Flow-TSVAD: Target-Speaker Voice Activity Detection via Latent Flow Matching
Paper and Code
Sep 07, 2024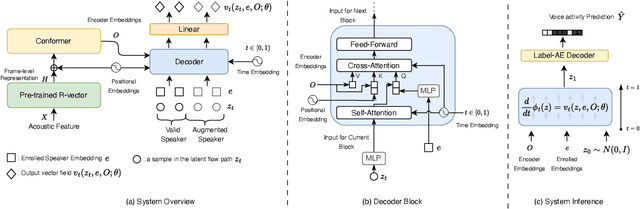
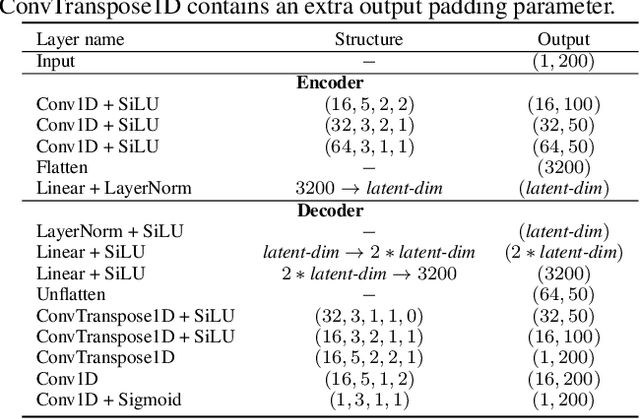
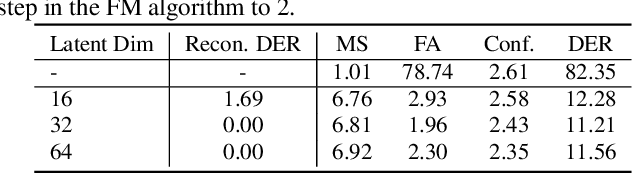
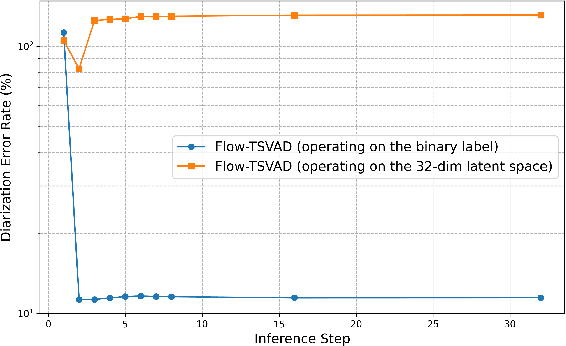
Speaker diarization is typically considered a discriminative task, using discriminative approaches to produce fixed diarization results. In this paper, we explore the use of neural network-based generative methods for speaker diarization for the first time. We implement a Flow-Matching (FM) based generative algorithm within the sequence-to-sequence target speaker voice activity detection (Seq2Seq-TSVAD) diarization system. Our experiments reveal that applying the generative method directly to the original binary label sequence space of the TS-VAD output is ineffective. To address this issue, we propose mapping the binary label sequence into a dense latent space before applying the generative algorithm and our proposed Flow-TSVAD method outperforms the Seq2Seq-TSVAD system. Additionally, we observe that the FM algorithm converges rapidly during the inference stage, requiring only two inference steps to achieve promising results. As a generative model, Flow-TSVAD allows for sampling different diarization results by running the model multiple times. Moreover, ensembling results from various sampling instances further enhances diarization performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge