We attribute this limitation to the scarcity of meticulously annotated data, which is both costly and difficult to scale manually. Since manual annotations are costly and hard to scale, we propose proxy tasks to enhance the model perception ability in both spatial and temporal dimensions. These proxy tasks are carefully crafted to be driven by data automatically generated from existing MLLMs, thereby reducing the reliance on costly manual labels. Experimental results show that the proposed proxy tasks significantly narrow the gap toward the performance achieved with manually annotated fine-grained data.
Modeling Multiple Normal Action Representations for Error Detection in Procedural Tasks
Apr 02, 2025



Abstract:Error detection in procedural activities is essential for consistent and correct outcomes in AR-assisted and robotic systems. Existing methods often focus on temporal ordering errors or rely on static prototypes to represent normal actions. However, these approaches typically overlook the common scenario where multiple, distinct actions are valid following a given sequence of executed actions. This leads to two issues: (1) the model cannot effectively detect errors using static prototypes when the inference environment or action execution distribution differs from training; and (2) the model may also use the wrong prototypes to detect errors if the ongoing action label is not the same as the predicted one. To address this problem, we propose an Adaptive Multiple Normal Action Representation (AMNAR) framework. AMNAR predicts all valid next actions and reconstructs their corresponding normal action representations, which are compared against the ongoing action to detect errors. Extensive experiments demonstrate that AMNAR achieves state-of-the-art performance, highlighting the effectiveness of AMNAR and the importance of modeling multiple valid next actions in error detection. The code is available at https://github.com/iSEE-Laboratory/AMNAR.
Decoupled Distillation to Erase: A General Unlearning Method for Any Class-centric Tasks
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:In this work, we present DEcoupLEd Distillation To Erase (DELETE), a general and strong unlearning method for any class-centric tasks. To derive this, we first propose a theoretical framework to analyze the general form of unlearning loss and decompose it into forgetting and retention terms. Through the theoretical framework, we point out that a class of previous methods could be mainly formulated as a loss that implicitly optimizes the forgetting term while lacking supervision for the retention term, disturbing the distribution of pre-trained model and struggling to adequately preserve knowledge of the remaining classes. To address it, we refine the retention term using "dark knowledge" and propose a mask distillation unlearning method. By applying a mask to separate forgetting logits from retention logits, our approach optimizes both the forgetting and refined retention components simultaneously, retaining knowledge of the remaining classes while ensuring thorough forgetting of the target class. Without access to the remaining data or intervention (i.e., used in some works), we achieve state-of-the-art performance across various benchmarks. What's more, DELETE is a general solution that can be applied to various downstream tasks, including face recognition, backdoor defense, and semantic segmentation with great performance.
ViSpeak: Visual Instruction Feedback in Streaming Videos
Mar 17, 2025
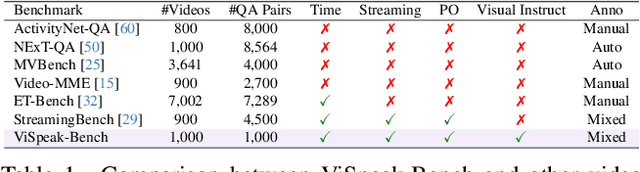
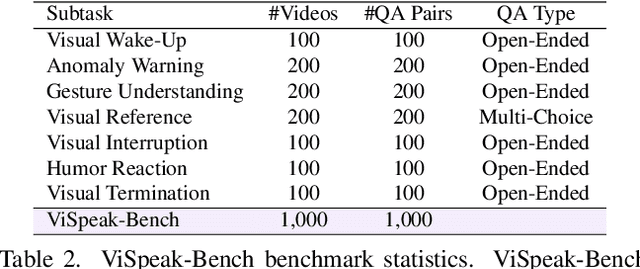
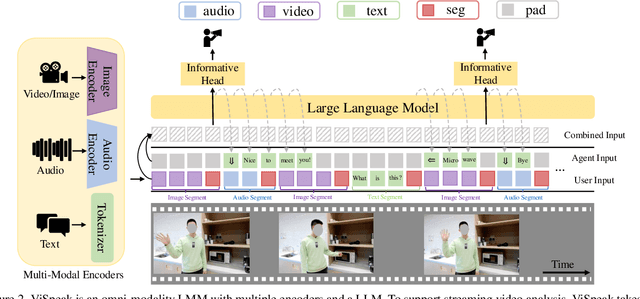
Abstract:Recent advances in Large Multi-modal Models (LMMs) are primarily focused on offline video understanding. Instead, streaming video understanding poses great challenges to recent models due to its time-sensitive, omni-modal and interactive characteristics. In this work, we aim to extend the streaming video understanding from a new perspective and propose a novel task named Visual Instruction Feedback in which models should be aware of visual contents and learn to extract instructions from them. For example, when users wave their hands to agents, agents should recognize the gesture and start conversations with welcome information. Thus, following instructions in visual modality greatly enhances user-agent interactions. To facilitate research, we define seven key subtasks highly relevant to visual modality and collect the ViSpeak-Instruct dataset for training and the ViSpeak-Bench for evaluation. Further, we propose the ViSpeak model, which is a SOTA streaming video understanding LMM with GPT-4o-level performance on various streaming video understanding benchmarks. After finetuning on our ViSpeak-Instruct dataset, ViSpeak is equipped with basic visual instruction feedback ability, serving as a solid baseline for future research.
Task-Oriented 6-DoF Grasp Pose Detection in Clutters
Feb 24, 2025



Abstract:In general, humans would grasp an object differently for different tasks, e.g., "grasping the handle of a knife to cut" vs. "grasping the blade to hand over". In the field of robotic grasp pose detection research, some existing works consider this task-oriented grasping and made some progress, but they are generally constrained by low-DoF gripper type or non-cluttered setting, which is not applicable for human assistance in real life. With an aim to get more general and practical grasp models, in this paper, we investigate the problem named Task-Oriented 6-DoF Grasp Pose Detection in Clutters (TO6DGC), which extends the task-oriented problem to a more general 6-DOF Grasp Pose Detection in Cluttered (multi-object) scenario. To this end, we construct a large-scale 6-DoF task-oriented grasping dataset, 6-DoF Task Grasp (6DTG), which features 4391 cluttered scenes with over 2 million 6-DoF grasp poses. Each grasp is annotated with a specific task, involving 6 tasks and 198 objects in total. Moreover, we propose One-Stage TaskGrasp (OSTG), a strong baseline to address the TO6DGC problem. Our OSTG adopts a task-oriented point selection strategy to detect where to grasp, and a task-oriented grasp generation module to decide how to grasp given a specific task. To evaluate the effectiveness of OSTG, extensive experiments are conducted on 6DTG. The results show that our method outperforms various baselines on multiple metrics. Real robot experiments also verify that our OSTG has a better perception of the task-oriented grasp points and 6-DoF grasp poses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge