Jianhuang Lai
Style4D-Bench: A Benchmark Suite for 4D Stylization
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:We introduce Style4D-Bench, the first benchmark suite specifically designed for 4D stylization, with the goal of standardizing evaluation and facilitating progress in this emerging area. Style4D-Bench comprises: 1) a comprehensive evaluation protocol measuring spatial fidelity, temporal coherence, and multi-view consistency through both perceptual and quantitative metrics, 2) a strong baseline that make an initial attempt for 4D stylization, and 3) a curated collection of high-resolution dynamic 4D scenes with diverse motions and complex backgrounds. To establish a strong baseline, we present Style4D, a novel framework built upon 4D Gaussian Splatting. It consists of three key components: a basic 4DGS scene representation to capture reliable geometry, a Style Gaussian Representation that leverages lightweight per-Gaussian MLPs for temporally and spatially aware appearance control, and a Holistic Geometry-Preserved Style Transfer module designed to enhance spatio-temporal consistency via contrastive coherence learning and structural content preservation. Extensive experiments on Style4D-Bench demonstrate that Style4D achieves state-of-the-art performance in 4D stylization, producing fine-grained stylistic details with stable temporal dynamics and consistent multi-view rendering. We expect Style4D-Bench to become a valuable resource for benchmarking and advancing research in stylized rendering of dynamic 3D scenes. Project page: https://becky-catherine.github.io/Style4D . Code: https://github.com/Becky-catherine/Style4D-Bench .
ObjFiller-3D: Consistent Multi-view 3D Inpainting via Video Diffusion Models
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:3D inpainting often relies on multi-view 2D image inpainting, where the inherent inconsistencies across different inpainted views can result in blurred textures, spatial discontinuities, and distracting visual artifacts. These inconsistencies pose significant challenges when striving for accurate and realistic 3D object completion, particularly in applications that demand high fidelity and structural coherence. To overcome these limitations, we propose ObjFiller-3D, a novel method designed for the completion and editing of high-quality and consistent 3D objects. Instead of employing a conventional 2D image inpainting model, our approach leverages a curated selection of state-of-the-art video editing model to fill in the masked regions of 3D objects. We analyze the representation gap between 3D and videos, and propose an adaptation of a video inpainting model for 3D scene inpainting. In addition, we introduce a reference-based 3D inpainting method to further enhance the quality of reconstruction. Experiments across diverse datasets show that compared to previous methods, ObjFiller-3D produces more faithful and fine-grained reconstructions (PSNR of 26.6 vs. NeRFiller (15.9) and LPIPS of 0.19 vs. Instant3dit (0.25)). Moreover, it demonstrates strong potential for practical deployment in real-world 3D editing applications. Project page: https://objfiller3d.github.io/ Code: https://github.com/objfiller3d/ObjFiller-3D .
Distilled-3DGS:Distilled 3D Gaussian Splatting
Aug 19, 2025Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has exhibited remarkable efficacy in novel view synthesis (NVS). However, it suffers from a significant drawback: achieving high-fidelity rendering typically necessitates a large number of 3D Gaussians, resulting in substantial memory consumption and storage requirements. To address this challenge, we propose the first knowledge distillation framework for 3DGS, featuring various teacher models, including vanilla 3DGS, noise-augmented variants, and dropout-regularized versions. The outputs of these teachers are aggregated to guide the optimization of a lightweight student model. To distill the hidden geometric structure, we propose a structural similarity loss to boost the consistency of spatial geometric distributions between the student and teacher model. Through comprehensive quantitative and qualitative evaluations across diverse datasets, the proposed Distilled-3DGS, a simple yet effective framework without bells and whistles, achieves promising rendering results in both rendering quality and storage efficiency compared to state-of-the-art methods. Project page: https://distilled3dgs.github.io . Code: https://github.com/lt-xiang/Distilled-3DGS .
CoopDiff: Anticipating 3D Human-object Interactions via Contact-consistent Decoupled Diffusion
Aug 10, 2025Abstract:3D human-object interaction (HOI) anticipation aims to predict the future motion of humans and their manipulated objects, conditioned on the historical context. Generally, the articulated humans and rigid objects exhibit different motion patterns, due to their distinct intrinsic physical properties. However, this distinction is ignored by most of the existing works, which intend to capture the dynamics of both humans and objects within a single prediction model. In this work, we propose a novel contact-consistent decoupled diffusion framework CoopDiff, which employs two distinct branches to decouple human and object motion modeling, with the human-object contact points as shared anchors to bridge the motion generation across branches. The human dynamics branch is aimed to predict highly structured human motion, while the object dynamics branch focuses on the object motion with rigid translations and rotations. These two branches are bridged by a series of shared contact points with consistency constraint for coherent human-object motion prediction. To further enhance human-object consistency and prediction reliability, we propose a human-driven interaction module to guide object motion modeling. Extensive experiments on the BEHAVE and Human-object Interaction datasets demonstrate that our CoopDiff outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
GuardSplat: Efficient and Robust Watermarking for 3D Gaussian Splatting
Dec 02, 2024



Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has recently created impressive assets for various applications. However, the copyright of these assets is not well protected as existing watermarking methods are not suited for 3DGS considering security, capacity, and invisibility. Besides, these methods often require hours or even days for optimization, limiting the application scenarios. In this paper, we propose GuardSplat, an innovative and efficient framework that effectively protects the copyright of 3DGS assets. Specifically, 1) We first propose a CLIP-guided Message Decoupling Optimization module for training the message decoder, leveraging CLIP's aligning capability and rich representations to achieve a high extraction accuracy with minimal optimization costs, presenting exceptional capability and efficiency. 2) Then, we propose a Spherical-harmonic-aware (SH-aware) Message Embedding module tailored for 3DGS, which employs a set of SH offsets to seamlessly embed the message into the SH features of each 3D Gaussian while maintaining the original 3D structure. It enables the 3DGS assets to be watermarked with minimal fidelity trade-offs and prevents malicious users from removing the messages from the model files, meeting the demands for invisibility and security. 3) We further propose an Anti-distortion Message Extraction module to improve robustness against various visual distortions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that GuardSplat outperforms the state-of-the-art methods and achieves fast optimization speed.
Progressive Pretext Task Learning for Human Trajectory Prediction
Jul 16, 2024



Abstract:Human trajectory prediction is a practical task of predicting the future positions of pedestrians on the road, which typically covers all temporal ranges from short-term to long-term within a trajectory. However, existing works attempt to address the entire trajectory prediction with a singular, uniform training paradigm, neglecting the distinction between short-term and long-term dynamics in human trajectories. To overcome this limitation, we introduce a novel Progressive Pretext Task learning (PPT) framework, which progressively enhances the model's capacity of capturing short-term dynamics and long-term dependencies for the final entire trajectory prediction. Specifically, we elaborately design three stages of training tasks in the PPT framework. In the first stage, the model learns to comprehend the short-term dynamics through a stepwise next-position prediction task. In the second stage, the model is further enhanced to understand long-term dependencies through a destination prediction task. In the final stage, the model aims to address the entire future trajectory task by taking full advantage of the knowledge from previous stages. To alleviate the knowledge forgetting, we further apply a cross-task knowledge distillation. Additionally, we design a Transformer-based trajectory predictor, which is able to achieve highly efficient two-step reasoning by integrating a destination-driven prediction strategy and a group of learnable prompt embeddings. Extensive experiments on popular benchmarks have demonstrated that our proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art performance with high efficiency. Code is available at https://github.com/iSEE-Laboratory/PPT.
View-decoupled Transformer for Person Re-identification under Aerial-ground Camera Network
Mar 21, 2024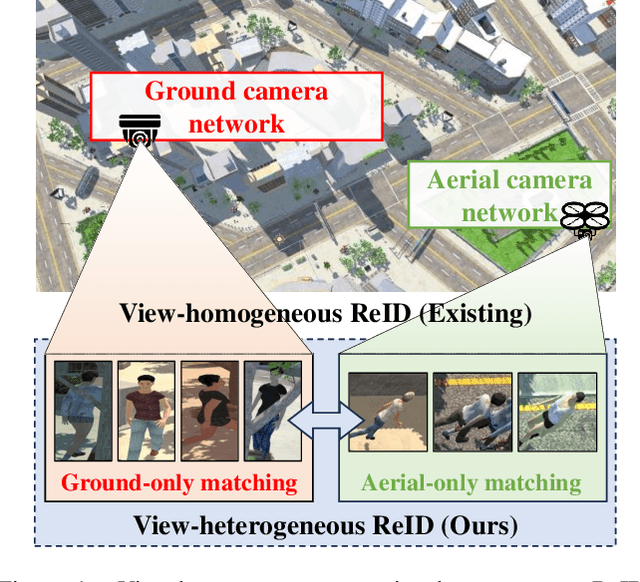

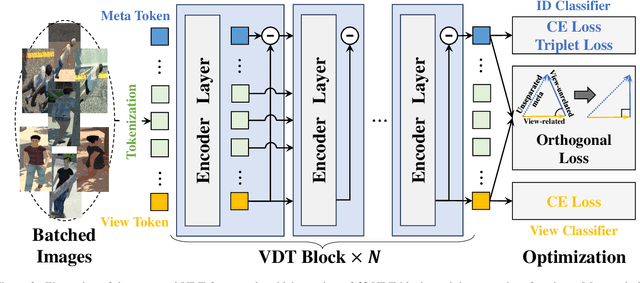

Abstract:Existing person re-identification methods have achieved remarkable advances in appearance-based identity association across homogeneous cameras, such as ground-ground matching. However, as a more practical scenario, aerial-ground person re-identification (AGPReID) among heterogeneous cameras has received minimal attention. To alleviate the disruption of discriminative identity representation by dramatic view discrepancy as the most significant challenge in AGPReID, the view-decoupled transformer (VDT) is proposed as a simple yet effective framework. Two major components are designed in VDT to decouple view-related and view-unrelated features, namely hierarchical subtractive separation and orthogonal loss, where the former separates these two features inside the VDT, and the latter constrains these two to be independent. In addition, we contribute a large-scale AGPReID dataset called CARGO, consisting of five/eight aerial/ground cameras, 5,000 identities, and 108,563 images. Experiments on two datasets show that VDT is a feasible and effective solution for AGPReID, surpassing the previous method on mAP/Rank1 by up to 5.0%/2.7% on CARGO and 3.7%/5.2% on AG-ReID, keeping the same magnitude of computational complexity. Our project is available at https://github.com/LinlyAC/VDT-AGPReID
Siamese Learning with Joint Alignment and Regression for Weakly-Supervised Video Paragraph Grounding
Mar 18, 2024



Abstract:Video Paragraph Grounding (VPG) is an emerging task in video-language understanding, which aims at localizing multiple sentences with semantic relations and temporal order from an untrimmed video. However, existing VPG approaches are heavily reliant on a considerable number of temporal labels that are laborious and time-consuming to acquire. In this work, we introduce and explore Weakly-Supervised Video Paragraph Grounding (WSVPG) to eliminate the need of temporal annotations. Different from previous weakly-supervised grounding frameworks based on multiple instance learning or reconstruction learning for two-stage candidate ranking, we propose a novel siamese learning framework that jointly learns the cross-modal feature alignment and temporal coordinate regression without timestamp labels to achieve concise one-stage localization for WSVPG. Specifically, we devise a Siamese Grounding TRansformer (SiamGTR) consisting of two weight-sharing branches for learning complementary supervision. An Augmentation Branch is utilized for directly regressing the temporal boundaries of a complete paragraph within a pseudo video, and an Inference Branch is designed to capture the order-guided feature correspondence for localizing multiple sentences in a normal video. We demonstrate by extensive experiments that our paradigm has superior practicability and flexibility to achieve efficient weakly-supervised or semi-supervised learning, outperforming state-of-the-art methods trained with the same or stronger supervision.
APRF: Anti-Aliasing Projection Representation Field for Inverse Problem in Imaging
Jul 11, 2023



Abstract:Sparse-view Computed Tomography (SVCT) reconstruction is an ill-posed inverse problem in imaging that aims to acquire high-quality CT images based on sparsely-sampled measurements. Recent works use Implicit Neural Representations (INRs) to build the coordinate-based mapping between sinograms and CT images. However, these methods have not considered the correlation between adjacent projection views, resulting in aliasing artifacts on SV sinograms. To address this issue, we propose a self-supervised SVCT reconstruction method -- Anti-Aliasing Projection Representation Field (APRF), which can build the continuous representation between adjacent projection views via the spatial constraints. Specifically, APRF only needs SV sinograms for training, which first employs a line-segment sampling module to estimate the distribution of projection views in a local region, and then synthesizes the corresponding sinogram values using center-based line integral module. After training APRF on a single SV sinogram itself, it can synthesize the corresponding dense-view (DV) sinogram with consistent continuity. High-quality CT images can be obtained by applying re-projection techniques on the predicted DV sinograms. Extensive experiments on CT images demonstrate that APRF outperforms state-of-the-art methods, yielding more accurate details and fewer artifacts. Our code will be publicly available soon.
CuNeRF: Cube-Based Neural Radiance Field for Zero-Shot Medical Image Arbitrary-Scale Super Resolution
Apr 09, 2023



Abstract:Medical image arbitrary-scale super-resolution (MIASSR) has recently gained widespread attention, aiming to super sample medical volumes at arbitrary scales via a single model. However, existing MIASSR methods face two major limitations: (i) reliance on high-resolution (HR) volumes and (ii) limited generalization ability, which restricts their application in various scenarios. To overcome these limitations, we propose Cube-based Neural Radiance Field (CuNeRF), a zero-shot MIASSR framework that can yield medical images at arbitrary scales and viewpoints in a continuous domain. Unlike existing MIASSR methods that fit the mapping between low-resolution (LR) and HR volumes, CuNeRF focuses on building a coordinate-intensity continuous representation from LR volumes without the need for HR references. This is achieved by the proposed differentiable modules: including cube-based sampling, isotropic volume rendering, and cube-based hierarchical rendering. Through extensive experiments on magnetic resource imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) modalities, we demonstrate that CuNeRF outperforms state-of-the-art MIASSR methods. CuNeRF yields better visual verisimilitude and reduces aliasing artifacts at various upsampling factors. Moreover, our CuNeRF does not need any LR-HR training pairs, which is more flexible and easier to be used than others. Our code will be publicly available soon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge