Soumi Maiti
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
ASVspoof 5: Design, Collection and Validation of Resources for Spoofing, Deepfake, and Adversarial Attack Detection Using Crowdsourced Speech
Feb 13, 2025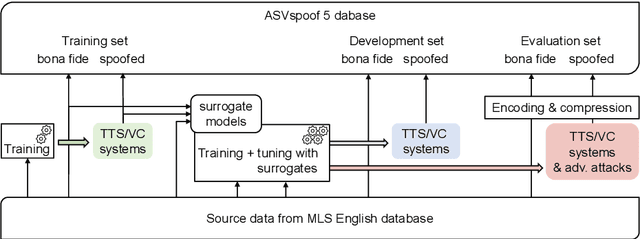

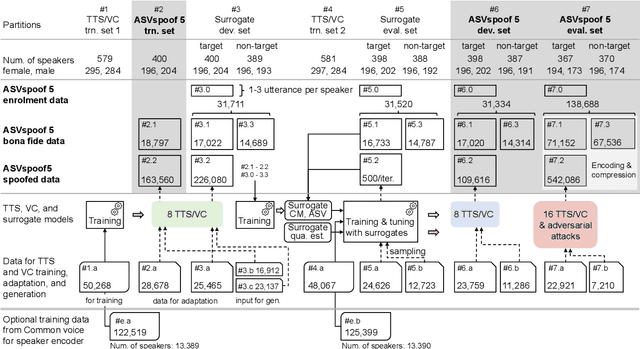
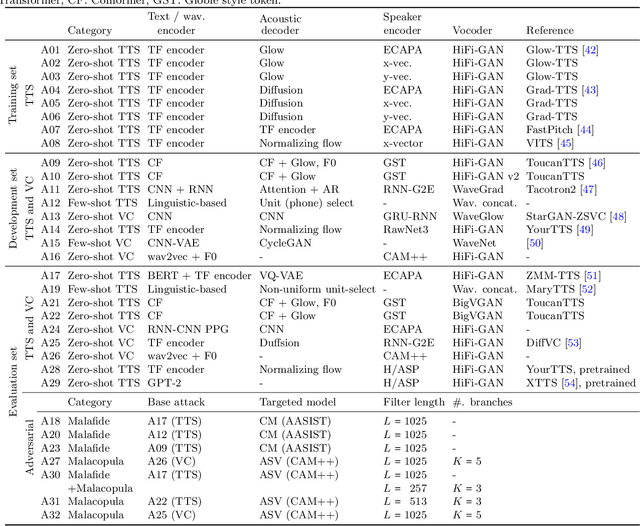
Abstract:ASVspoof 5 is the fifth edition in a series of challenges which promote the study of speech spoofing and deepfake attacks as well as the design of detection solutions. We introduce the ASVspoof 5 database which is generated in crowdsourced fashion from data collected in diverse acoustic conditions (cf. studio-quality data for earlier ASVspoof databases) and from ~2,000 speakers (cf. ~100 earlier). The database contains attacks generated with 32 different algorithms, also crowdsourced, and optimised to varying degrees using new surrogate detection models. Among them are attacks generated with a mix of legacy and contemporary text-to-speech synthesis and voice conversion models, in addition to adversarial attacks which are incorporated for the first time. ASVspoof 5 protocols comprise seven speaker-disjoint partitions. They include two distinct partitions for the training of different sets of attack models, two more for the development and evaluation of surrogate detection models, and then three additional partitions which comprise the ASVspoof 5 training, development and evaluation sets. An auxiliary set of data collected from an additional 30k speakers can also be used to train speaker encoders for the implementation of attack algorithms. Also described herein is an experimental validation of the new ASVspoof 5 database using a set of automatic speaker verification and spoof/deepfake baseline detectors. With the exception of protocols and tools for the generation of spoofed/deepfake speech, the resources described in this paper, already used by participants of the ASVspoof 5 challenge in 2024, are now all freely available to the community.
Text-To-Speech Synthesis In The Wild
Sep 13, 2024Abstract:Text-to-speech (TTS) systems are traditionally trained using modest databases of studio-quality, prompted or read speech collected in benign acoustic environments such as anechoic rooms. The recent literature nonetheless shows efforts to train TTS systems using data collected in the wild. While this approach allows for the use of massive quantities of natural speech, until now, there are no common datasets. We introduce the TTS In the Wild (TITW) dataset, the result of a fully automated pipeline, in this case, applied to the VoxCeleb1 dataset commonly used for speaker recognition. We further propose two training sets. TITW-Hard is derived from the transcription, segmentation, and selection of VoxCeleb1 source data. TITW-Easy is derived from the additional application of enhancement and additional data selection based on DNSMOS. We show that a number of recent TTS models can be trained successfully using TITW-Easy, but that it remains extremely challenging to produce similar results using TITW-Hard. Both the dataset and protocols are publicly available and support the benchmarking of TTS systems trained using TITW data.
SynesLM: A Unified Approach for Audio-visual Speech Recognition and Translation via Language Model and Synthetic Data
Aug 01, 2024Abstract:In this work, we present SynesLM, an unified model which can perform three multimodal language understanding tasks: audio-visual automatic speech recognition(AV-ASR) and visual-aided speech/machine translation(VST/VMT). Unlike previous research that focused on lip motion as visual cues for speech signals, our work explores more general visual information within entire frames, such as objects and actions. Additionally, we use synthetic image data to enhance the correlation between image and speech data. We benchmark SynesLM against the How2 dataset, demonstrating performance on par with state-of-the-art (SOTA) models dedicated to AV-ASR while maintaining our multitasking framework. Remarkably, for zero-shot AV-ASR, SynesLM achieved SOTA performance by lowering the Word Error Rate (WER) from 43.4% to 39.4% on the VisSpeech Dataset. Furthermore, our results in VST and VMT outperform the previous results, improving the BLEU score to 43.5 from 37.2 for VST, and to 54.8 from 54.4 for VMT.
Towards Robust Speech Representation Learning for Thousands of Languages
Jul 02, 2024Abstract:Self-supervised learning (SSL) has helped extend speech technologies to more languages by reducing the need for labeled data. However, models are still far from supporting the world's 7000+ languages. We propose XEUS, a Cross-lingual Encoder for Universal Speech, trained on over 1 million hours of data across 4057 languages, extending the language coverage of SSL models 4-fold. We combine 1 million hours of speech from existing publicly accessible corpora with a newly created corpus of 7400+ hours from 4057 languages, which will be publicly released. To handle the diverse conditions of multilingual speech data, we augment the typical SSL masked prediction approach with a novel dereverberation objective, increasing robustness. We evaluate XEUS on several benchmarks, and show that it consistently outperforms or achieves comparable results to state-of-the-art (SOTA) SSL models across a variety of tasks. XEUS sets a new SOTA on the ML-SUPERB benchmark: it outperforms MMS 1B and w2v-BERT 2.0 v2 by 0.8% and 4.4% respectively, despite having less parameters or pre-training data. Checkpoints, code, and data are found in https://www.wavlab.org/activities/2024/xeus/.
TMT: Tri-Modal Translation between Speech, Image, and Text by Processing Different Modalities as Different Languages
Feb 25, 2024



Abstract:The capability to jointly process multi-modal information is becoming an essential task. However, the limited number of paired multi-modal data and the large computational requirements in multi-modal learning hinder the development. We propose a novel Tri-Modal Translation (TMT) model that translates between arbitrary modalities spanning speech, image, and text. We introduce a novel viewpoint, where we interpret different modalities as different languages, and treat multi-modal translation as a well-established machine translation problem. To this end, we tokenize speech and image data into discrete tokens, which provide a unified interface across modalities and significantly decrease the computational cost. In the proposed TMT, a multi-modal encoder-decoder conducts the core translation, whereas modality-specific processing is conducted only within the tokenization and detokenization stages. We evaluate the proposed TMT on all six modality translation tasks. TMT outperforms single model counterparts consistently, demonstrating that unifying tasks is beneficial not only for practicality but also for performance.
SpeechComposer: Unifying Multiple Speech Tasks with Prompt Composition
Jan 31, 2024Abstract:Recent advancements in language models have significantly enhanced performance in multiple speech-related tasks. Existing speech language models typically utilize task-dependent prompt tokens to unify various speech tasks in a single model. However, this design omits the intrinsic connections between different speech tasks, which can potentially boost the performance of each task. In this work, we propose a novel decoder-only speech language model, SpeechComposer, that can unify common speech tasks by composing a fixed set of prompt tokens. Built upon four primary tasks -- speech synthesis, speech recognition, speech language modeling, and text language modeling -- SpeechComposer can easily extend to more speech tasks via compositions of well-designed prompt tokens, like voice conversion and speech enhancement. The unification of prompt tokens also makes it possible for knowledge sharing among different speech tasks in a more structured manner. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed SpeechComposer can improve the performance of both primary tasks and composite tasks, showing the effectiveness of the shared prompt tokens. Remarkably, the unified decoder-only model achieves a comparable and even better performance than the baselines which are expert models designed for single tasks.
SpeechBERTScore: Reference-Aware Automatic Evaluation of Speech Generation Leveraging NLP Evaluation Metrics
Jan 30, 2024Abstract:While subjective assessments have been the gold standard for evaluating speech generation, there is a growing need for objective metrics that are highly correlated with human subjective judgments due to their cost efficiency. This paper proposes reference-aware automatic evaluation methods for speech generation inspired by evaluation metrics in natural language processing. The proposed SpeechBERTScore computes the BERTScore for self-supervised dense speech features of the generated and reference speech, which can have different sequential lengths. We also propose SpeechBLEU and SpeechTokenDistance, which are computed on speech discrete tokens. The evaluations on synthesized speech show that our method correlates better with human subjective ratings than mel cepstral distortion and a recent mean opinion score prediction model. Also, they are effective in noisy speech evaluation and have cross-lingual applicability.
Reproducing Whisper-Style Training Using an Open-Source Toolkit and Publicly Available Data
Oct 02, 2023Abstract:Pre-training speech models on large volumes of data has achieved remarkable success. OpenAI Whisper is a multilingual multitask model trained on 680k hours of supervised speech data. It generalizes well to various speech recognition and translation benchmarks even in a zero-shot setup. However, the full pipeline for developing such models (from data collection to training) is not publicly accessible, which makes it difficult for researchers to further improve its performance and address training-related issues such as efficiency, robustness, fairness, and bias. This work presents an Open Whisper-style Speech Model (OWSM), which reproduces Whisper-style training using an open-source toolkit and publicly available data. OWSM even supports more translation directions and can be more efficient to train. We will publicly release all scripts used for data preparation, training, inference, and scoring as well as pre-trained models and training logs to promote open science.
Evaluating Speech Synthesis by Training Recognizers on Synthetic Speech
Oct 01, 2023Abstract:Modern speech synthesis systems have improved significantly, with synthetic speech being indistinguishable from real speech. However, efficient and holistic evaluation of synthetic speech still remains a significant challenge. Human evaluation using Mean Opinion Score (MOS) is ideal, but inefficient due to high costs. Therefore, researchers have developed auxiliary automatic metrics like Word Error Rate (WER) to measure intelligibility. Prior works focus on evaluating synthetic speech based on pre-trained speech recognition models, however, this can be limiting since this approach primarily measures speech intelligibility. In this paper, we propose an evaluation technique involving the training of an ASR model on synthetic speech and assessing its performance on real speech. Our main assumption is that by training the ASR model on the synthetic speech, the WER on real speech reflects the similarity between distributions, a broader assessment of synthetic speech quality beyond intelligibility. Our proposed metric demonstrates a strong correlation with both MOS naturalness and MOS intelligibility when compared to SpeechLMScore and MOSNet on three recent Text-to-Speech (TTS) systems: MQTTS, StyleTTS, and YourTTS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge